
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
JDMF
0
VMF
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
Annual Reports
NA
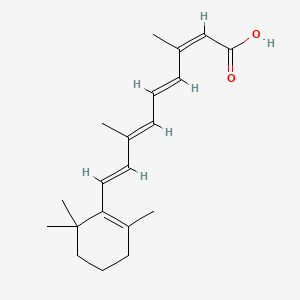

1. 13 Cis Retinoic Acid
2. 13-cis-retinoic Acid
3. Accutane
4. Isotretinoin Zinc Salt, 13 Cis Isomer
5. Isotretinoin Zinc Salt, 13-cis-isomer
6. Ro 4 3780
7. Ro 4-3780
8. Ro 43780
9. Roaccutane
1. 4759-48-2
2. 13-cis-retinoic Acid
3. Accutane
4. Roaccutane
5. Claravis
6. Neovitamin A Acid
7. 13-cis-vitamin A Acid
8. Amnesteem
9. Isotrex
10. Sotret
11. 13-cis Retinoic Acid
12. Teriosal
13. Isotretinon
14. Isotretinoino
15. Isotretinoine
16. Isotretinoinum
17. Absorica
18. Roaccutan
19. 13-ra
20. Retinoic Acid, 13-cis-
21. Roacutan
22. Isotretinoine [inn-french]
23. Isotretinoinum [inn-latin]
24. Isotretinoino [inn-spanish]
25. Cip-isotretinoin
26. Ro-4-3780
27. Accutane (tn)
28. Isotretinoin (usp)
29. Ro 4-3780
30. Cis-ra
31. (7e,9e,11e,13z)-retinoic Acid
32. Ro-43780
33. (13cis)-retinoic Acid
34. 13-cis Ra
35. Vitamin A Acid, 13-cis
36. Chembl547
37. Nsc-758156
38. Eh28up18if
39. Chebi:6067
40. 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)2-cis-4-trans-6-trans-8-trans-nonatetraenoic Acid
41. Retinoic Acid, (9,13-cis)-
42. Pat-001
43. 13-cis-retinoic Acid,isotretinoin
44. (2z,4e,6e,8e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic Acid
45. Isotane
46. (2z,4e6e,8e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic Acid
47. Cis-retinoic Acid
48. Myorisan
49. Zenatane
50. Isosuprea Lidose
51. 286464-92-4
52. Sotret (tn)
53. Ccris 4286
54. Hsdb 3929
55. 13 Cis-retinoic Acid
56. Sr-01000076103
57. Einecs 225-296-0
58. Unii-eh28up18if
59. Brn 1885770
60. Isotretinoina
61. Cis-retinoate
62. Bml2-e07
63. Isotretinoin [usan:ban:inn]
64. Cis Retinoic Acid
65. Trans-retinoicacid
66. Absorica (tn)
67. Prestwick_642
68. Cas-4759-48-2
69. Isotretinoin [usan:usp:inn:ban]
70. (2z,4e,6e,8e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexen-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic Acid
71. Absorica Ld
72. (13-cis)-retinoate
73. Cpd000471891
74. 13cra
75. Prestwick2_000256
76. Prestwick3_000256
77. Spectrum5_001795
78. Spectrum5_001937
79. Isotretinoin [mi]
80. (13-cis)-retinoic Acid
81. Dsstox_cid_3177
82. Isotretinoin [inn]
83. Isotretinoin [hsdb]
84. Isotretinoin [usan]
85. R 3255
86. Retinoic Acid 13-cis-form
87. Retinoic Acid, (13cis)-
88. Dsstox_rid_76906
89. Isotretinoin [vandf]
90. Dsstox_gsid_23177
91. Lopac0_001081
92. Schembl38299
93. Bspbio_000072
94. Bspbio_001331
95. Bspbio_003345
96. Isotretinoin [mart.]
97. 4-09-00-02388 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
98. Mls001074662
99. Isotretinoin [usp-rs]
100. Isotretinoin [who-dd]
101. Spectrum1502013
102. Bpbio1_000080
103. Gtpl7600
104. Dtxsid4023177
105. Hms1361c13
106. Hms1568d14
107. Hms1791c13
108. Hms1921d08
109. Hms1989c13
110. Hms2092n07
111. Hms2095d14
112. Hms2233a07
113. Hms3259j09
114. Hms3263i04
115. Hms3402c13
116. Hms3712d14
117. Hms3884a13
118. Isotretinoin [orange Book]
119. Pharmakon1600-01502013
120. Isotretinoin [ep Monograph]
121. Bcp18950
122. Zinc3792789
123. Isotretinoin [usp Monograph]
124. Tox21_200093
125. Tox21_501081
126. Bdbm50031459
127. Lmpr01090021
128. Mfcd00079542
129. Nsc758156
130. Akos015841158
131. Ccg-205158
132. Cs-1864
133. Db00982
134. Ds-3367
135. Lp01081
136. Nc00635
137. Nsc 758156
138. Sdccgsbi-0051051.p004
139. Idi1_033801
140. Ncgc00094358-01
141. Ncgc00094358-02
142. Ncgc00094358-03
143. Ncgc00094358-04
144. Ncgc00094358-05
145. Ncgc00094358-06
146. Ncgc00094358-07
147. Ncgc00094358-08
148. Ncgc00094358-09
149. Ncgc00094358-10
150. Ncgc00094358-11
151. Ncgc00094358-12
152. Ncgc00094358-13
153. Ncgc00094358-14
154. Ncgc00094358-15
155. Ncgc00094358-26
156. Ncgc00257647-01
157. Ncgc00261766-01
158. Retinoic Acid 13-cis-form [mi]
159. Br164589
160. Hy-15127
161. Smr000471891
162. 13-cis-retinoic Acid, >=98% (hplc)
163. Sbi-0051051.p003
164. Tretinoin Impurity A [ep Impurity]
165. Eu-0101081
166. R0088
167. 59i482
168. C07058
169. D00348
170. A917531
171. Q287029
172. Sr-01000076103-2
173. Sr-01000076103-5
174. Sr-01000076103-6
175. Sr-01000076103-9
176. Brd-k76723084-001-05-9
177. Sr-01000076103-10
178. Isotretinoin, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
179. Isotretinoin, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
180. (2z,4e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexenyl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid
181. Isotretinoin For Peak Identification, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
182. Isotretinoin, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
183. (2z,4e,6e,8e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid
184. (2z,4e,6e,8e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexenyl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic Acid
185. (2z,4e,6e,8e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoicacid
186. 3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2-cis-4-trans-6-trans-8-trans-nonatetraenoic Acid
| Molecular Weight | 300.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H28O2 |
| XLogP3 | 6.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 300.208930132 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 300.208930132 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 37.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 567 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Absorica |
| PubMed Health | Isotretinoin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiacne, Dermatological Agent |
| Drug Label | ABSORICA (isotretinoin) Capsules contain 10 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg, 30 mg, 35 mg or 40 mg of isotretinoin (a retinoid) in hard gelatin capsules for oral administration. In addition to the active ingredient, isotretinoin, each capsule contains the following... |
| Active Ingredient | Isotretinoin |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 30mg; 10mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ranbaxy |
| 2 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Amnesteem |
| PubMed Health | Isotretinoin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiacne, Dermatological Agent |
| Drug Label | Isotretinoin, USP a retinoid, is available as Amnesteem (isotretinoin capsules, USP) in 10 mg, 20 mg and 40 mg soft gelatin capsules for oral administration. Each capsule contains yellow wax, butylated hydroxyanisole, edetate disodium, hydrogenated v... |
| Active Ingredient | Isotretinoin |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 10mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms |
| 3 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Claravis |
| Drug Label | Isotretinoin, USP, a retinoid, is available as Claravis (isotretinoin capsules USP) in 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg and 40 mg hard gelatin capsules for oral administration. Chemically, isotretinoin is 13-cis-retinoic acid and is related to both retinoic ac... |
| Active Ingredient | Isotretinoin |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 30mg; 10mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva Pharms Usa |
| 4 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Sotret |
| PubMed Health | Isotretinoin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiacne, Dermatological Agent |
| Drug Label | Isotretinoin USP, a retinoid, is available as Zenatane (isotretinoin capsules USP) in 10 mg, 20 mg and 40 mg soft gelatin capsules for oral administration. Each capsule contains butylated hydroxyanisole, edetate disodium, hydrogenated vegetable oil... |
| Active Ingredient | Isotretinoin |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 30mg; 10mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ranbaxy |
| 5 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Absorica |
| PubMed Health | Isotretinoin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiacne, Dermatological Agent |
| Drug Label | ABSORICA (isotretinoin) Capsules contain 10 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg, 30 mg, 35 mg or 40 mg of isotretinoin (a retinoid) in hard gelatin capsules for oral administration. In addition to the active ingredient, isotretinoin, each capsule contains the following... |
| Active Ingredient | Isotretinoin |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 30mg; 10mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ranbaxy |
| 6 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Amnesteem |
| PubMed Health | Isotretinoin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiacne, Dermatological Agent |
| Drug Label | Isotretinoin, USP a retinoid, is available as Amnesteem (isotretinoin capsules, USP) in 10 mg, 20 mg and 40 mg soft gelatin capsules for oral administration. Each capsule contains yellow wax, butylated hydroxyanisole, edetate disodium, hydrogenated v... |
| Active Ingredient | Isotretinoin |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 10mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Mylan Pharms |
| 7 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Claravis |
| Drug Label | Isotretinoin, USP, a retinoid, is available as Claravis (isotretinoin capsules USP) in 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg and 40 mg hard gelatin capsules for oral administration. Chemically, isotretinoin is 13-cis-retinoic acid and is related to both retinoic ac... |
| Active Ingredient | Isotretinoin |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 30mg; 10mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva Pharms Usa |
| 8 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Sotret |
| PubMed Health | Isotretinoin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiacne, Dermatological Agent |
| Drug Label | Isotretinoin USP, a retinoid, is available as Zenatane (isotretinoin capsules USP) in 10 mg, 20 mg and 40 mg soft gelatin capsules for oral administration. Each capsule contains butylated hydroxyanisole, edetate disodium, hydrogenated vegetable oil... |
| Active Ingredient | Isotretinoin |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 30mg; 10mg; 40mg; 20mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Ranbaxy |
Dermatologic Agents; Teratogens
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Isotretinoin. Online file (MeSH, 2018). Available from, as of August 29, 2018: https://meshb.nlm.nih.gov/search
/CLINICAL TRIALS/ ClinicalTrials.gov is a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world. The Web site is maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Each ClinicalTrials.gov record presents summary information about a study protocol and includes the following: Disease or condition; Intervention (for example, the medical product, behavior, or procedure being studied); Title, description, and design of the study; Requirements for participation (eligibility criteria); Locations where the study is being conducted; Contact information for the study locations; and Links to relevant information on other health Web sites, such as NLM's MedlinePlus for patient health information and PubMed for citations and abstracts for scholarly articles in the field of medicine. Isotretinoin is included in the database.
NIH/NLM; ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available from, as of August 29, 2018: https://clinicaltrials.gov/
Isotretinoin capsules are indicated for the treatment of severe recalcitrant nodular acne. Nodules are inflammatory lesions with a diameter of 5 mm or greater. The nodules may become suppurative or hemorrhagic. "Severe," by definition, means "many" as opposed to "few or several" nodules. Because of significant adverse effects associated with its use, isotretinoin capsules should be reserved for patients with severe nodular acne who are unresponsive to conventional therapy, including systemic antibiotics. /Included in US product labeling/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Isotretinoin Capsule, Liquid Filled (Updated: June 30, 2017). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c2917c3d-3499-48a0-ba53-120cb979195d
Isotretinoin has been used in the treatment of cutaneous disorders of keratinization that are resistant to treatment with other agents (e.g., corticosteroids, topical tretinoin); however, the specific role of isotretinoin in the treatment of these disorders and the safety of long-term use and high dosages of the drug have not been determined. /NOT included in US product labeling/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; Drug Information 2018. Bethesda, MD. 2018
Isotretinoin has been used in a limited number of patients in the prevention, treatment, and adjunctive treatment of various cutaneous and extracutaneous malignant neoplasms (of epithelial origin); however, the specific role of the drug in the treatment of these conditions has not been determined and additional study is needed. /NOT included in US product labeling/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; Drug Information 2018. Bethesda, MD. 2018
/BOXED WARNING/ Isotretinoin must not be used by female patients who are or may become pregnant. There is an extremely high risk that severe birth defects will result if pregnancy occurs while taking isotretinoin in any amount, even for short periods of time. Potentially any fetus exposed during pregnancy can be affected. There are no accurate means of determining whether an exposed fetus has been affected. Birth defects which have been documented following isotretinoin exposure include abnormalities of the face, eyes, ears, skull, central nervous system, cardiovascular system and thymus and parathyroid glands. Cases of IQ scores less than 85 with or without other abnormalities have been reported. There is an increased risk of spontaneous abortion, and premature births have been reported. Documented external abnormalities include: skull abnormality; ear abnormalities (including anotia, micropinna, small or absent external auditory canals); eye abnormalities (including microphthalmia); facial dysmorphia; cleft palate. Documented internal abnormalities include: CNS abnormalities (including cerebral abnormalities, cerebellar malformation, hydrocephalus, microcephaly, cranial nerve deficit); cardiovascular abnormalities; thymus gland abnormality; parathyroid hormone deficiency. In some cases death has occurred with certain of the abnormalities previously noted. If pregnancy does occur during treatment of a female patient who is taking isotretinoin, isotretinoin must be discontinued immediately and she should be referred to an Obstetrician-Gynecologist experienced in reproductive toxicity for further evaluation and counseling. Special Prescribing Requirements Because of isotretinoin's teratogenicity and to minimize fetal exposure, isotretinoin is approved for marketing only under a special restricted distribution program approved by the Food and Drug Administration. This program is called iPLEDGE. Isotretinoin must only be prescribed by prescribers who are registered and activated with the iPLEDGE Program. Isotretinoin must only be dispensed by a pharmacy registered and activated with iPLEDGE, and must only be dispensed to patients who are registered and meet all the requirements of iPLEDGE.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Isotretinoin Capsule, Liquid Filled (Updated: June 30, 2017). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c2917c3d-3499-48a0-ba53-120cb979195d
Pregnancy risk category: X /CONTRAINDICATED IN PREGNANCY. Studies in animals or humans, or investigational or post-marketing reports, have demonstrated positive evidence of fetal abnormalities or risk which clearly outweights any possible benefit to the patient./
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Isotretinoin Capsule, Liquid Filled (Updated: June 30, 2017). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c2917c3d-3499-48a0-ba53-120cb979195d
Isotretinoin is teratogenic in humans and is contraindicated during pregnancy. Unless abstinence is the chosen method, it is recommended that the patient use two forms of effective contraception to prevent pregnancy, starting 1 month before initiation of treatment, during treatment, and for 1 month after discontinuation of treatment.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1696
Although not every fetus exposed to isotretinoin has been affected, the risk is high that an infant will have a deformity or abnormality if the pregnancy occurred while the mother was taking isotretinoin, even for a short period of time. Whenever an unexpected pregnancy occurs during the time of teratogenic risk, the risk-benefit ratio of continuing the pregnancy must be considered. The risks include: 15% incidence of major malformations, 5% incidence of perinatal mortality, 16% incidence of premature birth, and 40% incidence of spontaneous abortion.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 24th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2004., p. 1696
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for 13-cis-Retinoic acid (40 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Isotretinoin is indicated to treat severe recalcitrant nodular acne and patients 12 years enrolled in the iPLEDGE program.
FDA Label
The pharmacodynamics of isotretinoin are poorly understood.
Dermatologic Agents
Drugs used to treat or prevent skin disorders or for the routine care of skin. (See all compounds classified as Dermatologic Agents.)
Teratogens
An agent that causes the production of physical defects in the developing embryo. (See all compounds classified as Teratogens.)
D - Dermatologicals
D10 - Anti-acne preparations
D10A - Anti-acne preparations for topical use
D10AD - Retinoids for topical use in acne
D10AD04 - Isotretinoin
D - Dermatologicals
D10 - Anti-acne preparations
D10B - Anti-acne preparations for systemic use
D10BA - Retinoids for treatment of acne
D10BA01 - Isotretinoin
Absorption
Patients reach a maximum concentration of 74-511ng/mL after 1-4 hours following a 100mg oral dose. Isotretinoin is better absorbed with a high fat meal and bioavailability may change from one brand to another. Following a 40mg oral dose, fasted subjects reached a maximum concentration of 314ng/mL in 2.9 hours with an area under the curve of 4055ng/mL\*hr. Subjects given a high fat meal and a 40mg oral doses reached a maximum concentration of 395ng/mL in 6.4 hours with an area under the curve of 6095ng/mL\*mL.
Route of Elimination
Isotretinoin and its metabolites are conjugated and excreted in the urine and feces in similar amounts. 53-74% of an oral dose is eliminated as unchanged isotretinoin in the feces.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution in humans is unknown because there is no intravenous preparation. In a study of pediatric patients with neuroblastoma the volume of distribution was found to be 85L. The volume of distribution was also found to be 2432mL/kg in guinea pigs and 1716mL/kg in obese rats.
Clearance
The clearance of isotretinoin is 15.9L/h in pediatric patients with neuroblastoma. Clearance is also 21.3mL/min/kg in guinea pigs and 7.2mL/min/kg in obese rats.
Following oral administration of isotretinoin, there is an apparent lag time of about 0.5-2 hours before the drug appears in systemic circulation. The lag time is thought to result from disintegration of the capsule and subsequent dissolution of the drug in GI contents. Absorption of the drug after this lag time is rapid. The actual bioavailability of orally administered isotretinoin has not been determined in humans, but studies in animals indicate that about 25% of an oral dose of the drug reaches systemic circulation as unchanged isotretinoin The low bioavailability observed in animals may result from biodegradation of the drug in the GI lumen and/or metabolism of the drug during absorption (in the GI mucosa) and first pass through the liver. Food and/or milk increase GI absorption of isotretinoin. Peak blood isotretinoin concentrations are slightly delayed and substantially increased and the area under the blood concentration-time curve (AUC) of the drug is approximately 1.5-2 times greater when isotretinoin is administered 1 hour before, concomitantly with, or 1 hour after a meal than when the drug is administered in the fasting state. Because of its high lipophilicity, oral absorption of isotretinoin is enhanced when the drug is administered with a high-fat meal. In a crossover study of 74 healthy adults who received a single 80-mg isotretinoin dose (as two 40-mg capsules) under fasted and fed conditions, both the peak plasma concentration and total area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) of the drug were more than doubled when isotretinoin was administered immediately after a standardized high-fat meal compared with administration in the fasted state. Because the observed elimination half-life of the drug remained unchanged, it is suggested that food appears to increase the bioavailability of isotretinoin without altering its disposition. The time to peak concentration was also increased with food and may be related to a longer absorption phase. Consequently, the manufacturers recommend that isotretinoin capsules always be administered with food.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; Drug Information 2018. Bethesda, MD. 2018
The harmonic mean elimination for the simultaneous iv and oral administration of isotretinoin was approx 5.5 hr. The mean blood clearance, following iv admin, and the intrinsic clearance, following oral administration, were 5.19 and 6.63 mL/min/kg, respectively. The average abs bioavailability was approx 21% indicating an overall 1st-pass effect of approx 80%. Analysis of gut contents for total (14)-C activity suggested that a fraction of the isotretinoin dose was biologically or chemically degraded in the gut lumen prior to absorption.
PMID:6138231 Cotler S et al; DRUG METAB DISPOS 11 (5): 458-62 (1983)
Clinical doses of isotretinoin range from 0.5 to 8 mg/kg/day, with acute side effects appearing following doses of 1 mg/kg/day or greater. Plasma concn of isotretinoin following single and multiple doses peak between 2 to 4 hr and exhibit elimination half-lives of 10 to 20 hr. Isotretinoin blood concn-time curves following a single- or multiple-dose regimen are well described by a linear model with biphasic disposition characteristics. ... In most conditions, the retinoids produce a maximal effect in about 8 weeks (at the highest tolerated dose), with a slow recurrence of symptoms usually occurring within several weeks following cessation of treatment - except in the treatment of cystic acne with isotretinoin. Maintenance or intermittent dosing usually results in a prolongation of remission.
PMID:3882304 Lucek RW, Colburn WA; Clin Pharmacokinet 10 (1): 38-62 (1985)
A case study involving the disposition of 13-cis retinoic acid in embryonic tissues from a woman who unintentionally took 40 mg/day of isotretinoin from day 8-28 of gestation was discussed. When the pregnancy was terminated on day 31, between 72 and 80 hr after the last dose of isotretinoin, maternal serum samples were obtained. Retinoid concn in the maternal serum, embryonic tissue, and 6 samples of placental tissue were later measured by high performance liquid chromatography. The results showed that in humans, the intake of isotretinoin during pregnancy results in high placental and embryonic concn of all-trans-retoinic acid, in contrast to what was previously discovered in mice experiments. It was concluded that the metabolic activation of isotretinoin to the all-trans isomer could be responsible for the teratogenicity of isotretinoin.
Kraft JC et al; N Engl J Med 321 (Jul 27): 262 (1989)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for 13-cis-Retinoic acid (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Isotretinoin, or 13-cis-retinoic acid can undergo reversible cis-trans isomerization to all-trans-retinoic acid. Isotretinoin undergoes 4-hydroxylation to 4-hydroxy-13-cis-retinoic acid, which is oxidized to the main metabolite 4-oxo-13-cis-retinoic acid.. All-trans-retinoic acid undergoes 4-hydroxylation to 4-hydroxy-all-trans-retinoic acid, which is oxidized to 4-oxo-all-trans-retinoic acid. 4-oxo-13-cis-retinoic acid can undergo reversible cis-trans isomerization to 4-oxo-all-trans-retinoic acid.
... In human volunteers and patients, one major blood metabolite of isotretinoin is 4-oxo-isotretinoin which undergoes slower elimination than isotretinoin and may itself be a participant in teratogenesis.
PMID:3478842 Kochhar DM, Penner JD; Teratology 36 (1): 67-75 (1987)
This paper reviews the teratogenicity of isotretinoin in regard to aspects of species variation, toxicokinetics, and metabolism. The insensitive species (rat, mouse) eliminate the drug rapidly through detoxification to the beta-glucuronide; also, placental transfer is limited in these species. On the other hand, in sensitive species (primates), the drug is predominantly metabolized to the active 13-cis-4-oxo-retinoic acid; placental transfer is more extensive here. The beta-glucuronides showed limited placental transfer in all species examined; these metabolites exhibited very low, if any, measurable concentrations in the human. The 13-cis-retinoic acid is not appreciably bound to cellular retinoid-binding proteins or nuclear receptors and exhibits low tissue distribution and placental transfer. Its access to the nucleus may be extensive. Because of the long half life of 13-cis-retinoic acid, continuous isomerization results in significant area under the concentration-time curve levels of all-trans-retinoic acid in the mouse, monkey and the human; the all-trans-retinoic acid formed is extensively distributed across the placenta and may be an important factor that contributes to the teratogenic potency of 13-cis-retinoic acid. Isomerization cannot explain the teratogenic effects of 13-cis-retinoic acid in the rat and rabbit. It is concluded that the high teratogenic activity of isotretinoin in sensitive species (human, monkey) is related to slow elimination of the 13-cis-isomer, to metabolism to the 4-oxo-derivative, to increased placental transfer, to continuous isomerization and significant exposure of the target tissue to all-trans-retinoic acid; and to lack of binding to cytoplasmic retinoid binding proteins that could possibly result in ready access to the nucleus.
Nau H; J Am Acad Dermatol 45 (5): S183-7 (2001)
Isotretinoin is metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P-450 (CYP) microsomal enzyme system, principally by CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP3A4, and CYP2B6 isoenzymes, to several metabolites (e.g., 4-oxo-isotretinoin, retinoic acid [tretinoin], and 4-oxo-retinoic acid [4-oxo-tretinoin]). Retinoic acid and 13-cis-retinoic acid are geometric isomers and show reversible interconversion, and the administration of one isomer will give rise to the other. Isotretinoin also is irreversibly oxidized to 4-oxo-isotretinoin, which forms its own geometric isomer, 4-oxo-tretinon. All of these metabolites possess retinoid activity that is more than that of the parent compound in some in vitro models. However, the clinical importance of these models is unknown. Concurrent administration of food has been shown to increase the extent of formation of all metabolites in plasma when compared to administration of isotretinoin under fasted conditions. In addition, the exposure of patients to 4-oxo-isotretinoin at steady-state under fasted and fed conditions was approximately 3.4 times higher than that of isotretinoin.
In vitro studies indicate that the primary P450 isoforms involved in isotretinoin metabolism are 2C8, 2C9, 3A4 and 2B6. Isotretinoin and its metabolites are further metabolized into conjugates, which are then excreted in urine and feces.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Isotretinoin Capsule, Liquid Filled (Updated: June 30, 2017). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c2917c3d-3499-48a0-ba53-120cb979195d
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for 13-cis-Retinoic acid (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Isotretinoin has known human metabolites that include (2Z,4E,6Z,8E)-6-hydroxy-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexen-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic acid.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
The half life ranges from 7-39 hours with a mean elimination half life of 20 hours. The half life of 4-oxo-13-cis-retinoic acid ranges from 17-50 hours with a mean elimination half life of 25 hours.
Following oral administration of an 80 mg dose of (14)C-isotretinoin as a liquid suspension, (14)C-activity in blood declined with a half-life of 90 hours.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Isotretinoin Capsule, Liquid Filled (Updated: June 30, 2017). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c2917c3d-3499-48a0-ba53-120cb979195d
After a single 80 mg oral dose of isotretinoin to 74 healthy adult subjects under fed conditions, the mean +/- SD elimination half-lives of isotretinoin and 4-oxo-isotretinoin were 21 +/- 8.2 hours and 24 +/- 5.3 hours, respectively.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Isotretinoin Capsule, Liquid Filled (Updated: June 30, 2017). Available from, as of September 13, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=c2917c3d-3499-48a0-ba53-120cb979195d
Blood concentrations of isotretinoin decline in a biphasic manner. In adults with normal renal function, the half-life in the initial phase averages 0.5 hours and the half-life in the terminal phase averages 10-20 hours (range: 7-39 hours).
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; Drug Information 2018. Bethesda, MD. 2018
... Plasma concentration of isotretinoin following single and multiple doses peak between 2 to 4 hr and exhibit elimination half-lives of 10 to 20 hr ...
PMID:3882304 Lucek RW, Colburn WA; Clin Pharmacokinet 10 (1): 38-62 (1985)
For more Biological Half-Life (Complete) data for 13-cis-Retinoic acid (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Isotretinoin produces its effects through altering progress through the cell cycle, cell differentiation, survival, and apoptosis. These actions reduce sebum production, preventing the blockage of pores, and growth of acne causing bacteria. Isotretinoin and 4-oxo-isotretinoin both significantly reduce the production of sebum. Isotretinoin has little to no affinity for retinol binding proteins (RBPs) and retinoic acid nuclear receptors (RARs). Tretinoin and 4-oxo-tretinion bind to the RAR- receptor, which is suspected to be part of the action of acne treatment by isotretinoin. Isotretinoin induces apoptosis in sebocytes, leading to a decrease in sebum production. Isotretinoin also reduces the formation of comedones by reducing hyperkeratinization through an unknown mechanism. Isotretinoin does not directly kill bacteria but it does reduce the size of sebum ducts and makes the microenvironment less hospitable to acne causing bacteria. It may also increase immune mechanisms and alter chemotaxis of monocytes to reduce inflammation. There is preliminary evidence suggesting isotretinoin may interact with FoxO1, which may explain a substantial number of isotretinoin's unexplained actions.
This paper reviews the teratogenicity of isotretinoin in regard to aspects of species variation, toxicokinetics, and metabolism. The insensitive species (rat, mouse) eliminate the drug rapidly through detoxification to the beta-glucuronide; also, placental transfer is limited in these species. On the other hand, in sensitive species (primates), the drug is predominantly metabolized to the active 13-cis-4-oxo-retinoic acid; placental transfer is more extensive here. The beta-glucuronides showed limited placental transfer in all species examined; these metabolites exhibited very low, if any, measurable concentrations in the human. The 13-cis-retinoic acid is not appreciably bound to cellular retinoid-binding proteins or nuclear receptors and exhibits low tissue distribution and placental transfer. Its access to the nucleus may be extensive. Because of the long half life of 13-cis-retinoic acid, continuous isomerization results in significant area under the concentration-time curve levels of all-trans-retinoic acid in the mouse, monkey and the human; the all-trans-retinoic acid formed is extensively distributed across the placenta and may be an important factor that contributes to the teratogenic potency of 13-cis-retinoic acid. Isomerization cannot explain the teratogenic effects of 13-cis-retinoic acid in the rat and rabbit. It is concluded that the high teratogenic activity of isotretinoin in sensitive species (human, monkey) is related to slow elimination of the 13-cis-isomer, to metabolism to the 4-oxo-derivative, to increased placental transfer, to continuous isomerization and significant exposure of the target tissue to all-trans-retinoic acid; and to lack of binding to cytoplasmic retinoid binding proteins that could possibly result in ready access to the nucleus.
Nau H; J Am Acad Dermatol 45 (5): S183-7 (2001)

API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS

Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE


LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?