
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
VMF
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers

1. Bms 562247
2. Bms-562247
3. Bms-562247-01
4. Bms562247
5. Eliquis
1. 503612-47-3
2. Eliquis
3. Bms-562247
4. Bms-562247-01
5. Bms 562247-01
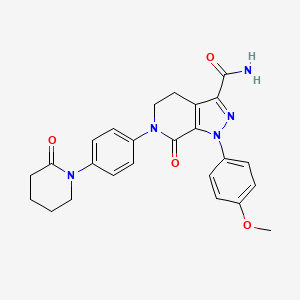
6. 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-[4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl]-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1h-pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridine-3-carboxamide
7. 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-(4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1h-pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridine-3-carboxamide
8. 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-[4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl]-4,5-dihydropyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridine-3-carboxamide
9. 3z9y7uwc1j
10. Chembl231779
11. Chebi:72296
12. Bms562247-01
13. Apixaban-13c,d3
14. 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-[4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl]-1h,4h,5h,6h,7h-pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridine-3-carboxamide
15. 1-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-7-oxo-6-[4-(2-oxo-piperidin-1-yl)-phenyl]-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1h-pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridine-3-carboxylic Acid Amide
16. 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-[4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl]-4,5-dihydropyrazolo[5,4-c]pyridine-3-carboxamide
17. Apixaban [usan]
18. Gg2
19. Eliquis (tn)
20. Unii-3z9y7uwc1j
21. Apixabanum
22. Apixaban (jan/usan/inn)
23. Apixaban [usan:inn:jan]
24. Hsdb 8223
25. Apixaban- Bio-x
26. Apixaban(bms-562247-01)
27. Apixaban-[d3]
28. Bms 562247
29. Apixaban [inn]
30. Apixaban [jan]
31. Apixaban [mi]
32. Apixaban [vandf]
33. Apixaban [mart.]
34. Apixaban [who-dd]
35. Apixaban - Adooq Bioscience
36. Apixaban [ema Epar]
37. Mls006010026
38. Schembl118023
39. Apixaban [orange Book]
40. Gtpl6390
41. Apixaban,bms-562247-01
42. Bdbm19023
43. Amy1826
44. Dtxsid80436500
45. Ex-a048
46. 2p16
47. Bcpp000396
48. Hms3655o07
49. Bcp02451
50. 503612-47-3, Eliquis,
51. Apixaban (bms 562247-01)
52. Bms562247
53. Mfcd11977295
54. Nsc784102
55. S1593
56. Zinc11677837
57. Akos005146204
58. Bcp9000310
59. Ccg-229675
60. Cs-0401
61. Db06605
62. Me-0152
63. Nsc-784102
64. Pb10976
65. Ncgc00346555-01
66. Ncgc00346555-02
67. Ncgc00346555-05
68. Ncgc00346555-08
69. Ac-26301
70. Bm164185
71. Hy-50667
72. Smr004676529
73. Ft-0686944
74. Sw220177-1
75. D03213
76. Ab01565766_02
77. 612a473
78. Ar-270/43507990
79. Q414462
80. J-200194
81. 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-(4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyi)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1h-pyrazolo(3,4-c)pyridine-3-carboxamide
82. 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-(4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1h-pyrazolo(3,4c)pyridine-3-carboxamide
83. 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-[4-(2-oxo Piperidin-1-yl)phenyl]-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1h-pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridine-3-carboxamide
84. 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-[4-(2-oxo-1-piperidinyl)phenyl]-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1h-pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridine-3-carboxamide
85. 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-[4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl]-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1h-pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridine-3-carboxamide?bms-562247; Bms-562247-01
86. 1h-pyrazolo(3,4-c)pyridine-3-carboxamide, 4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1-( 4-methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-(4-(2-oxo-1-piperidinyl)phenyl)-
87. 1h-pyrazolo(3,4-c)pyridine-3-carboxamide,4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-(4-(2-oxo-1-piperidinyl)phenyl)-
| Molecular Weight | 459.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C25H25N5O4 |
| XLogP3 | 2.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 459.19065430 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 459.19065430 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 111 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 34 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 777 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Eliquis |
| PubMed Health | Apixaban (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Anticoagulant |
| Drug Label | ELIQUIS (apixaban), a factor Xa (FXa) inhibitor, is chemically described as 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-[4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl]-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridine-3-carboxamide. Its molecular formula is C25H25N5O4, which correspond... |
| Active Ingredient | Apixaban |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg; 5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Bristol Myers Squibb |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Eliquis |
| PubMed Health | Apixaban (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Anticoagulant |
| Drug Label | ELIQUIS (apixaban), a factor Xa (FXa) inhibitor, is chemically described as 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-[4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl]-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridine-3-carboxamide. Its molecular formula is C25H25N5O4, which correspond... |
| Active Ingredient | Apixaban |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 2.5mg; 5mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Bristol Myers Squibb |
Eliquis (apixaban) is indicated to reduce the risk of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Eliquis (Apixaban) Tablet, Film Coated (Revised: August 2014). Available from, as of March 26, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=e9481622-7cc6-418a-acb6-c5450daae9b0
Eliquis is indicated for the prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which may lead to pulmonary embolism (PE), in patients who have undergone hip or knee replacement surgery. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Eliquis (Apixaban) Tablet, Film Coated (Revised: August 2014). Available from, as of March 26, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=e9481622-7cc6-418a-acb6-c5450daae9b0
Eliquis is indicated for the treatment of pulmonary embolism (PE). /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Eliquis (Apixaban) Tablet, Film Coated (Revised: August 2014). Available from, as of March 26, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=e9481622-7cc6-418a-acb6-c5450daae9b0
Eliquis is indicated for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Eliquis (Apixaban) Tablet, Film Coated (Revised: August 2014). Available from, as of March 26, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=e9481622-7cc6-418a-acb6-c5450daae9b0
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Apixaban (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: PREMATURE DISCONTINUATION OF ELIQUIS INCREASES THE RISK OF THROMBOTIC EVENTS. Premature discontinuation of any oral anticoagulant, including Eliquis, increases the risk of thrombotic events. If anticoagulation with Eliquis is discontinued for a reason other than pathological bleeding or completion of a course of therapy, consider coverage with another anticoagulant.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Eliquis (Apixaban) Tablet, Film Coated (Revised: August 2014). Available from, as of March 26, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=e9481622-7cc6-418a-acb6-c5450daae9b0
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: SPINAL/EPIDURAL HEMATOMA. Epidural or spinal hematomas may occur in patients treated with Eliquis who are receiving neuraxial anesthesia or undergoing spinal puncture. These hematomas may result in long-term or permanent paralysis. Consider these risks when scheduling patients for spinal procedures. Factors that can increase the risk of developing epidural or spinal hematomas in these patients include: use of indwelling epidural catheters concomitant use of other drugs that affect hemostasis, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), platelet inhibitors, other anticoagulants a history of traumatic or repeated epidural or spinal punctures a history of spinal deformity or spinal surgery optimal timing between the administration of Eliquis and neuraxial procedures is not known. Monitor patients frequently for signs and symptoms of neurological impairment. If neurological compromise is noted, urgent treatment is necessary. Consider the benefits and risks before neuraxial intervention in patients anticoagulated or to be anticoagulated.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Eliquis (Apixaban) Tablet, Film Coated (Revised: August 2014). Available from, as of March 26, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=e9481622-7cc6-418a-acb6-c5450daae9b0
FDA Pregnancy Risk Category: B /NO EVIDENCE OF RISK IN HUMANS. Adequate, well controlled studies in pregnant women have not shown increased risk of fetal abnormalities despite adverse findings in animals, or, in the absence of adequate human studies, animal studies show no fetal risk. The chance of fetal harm is remote but remains a possibility./
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Eliquis (Apixaban) Tablet, Film Coated (Revised: August 2014). Available from, as of March 26, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=e9481622-7cc6-418a-acb6-c5450daae9b0
It is unknown whether apixaban or its metabolites are excreted in human milk. Rats excrete apixaban in milk (12% of the maternal dose). Women should be instructed either to discontinue breastfeeding or to discontinue Eliquis therapy, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Eliquis (Apixaban) Tablet, Film Coated (Revised: August 2014). Available from, as of March 26, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=e9481622-7cc6-418a-acb6-c5450daae9b0
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Apixaban (17 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Apixaban is indicated for reducing the risk of stroke and systemic embolism in patients who have nonvalvular atrial fibrillation, prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis(DVT) leading to pulmonary embolism(PE) in patients after a hip or knee replacement surgery, and treatment of DVT and PE to reduce the risk of recurrence.
FDA Label
For
* Eliquis 2. 5 mg film-coated tablets: :
- Prevention of venous thromboembolic events (VTE) in adult patients who have undergone elective hip or knee replacement surgery.
- Prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in adult patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF), with one or more risk factors, such as prior stroke or transient ischaemic attack (TIA); age 75 years; hypertension; diabetes mellitus; symptomatic heart failure (NYHA Class II).
- Treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), and prevention of recurrent DVT and PE in adults (see section 4. 4 for haemodynamically unstable PE patients).
For
* Eliquis 5 mg film-coated tablets: :
- Prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in adult patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF), with one or more risk factors, such as prior stroke or transient ischaemic attack (TIA); age 75 years; hypertension; diabetes mellitus; symptomatic heart failure (NYHA Class II).
- Treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), and prevention of recurrent DVT and PE in adults (see section 4. 4 for haemodynamically unstable PE patients).
Prevention of venous thromboembolic events (VTE) in adult patients who have undergone elective hip or knee replacement surgery.
Prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in adult patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF), with one or more risk factors, such as prior stroke or transient ischaemic attack (TIA); age 75 years; hypertension; diabetes mellitus; symptomatic heart failure (NYHA Class II).
Treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), and prevention of recurrent DVT and PE in adults (see section 4. 4 for haemodynamically unstable PE patients).
Prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in adult patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF), with one or more risk factors, such as prior stroke or transient ischaemic attack (TIA); age 75 years; hypertension; diabetes mellitus; symptomatic heart failure (NYHA Class II).
Treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), and prevention of recurrent DVT and PE in adults (see section 4. 4 for haemodynamically unstable PE patients).
Treatment of venous thromboembolism
Prevention of arterial thromboembolism, Prevention of venous thromboembolism
Apixaban selectively inhibits factor Xa in its free and bound forms, independant of antithrombin III. Apixaban also inhibits prothrominase. These effects prevent the formation of a thrombus.
Factor Xa Inhibitors
Endogenous factors and drugs that inhibit or block the activity of FACTOR XA. (See all compounds classified as Factor Xa Inhibitors.)
B01AF02
B01AF02
B01AF02
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
B - Blood and blood forming organs
B01 - Antithrombotic agents
B01A - Antithrombotic agents
B01AF - Direct factor xa inhibitors
B01AF02 - Apixaban
Absorption
Apixaban is approximately 50% bioavailable though other studies report 43-46% oral bioavailability.
Route of Elimination
56% of an orally administered dose is recovered in the feces and 24.5-28.8% of the dose is recovered in the urine. 83-88% of the dose recovered in the urine was the unchanged parent compound.
Volume of Distribution
Approximately 21L.
Clearance
3.3L/h though other studies report 4876mL/h.
Distribution in pregnant rats/fetuses: Cmax in amnion was high. Significant concentrations were found in placenta and fetal blood, kidney and liver. Toxicokinetic data collected in the reproductive and developmental toxicity studies in rats, mice and rabbits showed that generally fetal plasma concentrations of apixaban were lower than those in the dams.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Eliquis (Apixaban) p.13 (2011). Available from, as of March 26, 2015: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/002148/WC500107726.pdf
Two single dose radiolabel distribution studies were provided in rats. The data show a wide distribution, with the highest values in excretory organs (liver, kidney, urinary bladder (and contents), bile) and intestinal tract (and contents). After a dose of 20 mg/kg in male Long-Evans rats also relatively high Cmax and AUC were found in adrenals, lungs, thyroid gland, but after a dose of 5 mg/kg in Sprague Dawley rats (both sexes) these organs showed Cmax similar to most other organs and tissues. There was no qualitative difference in distribution between male and female rats, but the female rats showed higher Cmax values in the intestinal tract.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Eliquis (Apixaban) p.13 (2011). Available from, as of March 26, 2015: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/002148/WC500107726.pdf
Protein binding differs between the species. The unbound fraction at concentrations of 1-10 uM is about 13% in human vs about 4% in rats and 8% in dogs. At the tested concentrations there was no effect of concentration or gender. In mice protein binding is much lower, with 44-6 % unbound, dependent on the tested concentration (range 100-2000 ng apixaban/mL).
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Eliquis (Apixaban) p.13 (2011). Available from, as of March 26, 2015: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/002148/WC500107726.pdf
Plasma to blood ratios of about one in dog and human blood indicate uniform distribution between plasma and red blood cells and thus no specific distribution to red blood cells.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Eliquis (Apixaban) p.13 (2011). Available from, as of March 26, 2015: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/002148/WC500107726.pdf
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Apixaban (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
50% of the orally administered dose is excreted as the unchanged parent compound, however 25% of the dose is excreted as O-demethyl apixaban sulfate. All apixaban metabolites account for approximately 32% of the excreted dose though the structure of all metabolites are not well defined. Apixaban is mainly metabolized by cytochrome p450(CYP)3A4 and to a lesser extent by CYP1A2, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP2J2.
Approximately 25% of an orally administered apixaban dose is recovered in urine and feces as metabolites. Apixaban is metabolized mainly via CYP3A4 with minor contributions from CYP1A2, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, and 2J2. O-demethylation and hydroxylation at the 3-oxopiperidinyl moiety are the major sites of biotransformation. Unchanged apixaban is the major drug-related component in human plasma; there are no active circulating metabolites.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Eliquis (Apixaban) Tablet, Film Coated (Revised: August 2014). Available from, as of December 31, 2014: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=e9481622-7cc6-418a-acb6-c5450daae9b0
Apixaban is mainly metabolized by CYP3A4/5 with conjugation via SULT1A1, but several other CYP and SULT isozymes are also involved. No apixaban metabolites were found to have pharmacological activity and there were no unique human metabolites.
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Eliquis (Apixaban) p.13 (2011). Available from, as of March 26, 2015: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/002148/WC500107726.pdf
The metabolism and disposition of (14)C-apixaban, an orally bioavailable, highly selective, and direct acting/reversible factor Xa inhibitor, was investigated in 10 healthy male subjects without (group 1, n=6) and with bile collection (group 2, n=4) after a single 20-mg oral dose. Urine, blood, and feces samples were collected from all subjects. Bile samples were also collected for 3 to 8 hr after dosing from group 2 subjects. There were no serious adverse events or discontinuations due to adverse effects. In plasma, apixaban was the major circulating component and O-demethyl apixaban sulfate, a stable and water-soluble metabolite, was the significant metabolite. The exposure of apixaban (C(max) and area under the plasma concentration versus time curve) in subjects with bile collection was generally similar to that in subjects without bile collection. The administered dose was recovered in feces (group 1, 56.0%; group 2, 46.7%) and urine (group 1, 24.5%; group 2, 28.8%), with the parent drug representing approximately half of the recovered dose. Biliary excretion represented a minor elimination pathway (2.44% of the administered dose) from group 2 subjects within the limited collection period. Metabolic pathways identified for apixaban included O-demethylation, hydroxylation, and sulfation of hydroxylated O-demethyl apixaban. Thus, apixaban is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of factor Xa with elimination pathways that include metabolism and renal excretion.
PMID:18832478 Raghavan N et al; Drug Metab Dispos 37 (1): 74-81 (2009)
The metabolism and disposition of (14)C-apixaban, a potent, reversible, and direct inhibitor of coagulation factor Xa, were investigated in mice, rats, rabbits, dogs, and humans after a single oral administration and in incubations with hepatocytes. In plasma, the parent compound was the major circulating component in mice, rats, dogs, and humans. O-Demethyl apixaban sulfate (M1) represented approximately 25% of the parent area under the time curve in human plasma. This sulfate metabolite was present, but in lower amounts relative to the parent, in plasma from mice, rats, and dogs. Rabbits showed a plasma metabolite profile distinct from that of other species with apixaban as a minor component and M2 (O-demethyl apixaban) and M14 (O-demethyl apixaban glucuronide) as prominent components. The fecal route was a major elimination pathway, accounting for >54% of the dose in animals and >46% in humans. The urinary route accounted for <15% of the dose in animals and 25 to 28% in humans. Apixaban was the major component in feces of every species and in urine of all species except rabbit. M1 and M2 were common prominent metabolites in urine and feces of all species as well as in bile of rats and humans. In vivo metabolite profiles showed quantitative differences between species and from in vitro metabolite profiles, but all human metabolites were found in animal species. After intravenous administration of (14)C-apixaban to bile duct-cannulated rats, the significant portion (approximately 22%) of the dose was recovered as parent drug in the feces, suggesting direct excretion of the drug from gastrointestinal tracts of rats. Overall, apixaban was effectively eliminated via multiple elimination pathways in animals and humans, including oxidative metabolism, and direct renal and intestinal excretion.
PMID:19420130 Zhang D et al; Drug Metab Dispos 37 (8): 1738-48 (2009)
... The O-demethyl apixaban sulfate is a major circulating metabolite in humans but circulates at lower concentrations relative to parent in animals. The aim of this study was to identify the sulfotransferases (SULTs) responsible for the sulfation reaction. Apixaban undergoes O-demethylation catalyzed by cytochrome P450 enzymes to O-demethyl apixaban, and then is conjugated by SULTs to form O-demethyl apixaban sulfate. Of the five human cDNA-expressed SULTs tested, SULT1A1 and SULT1A2 exhibited significant levels of catalytic activity for formation of O-demethyl apixaban sulfate, and SULT1A3, SULT1E1, and SULT2A1 showed much lower catalytic activities. In human liver S9, quercetin, a highly selective inhibitor of SULT1A1 and SULT1E1, inhibited O-demethyl apixaban sulfate formation by 99%; 2,6-dichloro-4-nitrophenol, another inhibitor of SULT1A1, also inhibited this reaction by >90%; estrone, a competitive inhibitor for SULT1E1, had no effect on this reaction. The comparable K(m) values for formation of O-demethyl apixaban sulfate were 41.4 microM (human liver S9), 36.8 microM (SULT1A1), and 70.8 microM (SULT1A2). Because of the high level of expression of SULT1A1 in liver and its higher level of catalytic activity for formation of O-demethyl apixaban sulfate, SULT1A1 might play a major role in humans for formation of O-demethyl apixaban sulfate. O-Demethyl apixaban was also investigated in liver S9 of mice, rats, rabbits, dogs, monkeys, and humans. The results indicated that liver S9 samples from dogs, monkeys, and humans had higher activities for formation of O-demethyl apixaban sulfate than those of mice, rats, and rabbits.
PMID:19131519 Wang L et al; Drug Metab Dispos 37 (4): 802-8 (2009)
12.78.55h.
Apixaban has ... an apparent half-life of approximately 12 hours following oral administration.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Eliquis (Apixaban) Tablet, Film Coated (Revised: August 2014). Available from, as of March 26, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=e9481622-7cc6-418a-acb6-c5450daae9b0
In a comparative study elimination half-life in rats (2-3 hrs) was shorter than in dogs (5-6 hrs) and chimpanzees (5-7 hrs). Distribution volume is relatively low in rats (0.31 L/kg), dogs (0.30 L/kg) and chimpanzees (0.17 L/kg).
European Medicines Agency (EMA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Eliquis (Apixaban) p.13 (2011). Available from, as of March 26, 2015: https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/002148/WC500107726.pdf
... After a single oral administration ... the elimination half life of radioactivity in blood was 1.7 to 4.2 hr.
PMID:2107152 Wang L et al; Drug Metab Dispos 39 (2): 256-64 (2011)
Apixaban selectively inhibits factor Xa in its free and bound forms, independant of antithrombin III. Apixaban also inhibits prothrominase. These effects prevent the formation of a thrombus.

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
15
PharmaCompass offers a list of Apixaban API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Apixaban manufacturer or Apixaban supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Apixaban manufacturer or Apixaban supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Apixaban API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Apixaban API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Apixaban Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Apixaban Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Apixaban manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Apixaban, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Apixaban manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Apixaban API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Apixaban manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Apixaban supplier is an individual or a company that provides Apixaban active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Apixaban finished formulations upon request. The Apixaban suppliers may include Apixaban API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Apixaban suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Apixaban DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Apixaban active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Apixaban DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Apixaban USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Apixaban DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Apixaban USDMF includes data on Apixaban's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Apixaban USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Apixaban suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Apixaban Drug Master File in Japan (Apixaban JDMF) empowers Apixaban API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Apixaban JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Apixaban JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Apixaban suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Apixaban Drug Master File in Korea (Apixaban KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Apixaban. The MFDS reviews the Apixaban KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Apixaban KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Apixaban KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Apixaban API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Apixaban suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Apixaban written confirmation (Apixaban WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Apixaban manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Apixaban active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Apixaban APIs or Apixaban finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Apixaban WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Apixaban suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Apixaban as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Apixaban API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Apixaban as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Apixaban and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Apixaban NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Apixaban suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Apixaban Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Apixaban GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Apixaban GMP manufacturer or Apixaban GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Apixaban CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Apixaban's compliance with Apixaban specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Apixaban CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Apixaban CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Apixaban may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Apixaban EP), Apixaban JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Apixaban USP).
