
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
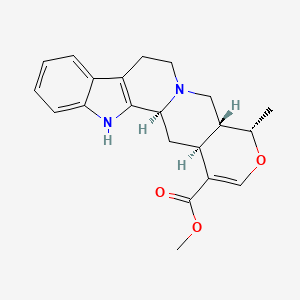

1. 19-epiajmalicine
2. Ajmalicine Hydrochloride
3. Ajmalicine, (19alpha,20alpha)-isomer
4. Ajmalicine, (19beta)-isomer
5. Ajmalicine, (19beta,20alpha)-isomer
6. Ajmalicine, (3-beta,19beta)-isomer
7. Ajmalicine, (3beta,19alpha)-isomer
8. Ajmalicine, (3beta,19alpha,20alpha)-isomer
9. Ajmalicine, (hydrochloride(19beta,20alpha))-isomer
10. Ajmalicine, Hydrochloride(19alpha)-isomer
11. Ajmalicine, Po4(19alpha)-isomer
12. Akuammigine
13. Delta-yohimbine
14. Lamuran
15. Raubasine
16. Raubasine Hcl
17. Raubasine Hydrochloride
18. Rauvasan
19. Tetrahydro-alstonine
20. Tetrahydroalstonine
1. Raubasine
2. 483-04-5
3. Delta-yohimbine
4. Ajmalicin
5. Circolene
6. Tetrahydroserpentine
7. Lamuran
8. Rauvasan
9. Hydrosarpan
10. Sarpan
11. Alkaloid C
12. Substance Ii
13. Py-tetrahydroserpentine
14. Rauwolfia Serpentina Root
15. 4qjl8ox71z
16. Chebi:2524
17. Chembl123325
18. .delta.-yohimbine
19. Nsc 72133
20. Methyl (19alpha)-19-methyl-16,17-didehydro-18-oxayohimban-16-carboxylate
21. Isoarteril
22. Methyl (1s,15r,16s,20s)-16-methyl-17-oxa-3,13-diazapentacyclo[11.8.0.0^{2,10}.0^{4,9}.0^{15,20}]henicosa-2(10),4,6,8,18-pentaene-19-carboxylate
23. 16,17-didehydro-19-methyloxayohimban-16-carboxylic Acid Methyl Ester
24. Ajmalicine(-yohimbine)
25. Einecs 207-589-5
26. Unii-4qjl8ox71z
27. Brn 0097268
28. Cristanyl
29. Del.-yohimbine
30. Nsc-72133
31. Rauwolfia Alkaloid
32. Raubasine,(s)
33. Raubasine (dcf)
34. Lamuran (tn)
35. Spectrum_000775
36. Specplus_000425
37. Raubasine [mi]
38. Prestwick0_000592
39. Prestwick1_000592
40. Prestwick2_000592
41. Prestwick3_000592
42. Methyl 16,17-didehydro-19alpha-methyl-18-oxayohimban-16-carboxylat
43. Raubasine [mart.]
44. Pytetrahydroserpentine
45. Raubasine [who-dd]
46. Methyl (19-methyl-16,17-dehydro-18-oxa-3alpha,15alpha,19beta,20beta-yohimban-16-carboxylat)
47. Bspbio_000464
48. Kbioss_001255
49. 4-27-00-07927 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
50. Divk1c_006521
51. Schembl309914
52. Spbio_002683
53. Bpbio1_000512
54. Gtpl8746
55. Megxp0_001818
56. Acon1_001630
57. Kbio1_001465
58. Kbio2_001255
59. Kbio2_003823
60. Kbio2_006391
61. Dtxsid60904151
62. Hy-n1919
63. Bdbm50030612
64. Mfcd00042748
65. Zinc53147422
66. Akos015895125
67. Oxayohimban-16-carboxylic Acid, 16,17-didehydro-19-methyl-, Methyl Ester, (19-alpha)-
68. Ncgc00016647-01
69. Ncgc00016647-02
70. Ncgc00016647-03
71. Ncgc00016647-04
72. Ac-20175
73. As-35306
74. Cas-4373-34-6
75. Cas-6474-90-4
76. (4s,4ar,13bs,14as)-methyl 4-methyl-
77. Cs-0018230
78. C09024
79. D08470
80. [2,3-a]pyrano[3,4-g]quinolizine-1-carboxylate
81. 483a045
82. Q412957
83. 4a,5,7,8,13,13b,14,14a-octahydro-4h-indolo
84. W-106052
85. Brd-k83028735-001-01-6
86. Brd-k83028735-003-03-8
87. 19b-methyl-16-methoxycarbonyl-16,17-didehydro-oxayohimbane
88. Methyl (19alpha)-19-methyl-16,17-didehydrooxayohimban-16-carboxylate
89. (19.alpha.)-16,17-didehydro-19-methyloxayohimban-16-carboxylic Acid Methyl Ester
90. (19alpha)-16,17-didehydro-19-methyl-oxayohimban-16-carboxylic Acid Methyl Ester
91. Oxayohimban-16-carboxylic Acid, 16,17-didehydro-19-methyl-, Methyl Ester, (19-.alpha).-
92. Oxayohimban-16-carboxylic Acid, 16,17-didehydro-19-methyl-, Methylester, (19a)-
93. Oxayohimban-16-carboxylicacid, 16,17-didehydro-19-methyl-, Methyl Ester, (19a)-
94. (4s,4ar,13bs,14as)-methyl 4-methyl-4a,5,7,8,13,13b,14,14a-octahydro-4h-indolo[2,3-a]pyrano[3,4-g]quinolizine-1-carboxylate
95. (7ar,8s,11as,12as)-8-methyl-5,6,7a,8,11a,12,12a,13-octahydro-7h-9-oxa-6a,13-diaza-indeno[2,1-a]anthracene-11-carboxylic Acid Methyl Ester
96. Ajn
97. Methyl (1s,15r,16s,20s)-16-methyl-17-oxa-3,13-diazapentacyclo[11.8.0.02,10.04,9.015,20]henicosa-2(10),4,6,8,18-pentaene-19-carboxylate
98. Methyl (4s,4ar,13bs,14as)-4-methyl-4a,5,7,8,13,13b,14,14a-octahydro-4h-indolo[2,3-a]pyrano[3,4-g]quinolizine-1-carboxylate
| Molecular Weight | 352.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H24N2O3 |
| XLogP3 | 2.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 352.17869263 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 352.17869263 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 54.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 606 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Rauwolfia alkaloids are indicated in the treatment of hypertension. Rauwolfia alkaloids have been used for relief of symptoms in agitated psychotic states such as schizophrenia; however, use as antipsychotics and sedatives have been replaced with the use of more effective, safer agents.
Reserpine is used to treat high blood pressure. It also is used to treat severe agitation in patients with mental disorders. Reserpine is in a class of medications called rauwolfia alkaloids. It works by slowing the activity of the nervous system, causing the heart rate to slow and the blood vessels to dilate.
Vasodilator Agents
Drugs used to cause dilation of the blood vessels. (See all compounds classified as Vasodilator Agents.)
Absorption
Mean maximum plasma levels of plasma concentrations after 0.5 mg of Reserpine, administered as two 0.25 mg tablets or as an aqueous solution, peaked after 2.5 hours. The mean peak level was approximately 1.1 ng/ml. Bioavailability of Reserpine, has been reported to be approximately 50%.
Route of Elimination
The elimination of reserpine and its metabolites in the feces ranges from 30% after intramuscular administration to about 60% after oral ingestion, primarily as unmetabolized reserpine, over a 4 day period after the ingestionof 0.25 mg to 0.50 mg doses. Over the same time period, about 8% of the ingested dose was recovered in the urine, primarily as the trimethoxybenzoic acid metabolite.
Clearance
Hepatically and renally.
Reserpine is almost completely metabolized in the body, and only about 1% is excreted as unchanged drug in the urine. Hepatic metabolism accounts for less than 50% of the elimination of reserpine, with the remainder being eliminated in the faeces, and some unmetabolized reserpine and metabolites being eliminated in the urine. In man, metabolites are methylreserpate and trimethoxybenzoic acid. Metabolism may be more important with intramuscular administration.
After oral ingestion, an initial half-life of approximately 5 hours is followed by a terminal half-life of approximately 200 hours.
Reserpine is an adrenergic blocking agent used to treat mild to moderate hypertension via the disruption of norepinephrine vesicular storage. The antihypertensive actions of Reserpine are a result of its ability to deplete catecholamines from peripheral sympathetic nerve endings. These substances are normally involved in controlling heart rate, the work of cardiac contraction and peripheral resistance. Reserpine depletes brain (depression) and peripheral (PPH) noradrenaline (NA) storage sites, guanethidine depleted NA storage via blockade of reuptake. This agent binds and inhibits catecholamine pump on the storage vesicles in central and peripheral adrenergic neurons, thereby inhibiting the uptake of norepinephrine, dopamine serotonin into presynaptic storage vesicles. This results in catecholamines and serotonin lingering in the cytoplasm where they are destroyed by intraneuronal monoamine oxidase, thereby causing the depletion of catecholamine and serotonin stores in central and peripheral nerve terminals. Depletion results in a lack of active transmitter discharge from nerve endings upon nerve depolarization, and consequently leads to a decreased heart rate and decreased arterial blood pressure as well as sedative effects.
Global Sales Information

ABOUT THIS PAGE
75
PharmaCompass offers a list of Ajmalicin API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Ajmalicin manufacturer or Ajmalicin supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Ajmalicin manufacturer or Ajmalicin supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Ajmalicin API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Ajmalicin API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Ajmalicin Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Ajmalicin Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Ajmalicin manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Ajmalicin, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Ajmalicin manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Ajmalicin API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Ajmalicin supplier is an individual or a company that provides Ajmalicin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Ajmalicin finished formulations upon request. The Ajmalicin suppliers may include Ajmalicin API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
Ajmalicin Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Ajmalicin GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Ajmalicin GMP manufacturer or Ajmalicin GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Ajmalicin CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Ajmalicin's compliance with Ajmalicin specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Ajmalicin CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Ajmalicin CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Ajmalicin may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Ajmalicin EP), Ajmalicin JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Ajmalicin USP).
