
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz

1. Cytadren
2. Orimeten
1. 125-84-8
2. Dl-aminoglutethimide
3. Cytadren
4. Orimeten
5. P-aminoglutethimide
6. Elipten
7. 3-(4-aminophenyl)-3-ethylpiperidine-2,6-dione
8. 3-(4-aminophenyl)-3-ethyl-2,6-piperidinedione
9. 2-(p-aminophenyl)-2-ethylglutarimide
10. Aminoglutetimida
11. 2,6-piperidinedione, 3-(4-aminophenyl)-3-ethyl-
12. Aminoglutethimidum
13. Ba-16038
14. 3-ethyl-3-(p-aminophenyl)-2,6-dioxopiperidine
15. (+/-)-p-aminoglutethimide
16. Nsc-330915
17. Glutethimide, Para-amino
18. Ag-1
19. 3-(4-aminophenyl)-3-ethyl-piperidine-2,6-dione
20. Glutarimide, 2-(p-aminophenyl)-2-ethyl-
21. Mfcd00010122
22. Chembl488
23. Chebi:2654
24. Alpha-(p-aminophenyl)-alpha-ethylglutarimide
25. 0o54zq14i9
26. Dsstox_cid_2589
27. Dsstox_rid_76647
28. .alpha.-(p-aminophenyl)-.alpha.-ethylglutarimide
29. Dsstox_gsid_22589
30. (rs)-2-(4-amino-phenyl)-2-ethyl-glutarimide;(rs)-3-(4-amino-phenyl)-3-ethyl-2,6-dioxo-piperidine
31. Aminoglutethimidum [inn-latin]
32. Aminoglutetimida [inn-spanish]
33. Aminoglutetimide
34. Ba 16038
35. Cytadren (tn)
36. Smr000326785
37. C 16038-ba
38. Ccris 7562
39. Aminoglutethimide (ag)
40. Sr-01000075596
41. 3-(4-aminophenyl)-3-ethyl-2,6-piperidindion
42. Einecs 204-756-4
43. Brn 0210656
44. Aminoglutethimide (usp/inn)
45. Unii-0o54zq14i9
46. Hsdb 7494
47. Aminoglutethimide [usp:inn:ban]
48. Ncgc00016379-01
49. Cas-125-84-8
50. Prestwick_243
51. Spectrum_000040
52. (y)-p-aminoglutethimide
53. Aminoglutethimide Ag, 4
54. Aminoglutethimide- Bio-x
55. (?)-p-aminoglutethimide
56. Prestwick0_000244
57. Prestwick1_000244
58. Prestwick2_000244
59. Prestwick3_000244
60. Spectrum2_000093
61. Spectrum3_000296
62. Spectrum4_000144
63. Spectrum5_000802
64. A 9657
65. Schembl4306
66. Aminoglutethimide (cytadren)
67. Lopac0_000124
68. Bspbio_000028
69. Bspbio_001832
70. Kbiogr_000588
71. Kbioss_000400
72. (a+/-)-p-aminoglutethimide
73. Mls000859924
74. Mls001213216
75. Aminoglutethimide [mi]
76. Divk1c_000884
77. Spectrum1500115
78. Spbio_000046
79. Spbio_002247
80. Aminoglutethimide [inn]
81. Bdbm9460
82. Bpbio1_000032
83. Gtpl7054
84. Aminoglutethimide [hsdb]
85. Dtxsid8022589
86. Aminoglutethimide [vandf]
87. Hms502m06
88. Kbio1_000884
89. Kbio2_000400
90. Kbio2_002968
91. Kbio2_005536
92. Kbio3_001332
93. Aminoglutethimide [mart.]
94. Ninds_000884
95. Aminoglutethimide [who-dd]
96. Hms1568b10
97. Hms1920c09
98. Hms2090i05
99. Hms2091i09
100. Hms2095b10
101. Hms2231m19
102. Hms3259h10
103. Hms3260i10
104. Hms3372m07
105. Hms3655o17
106. Hms3712b10
107. Pharmakon1600-01500115
108. Amy33415
109. Bcp28501
110. Hy-b0237
111. 2, 3-(4-aminophenyl)-3-ethyl-
112. Tox21_110406
113. Tox21_303497
114. Tox21_500124
115. Bbl010961
116. Ccg-38911
117. Nsc330915
118. Nsc755868
119. Stk802074
120. Akos004120070
121. Akos022060651
122. Tox21_110406_1
123. Aminoglutethimide [ep Impurity]
124. Aminoglutethimide [orange Book]
125. Db00357
126. Lp00124
127. Nc00714
128. Nsc 330915
129. Nsc 755868
130. Nsc-755868
131. Pb48252
132. Sdccgsbi-0050112.p005
133. Aminoglutethimide [ep Monograph]
134. Aminoglutethimide [usp Impurity]
135. Idi1_000884
136. Smp1_000017
137. Ncgc00015110-02
138. Ncgc00015110-03
139. Ncgc00015110-04
140. Ncgc00015110-05
141. Ncgc00015110-06
142. Ncgc00015110-07
143. Ncgc00015110-09
144. Ncgc00015110-12
145. Ncgc00015110-21
146. Ncgc00093615-01
147. Ncgc00093615-02
148. Ncgc00093615-03
149. Ncgc00093615-04
150. Ncgc00093615-05
151. Ncgc00257263-01
152. Ncgc00260809-01
153. Ac-12456
154. As-13282
155. Ba164155
156. Nci60_002900
157. Sbi-0050112.p004
158. Db-021640
159. Db-072002
160. Db-072275
161. 3-carboxy-1,1-dimethyl-, (e)-2-propenyl
162. Ab00051935
163. Eu-0100124
164. Ft-0773944
165. S1672
166. Sw196550-3
167. ( Inverted Question Mark)-p-aminoglutethimide
168. En300-53368
169. Vu0243029-3
170. C07617
171. D00574
172. D88489
173. Ab00051935-09
174. Ab00051935-11
175. Ab00051935_12
176. Ab00051935_13
177. 125a848
178. A805433
179. Q241150
180. Sr-01000075596-1
181. Sr-01000075596-4
182. Sr-01000075596-6
183. W-108399
184. Brd-a25234499-001-05-0
185. Brd-a25234499-001-09-2
186. Z1259341083
187. Aminoglutethimide, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
188. Aminoglutethimide, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
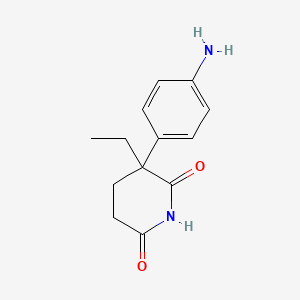
| Molecular Weight | 232.28 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C13H16N2O2 |
| XLogP3 | 1.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 232.121177757 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 232.121177757 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 72.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 321 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Adrenocortical suppressant; antineoplastic
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2006., p. 75
Aminoglutethimide is indicated for temporary suppression of adrenal function in selected patients with Cushing's syndrome including that associated withadrenal carcinoma and etopic adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)-producing tumors or adrenal hyperplasia. /Included in US product label/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 90
Aminoglutethimide is indicated to produce a "pharmacologic adrenalectomy" in the treatment of post menopausal metastatic breast cancer, especially inoperable or recurrent breast cancer proven to be hormone dependent, but resistant to therapy with tamoxifen. /Included in US product label/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 90
Aminoglutethimide is indicated for treatment of prostatic carcinoma unresponsive to hormonal or surgical therapy. /Included in US product label/
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 90
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for AMINOGLUTETHIMIDE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Cytadren may cause adrenocortical hypofunction, especially under conditions of stress, such as surgery, trauma, or acute illness. Patients should be carefully monitored and given hydrocortisone and mineralocorticoid supplements as indicated. Dexamethasone should not be used.
Physicians Desk Reference. 53rd ed. Thomson PDR. Montvale, NJ 1999.
Cytadren may also suppress aldosterone production by the adrenal cortex and may cause orthostatic or persistent hypotension. The blood pressure should be monitored in all patients at appropriate intervals. Patients should be advised of the possible occurrence of weakness and dizziness as symptoms of hypotension, and measures to be taken should they occur.
Physicians Desk Reference. 53rd ed. Thomson PDR. Montvale, NJ 1999.
Cytadren can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In the earlier experience with the drug in about 5000 patients, two cases of pseudohermaphroditism were reported in female infants whose mothers were treated with Cytadren ... If this drug must be used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking the drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
Physicians Desk Reference. 53rd ed. Thomson PDR. Montvale, NJ 1999.
Patients should be warned that drowsiness may occur and that they should not drive, operate potentially dangerous machinery, or engage in other activities that may become hazardous because of decreased alertness.
Physicians Desk Reference. 53rd ed. Thomson PDR. Montvale, NJ 1999.
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for AMINOGLUTETHIMIDE (19 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the suppression of adrenal function in selected patients with Cushing's syndrome, malignant neoplasm of the female breast, and carcinoma in situ of the breast.
FDA Label
Aminoglutethimide inhibits the enzymatic conversion of cholesterol to D5-pregnenolone, resulting in a decrease in the production of adrenal glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, estrogens, and androgens.
Antineoplastic Agents, Hormonal
Antineoplastic agents that are used to treat hormone-sensitive tumors. Hormone-sensitive tumors may be hormone-dependent, hormone-responsive, or both. A hormone-dependent tumor regresses on removal of the hormonal stimulus, by surgery or pharmacological block. Hormone-responsive tumors may regress when pharmacologic amounts of hormones are administered regardless of whether previous signs of hormone sensitivity were observed. The major hormone-responsive cancers include carcinomas of the breast, prostate, and endometrium; lymphomas; and certain leukemias. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1994, p2079) (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents, Hormonal.)
Aromatase Inhibitors
Compounds that inhibit AROMATASE in order to reduce production of estrogenic steroid hormones. (See all compounds classified as Aromatase Inhibitors.)
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L02 - Endocrine therapy
L02B - Hormone antagonists and related agents
L02BG - Aromatase inhibitors
L02BG01 - Aminoglutethimide
Absorption
Rapidly and completely absorbed from gastrointestinal tract. The bioavailability of tablets is equivalent to equal doses given as a solution.
Route of Elimination
After ingestion of a single oral dose, 34%-54% is excreted in the urine as unchanged drug during the first 48 hours, and an additional fraction as the N-acetyl derivative.
Cytadren is rapidly and completely absorbed after oral administration. In 6 healthy male volunteers, maximum plasma levels of Cytadren averaged 5.9 ug/mL at a medium of 1.5 hours after ingestion of 250 mg tablets. The bioavailability of tablets is equivalent to equal doses given as a solution.
Physicians Desk Reference. 53rd ed. Thomson PDR. Montvale, NJ 1999.
Aminoglutethimide crosses the placenta ...
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 91
It is not known weather aminoglutethimide is distributed into breast milk.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 91
After ingestion of a single oral dose, 34% to 54% is excreted in the urine as unchanged drug during the first 48 hours, and an additional fraction as the N-acetyl derivative.
Physicians Desk Reference. 53rd ed. Thomson PDR. Montvale, NJ 1999.
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for AMINOGLUTETHIMIDE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Hepatic. 34-54% of the administered dose is excreted in the urine as unchanged drug during the first 48 hours, and an additional fraction as an N-acetyl derivative.
Hepatic; the major metabolite is N-acetylaminoglutethimide; there may be genetic variation among individuals in the rate of acetylation.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 90
Four ... metabolites of aminoglutethimide have been identified in the urine of patients being treated chronically with the drug. These were products of hydroxylation of the 3-ethylpiperidine-2,6-dione residue, namely 3-(4-aminophenyl)-3-ethyl-5-hydroxypiperidine-2,6-dione and its acetylamino analog, 3-(4-aminophenyl)-3-(1-hydroxyethyl)piperidine-2,6-dione, and 3-(4-aminophenyl)-3-(2-carboxamidoethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-one, the lactone formed by rearrangement of 3-(4-aminophenyl)-3-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperidine-2,6-dione. ... These new metabolites were minor constituents compared with aminoglutethimide and with the previously identified major metabolites 3-(4-acetylaminophenyl)-3-ethylpiperidine-2,6-dione and 3-(4-hydroxylaminophenyl)-3-ethylpiperidine-2,6-dione. There were marked species differences between rat and human inasmuch as almost all the metabolites in the urine of the rat were N-acetylated whereas most of the human metabolites were not. However, 5-hydroxylation of the piperidinedione residue was stereoselective in the same sense in both species, the cis isomer being formed exclusively. Synthetic cis-3-(4-aminophenyl)-3-ethyl-5-hydroxypiperidine-2,6-dione did not inhibit the activity of the target enzyme systems desmolase and aromatase in vitro, and therefore, like other metabolites so far described, is an inactivation product of the drug.
PMID:6148221 Foster A et al; Drug Metab Dispos 12 (4): 511-6 (1984)
Hydroxylaminoglutethimide (3-ethyl-3-(4-hydroxylaminophenyl)-2,6-piperidinedione) has been identified as a novel metabolite of aminoglutethimide (3-(4-aminophenyl)-3-ethyl-2,6-piperidinedione) in the urine of patients treated chronically with this drug. The metabolite was isolated by reverse-phase thin-layer chromatography, and characterized by comparison of its mass spectrum and chromatographic properties with those of the synthetic compound. Hydroxylaminoglutethimide is unstable; it is readily oxidized to nitrosoglutethimide and disproportionates in the mass spectrometer into this compound and aminoglutethimide. In none of four patients studied was the metabolite detected in the urine after the first dose of the drug. In one patient it appeared after the second dose and in two more within seven to eight days suggesting that its formation is drug-induced, and that it may be the metabolite responsible for the diminished half-life of aminoglutethimide during chronic therapy. The profile of metabolites from one patient, examined by high-performance liquid chromatography after the first dose and again after six weeks of therapy afforded evidence that the formation of hydroxylaminoglutethimide was at the expense of a major metabolite N-acetylaminoglutethimide.
PMID:6689274 Jarman M et al; Biomed Mass Spectrom 10 (11): 620-5 (1983)
Hydroxylaminoglutethimide [3-ethyl-3-(4-hydroxylaminophenyl)piperidine-2,6-dione] (HxAG), aminoglutethimide [3-(4-aminophenyl)-3-ethylpiperidine-2,6-dione] (AG) and N-acetyl-aminoglutethimide (N-AcAG) have been quantified by high performance liquid chromatography using m-aminoglutethimide (metaAG) as the internal standard in serial 24 hr urine collections from a patient on chronic AG therapy without steroid supplementation. HxAG is the product of a major AG-induced metabolic pathway since the ratio [HxAG]/[AG] rises with time. In contrast the ratio [N-AcAG]/[AG] decreases with time. A rapid, simple colorimetric assay has been used to quantify HxAG in urine from both male and female patients receiving a range of doses of AG and to show that induced metabolism is a general phenomenon even at low doses (125 mg twice daily).
PMID:3838134 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1977034 Goss P et al; Br J Cancer 51 (2):259-62 (1985)
Extensive metabolism occurred in all species, with N-acetylaminoglutethimide being the major metabolite except for dog and man. In the latter two species unchanged drug was the main product excreted. A metabolite, 3-(4-acetamidophenyl)-3-(2-carboxamidoethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-one, not previously found in human urine, was identified. Chronic administration of aminoglutethimide to rats produced no detectable change in the excretory or metabolite patterns of the drug. However chronic administration of phenobarbitone decreased the urinary excretion of (14)C over a 72 hr period. Residual (72 hr) tissue levels of (14)C were less than 1 microgram equivalent of (14)C-aminoglutethimide/g tissue in the rat, guinea-pig and rabbit. Dog tissues retained a considerable quantity of (14)C at this time.
PMID:3354234 Dalrymple P et al; Xenobiotica 18 (1): 75-81(1988)
12.5 ± 1.6 hours
12.5 hours; reduced to 7 hours after prolonged (2 to 32 weeks) treatment because aminoglutethimide induces hepatic enzymes and accelerates its own metabolism.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 90
Aminoglutethimide reduces the production of D5-pregnenolone and blocks several other steps in steroid synthesis, including the C-11, C-18, and C-21 hydroxylations and the hydroxylations required for the aromatization of androgens to estrogens, mediated through the binding of aminoglutethimide to cytochrome P-450 complexes. Specifically, the drug binds to and inhibits aromatase which is essential for the generation of estrogens from androstenedione and testosterone. A decrease in adrenal secretion of cortisol is followed by an increased secretion of pituitary adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which will overcome the blockade of adrenocortical steroid synthesis by aminoglutethimide. The compensatory increase in ACTH secretion can be suppressed by the simultaneous administration of hydrocortisone. Since aminoglutethimide increases the rate of metabolism of dexamethasone but not that of hydrocortisone, the latter is preferred as the adrenal glucocorticoid replacement. Although aminoglutethimide inhibits the synthesis of thyroxine by the thyroid gland, the compensatory increase in thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is frequently of sufficient magnitude to overcome the inhibition of thyroid synthesis due to aminoglutethimide. In spite of an increase in TSH, aminoglutethimide has not been associated with increased prolactin secretion.
Aminoglutethimide produces suppression of the adrenal cortex by inhibiting enzyme conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone, thus blocking synthesis of adrenal steroid; it may also affect other steps in the synthesis and metabolism of these steroids. A compensatory increase in secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH by the pituitary occurs (except in patients with ACTH-independent adenomas or carcinomas), necessitating glucocorticoid administration to maintain aminoglutethimide's effect. Aminoglutethimide also inhibits estrogen production from androgens in peripheral tissues by blocking the aromatase enzyme. An additional mechanism in breast cancer, involving enhanced metabolism of estrone sulfate, has also been proposed.
Thomson.Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 25th ed. Volume 1. Plus Updates. Content Reviewed by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. Greenwood Village, CO. 2005., p. 90
Cytadren blocks several other steps in steroid synthesis, including the C11, C18, and C21 hydroxylations and the hydroxylations required for the aromatization of androgens to estrogens, mediated through binding of Cytadren to cytochrome complexes.
Physicians Desk Reference. 53rd ed. Thomson PDR. Montvale, NJ 1999.
Although Cytadren inhibits the synthesis of thyroxine by the thyroid gland, the compensatory increase in thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) is frequently sufficient magnitude to overcome the inhibition of thyroid synthesis due to Cytadren. In spite of an increase of TSH, Cytadren has not been associated with increased prolactin secretion.
Physicians Desk Reference. 53rd ed. Thomson PDR. Montvale, NJ 1999.
In this small study, the effect of aminoglutethimide on the disposition of estrogens in women with advanced breast cancer was investigated using bolus injections of 4-(14)C-estradiol and 6,7-(3)H-estrone sulfate, alone or in combination. No alterations in estrogen disposition were seen after short term (6 hours) aminoglutethimide administration. During long term (3 weeks to 8 months) aminoglutethimide treatment mean 4-(14)C-estradiol clearance was not changed. (14)C-Estrone sulfate AUC was reduced by 43% at a low dose of aminoglutethimide (125 mg twice daily) and by 65% at a high dose (250 mg 4 times daily) with hydrocortisone acetate 25 mg twice daily. The estrone sulfate terminal elimination rate constant (lambda z) was concurrently increased (mean of 46 and 79%, respectively, with the 2 dosage regimens). A possible increase in estrone sulfate clearance during long term treatment was tested for by injecting 6,7-(3)H-estrone sulfate. These studies revealed a marked increase (mean 104%) in estrone sulfate clearance in patients receiving the high dose aminoglutethimide schedule. Following injection of 4-(14)C-estradiol plus 6,7-(3)H-estrone sulfate, the fraction of 4-(14)C-estradiol metabolized to estrone sulfate was found to be reduced in all patients (mean 13%). A mean increase of 80% in the urinary excretion of (14)C-estriol was observed after 4-(14)C-estradiol administration.
PMID:3436111 Lonning PE et al; Clin Pharmacokinet 13 (6): 393-406 (1987)
Aminoglutethimide (AMG), a potent inhibitor of steroidogenesis used in the treatment of breast cancer and some adrenal pathologies, abolished the induction of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) elicited by peptide hormones and by dibutyryl-cAMP in steroidogenic tissues. This effect seems to be related to an inhibition of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (IC50 = 287 uM) rather than blockade of the steroidogenic pathway. This inhibition may explain some of the effects observed in AMG treatment which cannot be ascribed to its direct effect on the cytochrome P450scc complex or aromatase. Taking into account that ODC, the rate-limiting enzyme in polyamine synthesis, is elevated in many types of cancer and that overexpression of this enzyme is associated with cell transformation, one may speculate that the inhibitory action of AMG on protein kinase A represents a positive colateral effect of this drug in cancer therapy.
PMID:11178987 Bastida CM et al; Biochem Biophys Res Commun 281 (1): 244-8 (2001)
Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
13
PharmaCompass offers a list of Aminoglutethimide API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Aminoglutethimide manufacturer or Aminoglutethimide supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Aminoglutethimide manufacturer or Aminoglutethimide supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Aminoglutethimide API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Aminoglutethimide API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Aminoglutethimide Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Aminoglutethimide Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Aminoglutethimide manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Aminoglutethimide, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Aminoglutethimide manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Aminoglutethimide API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Aminoglutethimide manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Aminoglutethimide supplier is an individual or a company that provides Aminoglutethimide active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Aminoglutethimide finished formulations upon request. The Aminoglutethimide suppliers may include Aminoglutethimide API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Aminoglutethimide suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
Aminoglutethimide Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Aminoglutethimide GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Aminoglutethimide GMP manufacturer or Aminoglutethimide GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Aminoglutethimide CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Aminoglutethimide's compliance with Aminoglutethimide specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Aminoglutethimide CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Aminoglutethimide CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Aminoglutethimide may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Aminoglutethimide EP), Aminoglutethimide JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Aminoglutethimide USP).
