


1. Aristada
1. 1259305-29-7
2. Aristada
3. Rdc-3317
4. Alks 9072
5. Aristada Initio
6. Aripiprazole Lauroxil [usan]
7. Alks 9070
8. Rdc 3317
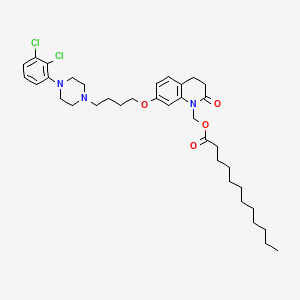
9. [7-[4-[4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]butoxy]-2-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinolin-1-yl]methyl Dodecanoate
10. Alks-9070
11. Alks-9072
12. Rdc3317
13. B786j7a343
14. Aripiprazole Lauroxil (usan)
15. Dodecanoic Acid, (7-(4-(4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1-piperazinyl)butoxy)-3,4-dihydro-2-oxo-1(2h)-quinolinyl)methyl Ester
16. (7-(4-(4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl)butoxy)-2-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinolin-1(2h)-yl)methyl Dodecanoate
17. Unii-b786j7a343
18. Aristada (tn)
19. [7-{4-[4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]butoxy}-2-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinolin-1(2h)-yl]methyl Dodecanoate
20. Aripiprazole-lauroxil
21. Aripiprazol- Lauroxil
22. Schembl1044330
23. Chembl2219425
24. Chebi:90930
25. Dtxsid60154997
26. Aripiprazole Lauroxil [mi]
27. Bcp14993
28. Ex-a4069
29. Mfcd26967976
30. Zinc95564895
31. Aripiprazole Lauroxil [who-dd]
32. Db14185
33. Ncgc00532501-01
34. Ac-36504
35. As-35241
36. Aripiprazole Lauroxil [orange Book]
37. Hy-108751
38. Cs-0030962
39. D10364
40. A856290
41. Q25323757
42. Dodecanoic Acid [7-[4-[4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1-piperazinyl]butoxy]-3,4-dihydro-2-oxo-1(2h)-quinolinyl]methyl Ester
| Molecular Weight | 660.7 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C36H51Cl2N3O4 |
| XLogP3 | 10 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 20 |
| Exact Mass | 659.3256625 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 659.3256625 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 62.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 45 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 858 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Aripiprazole lauroxil is indicated for the treatment of schizophrenia and related psychotic disorders.
FDA Label
Aripiprazole, which is a major pharmacological metabolite of aripiprazole lauroxil, serves to improve the positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia by modulating dopaminergic signalling pathways. Aripiprazole lauroxil is reported to have minimal effects on sexual function or prolactin levels.
Antipsychotic Agents
Agents that control agitated psychotic behavior, alleviate acute psychotic states, reduce psychotic symptoms, and exert a quieting effect. They are used in SCHIZOPHRENIA; senile dementia; transient psychosis following surgery; or MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION; etc. These drugs are often referred to as neuroleptics alluding to the tendency to produce neurological side effects, but not all antipsychotics are likely to produce such effects. Many of these drugs may also be effective against nausea, emesis, and pruritus. (See all compounds classified as Antipsychotic Agents.)
Absorption
Following a single extended-release intramuscular injection of aripiprazole lauroxil, aripiprazole can be detected in the systemic circulation from 5 to 6 days and is continued to be released for an additional 36 days. The concentrations of aripiprazole increases with consecutive doses of aripiprazole lauroxil and the steady state is reached following the fourth monthly injection. The systemic exposure to aripiprazole was similar when comparing deltoid and gluteal intramuscular injections.
Route of Elimination
Based on the pharmacokinetic study for aripiprazole, less than 1% of unchanged aripiprazole was excreted in the urine and approximately 18% of the oral dose was recovered unchanged in the feces.
Volume of Distribution
Based on population pharmacokinetic analysis, the apparent volume of distribution of aripiprazole following intramuscular injection of aripiprazole lauroxil was 268 L, indicating extensive extravascular distribution following absorption. Health human volunteer study indicates that aripiprazole crosses the blood-brain barrier.
Clearance
In rats, the clearance for aripiprazole lauroxil was 0.32 0.11 L/h/kg following injection of aripiprazole lauroxil molar equivalent to 5 mg aripiprazole/kg.
Aripiprazole lauroxil is hydrolyzed to form N-hydroxymethyl-aripiprazole via esterases. N-hydroxymethyl-aripiprazole undergoes a rapid, nonenzymatic spontaneous cleavage, or water-mediated hydrolysis, to form aripiprazole, which mainly contributes to the pharmacological actions of aripiprazole lauroxil. Aripiprazole is further metabolized by hepatic CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 to form dehydro-aripiprazole, which retains some pharmacological activity. Dehydro-aripiprazole displays affinities for D2 receptors similar to aripiprazole and represents 30-40% of the aripiprazole exposure in plasma. Cytochrome P450 2D6 is subject to genetic polymorphism, which results in pharmacokinetic differences among CYP2D6 metabolizer phenotypes and dosage adjustments accordingly.
The mean aripiprazole terminal elimination half-life ranged from 29.2 days to 34.9 days after every 4-week injection of aripiprazole lauroxil 441, 662 and 882 mg.
The pharmacological activity of aripiprazole lauroxil is thought to be mainly mediated by its metabolite aripiprazole, and to a lesser extent, dehydro-aripiprazole. Aripiprazole functions as a partial agonist at the dopamine D2 and the serotonin 5-HT1A receptors, and as an antagonist at the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor. The desired outcome of antipsuchotic agents in schizophrenia is to inhibit dopaminergic transmission in the limbic system and enhance dopaminergic transmission in the prefrontal cortex. As a partial agonist at D2 receptors in the mesolimbic dopaminergic pathway, aripiprazole acts as a functional antagonist in the mesolimbic dopamine pathway and reduces the extent of dopaminergic pathway activity. This results in reduced positive symptoms in schizophrenia and extrapyramidal motor side effects. In contrast, aripiprazole is thought to act as a functional agonist in the mesocortical pathway, where reduced dopamine activity is seen in association with negative symptoms and cognitive impairment. Antagonism at 5-HT2A receptors by aripiprazole alleviates the negative symptoms and cognitive impairment of schizophrenia. 5-HT2A receptors are Gi/Go-coupled that upon activation, produce neuronal inhibition via decreased neuronal excitability and decreased transmitter release at the nerve terminals. In the nigrostriatal pathway, 5-HT2A regulates the release of dopamine. Through antagonism of 5-HT2A receptors, aripiprazole disinhibits the release of dopamine in the striatum and enhance the levels of the transmitters at the nerve terminals. The combined effects of D2 and 5-HT2A antagonism are thought to counteract the increased dopamine function causing increased extrapyramidal side effects. Blocking 5-HT2A receptors may also lead to the modulation of glutamate release in the mesocortical circuit, which is a transmitter that plays a role in schizophrenia. 5-HT1A receptors are autoreceptors that inhibit 5-HT release upon activation. Aripiprazole is a partial agonist at theses receptors and reduces 5-HT release; this results in potentiated dopamine release in the striatum and prefrontal cortex. It is reported that therapeutic doses of aripiprazole occupies up to 90% of brain D2 receptors in a dose-dependent manner. Apripiprazole targets different receptors that lead to drug-related adverse reactions; for example, the antagonist activity at the alpha-1 adrenergic receptors results in orthostatic hypotension. Aripiprazole's antagonism of histamine H1 receptors may explain the somnolence observed with this drug.

LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?
