
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
FDA Orange Book
0
Europe
0
Canada
0
Australia
0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
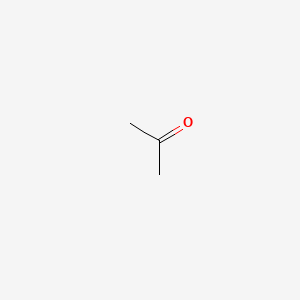

1. 2-propanone
2. 67-64-1
3. Propanone
4. Dimethyl Ketone
5. Propan-2-one
6. Methyl Ketone
7. Pyroacetic Ether
8. Dimethylformaldehyde
9. Beta-ketopropane
10. Dimethylketal
11. Chevron Acetone
12. Ketone Propane
13. Aceton
14. Pyroacetic Acid
15. Ketone, Dimethyl
16. Dimethylketone
17. Fema No. 3326
18. .beta.-ketopropane
19. Rcra Waste Number U002
20. Dimethyl Formaldehyde
21. Taimax
22. Aceton [german, Dutch, Polish]
23. Ketone, Dimethyl-
24. Acetone [nf]
25. Nsc 135802
26. Mfcd00008765
27. Nsc-135802
28. (ch3)2co
29. Chebi:15347
30. 1364ps73af
31. Acetone (nf)
32. Ncgc00091179-01
33. Dsstox_cid_1482
34. Dsstox_rid_76176
35. Acetone (natural)
36. Dsstox_gsid_21482
37. Caswell No. 004
38. 3-methyl-4-(2,2-dimethyl-6-methylenecyclohexyl)-3-buten-2-one
39. Acetone, For Hplc, >=99.8%
40. Acetone, For Hplc, >=99.9%
41. Acetone, Acs Reagent, >=99.5%
42. Cas-67-64-1
43. Hsdb 41
44. Ccris 5953
45. Acetone (1,1,1,3,3,3-d6)
46. Einecs 200-662-2
47. Un1090
48. Rcra Waste No. U002
49. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 004101
50. Dimethylcetone
51. Isopropanal
52. Methylketone
53. Dimethylketon
54. Propanon
55. Sasetone
56. Methyl-ketone
57. 2propanone
58. B-ketopropane
59. Unii-1364ps73af
60. Ai3-01238
61. 2-propanal
62. Acetone Hp
63. Acetone Acs
64. Acetone, Puriss.
65. Acetone P.a.
66. Acetone (tn)
67. Acetone Hplc Grade
68. Methyl Methyl Ketone
69. Acetone, For Hplc
70. Acetone, Acs Reagent
71. Acetone, Hplc Grade
72. Acetone [vandf]
73. Acetone [fhfi]
74. Acetone [hsdb]
75. Acetone [inci]
76. Acetone Acs Low Benzene
77. Acetone, Technical Grade
78. Acetone [fcc]
79. Acetone [mi]
80. Acetone Oil (salt/mix)
81. Ch3coch3
82. Acetone [mart.]
83. Acetone [usp-rs]
84. Acetone [who-dd]
85. Acetone Reagent Grade Acs
86. Acetone, Histological Grade
87. Ec 200-662-2
88. Acetone, Analytical Standard
89. Acetone, Environmental Grade
90. Acetone, Semiconductor Grade
91. Acetone, Lr, >=99%
92. Acetone, Natural, >=97%
93. Un 1091 (salt/mix)
94. Aceton (german, Polish)
95. Acetone [ep Impurity]
96. Acetone, Puriss., 99.0%
97. Chembl14253
98. Acetone [ep Monograph]
99. Dimethylketone, Pyroacetic Acid
100. Wln: 1v1
101. Acetone, Ar, >=99.5%
102. Dtxsid8021482
103. Acetone, Spectrophotometric Grade
104. Citronellidene Acetone; Baccartol
105. Zinc895111
106. Acetone, Gc, For Residue Analysis
107. Acetone, >=99.5%, Acs Reagent
108. Tox21_111096
109. Tox21_202480
110. C0556
111. Lmfa12000057
112. Nsc135802
113. Acetone 5000 Microg/ml In Methanol
114. Acetone, Purum, >=99.0% (gc)
115. Akos000120890
116. Acetone 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
117. Un 1090
118. Acetone, Saj First Grade, >=99.0%
119. Acetone [un1090] [flammable Liquid]
120. Acetone, For Chromatography, >=99.8%
121. Acetone, Histological Grade, >=99.5%
122. Acetone, Jis Special Grade, >=99.5%
123. Acetone, Laboratory Reagent, >=99.5%
124. Ncgc00260029-01
125. Acetone, For Hplc, >=99.8% (gc)
126. Acetone, Uv Hplc Spectroscopic, 99.8%
127. Acetone, >=99.5%, For Residue Analysis
128. Acetone, For Residue Analysis, >=99.5%
129. Isoflurane Impurity F [ep Impurity]
130. A0054
131. Acetone, For Luminescence, >=99.5% (gc)
132. Ft-0621803
133. Acetone, Suitable For Determination Of Dioxins
134. Chlorobutanol Impurity B [ep Impurity]
135. Acetone, Glass Distilled Hrgc/hplc Trace Grade
136. C00207
137. D02311
138. Q49546
139. Acetone, Acs Spectrophotometric Grade, >=99.5%
140. Acetone, Reagentplus(r), Phenol Free, >=99.5%
141. Acetone, >=99%, Meets Fcc Analytical Specifications
142. Acetone, Acs Reagent, >=99.5%, <=2 Ppm Low Benzene
143. Acetone, Contains 20.0 % (v/v) Acetonitrile, For Hplc
144. Acetone, For Residue Analysis, Suitable For 5000 Per Jis
145. Acetone, For Uv-spectroscopy, Acs Reagent, >=99.7% (gc)
146. Acetone, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
147. Acetone Solution, Contains 20.0 % (v/v) Acetonitrile, For Hplc
148. Acetone, Hplc Plus, For Hplc, Gc, And Residue Analysis, >=99.9%
149. Acetone, Semiconductor Grade Mos Puranal(tm) (honeywell 17921)
150. Acetone, Semiconductor Grade Ulsi Puranal(tm) (honeywell 17014)
151. Acetone, Semiconductor Grade Vlsi Puranal(tm) (honeywell 17617)
152. Acetone, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
153. Acetone Solution, Certified Reference Material, 2000 Mug/ml In Methanol: Water (9:1)
154. Acetone, Puriss. P.a., Acs Reagent, Reag. Iso, Reag. Ph. Eur., >=99.5% (gc)
155. Acetone, Puriss., Meets Analytical Specification Of Ph. Eur., Bp, Nf, >=99% (gc)
| Molecular Weight | 58.08 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C3H6O |
| XLogP3 | -0.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 1 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 58.041864811 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 58.041864811 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 17.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 4 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 26.3 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Solvents
Liquids that dissolve other substances (solutes), generally solids, without any change in chemical composition, as, water containing sugar. (Grant and Hackh's Chemical Dictionary, 5th ed) (See all compounds classified as Solvents.)
In rats receiving acetone in drinking water (7.5% v/v) for 11 consecutive days, plasma concentrations of acetone on day 1 were in the range of 315-800 ug/mL. The plasma concentration appeared to plateau at about 1,200 ug/mL by day 4.
DHHS/ATSDR; Addendum to the Toxicological Profile for Acetone p.? (August 2011). Available from, as of January 7, 2015: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/index.asp
Physiologically based toxicokinetic (PBTK) modeling of human experimental data suggests difficulties to simultaneously describe the time courses of inhaled polar solvents in blood and breath, especially if exposures occur during physical exercise. We attribute this to the washin-washout effect in the airways. The aim was to develop a PBTK-model that explains the behavior of acetone in blood and exhaled air at different levels of physical exercise. The model includes exchange of inhaled solvent vapor with the blood flow via the mucosa and separate compartments to describe working and resting muscles. The developed model was contrasted to a traditional PBTK-model where the conducting airways were regarded as an inert tube. Our model predictions agrees well with experimentally observed acetone levels in both arterial blood and end- and mixed-exhaled air from 26 inhalation experiments conducted with 18 human volunteers at 0, 50, 100 and 150 W workload. In contrast, the inert-tube model was unable to describe the data. The developed model is to our knowledge the first which explains the toxicokinetics of acetone at such various levels of physical exercise. It may be useful in breath monitoring and to obtain more accurate estimates of absorbed dose during inhalation of polar volatiles.
PMID:16364574 Mork AK, Johanson G; Toxicol Lett 164 (1): 6-15 (2006)
Patients with severe diabetic ketoacidosis can have plasma acetone levels as high as 750 mg/L, which is up to 300 times the normal limit.
European Chemicals Bureau; IUCLID Dataset, ACETONE (67-64-1). Available from, as of January 22, 2007: https://esis.jrc.ec.europa.eu/
Acetone is one of the least hazardous industrial solvents, but is highly volatile and may be inhaled in large quantities. It may be absorbed into the blood through the lungs and diffused throughout the body. Small quantities may be absorbed through the skin.
International Labour Office. Encyclopedia of Occupational Health and Safety. Vols. I&II. Geneva, Switzerland: International Labour Office, 1983., p. 38
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ACETONE (19 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
... The role of CYP2E1 in acetone catabolism /was assessed/ by measuring acetone levels at different time points in rats that had been treated with diallyl sulfide (DAS, a CYP2E1 inhibitor) at a variety of dose levels. The study noted DAS dose-dependent increases in the time to peak blood acetone level and in the time to return to pre-dose levels, suggesting an important role of CYP2E1 in acetone catabolism.
DHHS/ATSDR; Addendum to the Toxicological Profile for Acetone p.6 (August 2011). Available from, as of January 7, 2015: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/index.asp
Acetone, one of the principal ketone bodies elevated during treatment with the ketogenic diet, exhibits anticonvulsant properties that may contribute to the seizure protection conferred by the diet. The anticonvulsant mechanism of acetone is unknown, but it is metabolized to several bioactive substances that could play a role. Acetone and its major metabolites-acetol, 1,2-propanediol, methylglyoxal, and pyruvic acid-were assessed for anticonvulsant activity in two mouse seizure models. Various doses of the substances administered intraperitoneally were characterized for their ability to elevate the threshold for clonic seizures induced by intravenous infusion of pentylenetetrazol (PTZ) and for protection against tonic seizures induced by subcutaneous bolus administration of 4-aminopyridine (4-AP). The inverted-screen test was used to assess acute neurological toxicity. Acetone (1-32 mmol/kg, i.p.), in a dose-dependent fashion, elevated the PTZ threshold and conferred protection against 4-AP seizures (ED(50), 26.3 mmol/kg). Effective doses of acetone (10-32 mmol/kg) did not cause motor impairment in the inverted-screen test (TD(50), 45.7 mmol/kg). In doses 10-fold greater than the minimally effective dose ofacetone (3.2 mmol/kg), the metabolites acetol, 1,2-propanediol, and pyruvic acid were inactive in the PTZ model. At higher doses that produced motor impairment, acetol and 1,2-propanediol (but not pyruvic acid) did elevate the PTZ threshold. Methylglyoxal had both proconvulsant and anticonvulsant actions, and had substantial toxicity, producing respiratory distress, motor impairment, and death. None of the acetone metabolites protected against 4-AP seizures. This study confirms the broad-spectrum anticonvulsant properties of acetone and indicates that the seizure protection conferred is unlikely to result from its major metabolic products.
PMID:17386058 Gasior M et al; Epilepsia 48 (4): 793-800 (2007)
Two pathways for the conversion of acetone to glucose are proposed, the methylglyoxal & the propanediol pathways. The methylglyoxal pathway is responsible for the conversion to acetol, acetol to methylglyoxal, & subsequent conversion of methylglyoxal to glucose. The propanediol pathway involves the conversion of acetol to L-1,2-propanediol by an as yet unknown process. L-1,2-propanediol is converted to L-lactaldehyde by alcohol dehydrogenase, & L-lactaldehyde is converted to L-lactic acid by aldehyde dehydrogenase. Expression of these metabolic pathways in rat appears to be dependent on the induction of /acetone/ oxygenase & acetol monooxygenase by acetone.
PMID:6706932 Casazza JP et al; J Biol Chem 259 (1): 231-6 (1984)
Hepatic NAD-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase... enzyme is capable of catalyzing reverse reaction in which... acetone.../is reduced to alcohol/.
Testa, B. and P. Jenner. Drug Metabolism: Chemical & Biochemical Aspects. New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc., 1976., p. 310
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for ACETONE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Blood: 3 hours; whole body: 19-31 hours; [TDR, p. 17]
TDR - Ryan RP, Terry CE, Leffingwell SS (eds). Toxicology Desk Reference: The Toxic Exposure and Medical Monitoring Index, 5th Ed. Washington DC: Taylor & Francis, 1999., p. 17
Half-times for blood elimination of 3-3.9 hrs have been estimated in humans exposed to 100-500 ppm for 2-4 hrs. Elimination half-times of 3.9 hrs and 6.2 hrs have been estimated for arterial and venous blood, respectively. No differences in elimination half-times were found between men and women.
DHHS/ATSDR; Toxicological Profile for Acetone p. 79 (1994)
Tissue distribution of 2(14)C-acetone following inhalation exposure to 1,200 mg/cu m (500 ppm) was studied in mice. .... Half-times for acetone elimination were 2-3 hr for blood, kidney, lung, brain, and muscle, and greater than 5 hr for subcutaneous adipose tissue. By 24 hr after exposure, acetone concentrations had returned to endogenous levels in all tissues.
European Chemicals Bureau; IUCLID Dataset, ACETONE (67-64-1). Available from, as of January 22, 2007: https://esis.jrc.ec.europa.eu/
Two instances of finding abnormally high concentrations of acetone in urine (0.10 g/dL and 0.052 g/dL) without any measurable amounts of ethanol (<0.005 g/dL) or isopropanol (<0.005 g/dL) prompted a survey of the elimination kinetics of isopropanol and its metabolite acetone in humans. In a hospital patient who had ingested denatured alcohol, the elimination half-life (t(1/2)) of acetone during detoxification was 27 hr and not 3-5 hr as reported by other workers. Several other literature reports of individuals who had ingested isopropanol as well as controlled studies after administration of moderate amounts of acetone and/or isopropanol support the notion of a long elimination half-life of 17-27 hr for acetone compared with a t(1/2) of 1-3 hr for isopropanol.
PMID:10654562 Jones AW; J Anal Toxicol 24 (1): 8-10
The elimination half life in mice for acetone in various tissues was between 2 and 5 hr, with the subcutaneous adipose tissue showing the slowest release of acetone. Daily exposure of mice to 500 ppm acetone for 6 hr did not result in any day-to-day accumulation of acetone.
European Chemicals Bureau; IUCLID Dataset, ACETONE (67-64-1). Available from, as of January 22, 2007: https://esis.jrc.ec.europa.eu/
Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
19
PharmaCompass offers a list of Acetone API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Acetone manufacturer or Acetone supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Acetone manufacturer or Acetone supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Acetone API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Acetone API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Acetone Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Acetone Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Acetone manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Acetone, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Acetone manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Acetone API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Acetone manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Acetone supplier is an individual or a company that provides Acetone active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Acetone finished formulations upon request. The Acetone suppliers may include Acetone API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Acetone suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
Acetone Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Acetone GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Acetone GMP manufacturer or Acetone GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Acetone CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Acetone's compliance with Acetone specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Acetone CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Acetone CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Acetone may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Acetone EP), Acetone JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Acetone USP).

