
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
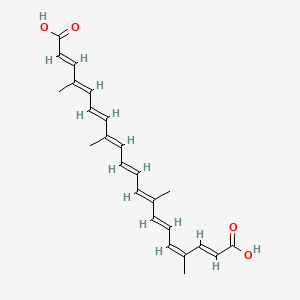

1. 1393-63-1
2. Natural Orange 4
3. Alpha-norbixin
4. Annatto Pigment
5. C.i. Natural Orange 4
6. 626-76-6
7. Cis-norbixin
8. Mh1wze9gbd
9. Annatto Extract Acid Proof
10. (2e,4e,6e,8e,10e,12e,14e,16z,18e)-4,8,13,17-tetramethylicosa-2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18-nonaenedioic Acid
11. Annatto Extract
12. Annotta Extract
13. Annatto (color)
14. Annatto Coloring Dye
15. Fema No. 2103
16. Fema No. 2104
17. Ccris 3651
18. Annatto Seed (bixa Orellana L.)
19. Unii-mh1wze9gbd
20. Annatto Extract (bixa Orellana L.)
21. Einecs 215-735-4
22. Unii-6pqp1v1b6o
23. Ci 75120
24. Hsdb 7976
25. Annatto Seed Powder
26. .alpha.-norbixin
27. Bixa Orellana Seed Powder
28. 9-cis-6,6'-diapo-psi,psi-carotenedioic Acid
29. 6,6'-diapo-psi,psi-carotenedioic Acid, 9-cis-
30. 6pqp1v1b6o
31. Schembl340220
32. .alpha.-norbixin [mi]
33. Chembl1420783
34. Dtxsid60274023
35. Zinc8582047
36. Ncgc00091523-01
37. W-108218
38. Q27284028
39. 9-cis-6,6'-diapo-.psi.,.psi.-carotenedioic Acid
40. (2e,4e,6e,8e,10e,12e,14e,16z,18e)-4,8,13,17-tetramethyl-2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18-eicosanonaenedioic Acid
41. 2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18-eicosanonaenedioic Acid, 4,8,13,17-tetramethyl-, (2e,4e,6e,8e,10e,12e,14e,16z,18e)-
| Molecular Weight | 380.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C24H28O4 |
| XLogP3 | 7.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Exact Mass | 380.19875937 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 380.19875937 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 74.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 740 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 9 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Food Coloring Agents
Natural or synthetic dyes used as coloring agents in processed foods. (See all compounds classified as Food Coloring Agents.)
Single oral doses of /solution containing 0.1% annatto (0.22% bixin) and thermal degradation products, in vegetable oil/ OSB (7 mg/kg), /suspension of 0.2% annatto (mainly bixin, 1.84%), in vegetable oil) R10 (7 mg/kg) and a water-soluble preparation of 0.1% annatto (mainly norbixin, 0.27%) WSA (14 mg/kg) were given to adult male /volunteers/ and the blood and excreta were analyzed for annatto pigments. Blood samples were taken between 2-12 hours after treatment, urine was collected during 7 hours after the dose and feces over the 2 days following the day of treatment. WSA (14 mg/kg) produced a blood level of 12 ug/mL after 2-1/4 hours which corresponds to 6% of the dose. OSB (7 mg/kg) produced a blood level of 2.4 ug/mL after 3 hours which corresponds to 2.4% of the dose. R10 (7 mg/kg) produced a blood level of 0.44 ul/mL after 3-1/4 hours which corresponds to 0.32% of the dose. Blood levels had returned to zero 6 hours after WSA (14 mg/kg), OSB (7 mg/kg) and R10 (7 mg/kg) respectively. No annatto pigments were detected in the urine samples and none were detected in feces samples collected the next day. The feces collected the second day after treatment contained 0.17 mg R10 (0.03% of the dose) and 0.44 mg WSA (0.06% of the dose) but no pigments associated with the consumption of OSB were detected. Thus, as in the rat, the annatto pigments were absorbed and rapidly cleared from the blood.
WHO/FAO; Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA): Food Additive Series 17: Annatto Extracts. Available from, As of June 22, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
A technique /was developed/ using reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to determine concentrations of bixin and norbixin in human plasma, to a sensitivity of 5 ug/L. After a normal breakfast, seven male and female volunteers each ingested a single dose of 1 mL of a commercial annatto food color containing 16 mg of cis-bixin and approximately 0.5 mg of cis-norbixin in soya bean oil, followed by a glass of milk. Blood samples were taken 0, 2, 4, 6 and 8 hr after ingestion; in some subjects, additional samples were taken after 24 and 48 hr. No control of food intake was made after 6 hr . The average values and range of concentrations of bixin and norbixin in the plasma of the subjects are shown in the table provided.
Table: Plasma concentrations of bixin and norbixin in volunteers given a single dose of commercial annatto food color [Table#7917]
WHO/FAO; Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA): Food Additive Series 52: Annatto Extracts. Available from, As of June 22, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
[Table#7917]
In a 4-week study, groups of four male and four female Wistar rats were fed diets containing 0% or 5% of a solution containing 0.1% annatto (0.22% bixin) and thermal degradation products, in vegetable oil (OSB), a suspension containing 0.02% annatto (mainly bixin, 1.84%), in vegetable oil (R10) or a water-soluble preparation containing 0.1% annatto (mainly norbixin, 0.27%) (WSA). Animals received either: (1) diet containing annatto extract during the first 2 weeks and normal diet for the second 2 weeks; or (2) normal diet for 2 weeks followed by the diet containing annatto extract for 2 weeks. In the animals that were killed immediately after receiving annatto extract for 2 weeks, measurable amounts of yellow pigment were observed in the blood, but in animals that were killed 2 weeks after treatment with annatto extract had stopped, only trace amounts were detected. Yellow pigment was also found in the adipose tissue of animals treated with OSB and R10, but not in animals receiving WSA. Chromatographic analysis of these pigments confirmed that they were not major annatto pigments (bixin or norbixin). There was also a clear difference in the degree of discoloration of the fat in animals killed immediately after cessation of treatment, compared with that in animals killed 2 weeks after treatment had stopped, indicating that clearance of the pigment was rapid. Feces were collected during the second week of treatment and analyzed for pigment content. About 20% of the administered dose of OSB and WSA and about 55% of R10 was recovered unchanged from the feces.
WHO/FAO; Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA): Food Additive Series 52: Annatto Extracts. Available from, As of June 22, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
After dosing orally with annatto B at 100 or 1000 mg/kg bw, the following chemical species were present in the plasma of male and female rats: 9'cisbixin, trans-bixin (retention time, 26 min), 9'cis-norbixin, trans-norbixin, di cis-norbixin and a norbixin isomer with retention time, 6.8 min. After dosing with annatto E (at both concentrations), the above isomers plus an additional trans-bixin species with retention time of 267 min were detected in the plasma of both sexes. In contrast, after administration of annatto F (at both doses), only the norbixin isomers (9'cis-norbixin, trans-norbixin, di cis-norbixin and the isomer with a retention time 6.8 minutes) were present in the plasma of male and female rats. Plasma concentrations of 9'cis-norbixin were higher than those of 9'cis-bixin after the administration of annatto B, E or F, despite the fact that annatto B and E contain >90% 9'cis-bixin. The Tmax for the major component in plasma for each extract in males and females at both doses was 2-4 hr; by 12 hr, only trace amounts of bixin remained, although concentrations of norbixin were still measurable at 24 hr. When the oral dose was raised from 100 mg/kg bw to 1000 mg/kg bw, the plasma concentrations of the major components of annatto B (9'cis-bixin), annatto E (9'cis-bixin) and annatto F (9'cis-norbixin) were increased.
WHO/FAO; Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA): Food Additive Series 52: Annatto Extracts. Available from, As of June 22, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
Bixin, together with other carotenoids such as beta-carotene, lutein and canthaxanthin, has been shown to suppress the respiratory burst induced by paramethoxyamphetamine (PMA) in rat peritoneal macrophages. The action appears to be associated with the ability of carotenoids to scavenge superoxide, and the authors suggested a protective role for carotenoids in vivo to protect host cells from the harmful effects of oxygen metabolites. Earlier work showed that bixin binds to the non-polar regions of mitochondria thought to be associated with high-energy states. Furthermore, bixin acts as an inhibitor of the ATP-forming process (state 3) associated with mitochondrial respiration.
WHO/FAO; Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA): Food Additive Series 52: Annatto Extracts. Available from, As of June 22, 2011: https://www.inchem.org/pages/jecfa.html
Insulin resistance is partly due to suppression of insulin-induced glucose uptake into adipocytes. The uptake is dependent on adipocyte differentiation, which is controlled at mRNA transcription level. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR), a ligand-regulated nuclear receptor, is involved in the differentiation. Many food-derived compounds serve as ligands to activate or inactivate PPAR. In this study, we demonstrated that bixin and norbixin (annatto extracts) activate PPARgamma by luciferase reporter assay using GAL4-PPAR chimera proteins. To examine the effects of bixin on adipocytes, 3T3-L1 adipocytes were treated with bixin or norbixin. The treatment induced mRNA expression of PPARgamma target genes such as adipocyte-specific fatty acid-binding protein (aP2), lipoprotein lipase (LPL), and adiponectin in differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes and enhanced insulin-dependent glucose uptake. The observations indicate that bixin acts as an agonist of PPARgamma and enhances insulin sensitivity in 3T3-L1 adipocytes, suggesting that bixin is a valuable food-derived compound as a PPAR ligand to regulate lipid metabolism and to ameliorate metabolic syndrome.
Takahashi N et al; Biochem Biophys Res Commun 390 (4):1372-1376 (2009)
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ANALYTICAL

ABOUT THIS PAGE
41
PharmaCompass offers a list of Annatto API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Annatto manufacturer or Annatto supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Annatto manufacturer or Annatto supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Annatto API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Annatto API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Annatto Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Annatto Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A alpha-Norbixin manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of alpha-Norbixin, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates alpha-Norbixin manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. alpha-Norbixin API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A alpha-Norbixin supplier is an individual or a company that provides alpha-Norbixin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or alpha-Norbixin finished formulations upon request. The alpha-Norbixin suppliers may include alpha-Norbixin API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
alpha-Norbixin Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of alpha-Norbixin GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right alpha-Norbixin GMP manufacturer or alpha-Norbixin GMP API supplier for your needs.
A alpha-Norbixin CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to alpha-Norbixin's compliance with alpha-Norbixin specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
alpha-Norbixin CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each alpha-Norbixin CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
alpha-Norbixin may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (alpha-Norbixin EP), alpha-Norbixin JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (alpha-Norbixin USP).
