
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDA Orange Book
0
Europe
0
Australia
0
South Africa
0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
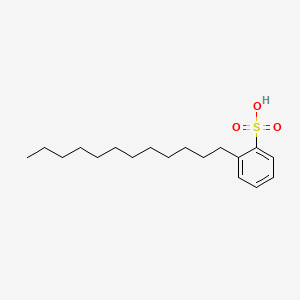

1. Deterlon
2. Dobanic Acid 83
3. Dodecyl Benzene Sulfonic Acid Sodium
4. Dodecylbenzenesulfonic Acid, Potassium Salt
5. Dodecylbenzenesulfonic Acid, Sodium Salt
6. Sodium Dodecyl Benzene Sulfonate
7. Sodium Dodecylbenzenesulfonate
8. Sodium Laurylbenzenesulfonate
9. Sulfanol
10. Sulfanol Np 1
11. Sulfonol
1. 27176-87-0
2. 2-dodecylbenzenesulfonic Acid
3. Dodecylbenzenesulphonic Acid
4. Dodecyl Benzene Sulfonic Acid
5. O-dodecylbenzenesulfonic Acid
6. Benzenesulfonic Acid, 2-dodecyl-
7. Dodecylbenzene Sulfonic Acid
8. 47221-31-8
9. 2-dodecylbenzene-1-sulfonic Acid
10. Qmo4a07h35
11. 1323-12-2
12. Unii-qmo4a07h35
13. Schembl24533
14. 2-dodecylbenzenesulphonic Acid
15. Dodecyl Benzene Sulphonic Acid
16. Dtxsid10860152
17. 2-dodecylbenzene-1-sulphonic Acid
18. Chebi:149774
19. 2-dodecylbenzenesulfonicacid
20. Zinc2014249
21. Akos015893068
22. As-76054
23. Cs-0256295
24. Ft-0698141
25. Q27287337
26. 111839-63-5
27. 124743-21-1
28. 147625-74-9
29. 27157-97-7
30. 39355-45-8
31. 54824-36-1
32. 889890-18-0
| Molecular Weight | 326.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H30O3S |
| XLogP3 | 6.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 12 |
| Exact Mass | 326.19156599 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 326.19156599 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 62.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 359 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Surface-Active Agents
Agents that modify interfacial tension of water; usually substances that have one lipophilic and one hydrophilic group in the molecule; includes soaps, detergents, emulsifiers, dispersing and wetting agents, and several groups of antiseptics. (See all compounds classified as Surface-Active Agents.)
Disinfectants
Substances used on inanimate objects that destroy harmful microorganisms or inhibit their activity. Disinfectants are classed as complete, destroying SPORES as well as vegetative forms of microorganisms, or incomplete, destroying only vegetative forms of the organisms. They are distinguished from ANTISEPTICS, which are local anti-infective agents used on humans and other animals. (From Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, 11th ed) (See all compounds classified as Disinfectants.)
Linear alkylbenzenesulfonic acid is absorbed through the gills and body surface of fish (carp), distributed via blood to the various tissues and organs, transported to the hepatopancreas (liver for goldfish and others), and subsequently, via bile, eliminated with the feces. /Linear alkylbenzenesulfonic acid/
Kikuchi M et al; Exotoxicol Environ Safety 2 (2): 115-27 (1978) as cited in ITC/USEPA; Information Review #236 (Draft) Mono(C10-16) Alkylbenzenesulfonic Acids and Their Sodium Salts p.56 (1981)
(14)C-labeled sodium dodecylbenzenesufonate (DBS) ... administered daily in the diet at a concn of 1.4 mg/kg to male rats for 5 weeks. ... From a total uptake of 1.213 + or - 0.08 mg/animal of DBS, 81.8% was excreted during the dosing period; 52.4% in feces and 29.4% in urine. Low levels of (14)C-DBS-derived residues were detected in all tissues analyzed on day 35 of the /study/. Following 1 week on normal diet only 7.8% of the nominally stored amount of (14)C was found in the excreta. Single ip injection of 0.385 mg (14)C-DBS/rat 2.26 + or - 0.15 mg/kg body weight resulted in total elimination of 94.5% within 10 days. 84.7% of the dose was eliminated the first 24 hr. All (14)C-DBS fecal and renal metabolites were ... highly polar. /Sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate/
PMID:6623504 Lay JP et al; Toxicol Lett 17 (1-2): 187-92 (1983)
After single oral dose of /(35)S-labeled/ sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate, rats excreted 64% and 24% of the dose in urine and feces, respectively. A similar study of repeated doses of /(14)C-labeled/ alkylbenzenesulfonate (mean molecular wt 349, a major constituent of detergents) to rhesus monkeys has shown that radioactivity did not accumulate in the tissues. /Aromatic, sulfur-containing cmpd/
The Royal Society of Chemistry. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 6: A Review of the Literature Published during 1978 and 1979. London: The Royal Society of Chemistry, 1981., p. 354
The bioconcentration factor for (14)C alkylbenzene in bluegill sunfish (L. machrochirus) was 35. The value was significantly smaller than the predicted bioconcentration factor of 6300; the discrepancy was ascribed to metabolism. Alkylbenzene had similar patterns of tissue distribution and depuration rates when compared to its sulfonated counterpart, linear alkylbenzene sulfonate, a surfactant in laundry detergents, which had been shown to be readily metabolized.
Werner AF, Kimerle RA; Environ Toxicol Chem 1 (2): 143 (1982)
(14)C labelled sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate was administered daily in the diet at a concentration of 1.4 mg/kg to male rats for 5 weeks. From the total uptake (1.213 +/- 0.08 mg/animal) of sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate, 81.8% was excreted during the dosing period; 52.4% in feces and 29.4% in urine. Low levels of (14)C sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate derived residues were detected in all tissues analyzed on day 35 of the experiment. Following 1 week on normal diet only 7.8% of the nominally stored amount of (14)C was found in the excreta. Single ip application of 0.385 mg (14)C sodium dodecylbenzene/rat (2.26 +/- 0.15 mg/kg body weight) resulted in a total elimination of 94.5% within 10 days. 84.7% of the dose was eliminated in the first 24 hours. All fecal and renal (14)C sodium dodecylbenzene derived activity consisted of highly polar metabolites.
PMID:6623504 Lay JP et al; Toxicol Lett 17 (1-2): 187 (1983)
/A study was conducted/ to investigate the action mechanism of sulfonate anionic surfactant against plant viral infection, inhibitory action of sodium and calcium salts of branched dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid to tobacco mosaic virus (TMN) ordinary strain ... using the French bean local lesion assay method. The results suggest that the inhibitory action of dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid to TMV infection is not due to disintegration or inactivation of TMV but due to the depression of viral replication resulting from the disturbance in metabolism of the host cell and the function of the membrane at an early stage of TMV infection in that cell. /Sodium and calcium salts of dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid/
Watanabe T el al: J Pest Sci 5 (4): 503-9 (1980)
ABOUT THIS PAGE
65
PharmaCompass offers a list of 27176-87-0 API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right 27176-87-0 manufacturer or 27176-87-0 supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred 27176-87-0 manufacturer or 27176-87-0 supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the 27176-87-0 API Price utilized in the formulation of products. 27176-87-0 API Price is not always fixed or binding as the 27176-87-0 Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The 27176-87-0 Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A 27176-87-0 manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of 27176-87-0, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates 27176-87-0 manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. 27176-87-0 API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A 27176-87-0 supplier is an individual or a company that provides 27176-87-0 active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or 27176-87-0 finished formulations upon request. The 27176-87-0 suppliers may include 27176-87-0 API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
27176-87-0 Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of 27176-87-0 GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right 27176-87-0 GMP manufacturer or 27176-87-0 GMP API supplier for your needs.
A 27176-87-0 CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to 27176-87-0's compliance with 27176-87-0 specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
27176-87-0 CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each 27176-87-0 CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
27176-87-0 may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (27176-87-0 EP), 27176-87-0 JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (27176-87-0 USP).

