
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
JDMF
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
Australia

DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
Annual Reports
NA
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
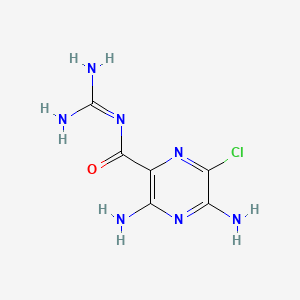

1. Amidal
2. Amiduret Trom
3. Amiloberag
4. Amiloride Hydrochloride
5. Amiloride Hydrochloride, Anhydrous
6. Anhydrous Amiloride Hydrochloride
7. Hydrochloride, Amiloride
8. Hydrochloride, Anhydrous Amiloride
9. Kaluril
10. Midamor
11. Midoride
12. Modamide
13. Trom, Amiduret
1. 2609-46-3
2. Amipramidin
3. Midamor
4. Guanamprazine
5. Amipramizid
6. Amipramizide
7. Guanamprazin
8. Amilorida
9. 3,5-diamino-n-carbamimidoyl-6-chloropyrazine-2-carboxamide
10. Amiloridum
11. Amyloride
12. Amiloridum [inn-latin]
13. Amilorida [inn-spanish]
14. Amiclaran
15. N-amidino-3,5-diamino-6-chloropyrazinecarboxamide
16. N-amidino-3,5-diamino-6-chlorpyrazincarboxamid
17. 3,5-diamino-6-chloro-n-(diaminomethylidene)pyrazine-2-carboxamide
18. Amiloride (inn)
19. Pyrazinecarboxamide, 3,5-diamino-n-(aminoiminomethyl)-6-chloro-
20. 3,5-diamino-n-(aminoiminomethyl)-6-chloropyrazinecarboxamide
21. Mk-870
22. Chembl945
23. 7dzo8eb0z3
24. Chebi:2639
25. 137053-86-2
26. Ncgc00015089-08
27. Amiloride [inn]
28. Amiloride [inn:ban]
29. Amipramidine
30. Dsstox_cid_23853
31. Dsstox_rid_80077
32. Dsstox_gsid_43853
33. Amiclaran (tn)
34. Cas-2609-46-3
35. Ccris 6545
36. Einecs 220-024-7
37. Unii-7dzo8eb0z3
38. Amiloridehcl
39. Amikal (hydrochloride Dihydrate)
40. Midamor (hydrochloride Dihydrate)
41. Mk-870 (hydrochloride Dihydrate)
42. Amipramidin, Midamor
43. N-amidino-3,5-diamino-6-chloro-2-pyrazinecarboxamide
44. Spectrum_000034
45. Tocris-0890
46. 1f5l
47. Amiloride [mi]
48. Prestwick0_000007
49. Prestwick1_000007
50. Prestwick2_000007
51. Prestwick3_000007
52. Spectrum2_000118
53. Spectrum3_000293
54. Spectrum4_000132
55. Spectrum5_000776
56. Amiloride [vandf]
57. Lopac-a-7410
58. Amiloride [who-dd]
59. Lopac0_000111
60. Schembl27562
61. Bspbio_000013
62. Bspbio_001572
63. Bspbio_001826
64. Kbiogr_000292
65. Kbiogr_000544
66. Kbioss_000292
67. Kbioss_000394
68. Mls001060798
69. Bidd:gt0466
70. Divk1c_000182
71. Spbio_000136
72. Spbio_001934
73. Bpbio1_000015
74. Gtpl2421
75. Dtxsid9043853
76. Bcbcmap01_000101
77. Bdbm16173
78. Kbio1_000182
79. Kbio2_000292
80. Kbio2_000394
81. Kbio2_002860
82. Kbio2_002962
83. Kbio2_005428
84. Kbio2_005530
85. Kbio3_000583
86. Kbio3_000584
87. Kbio3_001326
88. Ninds_000182
89. Bio1_000359
90. Bio1_000848
91. Bio1_001337
92. Bio2_000292
93. Bio2_000772
94. Hms1791o14
95. Hms1989o14
96. Hms2089h05
97. Hms2213e05
98. Hms3355k04
99. Act05635
100. Act05652
101. Bcp16815
102. Hy-b0285
103. Zinc4340269
104. Tox21_110080
105. 3,5-diamino-n-[amino(imino)methyl]-6-chloropyrazine-2-carboxamide
106. Bbl028157
107. Stl373007
108. Akos015961348
109. Tox21_110080_1
110. Ccg-204206
111. Db00594
112. Sb74937
113. Sdccgsbi-0050099.p005
114. Idi1_000182
115. Idi1_034042
116. Ncgc00015089-01
117. Ncgc00015089-02
118. Ncgc00015089-03
119. Ncgc00015089-04
120. Ncgc00015089-05
121. Ncgc00015089-06
122. Ncgc00015089-07
123. Ncgc00015089-09
124. Ncgc00015089-11
125. Ncgc00015089-12
126. Ncgc00015089-13
127. Ncgc00015089-14
128. Ncgc00015089-15
129. Ncgc00015089-16
130. Ncgc00015089-17
131. Ncgc00015089-24
132. Ncgc00024443-02
133. Ncgc00024443-05
134. Ncgc00024443-06
135. Ncgc00024443-07
136. Ncgc00024443-09
137. Ac-13631
138. Ls-13128
139. Smr000486264
140. (3,5-diamino-6-chloropyrazinoyl)guanidine
141. Sbi-0050099.p004
142. N-amidino-3,5-diamino-6-chloropyrazinamide
143. Ab00053415
144. Ft-0703177
145. C06821
146. D07447
147. Ab00053415-24
148. Ab00053415-25
149. Ab00053415_26
150. Ab00053415_27
151. Ab00053415_28
152. 609a463
153. Q419995
154. J-016249
155. Brd-k97181089-003-02-3
156. Brd-k97181089-310-03-0
157. N-amidino 3,5-diamino-6-chloro-2-pyrazinecarboxamide
158. F2173-0531
159. N-(3,5-diamino-6-chloro-pyrazine-2-carbonyl)-guanidine
160. 3,5-diamino-n-carbamimidoyl-6-chloro-pyrazine-2-carboxamide
161. 3,5-diamino-6-chloro-n-(diaminomethylene)pyrazinamide;hydrochloride
1. Amilorid Hydrochlorid-2-wasser
2. Amiloride Hydrochloride Dihydrate
| Molecular Weight | 229.63 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H8ClN7O |
| XLogP3 | -0.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 229.0478856 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 229.0478856 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 159 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 15 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 279 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Midamor |
| PubMed Health | Amiloride (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Amiloride HCl, an antikaliuretic-diuretic agent, is a pyrazine-carbonyl-guanidine that is unrelated chemically to other known antikaliuretic or diuretic agents. It is the salt of a moderately strong base (pKa 8.7). It is designated chemically as 3,5-... |
| Active Ingredient | Amiloride hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Paddock |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Midamor |
| PubMed Health | Amiloride (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Cardiovascular Agent |
| Drug Label | Amiloride HCl, an antikaliuretic-diuretic agent, is a pyrazine-carbonyl-guanidine that is unrelated chemically to other known antikaliuretic or diuretic agents. It is the salt of a moderately strong base (pKa 8.7). It is designated chemically as 3,5-... |
| Active Ingredient | Amiloride hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Paddock |
For use as adjunctive treatment with thiazide diuretics or other kaliuretic-diuretic agents in congestive heart failure or hypertension.
FDA Label
Amiloride, an antikaliuretic-diuretic agent, is a pyrazine-carbonyl-guanidine that is unrelated chemically to other known antikaliuretic or diuretic agents. It is an antihypertensive, potassium-sparing diuretic that was first approved for use in 1967 and helps to treat hypertension and congestive heart failure. The drug is often used in conjunction with thiazide or loop diuretics. Due to its potassium-sparing capacities, hyperkalemia (high blood potassium levels) are occasionally observed in patients taking amiloride. The risk is high in concurrent use of ACE inhibitors or spironolactone. Patients are also advised not to use potassium-containing salt replacements.
Acid Sensing Ion Channel Blockers
A subclass of sodium channel blockers that are specific for ACID-SENSING SODIUM CHANNELS. (See all compounds classified as Acid Sensing Ion Channel Blockers.)
Diuretics
Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. (See all compounds classified as Diuretics.)
Epithelial Sodium Channel Blockers
A subclass of sodium channel blockers that are specific for EPITHELIAL SODIUM CHANNELS. (See all compounds classified as Epithelial Sodium Channel Blockers.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C03 - Diuretics
C03D - Aldosterone antagonists and other potassium-sparing agents
C03DB - Other potassium-sparing agents
C03DB01 - Amiloride
Absorption
Readily absorbed following oral administration.
Route of Elimination
Amiloride HCl is not metabolized by the liver but is excreted unchanged by the kidneys. About 50 percent of a 20 mg dose of amiloride HCl is excreted in the urine and 40 percent in the stool within 72 hours.
Amiloride is not metabolized by the liver but is excreted unchanged by the kidneys.
Plasma half-life varies from 6 to 9 hours.
Amiloride works by inhibiting sodium reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts in the kidneys by binding to the amiloride-sensitive sodium channels. This promotes the loss of sodium and water from the body, but without depleting potassium. Amiloride exerts its potassium sparing effect through the inhibition of sodium reabsorption at the distal convoluted tubule, cortical collecting tubule and collecting duct; this decreases the net negative potential of the tubular lumen and reduces both potassium and hydrogen secretion and their subsequent excretion. Amiloride is not an aldosterone antagonist and its effects are seen even in the absence of aldosterone.

539.7
51 - 200
2.5k
1.3M
API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|---|---|---|
| INDIA | 210.50 | 1,203.0 | 11 - 50 |
| BRAZIL | 656.00 | 596.3 | 11 - 50 |
| GERMANY | 100.00 | 499.0 | <10 |
| NIGERIA | 650.00 | 387.9 | <10 |
| ZAMBIA | 458.00 | 396.0 | <10 |
| NEPAL | 14.00 | 594.1 | <10 |
| THAILAND | 170.00 | 388.4 | <10 |
| MALAYSIA | 50.00 | 587.9 | <10 |
| TAIWAN | 25.00 | 611.5 | <10 |
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ANALYTICAL

ABOUT THIS PAGE
35
PharmaCompass offers a list of Amiloride API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Amiloride manufacturer or Amiloride supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Amiloride manufacturer or Amiloride supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Amiloride API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Amiloride API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Amiloride Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Amiloride Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Amiloride Hydrochloride manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Amiloride Hydrochloride, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Amiloride Hydrochloride manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Amiloride Hydrochloride API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Amiloride Hydrochloride manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Amiloride Hydrochloride supplier is an individual or a company that provides Amiloride Hydrochloride active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Amiloride Hydrochloride finished formulations upon request. The Amiloride Hydrochloride suppliers may include Amiloride Hydrochloride API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Amiloride Hydrochloride suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Amiloride Hydrochloride DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Amiloride Hydrochloride active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Amiloride Hydrochloride DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Amiloride Hydrochloride USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Amiloride Hydrochloride DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Amiloride Hydrochloride USDMF includes data on Amiloride Hydrochloride's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Amiloride Hydrochloride USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Amiloride Hydrochloride suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Amiloride Hydrochloride CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Amiloride Hydrochloride Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Amiloride Hydrochloride CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Amiloride Hydrochloride EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Amiloride Hydrochloride to their clients by showing that a Amiloride Hydrochloride CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Amiloride Hydrochloride CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Amiloride Hydrochloride CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Amiloride Hydrochloride CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Amiloride Hydrochloride DMF.
A Amiloride Hydrochloride CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Amiloride Hydrochloride CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Amiloride Hydrochloride suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
A Amiloride Hydrochloride written confirmation (Amiloride Hydrochloride WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Amiloride Hydrochloride manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Amiloride Hydrochloride active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Amiloride Hydrochloride APIs or Amiloride Hydrochloride finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Amiloride Hydrochloride WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Amiloride Hydrochloride suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Amiloride Hydrochloride as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Amiloride Hydrochloride API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Amiloride Hydrochloride as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Amiloride Hydrochloride and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Amiloride Hydrochloride NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Amiloride Hydrochloride suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Amiloride Hydrochloride Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Amiloride Hydrochloride GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Amiloride Hydrochloride GMP manufacturer or Amiloride Hydrochloride GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Amiloride Hydrochloride CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Amiloride Hydrochloride's compliance with Amiloride Hydrochloride specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Amiloride Hydrochloride CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Amiloride Hydrochloride CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Amiloride Hydrochloride may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Amiloride Hydrochloride EP), Amiloride Hydrochloride JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Amiloride Hydrochloride USP).
