Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
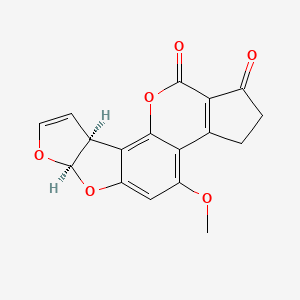

1. Aflatoxin B
2. Aflatoxin B(1)
3. Aflatoxin B1 Dihydrochloride, (6ar-cis)-isomer
4. Aflatoxin B1, (6ar-cis)-isomer, 14c-labeled
5. Aflatoxin B1, (6ar-cis)-isomer, 2h-labeled
6. Aflatoxin B1, (6ar-cis)-isomer, 3h-labeled
7. Aflatoxin B1, Cis(+,-)-isomer
8. Hsdb 3453
9. Hsdb-3453
10. Hsdb3453
11. Nsc 529592
12. Nsc-529592
13. Nsc529592
1. 1162-65-8
2. Afb1
3. Nsc-529592
4. 1h,11h-cyclopenta[c]furo[3',2':4,5]furo[2,3-h][1]benzopyran-1,11-dione,2,3,6a,9a-tetrahydro-4-methoxy-, (6ar,9as)-
5. Afbi
6. 9n2n2y55mh
7. Chebi:2504
8. 2,3,6aalpha,9aalpha-tetrahydro-4-methoxycyclopenta(c)furo(3',2':4,5)furo(2,3-h)(1)benzopyran-1,11-dione
9. (6ar,9as)-4-methoxy-2,3,6a,9a-tetrahydrocyclopenta[c]furo[3',2':4,5]furo[2,3-h]chromene-1,11-dione
10. Aflatoxin B
11. (3s,7r)-11-methoxy-6,8,19-trioxapentacyclo[10.7.0.02,9.03,7.013,17]nonadeca-1,4,9,11,13(17)-pentaene-16,18-dione
12. (-)-aflatoxin B1
13. Nsc 529592
14. Hsdb 3453
15. Nsc529592
16. Ccris 12
17. Aflatoxin B1 2 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
18. Cyclopenta(c)furo(3',2':4,5)furo(2,3-h)(1)benzopyran-1,11-dione, 2,3,6a,9a-tetrahydro-4-methoxy-
19. Einecs 214-603-3
20. Brn 1269174
21. Unii-9n2n2y55mh
22. Aflatoxin B1 From Aspergillus Flavus, From Aspergillus Flavus
23. 5-carboxylate
24. Mfcd00869647
25. (+/-)-aflatoxin B1
26. Aflatoxin B1 [mi]
27. Aflatoxin B1 [hsdb]
28. Cyclopenta(c)furo(3',2':4,5)furo(2,3-h)(1)benzopyran-1,11-dione, 2,3,6a,9a-tetrahydro-4-methoxy-, (6ar,9as)-
29. Bidd:er0313
30. Schembl126480
31. Aflatoxin B1 Standard Solution
32. Chembl1697694
33. Dtxsid9020035
34. Aflatoxin B1, Reference Material
35. Dtxsid00873175
36. Bdbm120261
37. Zinc402671
38. Amy22311
39. Ex-a5480
40. Hy-n6615
41. Akos030241596
42. Ncgc00247669-01
43. 2,3,6aalpha,9aalpha-tetrahydro-4-methoxycyclopenta(c)furo(2',3':4,5)furo(2,3-h)chromene-1,11-dione
44. Cyclopenta(c)furo(3',2':4,5)furo(2,3-h)(1)benzopyran-1,11-dione, 2,3,6aalpha,9aalpha-tetrahydro-4-methoxy-
45. Cs-0034371
46. Discontinued See D444270 (the Trihydrate)
47. 162a658
48. Q4689278
49. Wln: T F5 C6 B655 Dov Gv Oo Qo Rut&&ttj Lo1
50. Aflatoxin B1 Solution, 20 Mug/ml In Methanol, Analytical Standard
51. Methyl 4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-isopropyl-2-(methylsulfonyl)pyrimidine-
52. Aflatoxin B1 Solution, 2 Mug/ml In Acetonitrile, Analytical Standard
53. Aflatoxin B1 Solution, 3 Mug/ml In Benzene:acetonitrile (98:2), Analytical Standard
54. Aflatoxin B1 Solution, 3.79 Mug/g In Acetonitrile, Erm(r) Certified Reference Material
55. Aflatoxin B1 Solution, Certified Reference Material, 20 Mug/ml In Methanol, Ampule Of 1 Ml
56. (6ar-cis)-2,3,6a,9a-tetrahydro-4-methoxycyclopenta(c)furo(3',2':4,5)furo(2,3-h)(1)benzopyran-1,11-dione
57. 10279-73-9
58. 1h,11h-cyclopenta(c)furo(3',2':4,5)furo(2,3-h)(1)benzopyran-1,11-dione, 2,3,6a,9a-tetrahydro-4-methoxy-, (6ar,9as)-
59. Aflatoxin B1 Solution, Certified Reference Material, 3 Mug/ml In Benzene:acetonitrile (98:2), Ampule Of 1 Ml
60. Cyclopenta[c]furo[3',5]furo[2,3-h][1]benzopyran-1,11-dione, 2,3,6a,9a-tetrahydro-4-methoxy-
61. Cyclopenta[c]furo[3',5]furo[2,3-h][1]benzopyran-1,11-dione, 2,3,6a,9a-tetrahydro-4-methoxy-, (6ar-cis)-
62. Cyclopenta[c]furo[3',5]furo[2,3-h][1]benzopyran-1,11-dione, 2,3,6a.alpha.,9a.alpha.-tetrahydro-4-methoxy-
| Molecular Weight | 312.27 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H12O6 |
| XLogP3 | 1.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 312.06338810 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 312.06338810 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 71.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 650 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Poisons
Substances which, when ingested, inhaled, or absorbed, or when applied to, injected into, or developed within the body in relatively small amounts may, by their chemical action, cause damage to structure or disturbance of function. (From Dorland, 27th ed) (See all compounds classified as Poisons.)
Four days after /IP/ injection into monkeys, 5.6% of the dose was still retained by the liver, principally bound to liver proteins. After oral dose of aflatoxin B1, rhesus monkeys excreted about 20% as aflatoxin M1 during days 1-4; unchanged aflatoxin B1 accounted only for a small proportion & aflatoxin B1 beta-glucuronide accounted for 5% (3.3% as glucuronide & 1.2% as sulfate conjugate). Another 5% of the dose was excreted as aflatoxin B1 & aflatoxin M1 in the feces.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 364
Aflatoxicol & aflatoxin B1 & M1 were found in tissues of kidney, liver, & muscle of feeder pigs fed estimated LD50 dose of B1 (0.1 mg/kg body wt) provided as rice culture of aspergillus flavus & of market wt pigs, fed naturally contaminated feed containing aflatoxin B1 at level of 400 ng/g from corn for 14 days. B1 & M1, when found in the feeding experiment, were at about the same levels in all tissues except the kidney, in which M1 was the most dominant aflatoxin.
PMID:6811546 Trucksess MW et al; J Assoc Off Anal Chem 65 (4): 884 (1982)
Aflatoxin is excreted in the form of its metabolite aflatoxin M1 in the milk of lactating animals. In cattle given a single oral dose of aflatoxin, 85% of the total amount found in the milk and urine were detected in the first 48 hours after treatment. There was none in the milk after four days, nor in the urine or feces after six days. The total aflatoxin found in the milk was 0.39% of that ingested. ... Less than 0.6% of administered aflatoxin B1 was excreted in the milk. The amount of aflatoxin excreted in milk is unrelated to milk yield, and it disappears from the milk three to four days after the feeding of toxic meal is discontinued.
Humphreys, D.J. Veterinary Toxicology. 3rd ed. London, England: Bailliere Tindell, 1988., p. 286
Using aflatoxin B1, ring-labelled or methoxy-labelled with (14)carbon have shown that rats excrete 70-80% of a single ip dose within 24 hours.
WHO; Environmental Health Criteria II: Mycotoxins p.40 (1979)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for AFLATOXIN B1 (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Aflatoxins would be expected to undergo biotransformations by 4 routes: (i) by hydroxylation of carbon atom at junction of the two fused furan rings, aflatoxin B1 is converted into aflatoxin M1, & this occurs to some extent in mammalian liver, (ii) oxidative o-demethylation of single aromatic methoxy-substituent gives aflatoxin P1 ... (iii) hydration of vinyl ether double bond would afford hemiacetals, & aflatoxin B1 is ... converted into aflatoxin hemiacetal B2a in guinea pig, mouse, & avian livers, (iv) & by reduction of cyclopentenone ring, dihydroaflatoxicol, but this biotransformation seems to be confined to avian species, & may be irrelevant to mammals.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 2: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1970 and 1971. London: The Chemical Society, 1972., p. 283
In rhesus monkeys, injected ip ... the chloroform soluble urinary excretory products included aflatoxin M1 (2.3% of dose) & at least 3 other, unidentified ... compounds, as well as unchanged aflatoxin B1 (0.01-0.10%). Chloroform insoluble metabolites in urine were separated by ion exchange methods; major sub fraction consisted of aflatoxin P1 beta-glucuronide. Urinary aflatoxin P1 beta glucuronide represented about 20% of the dose; 17% as glucuronide, 3% as sulfate ester, & 1% as unconjugated phenol.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 364
Investigations of the in vitro metabolism of aflatoxin B1 by liver homogenates from humans ... indicate that aflatoxin B1-2,3 epoxide is produced ... .
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V 10 61 (1976)
Metabolism of Aflatoxin B1 was examined in isolated hepatocytes from rainbow trout. Intracellular DNA adduct formation was linearly related to aflatoxin B1 dose, & qualitatively similar to adducts formed in vivo. The rate of metabolism of adduct accumulation was constant during the first hr, after which an increased & gradual decrease in rate routinely occurred. Relative rates of production of the major unbound aflatoxin B1 metabolites aflatoxicol, aflatoxin M1 & polar conjugates, also remained constant over the 1st hr of preparation age, but subsequently changed in manner consistent with the changes in DNA binding.
Bailey GS et al; Carcinogenesis (Lond) 3 (5): 511 (1982)
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for AFLATOXIN B1 (23 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Aflatoxin b1 has known human metabolites that include Aflatoxin B1- exo-8,9-oxide, Aflatoxin M1, and Aflatoxin Q1.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
The potent hepatocarcinogenic fungal constituent aflatoxin B1, requires metabolic activation to yield its biological effects & is covalently bound to hepatic macromolecules in the rat.
Searle, C. E. (ed.). Chemical Carcinogens. ACS Monograph 173. Washington, DC: American Chemical Society, 1976., p. 97
With the 4 principal aflatoxins tested, the order of inhibitory effect on RNA polymerase II was: B1 greater than G1 greater than B2, G2.
Yu FL et al; Carcinogenesis (London) 3 (9): 1005 (1982)
The suspect human hepatocarcinogen aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) is a well-known potent initiator of hepatic tumors in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Both hepatocellular carcinomas and mixed hepatocellular/cholangiocellular carcinomas are induced by AFB1 in trout, with the mixed form predominating. Previously two c-ras genes were isolated from trout liver cDNA, and in the present study DNA was analyzed from 14 AFB1-induced trout liver tumors for point mutations in exon 1 of both genes. Using the polymerase chain reaction and oligonucleotide hybridization methods, a high proportion (10/14) of the AFB1 initiated tumor DNAs showed evidence of activating point mutations in the trout c-Ki-ras gene. Of the 10 mutant ras genotypes, seven were codon 12 GGA - GTA transversions, two were codon 13 GGT - GTT transversions, and one was a codon 12 GGA - AGA transition. Nucleotide sequence analysis of cloned polymerase chain reation products from four of these tumor DNAS provided definitive evidence for two codon 12 GGA - GTA mutations, one codon 12 GGA - AGA mutation, and one codon 13 GGT - GTT mutation, in complete agreement with the oligonucleotide hybridization results. No mutations were detected in exon 1 of a second trout ras gene also expressed in liver, nor in DNA from control livers. This is the first report of experimentally induced ras gene point mutations in a lower vertebrates fish model. The results indicates that the hepatocarcinogen AFB1 induces c-Ki-ras gene mutations in trout similar to those in rat liver tumors.
PMID:1645972 Chang Y-J et al; Mol Carcinog 4 (2): 112-9 (1991)
Aflatoxin B1 has been suggested as a causative agent for a G to T mutation at codon 249 in the p53 gene in human hepatocellular carcinomas from southern Africa and Qidong in China. To test this hypothesis, nine tumors induced by aflatoxin B1 in nonhuman primates were analyzed for mutations in the p53 gene. These included four hepatocellular carcinomas, two cholangiocarcinomas, a spindle cell carcinoma of the bile duct, a hemangioendothelial sarcoma of the liver, and an osteogenic sarcoma of the tibia. None of the tumors showed changes at the third position of codon 249 by cleavage analysis of the HaeIII enzyme site at codon 249. A point mutation was identified in one hepatocellular carcinoma at the second position of codon 175 (G to T transversion) by sequencing analysis of the four conserved domains (II to V) in the p53 gene. These data suggest that mutations in the p53 gene are not necessary in aflatoxin B1 induced hepatocarcinogenesis in nonhuman primates. The occurrence of mutation in codon 249 of the p53 gene in selective samples of human hepatocellular cancers may indicate involvement of environmental carcinogens other than aflatoxin B1 or that hepatitis B virus-related hepatitis is a prerequisite for aflatoxin B1 induction of G to T transversion in codon 249.
PMID:1310637 Fujimoto Y et al; Cancer Res 52 (4): 1044-6 (1992)
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for AFLATOXIN B1 (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
ABOUT THIS PAGE
38
PharmaCompass offers a list of Aflatoxin B1 API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Aflatoxin B1 manufacturer or Aflatoxin B1 supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Aflatoxin B1 manufacturer or Aflatoxin B1 supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Aflatoxin B1 API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Aflatoxin B1 API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Aflatoxin B1 Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Aflatoxin B1 Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Aflatoxin B1 manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Aflatoxin B1, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Aflatoxin B1 manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Aflatoxin B1 API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Aflatoxin B1 supplier is an individual or a company that provides Aflatoxin B1 active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Aflatoxin B1 finished formulations upon request. The Aflatoxin B1 suppliers may include Aflatoxin B1 API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
Aflatoxin B1 Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Aflatoxin B1 GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Aflatoxin B1 GMP manufacturer or Aflatoxin B1 GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Aflatoxin B1 CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Aflatoxin B1's compliance with Aflatoxin B1 specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Aflatoxin B1 CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Aflatoxin B1 CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Aflatoxin B1 may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Aflatoxin B1 EP), Aflatoxin B1 JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Aflatoxin B1 USP).
