
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
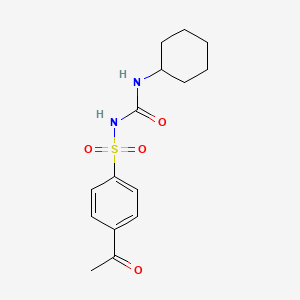

1. Dimelor
2. Dymelor
3. Gamadiabet
1. 968-81-0
2. Dymelor
3. Acetohexamid
4. Gamadiabet
5. Dimelor
6. Hypoglicil
7. Metaglucina
8. Tsiklamid
9. Minoral
10. Ordimel
11. Acetohexamida
12. Acetohexamidum
13. 1-(4-acetylphenyl)sulfonyl-3-cyclohexylurea
14. N-(p-acetylphenylsulfonyl)-n'-cyclohexylurea
15. 1-((p-acetylphenyl)sulfonyl)-3-cyclohexylurea
16. 4-acetyl-n-[(cyclohexylamino)carbonyl]benzenesulfonamide
17. Nci-c03247
18. 1-(p-acetylbenzenesulfonyl)-3-cyclohexylurea
19. U-14812
20. 4-acetyl-n-((cyclohexylamino)carbonyl)benzenesulfonamide
21. Benzenesulfonamide, 4-acetyl-n-[(cyclohexylamino)carbonyl]-
22. Nsc-759128
23. Qgc8w08i6i
24. Benzenesulfonamide, 4-acetyl-n-((cyclohexylamino)carbonyl)-
25. 3-(4-acetylbenzenesulfonyl)-1-cyclohexylurea
26. Chebi:28052
27. 4-acetyl-n-(cyclohexylcarbamoyl)benzenesulfonamide
28. Acetohexamide [usan)
29. Dsstox_cid_7
30. Ncgc00015014-05
31. Cas-968-81-0
32. 1-(4-acetylphenyl)sulfonyl-3-cyclohexyl-urea
33. 1-[(p-acetylphenyl)sulfonyl]-3-cyclohexylurea
34. Acetohexamide [usan]
35. Dsstox_rid_75319
36. Dsstox_gsid_20007
37. Urea, 1-((p-acetylphenyl)sulfonyl)-3-cyclohexyl-
38. Urea, 1-[(p-acetylphenyl)sulfonyl]-3-cyclohexyl-
39. Acetohexamidum [inn-latin]
40. Acetohexamida [inn-spanish]
41. Ccris 4
42. Dymelor (tn)
43. Hsdb 3280
44. Sr-01000075539
45. Einecs 213-530-4
46. U 14812
47. Unii-qgc8w08i6i
48. Brn 2225115
49. N-(p-acetylbenzenesulfonyl)-n'-cyclohexylurea
50. Prestwick_3
51. 3-aminomethylbenzamide
52. 4-acetyl-n-[(cyclohexylamino)-carbonyl]benzenesulfonamide
53. Acetohexamide [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
54. Lopac-a-178
55. Prestwick0_000055
56. Prestwick1_000055
57. Prestwick2_000055
58. Prestwick3_000055
59. A-178
60. Acetohexamide [mi]
61. Acetohexamide [inn]
62. Acetohexamide [jan]
63. Acetohexamide [hsdb]
64. Chembl1589
65. Lopac0_000088
66. Schembl37620
67. Acetohexamide [vandf]
68. Bspbio_000209
69. Mls002154186
70. Acetohexamide [mart.]
71. Spbio_002130
72. Acetohexamide [who-dd]
73. 4-acetyl-n-(cyclohexylcarbamoyl)benzene-1-sulfonamide
74. Bpbio1_000231
75. Gtpl6793
76. Dtxsid7020007
77. Acetohexamide (jp17/usp/inn)
78. Acetohexamide, Analytical Standard
79. Hms1568k11
80. Hms2093h21
81. Hms2095k11
82. Hms2236m07
83. Hms3260a18
84. Hms3372b02
85. Hms3712k11
86. Pharmakon1600-01505425
87. Acetohexamide [orange Book]
88. Bcp34666
89. Hy-b0881
90. Acetohexamide [usp Impurity]
91. Tox21_110067
92. Tox21_202022
93. Tox21_302735
94. Tox21_500088
95. Nsc759128
96. S5717
97. Zinc18067894
98. Akos015916290
99. Tox21_110067_1
100. Ccg-204183
101. Db00414
102. Lp00088
103. Nsc 759128
104. Sdccgsbi-0050076.p003
105. Ncgc00015014-01
106. Ncgc00015014-02
107. Ncgc00015014-03
108. Ncgc00015014-04
109. Ncgc00015014-06
110. Ncgc00015014-07
111. Ncgc00015014-08
112. Ncgc00015014-11
113. Ncgc00015014-15
114. Ncgc00016555-01
115. Ncgc00091230-01
116. Ncgc00091230-02
117. Ncgc00091230-03
118. Ncgc00091230-04
119. Ncgc00256467-01
120. Ncgc00259571-01
121. Ncgc00260773-01
122. Smr001233477
123. Sbi-0050076.p002
124. Db-057652
125. Eu-0100088
126. Ft-0661053
127. C06806
128. D00219
129. 1-[(4-acetylbenzene)sulfonyl]-3-cyclohexylurea
130. A845651
131. A935756
132. Dymelor; Gamadiabet; Acetohexamid; Dimelin; Dimelor
133. Q4673274
134. Sr-01000075539-1
135. Sr-01000075539-3
136. Sr-01000075539-6
137. Brd-k52960356-001-03-1
138. Brd-k52960356-001-06-4
139. Z1558572527
140. 1-acetyl-4-(([(cyclohexylamino)carbonyl]amino)sulfonyl)benzene #
141. Acetohexamide, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
142. Benzenesulfonamide, 4-acetyl-n-((cyclohexylamino)carbonyl)
143. 1-[(4-acetylbenzene)sulfonyl]-3-cyclohexylurea 4-acetyl-n-(cyclohexylcarbamoyl)benzenesulfonamide
| Molecular Weight | 324.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H20N2O4S |
| XLogP3 | 2.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 324.11437830 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 324.11437830 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 101 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 498 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Hypoglycemic Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
...USED IN TREATMENT OF MILD TO MODERATELY SEVERE DIABETES MELLITUS OF MATURITY-ONSET, NONKETOTIC TYPE IN PT IN WHOM DIET ALONE CANNOT CONTROL GLYCOSURIA.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 904
...MAY BE USEFUL IN PT WHO ARE ALLERGIC TO INSULIN & ARE UNWILLING OR UNABLE TO UNDERGO DESENSITIZATION OR...TO INJECT INSULIN. ...ESP USEFUL IN ELDERLY DIABETIC WITH POOR VISION WHO LIVES ALONE & IS IN DANGER OF DEVELOPING HYPOGLYCEMIA FROM INCORRECT INSULIN DOSAGE. /ORAL HYPOGLYCEMIC AGENTS/
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 593
...IT IS ONLY ONE WITH URICOSURIC PROPERTIES, SOME CLINICIANS PREFER THIS AGENT FOR DIABETIC WITH GOUT.
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 595
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for ACETOHEXAMIDE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
HEMATOLOGICAL (LEUKOPENIA, AGRANULOCYTOSIS, THROMBOCYTOPENIA, PANCYTOPENIA, & HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA), CUTANEOUS (RASHES, PHOTOSENSITIVITY), GI (NAUSEA, VOMITING, RARELY HEMORRHAGE), & HEPATIC (INCR SERUM ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE, CHOLESTATIC JAUNDICE) REACTIONS HAVE BEEN REPORTED.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1521
INCIDENCE OF UNTOWARD EFFECTS IS LOW & REACTIONS ARE REVERSIBLE WHEN...DISCONTINUED.
American Medical Association, AMA Department of Drugs, AMA Drug Evaluations. 3rd ed. Littleton, Massachusetts: PSG Publishing Co., Inc., 1977., p. 595
IT IS INEFFECTIVE IN JUVENILE-ONSET, UNSTABLE, OR BRITTLE DIABETES & IS CONTRAINDICATED IN DIABETES COMPLICATED BY ACIDOSIS, KETOSIS, SEVERE INFECTIONS, COMA, SEVERE TRAUMA, OR MAJOR SURGERY.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 904
Caution in elderly and patients with renal disease. Significant uricosuric effects. /from table/
Young, L.Y., M.A. Koda-Kimble (eds.). Applied Therapeutics. The Clinical Use of Drugs. 6th ed. Vancouver, WA., Applied Therapeutics, Inc. 1995., p. 48-37
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for ACETOHEXAMIDE (17 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Used in the management of diabetes mellitus type 2 (adult-onset).
Acetohexamide is an intermediate-acting, first-generation oral sulfonylurea. It lowers blood sugar by stimulating the pancreatic beta cells to secrete insulin and by helping the body use insulin efficiently. Due to its primary action on the pancreatic beta cells, the drug is only effective when there are functional pancreatic beta cells that can produce insulin granules. Acetohexamide has one-third the potency of chlorpropamide, and twice the potency of tolbutamide; however, similar hypoglycemic efficacy occurs with equipotent dosage of sulfonylureas.
Hypoglycemic Agents
Substances which lower blood glucose levels. (See all compounds classified as Hypoglycemic Agents.)
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A10 - Drugs used in diabetes
A10B - Blood glucose lowering drugs, excl. insulins
A10BB - Sulfonylureas
A10BB31 - Acetohexamide
Absorption
Rapidly absorbed from the GI tract.
ACETOHEXAMIDE IS RAPIDLY ABSORBED, & MAX HYPOGLYCEMIC ACTIVITY IS OBSERVED ABOUT 3 HR AFTER INGESTION. TOTAL DURATION OF ACTION IS 12-24 HR. MUCH OF ACTIVITY IS ASCRIBABLE TO METABOLITE, HYDROXYHEXAMIDE, WHICH HAS PLASMA T/2 OF ABOUT 6 HR...ACETOHEXAMIDE, HAS PLASMA T/2 OF 1.3 HR.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1521
IN PERSONS WITH NORMAL RENAL & HEPATIC FUNCTION, MORE THAN 80% IS EXCRETED, LARGELY AS METABOLITES, IN 24 HR.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1521
TIME OF PEAK CONCN AFTER ORAL DOSE: 3 HR /FROM TABLE/
Miller, R. R., and D. J. Greenblatt. Handbook of Drug Therapy. New York: Elsevier North Holland, 1979., p. 688
...5 DAYS AFTER ORAL DOSE...TO RATS. 86% WAS EXCRETED IN 24-HR URINE & 9% IN 48-HR FECES. RESULTS INDICATED RAPID ABSORPTION & EXCRETION...
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 1: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1960 and 1969. London: The Chemical Society, 1970., p. 64
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ACETOHEXAMIDE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Extensively metabolized in the liver to the active metabolite hydroxyhexamide, which exhibits greater hypoglycemic potency than acetohexamide. Hydroxyhexamide is believed to be responsible for prolonged hypoglycemic effects.
HYDROXYHEXAMIDE...MAJOR METABOLITE OF ACETOHEXAMIDE...IN HUMANS, HAS L-CONFIGURATION. ...CONTRIBUTES SIGNIFICANTLY TO HYPOGLYCEMIC RESPONSE THAT FOLLOWS ADMIN...
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 1: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1960 and 1969. London: The Chemical Society, 1970., p. 221
PRINCIPAL ROUTE OF METABOLIC DEGRADATION IN MAN...REDUCTION OF P-ACETYL GROUP TO /1-[(P-ALPHA-HYDROXYETHYLBENZENE)SULFONYL]-3-CYCLOHEXYLUREA WHICH/ EXHIBITS HYPOGLYCEMIA IN MAN & OTHER ANIMALS. &...MAY PROLONG HYPOGLYCEMIC ACTIVITY OF ACETOHEXAMIDE /ORAL/
American Society of Hospital Pharmacists. Data supplied on contract from American Hospital Formulary Service and other current ASHP sources., p. 1964
Sulfonylureas are rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, transported in the blood in highly protein-bound complexes, and subjected to extensive hepatic metabolism (except for chlorpropamide). Wide variation exists among the sulfonylureas in hepatic metabolism and remnal clearance, factors that tend to alter the steady-state serum levels. Metabolites may be active, so there may be a variation between the plasma half-life of the parent drug and the degree of hypoglycemia encountered. /Sulfonylurea/
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 722
Active metabolite greater than parent drug. Metabolite excreted, in part, by kidney. /from table/
Young, L.Y., M.A. Koda-Kimble (eds.). Applied Therapeutics. The Clinical Use of Drugs. 6th ed. Vancouver, WA., Applied Therapeutics, Inc. 1995., p. 48-37
Elimination half-life of the parent compound is 1.3 hours and the elimination half-life of the active metabolite is approximately 5-6 hours.
Half-life...3.5-11 /hours/ /from table/
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 722
Sulfonylureas such as acetohexamide bind to an ATP-dependent K+ channel on the cell membrane of pancreatic beta cells. This inhibits a tonic, hyperpolarizing outflux of potassium, which causes the electric potential over the membrane to become more positive. This depolarization opens voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. The rise in intracellular calcium leads to increased fusion of insulin granulae with the cell membrane, and therefore increased secretion of (pro)insulin.
SULFONYLUREAS STIMULATE ISLET TISSUE TO SECRETE INSULIN. ... ADMIN OF SULFONYLUREAS INCR CONCN OF INSULIN IN PANCREATIC REIN... /SULFONYLUREAS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1520
Sulfonylureas are now...thought to act by a number of different mechanisms. 1. ...produce a depolarization of the pancreatic islet beta cell membrane potassium ion permeability. This results in a release of preformed insulin into the circulation and occurs mostly in non-insulin dependent diabetics. 2. ...reduce basal glucose output from the liver... 3. increase insulin receptor binding... 4. ...increasing intracellular levels of AMP... 5. increase insulin secretion by suppressing the release of glucagon and somatostatin from alpha and delta pancreatic cells. /Sulfonylureas/
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 723
Sulfonylureas lower blood glucose in NIDDM by directly stimulating the acute release of insulin from functioning beta cells of pancreatic islet tissue by an unknown process that involves a sulfonylurea receptor on the beta cell. Sulfonylureas inhibit the ATP potassium channels on the beta cell membrane and potassium efflux, which results in depolarization and calcium influx, calcium-calmodulin binding, kinase activation, and release of insulin containing granules by exocytosis, an effect similar to that of glucose. Insulin is a hormone that lowers blood glucose and controls the storage and metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Therefore, sulfonylureas are effective only in patients whose pancreata are capable of producing insulin. /Sulfonylurea antidiabetic agents/
USP. Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 19th ed. Volume I.Micromedex, Inc. Englewood, CO., 1999. Content Prepared by the U.S. Pharmacopieal Convention, Inc., p. 284
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
31
PharmaCompass offers a list of Acetohexamide API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Acetohexamide manufacturer or Acetohexamide supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Acetohexamide manufacturer or Acetohexamide supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Acetohexamide API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Acetohexamide API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Acetohexamide Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Acetohexamide Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Acetohexamide manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Acetohexamide, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Acetohexamide manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Acetohexamide API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Acetohexamide supplier is an individual or a company that provides Acetohexamide active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Acetohexamide finished formulations upon request. The Acetohexamide suppliers may include Acetohexamide API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Acetohexamide suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Acetohexamide DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Acetohexamide active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Acetohexamide DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Acetohexamide USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Acetohexamide DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Acetohexamide USDMF includes data on Acetohexamide's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Acetohexamide USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Acetohexamide suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
Acetohexamide Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Acetohexamide GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Acetohexamide GMP manufacturer or Acetohexamide GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Acetohexamide CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Acetohexamide's compliance with Acetohexamide specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Acetohexamide CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Acetohexamide CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Acetohexamide may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Acetohexamide EP), Acetohexamide JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Acetohexamide USP).
