
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
JDMF
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
Annual Reports
NA
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
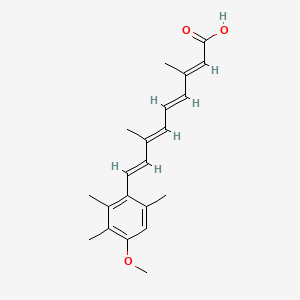

1. 13-cis-acitretin
2. Acitretin, (z,e,e,e)-isomer
3. Etretin
4. Isoacitretin
5. Isoetretin
6. Neotigason
7. Ro 10-1670
8. Ro 101670
9. Ro 13-7652
10. Ro 137652
11. Ro-10-1670
12. Ro-13-7652
13. Ro101670
14. Ro137652
15. Soriatane
1. 55079-83-9
2. Etretin
3. Soriatane
4. Neotigason
5. Acitretine
6. All-trans-acitretin
7. Retinoid Etretin
8. Ro 10-1670
9. (2e,4e,6e,8e)-9-(4-methoxy-2,3,6-trimethylphenyl)-3,7-dimethylnona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic Acid
10. Acitretina
11. Acitretinum
12. Tmmp
13. Ro 10-1670/000
14. 9-cis Acitretin
15. (all-e)-9-(4-methoxy-2,3,6-trimethylphenyl)-3,7-dimethyl-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid
16. 54757-46-9
17. All-trans-3,7-dimethyl-9-(4-methoxy-2,3,6-trimethylphenyl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid
18. Chebi:50173
19. 2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid, 9-(4-methoxy-2,3,6-trimethylphenyl)-3,7-dimethyl-, (all-e)-
20. Ro-101670000
21. Lch760e9t7
22. Ro-10-1670/000
23. Ncgc00163127-02
24. Acitretine [french]
25. Acitretinum [latin]
26. Acitretina [spanish]
27. Acitretin 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile:acetone
28. 2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid, 3,7-dimethyl-9-(4-methoxy-2,3,6-trimethylphenyl)-, (all-e)-
29. Acetretin
30. 9-(4-methoxy-2,3,6-trimethylphenyl)-3,7-dimethyl-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid
31. Soriatane Ck
32. Soriatane (tn)
33. Ccris 5534
34. Ro-10-1670
35. Hsdb 7187
36. 419534-31-9
37. Einecs 259-474-4
38. Chebi:50172
39. Unii-lch760e9t7
40. U0279
41. All-trans-etretin
42. Acitretin [usan:usp:inn:ban]
43. Acitretin,(s)
44. Acitretin- Bio-x
45. Acitretin (usp/inn)
46. Acitretin [inn]
47. Acitretin [mi]
48. Acitretin [hsdb]
49. Acitretin [usan]
50. Spectrum5_002065
51. Acitretin [vandf]
52. Dsstox_cid_2553
53. Acitretin [mart.]
54. Acitretin [usp-rs]
55. Acitretin [who-dd]
56. Schembl3759
57. Chembl1131
58. Dsstox_rid_76624
59. Dsstox_gsid_22553
60. (2e,4e,6e,8e)-9-(4-methoxy-2,3,6-trimethyl-phenyl)-3,7-dimethyl-nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic Acid
61. Mls001076667
62. Bidd:gt0617
63. Gtpl7598
64. Acitretin [orange Book]
65. Acitretin [ep Monograph]
66. Acitretin [usp Impurity]
67. Dtxsid6022553
68. Acitretin [usp Monograph]
69. Bcpp000437
70. Hms2234l17
71. Hms3259j12
72. Hms3714e17
73. Acitretin, >=98.0% (hplc)
74. Hy-b0107
75. Zinc3798734
76. Tox21_112012
77. Bdbm50088429
78. Mfcd00866632
79. S1368
80. Stl565770
81. Akos015889991
82. Ac-4702
83. Bcp9000229
84. Ccg-220668
85. Cs-1855
86. Db00459
87. Ks-5246
88. 2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid, 9-(4-methoxy-2,3,6-trimethylphenyl)-3,7-dimethyl-
89. Ncgc00163127-01
90. Ncgc00163127-03
91. (2e,4e,6e,8e)-3,7-dimethyl-9-[2,3,6-trimethyl-4-(methyloxy)phenyl]nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenoic Acid
92. (2e,4e,6e,8e)-9-(4-methoxy-2,3,6-trimethylphenyl)-3,7-dimethyl-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid
93. As-12644
94. Ba164136
95. Smr000499573
96. Cas-55079-83-9
97. Cs-0368934
98. Sw199134-2
99. C75579
100. D02754
101. Ab00698376-08
102. Ab00698376_09
103. 079a839
104. A830475
105. Q341500
106. Sr-01000763200
107. Sr-01000763200-3
108. Brd-k90699611-001-01-4
109. Acitretin, British Pharmacopoeia (bp) Reference Standard
110. Acitretin, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
111. Acitretin, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
112. Acitretin, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
113. 2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic Acid, 9-(4-methoxy-2,3,6-trimethylphenyl)-3,7-dimethyl-, (2e,4e,6e,8e)-
| Molecular Weight | 326.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H26O3 |
| XLogP3 | 6.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 326.18819469 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 326.18819469 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 46.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 539 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Acitretin |
| PubMed Health | Acitretin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antipsoriatic |
| Drug Label | Acitretin Capsules (acitretin), a retinoid, are available in 10 mg and 25 mg gelatin capsules for oral administration. Chemically, acitretin is all-trans-9-(4-methoxy-2,3,6-trimethylphenyl)-3,7-dimethyl-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid. It is a metabolite... |
| Active Ingredient | Acitretin |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 22.5mg; 25mg; 10mg; 17.5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva Pharms Usa; Barr Labs |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Soriatane |
| PubMed Health | Acitretin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antipsoriatic |
| Drug Label | SORIATANE (acitretin), a retinoid, is available in 10 mg, 17.5 mg, and 25 mg gelatin capsules for oral administration. Chemically, acitretin is all-trans-9-(4-methoxy-2,3,6-trimethylphenyl)-3,7-dimethyl-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid. It is a metabolite... |
| Active Ingredient | Acitretin |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 22.5mg; 25mg; 10mg; 17.5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Stiefel Labs |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Acitretin |
| PubMed Health | Acitretin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antipsoriatic |
| Drug Label | Acitretin Capsules (acitretin), a retinoid, are available in 10 mg and 25 mg gelatin capsules for oral administration. Chemically, acitretin is all-trans-9-(4-methoxy-2,3,6-trimethylphenyl)-3,7-dimethyl-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid. It is a metabolite... |
| Active Ingredient | Acitretin |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 22.5mg; 25mg; 10mg; 17.5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Teva Pharms Usa; Barr Labs |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Soriatane |
| PubMed Health | Acitretin (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antipsoriatic |
| Drug Label | SORIATANE (acitretin), a retinoid, is available in 10 mg, 17.5 mg, and 25 mg gelatin capsules for oral administration. Chemically, acitretin is all-trans-9-(4-methoxy-2,3,6-trimethylphenyl)-3,7-dimethyl-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid. It is a metabolite... |
| Active Ingredient | Acitretin |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 22.5mg; 25mg; 10mg; 17.5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Stiefel Labs |
Keratolytic Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Acitretin. Online file (MeSH, 2018). Available from, as of August 29, 2018: https://meshb.nlm.nih.gov/search
/CLINICAL TRIALS/ ClinicalTrials.gov is a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world. The Web site is maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Each ClinicalTrials.gov record presents summary information about a study protocol and includes the following: Disease or condition; Intervention (for example, the medical product, behavior, or procedure being studied); Title, description, and design of the study; Requirements for participation (eligibility criteria); Locations where the study is being conducted; Contact information for the study locations; and Links to relevant information on other health Web sites, such as NLM's MedlinePlus for patient health information and PubMed for citations and abstracts for scholarly articles in the field of medicine. Acitretin is included in the database.
NIH/NLM; ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available from, as of August 29, 2018: https://clinicaltrials.gov/
Acitretin Capsules, USP are indicated for the treatment of severe psoriasis in adults. Because of significant adverse effects associated with its use, Acitretin Capsules, USP should be prescribed only by those knowledgeable in the systemic use of retinoids. In females of reproductive potential, Acitretin Capsules, USP should be reserved for non-pregnant patients who are unresponsive to other therapies or whose clinical condition contraindicates the use of other treatments /Included in US product labeling/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Acitretin Capsule (Updated: January 9, 2018). Available from, as of November 20, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=6af396c2-af3e-436d-ba9a-583637495910
Acitretin has been used in a limited number of patients for the management of discoid lupus erythematosus; efficacy was similar to that of hydroxychloroquine, but adverse effects were more severe and frequent with acitretin. Further study is needed to establish the role of acitretin in treating this condition. /NOT included in US product labeling/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; Drug Information 2018. Bethesda, MD. 2018, p. 3548
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Acitretin (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
/BOXED WARNING/ CONTRAINDICATIONS AND WARNINGS: Pregnancy. Acitretin must not be used by females who are pregnant, or who intend to become pregnant during therapy or at any time for at least 3 years following discontinuation of therapy. Acitretin also must not be used by females who may not use reliable contraception while undergoing treatment and for at least 3 years following discontinuation of treatment. Acitretin is a metabolite of etretinate (TEGISON), and major human fetal abnormalities have been reported with the administration of acitretin and etretinate. Potentially, any fetus exposed can be affected. Clinical evidence has shown that concurrent ingestion of acitretin and ethanol has been associated with the formation of etretinate, which has a significantly longer elimination half-life than acitretin. Because the longer elimination half-life of etretinate would increase the duration of teratogenic potential for female patients, ethanol must not be ingested by female patients of childbearing potential either during treatment with acitretin or for 2 months after cessation of therapy. This allows for elimination of acitretin, thus removing the substrate for transesterification to etretinate. The mechanism of the metabolic process for conversion of acitretin to etretinate has not been fully defined. It is not known whether substances other than ethanol are associated with transesterification. Acitretin has been shown to be embryotoxic and/or teratogenic in rabbits, mice, and rats at oral doses of 0.6, 3, and 15 mg per kg, respectively. These doses are approximately 0.2, 0.3, and 3 times the maximum recommended therapeutic dose, respectively, based on a mg-per-m 2 comparison. Major human fetal abnormalities associated with acitretin and/or etretinate administration have been reported including meningomyelocele; meningoencephalocele; multiple synostoses; facial dysmorphia; syndactyly; absence of terminal phalanges; malformations of hip, ankle, and forearm; low-set ears; high palate; decreased cranial volume; cardiovascular malformation; and alterations of the skull and cervical vertebrae. Acitretin should be prescribed only by those who have special competence in the diagnosis and treatment of severe psoriasis, are experienced in the use of systemic retinoids, and understand the risk of teratogenicity. Because of the teratogenicity of acitretin, a program called P.P.E.T., Pregnancy Prevention is Essential with Treatment, has been developed to educate women of childbearing potential and their healthcare providers about the serious risks associated with acitretin and to help prevent pregnancies from occurring with the use of this drug and for 3 years after its discontinuation.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Acitretin Capsule (Updated: January 9, 2018). Available from, as of November 20, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=6af396c2-af3e-436d-ba9a-583637495910
/BOXED WARNING/ Hepatotoxicity: Of the 525 subjects treated in US clinical trials, 2 had clinical jaundice with elevated serum bilirubin and transaminases considered related to treatment with acitretin. Liver function test results in these subjects returned to normal after acitretin was discontinued. Two of the 1,289 subjects treated in European clinical trials developed biopsy-confirmed toxic hepatitis. A second biopsy in one of these subjects revealed nodule formation suggestive of cirrhosis. One subject in a Canadian clinical trial of 63 subjects developed a 3-fold increase of transaminases. A liver biopsy of this subject showed mild lobular disarray, multifocal hepatocyte loss, and mild triaditis of the portal tracts compatible with acute reversible hepatic injury. The subject's transaminase levels returned to normal 2 months after acitretin was discontinued. The potential of therapy with acitretin to induce hepatotoxicity was prospectively evaluated using liver biopsies in an open-label trial of 128 subjects. Pretreatment and posttreatment biopsies were available for 87 subjects. A comparison of liver biopsy findings before and after therapy revealed 49 (58%) subjects showed no change, 21 (25%) improved, and 14 (17%) subjects had a worsening of their liver biopsy status. For 6 subjects, the classification changed from class 0 (no pathology) to class I (normal fatty infiltration; nuclear variability and portal inflammation; both mild); for 7 subjects, the change was from class I to class II (fatty infiltration, nuclear variability, portal inflammation, and focal necrosis; all moderate to severe); and for 1 subject, the change was from class II to class IIIb (fibrosis, moderate to severe). No correlation could be found between liver function test result abnormalities and the change in liver biopsy status, and no cumulative dose relationship was found. Elevations of AST (SGOT), ALT (SGPT), GGT (GGTP), or LDH have occurred in approximately 1 in 3 subjects treated with acitretin. Of the 525 subjects treated in clinical trials in the US, treatment was discontinued in 20 (3.8%) due to elevated liver function test results. If hepatotoxicity is suspected during treatment with acitretin, the drug should be discontinued and the etiology further investigated. Ten of 652 subjects treated in US clinical trials of etretinate, of which acitretin is the active metabolite, had clinical or histologic hepatitis considered to be possibly or probably related to etretinate treatment. There have been reports of hepatitis-related deaths worldwide; a few of these subjects had received etretinate for a month or less before presenting with hepatic symptoms or signs.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Acitretin Capsule (Updated: January 9, 2018). Available from, as of November 20, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=6af396c2-af3e-436d-ba9a-583637495910
Acitretin is a known human teratogen, and there is a very high risk of severe birth defects if a patient becomes pregnant while receiving acitretin or upon drug discontinuance (birth defects have been reported 2 years or longer after the last dose of acitretin). Teratogenicity generally is characterized by malformations involving craniofacial, cardiovascular, skeletal, and CNS structures. Use of acitretin is contraindicated during pregnancy. The drug must not be used in female patients who are or may become pregnant during acitretin therapy or within at least 3 years following drug discontinuance or in females who may not use reliable contraception during and for at least 3 years following cessation of therapy. If pregnancy occurs during therapy or at any time for at least 3 years following drug discontinuance, the clinician and patient should discuss the possible effects on the pregnancy.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; Drug Information 2018. Bethesda, MD. 2018, p. 3549
Acitretin is distributed into milk; women receiving the drug should not breast-feed.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; Drug Information 2018. Bethesda, MD. 2018, p. 3549
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Acitretin (20 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of severe psoriasis in adults.
FDA Label
Acitretin is a retinoid. Retinoids have a structure similar to vitamin A and are involved in the normal growth of skin cells. Acitretin works by inhibiting the excessive cell growth and keratinisation (process by which skin cells become thickened due to the deposition of a protein within them) seen in psoriasis. It therefore reduces the thickening of the skin, plaque formation and scaling.
Keratolytic Agents
Agents that soften, separate, and cause desquamation of the cornified epithelium or horny layer of skin. They are used to expose mycelia of infecting fungi or to treat corns, warts, and certain other skin diseases. (See all compounds classified as Keratolytic Agents.)
D - Dermatologicals
D05 - Antipsoriatics
D05B - Antipsoriatics for systemic use
D05BB - Retinoids for treatment of psoriasis
D05BB02 - Acitretin
Absorption
Oral absorption of acitretin is optimal when given with food, and is linear and proportional with increasing doses from 25 to 100 mg. Approximately 72% (range 47% to 109%) of the administered dose was absorbed after a single 50 mg dose of acitretin was given to 12 healthy subjects.
Route of Elimination
Both parent compound and isomer are further metabolized into chain-shortened breakdown products and conjugates, which are excreted. The chain-shortened metabolites and conjugates of acitretin and cis-acitretin are ultimately excreted in the feces (34% to 54%) and urine (16% to 53%).
/MILK/ Acitretin is distributed into milk ... .
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists; Drug Information 2018. Bethesda, MD. 2018, p. 3549
/MILK/ Retinoid transfer into breast milk was studied in a psoriatric woman receiving oral acitretin at a dosage of 40 mg once daily. Concentrations of the parent compound and its main metabolite, 13-cis acitretin, were measured in serum and mature milk during the initial nine days of therapy, using reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatography. At steady-state, trace amounts of the drug and metabolite (30-40 ng/mL) appeared in breast milk corresponding to a milk/serum concentration ratio of about 0.18. Acitretin was almost exclusively distributed in the fatty layers of the milk. Although the estimated amount of the drug consumed by a suckling infant would correspond to only 1.5% of the maternal dose, the toxic potential of acitretin justifies its avoidance in breast-feeding women.
PMID:1981420 Rollman O, Pihl-Lundin I; Acta Derm Venereol 70 (6): 487-90 (1990)
Oral absorption of acitretin is optimal when given with food. For this reason, acitretin was given with food in all of the following trials. After administration of a single 50-mg oral dose of acitretin to 18 healthy subjects, maximum plasma concentrations ranged from 196 to 728 ng per mL (mean: 416 ng per mL) and were achieved in 2 to 5 hours (mean: 2.7 hours). The oral absorption of acitretin is linear and proportional with increasing doses from 25 to 100 mg. Approximately 72% (range: 47% to 109%) of the administered dose was absorbed after a single 50-mg dose of acitretin was given to 12 healthy subjects.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Acitretin Capsule (Updated: January 9, 2018). Available from, as of November 20, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=6af396c2-af3e-436d-ba9a-583637495910
Acitretin is more than 99.9% bound to plasma proteins, primarily albumin.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Acitretin Capsule (Updated: January 9, 2018). Available from, as of November 20, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=6af396c2-af3e-436d-ba9a-583637495910
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Acitretin (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Following oral absorption, acitretin undergoes extensive metabolism and interconversion by simple isomerization to its 13-cis form (cis-acitretin). Both parent compound and isomer are further metabolized into chain-shortened breakdown products and conjugates, which are excreted.
Following oral absorption, acitretin undergoes extensive metabolism and interconversion by simple isomerization to its 13-cis form (cis-acitretin). The formation of cis-acitretin relative to parent compound is not altered by dose or fed/fast conditions of oral administration of acitretin. Both parent compound and isomer are further metabolized into chain-shortened breakdown products and conjugates, which are excreted. Following multiple-dose administration of acitretin, steady-state concentrations of acitretin and cis-acitretin in plasma are achieved within approximately 3 weeks.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Acitretin Capsule (Updated: January 9, 2018). Available from, as of November 20, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=6af396c2-af3e-436d-ba9a-583637495910
... In the presence of ethanol the ethyl esterification of acitretin to etretinate proceeds via formation of acitretinoyl-CoA.
PMID:10874125 Knights KM et al; Biochem Pharmacol 60 (4): 507-16 (2000)
49 hours (range 33 to 96 hours)
... 10 patients with severe psoriasis were treated with 30 mg acitretin daily for 3 months. ... After discontinuation of therapy, the rate of elimination of both acitretin (half life range 1.0 to 25.4 days) and 13-cis-acitretin (half life range 1.5 to 25.7 days) was found to be related to the observed mean steady-state level of etretinate as evidenced by a longer terminal half life of patients with high levels of etretinate in plasma. ...
PMID:8491984 Larsen FG et al; J Invest Dermatol 100 (5): 623-7 (1993)
The terminal elimination half-life of acitretin following multiple-dose administration is 49 hours (range: 33 to 96 hours), and that of cis-acitretin under the same conditions is 63 hours (range: 28 to 157 hours).
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Acitretin Capsule (Updated: January 9, 2018). Available from, as of November 20, 2018: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=6af396c2-af3e-436d-ba9a-583637495910
The mechanism of action of acitretin is unknown, however it is believed to work by targeting specific receptors (retinoid receptors such as RXR and RAR) in the skin which help normalize the growth cycle of skin cells.

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS

Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
55
PharmaCompass offers a list of Acitretin API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Acitretin manufacturer or Acitretin supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Acitretin manufacturer or Acitretin supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Acitretin API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Acitretin API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Acitretin Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Acitretin Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Acitretin manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Acitretin, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Acitretin manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Acitretin API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Acitretin manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Acitretin supplier is an individual or a company that provides Acitretin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Acitretin finished formulations upon request. The Acitretin suppliers may include Acitretin API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Acitretin suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Acitretin DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Acitretin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Acitretin DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Acitretin USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Acitretin DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Acitretin USDMF includes data on Acitretin's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Acitretin USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Acitretin suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Acitretin CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Acitretin Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Acitretin CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Acitretin EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Acitretin to their clients by showing that a Acitretin CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Acitretin CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Acitretin CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Acitretin CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Acitretin DMF.
A Acitretin CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Acitretin CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Acitretin suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
A Acitretin written confirmation (Acitretin WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Acitretin manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Acitretin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Acitretin APIs or Acitretin finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Acitretin WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Acitretin suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Acitretin as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Acitretin API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Acitretin as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Acitretin and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Acitretin NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Acitretin suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Acitretin Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Acitretin GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Acitretin GMP manufacturer or Acitretin GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Acitretin CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Acitretin's compliance with Acitretin specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Acitretin CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Acitretin CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Acitretin may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Acitretin EP), Acitretin JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Acitretin USP).
