
Synopsis
0
VMF
0
Australia

Annual Reports
NA
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
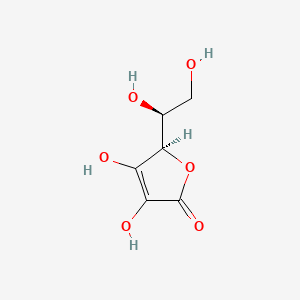

1. Acid, Ascorbic
2. Acid, L-ascorbic
3. Ascorbate, Ferrous
4. Ascorbate, Magnesium
5. Ascorbate, Sodium
6. Ascorbic Acid, Monosodium Salt
7. Di-l-ascorbate, Magnesium
8. Ferrous Ascorbate
9. Hybrin
10. L Ascorbic Acid
11. L-ascorbic Acid
12. Magnesium Ascorbate
13. Magnesium Ascorbicum
14. Magnesium Di L Ascorbate
15. Magnesium Di-l-ascorbate
16. Magnorbin
17. Sodium Ascorbate
18. Vitamin C
1. L-ascorbic Acid
2. Vitamin C
3. 50-81-7
4. L-ascorbate
5. L(+)-ascorbic Acid
6. Ascorbate
7. Ascoltin
8. Ascorbicap
9. Cevitamic Acid
10. Cenolate
11. Natrascorb
12. Hybrin
13. Allercorb
14. Ascorbajen
15. Ascorbutina
16. Ascorteal
17. Cescorbat
18. Cetemican
19. Cevitamin
20. Citriscorb
21. Laroscorbine
22. Lemascorb
23. Proscorbin
24. Roscorbic
25. Secorbate
26. Testascorbic
27. Vitacimin
28. Vitamisin
29. Vitascorbol
30. Ascorin
31. Ascorvit
32. Cantaxin
33. Cebicure
34. Cebione
35. Cegiolan
36. Ceglion
37. Celaskon
38. Cemagyl
39. Cenetone
40. Cergona
41. Cetamid
42. Cevatine
43. Cevimin
44. Cevital
45. Cevitan
46. Cevitex
47. Colascor
48. Concemin
49. Redoxon
50. Vicelat
51. Viforcit
52. Viscorin
53. Vitacee
54. Vitacin
55. Adenex
56. Ascorb
57. Cantan
58. Cebid
59. Cebion
60. Cecon
61. Cemill
62. Cereon
63. Cevex
64. Ciamin
65. Cipca
66. Hicee
67. Ribena
68. Vitace
69. Xitix
70. Davitamon C
71. Arco-cee
72. Planavit C
73. Catavin C
74. Ce Lent
75. Liqui-cee
76. Vicomin C
77. Cee-vite
78. Cevi-bid
79. Scorbu-c
80. C-level
81. C-vimin
82. Cetane-caps Td
83. Duoscorb
84. Scorbacid
85. Cewin
86. Antiscorbic Vitamin
87. C-long
88. C-quin
89. C-span
90. Meri-c
91. Cee-caps Td
92. L-lyxoascorbic Acid
93. L-xyloascorbic Acid
94. Cevalin
95. Antiscorbutic Vitamin
96. Cetane-caps Tc
97. 3-oxo-l-gulofuranolactone
98. 3-keto-l-gulofuranolactone
99. Ce-mi-lin
100. Ido-c
101. Natrascorb Injectable
102. Acidum Ascorbicum
103. L-(+)-ascorbic Acid
104. Ce-vi-sol
105. Ferrous Ascorbate
106. Acidum Ascorbinicum
107. Ascor-b.i.d.
108. (r)-5-((s)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl)-3,4-dihydroxyfuran-2(5h)-one
109. Celin
110. Dora-c-500
111. Kyselina Askorbova
112. Cortalex
113. Ferancee
114. Stuartinic
115. Tolfrinic
116. Acido Ascorbico
117. L-threoascorbic Acid
118. Acide Ascorbique
119. L-3-ketothreohexuronic Acid Lactone
120. Chromagen
121. Kyselina Askorbova [czech]
122. Caswell No. 061b
123. Fema No. 2109
124. Acide Ascorbique [inn-french]
125. Acido Ascorbico [inn-spanish]
126. Acidum Ascorbicum [inn-latin]
127. Sodascorbate
128. Ascorbicin
129. Nci-c54808
130. L-threo-hex-2-enonic Acid, Gamma-lactone
131. L-threo-ascorbic Acid
132. 3-oxo-l-gulofuranolactone (enol Form)
133. Ascor
134. Ascorbicum Acidum
135. Ascorbic Acid, L-
136. Cetebe
137. Ascorbin
138. (+)-ascorbic Acid
139. Hex-2-enonic Acid Gamma-lactone, L-threo-
140. Mfcd00064328
141. Iron(ii) Ascorbate
142. Pq6ck8pd0r
143. Component Of E And C-level
144. Component Of Endoglobin Forte
145. Vitamin C (as Ascorbic Acid)
146. Vasc
147. Ins No.300
148. Ascorbicab
149. E-300
150. Chebi:29073
151. Ins-300
152. Ccris 57
153. Nsc-33832
154. Component Of Cortalex
155. Component Of Ferancee
156. Hsdb 818
157. Nsc-218455
158. 6730-29-6
159. Antiscorbutic Factor
160. Ncgc00164357-01
161. E300
162. Ester-c
163. (2r)-2-[(1s)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-3,4-dihydroxy-2h-furan-5-one
164. (5r)-5-[(1s)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-3,4-dihydroxyfuran-2(5h)-one
165. Dsstox_cid_106
166. Hex-1-enofuranos-3-ulose
167. (5r)-5-[(1s)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-3,4-dihydroxy-2,5-dihydrofuran-2-one
168. Iron-ascorbic Acid Complexes
169. L-ascorbic Acid 1000 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
170. Dsstox_rid_75370
171. Dsstox_gsid_20106
172. Kangbingfeng
173. Chewcee
174. Citrovit
175. Juvamine
176. Ceklin
177. Rovimix C
178. Scorbu C
179. Ascorbinsaeure
180. Parentrovite
181. Cell C
182. Viscorin 100m
183. Ronotec 100
184. Suncoat Vc 40
185. Rontex 100
186. Ascorbicap (tn)
187. Xyloascorbic Acid, L-
188. Ascoltin (tn)
189. [14c]ascorbic Acid
190. Ascorbic Acid [ban:inn:jan]
191. Vitamin C (ascorbic Acid)
192. [14c]-ascorbic Acid
193. Ascorbic Acid (vit C)
194. L-ascorbic Acid, Meets Usp Testing Specifications
195. 2-(1,2-dihydroxyethyl)-4,5-dihydroxyfuran-3-one
196. Einecs 200-066-2
197. Unii-pq6ck8pd0r
198. Nsc 33832
199. Cevitamate
200. L-lyxoascorbate
201. L-xyloascorbate
202. .ascorbinsaure
203. (5r)-5-((1s)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl)-3,4-dihydroxyfuran-2(5h)-one
204. Vitamin B Mixture With Vitamin C
205. 3eka
206. Ester C
207. (+)-ascorbate
208. L(+)-ascorbate
209. L-threo-hex-2-enono-1,4-lactone
210. L-ascorbic Acid, Free Radical Form
211. L-(+)-ascorbate
212. Ascorbic Acid [usp:inn:ban:jan]
213. Ascorbic Acid Mixture With Vitamin B
214. Vitamin C,(s)
215. E 300
216. Ascorbic Acid Dc97sf
217. (2r)-2-[(1s)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-4,5-dihydroxyfuran-3-one
218. Prestwick3_000325
219. L-ascorbic Acid, 99%
220. Ascorbic Acid Mixture With Vitamin B Complex
221. Ascor (tn)
222. Schembl785
223. Bmse000182
224. Vitamin C [vandf]
225. Ascorbic Acid [ii]
226. Ascorbic Acid [mi]
227. Schembl4430
228. Ascorbic Acid [fcc]
229. Ascorbic Acid [inn]
230. Ascorbic Acid [jan]
231. L-ascorbic Acid, Fcc, Fg
232. L-ascorbic Acid, Free Acid
233. Ascorbic Acid [fhfi]
234. Ascorbic Acid [hsdb]
235. Ascorbic Acid [inci]
236. Bspbio_000329
237. (r)-5-(1,2-dihydroxy-ethyl)-3,4-dihydroxy-5h-furan-2-one
238. Mls002153776
239. Ascorbic Acid [vandf]
240. Chembl40274
241. L-ascorbic Acid, Cell Culture
242. Ascorbic Acid [mart.]
243. Bpbio1_000363
244. Gtpl4532
245. Gtpl4781
246. L-ascorbic Acid, Reagent Grade
247. Ascorbic Acid [usp-rs]
248. Ascorbic Acid [who-dd]
249. Ascorbic Acid [who-ip]
250. Dtxsid5020106
251. L-ascorbic Acid, >=99.0%
252. Dtxsid50986567
253. Ascorbic Acid (jp17/usp/inn)
254. Hms2096a11
255. Hms2231n16
256. Hms3713a11
257. L-ascorbic Acid Acs Reagent Grade
258. (2r)-2-[(1s)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-4,5-dihydroxy-furan-3-one
259. Ascorbic Acid [orange Book]
260. Bcp27915
261. Hy-b0166
262. Tox21_110315
263. Tox21_112104
264. Tox21_202127
265. Tox21_302958
266. Ascorbic Acid [ep Monograph]
267. Gamma-lactone L-threo-hex-2-enonate
268. L-ascorbic Acid, Analytical Standard
269. L-ascorbic Acid, Ar, >=99.5%
270. S3114
271. Ascorbic Acid [usp Monograph]
272. Akos016843589
273. Tox21_112104_1
274. Zinc100006770
275. Zinc100019304
276. Ccg-207946
277. Db00126
278. L-ascorbic Acid, Mixt. With Vitamin B
279. Nsc 218455
280. Acidum Ascorbicum [who-ip Latin]
281. Gamma-lactone L-threo-hex-2-enonic Acid
282. L-ascorbic Acid, Acs Reagent, >=99%
283. Ncgc00091517-01
284. Ncgc00091517-02
285. Ncgc00091517-03
286. Ncgc00091517-06
287. Ncgc00188972-01
288. Ncgc00256504-01
289. Ncgc00259676-01
290. 53262-66-1
291. Bp-12831
292. Smr001233160
293. L-ascorbic Acid, Plant Cell Culture Tested
294. L-ascorbic Acid, Reagent Grade, Crystalline
295. A0537
296. A8158
297. Ab00376923
298. Ascorbic Acid (l-ascorbic Acid; Vitamin C)
299. Sw198791-2
300. L-ascorbic Acid, Bioultra, >=99.5% (rt)
301. L-ascorbic Acid, Tested According To Ph.eur.
302. C 1000
303. C00072
304. D00018
305. E80759
306. L-ascorbic Acid, P.a., Acs Reagent, 99.0%
307. 2,3-dehydro-l-threo-hexono-1,4-lactone
308. Ab00376923_04
309. Ab00376923_05
310. L-ascorbic Acid, Jis Special Grade, >=99.0%
311. L-ascorbic Acid, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, 99%
312. L-ascorbic Acid, Bioxtra, >=99.0%, Crystalline
313. Q199678
314. L-ascorbic Acid, Puriss. P.a., >=99.0% (rt)
315. Q27101942
316. 47a605f0-4187-47a8-b0ce-f9e7da1b0076
317. L-ascorbic Acid, P.a., Acs Reagent, Reag. Iso, 99.7%
318. Ascorbic Acid, British Pharmacopoeia (bp) Reference Standard
319. Ascorbic Acid, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
320. L-ascorbic Acid, Certified Reference Material, Tracecert(r)
321. L-ascorbic Acid, Powder, Cell Culture Tested, Gamma-irradiated
322. 3,4-dihydroxy-5beta-[(s)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]furan-2(5h)-one
323. Ascorbic Acid, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
324. (2r)-2-[(1s)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-4,5-dihydroxy-2,3-dihydrofuran-3-one
325. 4-((e)-2-[(2-hydroxyethyl)sulfanyl]diazenyl)benzenecarboxylicacid
326. (5r)-5-[(1s)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-3,4-dihydroxyfuran-2(5h)-one (non-preferred Name)
327. L-ascorbic Acid Solution, 1.0 Mg/ml In Acetonitrile: Water, Certified Reference Material
328. L-ascorbic Acid, Anhydrous, Free-flowing, Redi-dri(tm), Acs Reagent, >=99%
329. L-ascorbic Acid, Suitable For Cell Culture, Suitable For Plant Cell Culture, >=98%
330. L-ascorbic Acid (vitamin C)-13c6 Solution, 500 Mug/ml In Acetonitrile: Water, Certified Reference Material, Ampule Of 1 Ml
331. L-ascorbic Acid, Puriss. P.a., Acs Reagent, Reag. Iso, Reag. Ph. Eur., 99.7-100.5% (oxidimetric)
332. Valeryl Fentanyl Hydrochloride Solution, 100 Mug/ml In Methanol (as A Free Base), Certified Reference Material, Ampule Of 0.5 Ml
| Molecular Weight | 176.12 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H8O6 |
| XLogP3 | -1.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 176.03208797 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 176.03208797 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 107 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 12 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 232 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Antioxidants; Free Radical Scavengers
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Prophylaxis and treatment of scurvy
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1579
Ascorbic acid 100 to 200 mg daily may be given with desferrioxamine in the treatment of patients with thalassemia, to improve the chelating action of desferrioxamine, thereby increasing the excretion of iron.
Sweetman SC (ed), Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. London: Pharmaceutical Press (2009), p.1985.
In iron deficiency states ascorbic acid may increase gastrointestinal iron absorption and ascorbic acid or ascorbate salts are therefore included in some oral iron preparations.
Sweetman SC (ed), Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. London: Pharmaceutical Press (2009), p.1985.
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for L-Ascorbic Acid (30 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Large doses are reported to cause diarrhea and other gastrointestinal disturbances. It has also been stated that large doses may result in hyperoxaluria and the formation of renal calcium oxalate calculi, and ascorbic acid should therefore be given with care to patients with hyperoxaluria. Tolerance may be induced with prolonged use of large doses, resulting in symptoms of deficiency when intake is reduced to normal. Prolonged or excessive use of chewable vitamin C preparations may cause erosion of tooth enamel.
Sweetman SC (ed), Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. London: Pharmaceutical Press (2009), p.1984.
Large doses of ascorbic acid have resulted in hemolysis in patients with G6PD deficiency.
Sweetman SC (ed), Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. London: Pharmaceutical Press (2009), p.1984.
Vitamin C intakes of 250 mg/day or higher have been associated with false-negative results for detecting stool and gastric occult blood. Therefore, high dose vitamin C supplements should be discontinued at least two weeks before physical exams to avoid interference with blood and urine tests.
Otten JJ, Hellwig JP, Meyers LD, eds; Dietary Reference Intakes: The Essential Guide to Nutrient Requirements, Washington, DC: The National Academies Press, 2006, p.208
Supplemental vitamin C may reduce the effectiveness of cancer chemotherapy, and its effectiveness in reducing risk from cancer and related death is unclear.
PDR Network, LLC. PDR for Nonprescription Drugs, Dietary Supplements, and Herbs. 31st Ed. PDR Network, LLC, Montvale, NJ. 2010 p. 603
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for L-Ascorbic Acid (25 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
1(?) = Practically non-toxic: probable oral lethal dose (human) above 15 g/kg, more than 1 qt for 70 kg person (150 lb). Human poisonings are unknown and even reliable estimates of lethal dose in animals are rare.
Gosselin, R.E., R.P. Smith, H.C. Hodge. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 5th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1984., p. II-266
Used to treat vitamin C deficiency, scurvy, delayed wound and bone healing, urine acidification, and in general as an antioxidant. It has also been suggested to be an effective antiviral agent.
Ascorbic Acid (vitamin C) is a water-soluble vitamin indicated for the prevention and treatment of scurvy, as ascorbic acid deficiency results in scurvy. Collagenous structures are primarily affected, and lesions develop in bones and blood vessels. Administration of ascorbic acid completely reverses the symptoms of ascorbic acid deficiency.
Antioxidants
Naturally occurring or synthetic substances that inhibit or retard oxidation reactions. They counteract the damaging effects of oxidation in animal tissues. (See all compounds classified as Antioxidants.)
Vitamins
Organic substances that are required in small amounts for maintenance and growth, but which cannot be manufactured by the human body. (See all compounds classified as Vitamins.)
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A11 - Vitamins
A11G - Ascorbic acid (vitamin c), incl. combinations
A11GA - Ascorbic acid (vitamin c), plain
A11GA01 - Ascorbic acid (vit C)
B - Blood and blood forming organs
B03 - Antianemic preparations
B03A - Iron preparations
B03AA - Iron bivalent, oral preparations
B03AA10 - Ferrous ascorbate
G - Genito urinary system and sex hormones
G01 - Gynecological antiinfectives and antiseptics
G01A - Antiinfectives and antiseptics, excl. combinations with corticosteroids
G01AD - Organic acids
G01AD03 - Ascorbic acid
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01X - Other ophthalmologicals
S01XA - Other ophthalmologicals
S01XA15 - Ascorbic acid
Absorption
70% to 90%
Ascorbic acid is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is widely distributed in the body tissues. Plasma concentrations of ascorbic acid rise as the dose ingested is increased until a plateau is reached with doses of about 90 to 150 mg daily. Body stores of ascorbic acid in health are about 1.5 g although more may be stored at intakes above 200 mg daily. The concentration is higher in leucocytes and platelets than in erythrocytes and plasma. In deficiency states the concentration in leucocytes declines later and at a slower rate, and has been considered to be a better criterion for the evaluation of deficiency than the concentration in plasma.
Sweetman SC (ed), Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. London: Pharmaceutical Press (2009), p.1984.
Ascorbic acid is reversibly oxidized to dehydroascorbic acid; some is metabolized to ascorbate-2-sulfate, which is inactive, and oxalic acid which are excreted in the urine. Ascorbic acid in excess of the body's needs is also rapidly eliminated unchanged in the urine; this generally occurs with intakes exceeding 100 mg daily.
Sweetman SC (ed), Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. London: Pharmaceutical Press (2009), p.1984.
Ascorbic acid crosses the placenta and is distributed into breast milk. It is removed by hemodialysis.
Sweetman SC (ed), Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. London: Pharmaceutical Press (2009), p.1984.
The renal threshold for ascorbic acid is approx 14 ug/mL, but this level varies among individuals. When the body is saturated with ascorbic acid and blood concentrations exceed the threshold, unchanged ascorbic acid is excreted in the urine. When tissue saturation and blood concentrations of ascorbic acid are low, administration of the vitamin results in little or no urinary excretion of ascorbic acid. Inactive metabolites of ascorbic acid such as ascorbic acid-2-sulfate and oxalic acid are excreted in the urine ... Ascorbic acid is also excreted in the bile but there is no evidence for enterohepatic circulation ...
IPCS; Poisons Information Monograph 046: Ascorbic acid (2006). Available from, as of March 9, 2010: https://www.inchem.org/pages/pims.html
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for L-Ascorbic Acid (29 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Hepatic. Ascorbic acid is reversibly oxidised (by removal of the hydrogen from the enediol group of ascorbic acid) to dehydroascorbic acid. The two forms found in body fluids are physiologically active. Some ascorbic acid is metabolized to inactive compounds including ascorbic acid-2-sulfate and oxalic acid.
Ascorbic acid-2-sulfate has ... been identified as metabolite of Vitamin C in human urine.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1548
Ascorbate is oxidized to CO2 in rats and guinea pigs, but considerably less conversion can be detected in man. One route of metabolism of the vitamin in man involves its conversion to oxalate and eventual excretion in the urine; dehydroascorbate is presumably an intermediate.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1548
... Young male guinea pigs /were fed/ diets containing either 2 g/kg (18 control animals) or 86 g/kg (29 treatment animals) of ascorbic acid for 275 days. The average weight gain was significantly higher in the control group. Eight control and eight treatment animals, chosen to maintain comparable weights between the groups, were then given a totally deficient ascorbic acid diet 24 hr before a metabolic study was initiated. In the metabolic study, (14)C-labeled L-ascorbic acid (628 g) was then injected intraperitoneally into both treatment and control guinea pigs to study the catabolism and excretion of the ascorbic acid. Catabolism of the labeled ascorbic acid to respiratory (14)CO2 was increased in treatment guinea pigs. The control and treatment animals were then divided into two groups. One group received 3 mg/kg ascorbic acid (chronic deficiency) for 68 days. The other received a diet devoid of ascorbic acid (acute deficiency) for 44 days. Four control and three treatment animals from the chronic deficiency group and three control and four treatment animals from the acute deficiency group were given a totally deficient ascorbic acid diet 24 hr before a second metabolic study was initiated. (14)C-labeled L-ascorbic acid (628 g) was injected intraperitoneally as above. Treatment animals in the chronic deficiency and the acute deficiency groups had increased catabolism of the labeled ascorbic acid to respiratory (14)CO2 compared to control animals in the chronic and acute deficiency groups. The amount of radioactivity recovered in the urine and feces was similar for both groups except for an increased urinary excretion of the label in treated animals exposed to the totally deficient diet. The treatment animals maintained higher tissue stores of ascorbic acid than the control animals. However, this difference was significant only in the testes. When subjected to a totally deficient diet the treatment animals were depleted of ascorbic acid at a faster rate than the control animals. The accelerated catabolism was not reversible by subnormal intakes of the vitamin ...
Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel; Int J Toxicol 24 (Suppl 2): 51-111 (2005).
... Hartley guinea pigs approximately 30 days pregnant /were divided/ into a control group receiving 25 mg ascorbic acid and a treated group receiving 300 mg/kg/day ascorbic acid daily. All animals were fed a 0.05% ascorbic acid diet. The groups were maintained for 10 days on their respective diets. Pups (both sexes) were randomly chosen on either day 5 or day 10 for the metabolic study. L-l-(14)C-Ascorbic Acid (10 uCi/mM) was injected intraperitoneally into the pups and they were placed in a metabolic chamber for five hours to collect expired (14)CO2. From day 11 all pups were caged individually and weaned to a diet containing only traces of ascorbic acid. Every third day the animals were examined for physical signs of scurvy. Once signs appeared, the animals were examined daily until death. Necropsies were performed on all animals. Pups from the treated group demonstrated a marked increase in (14)CO2 excretion following the intraperitoneal injection. Signs of scurvy appeared 4 days earlier in the treated group and mortality of the treated pups occurred approximately one week earlier. When excretion of labeled CO2 in both groups was correlated with the day of onset of scurvy signs, a linear correlation was found between the two parameters, suggesting that the earlier appearance of signs of scurvy on the experimental pups is secondary to an increased rate of ascorbic acid catabolism ...
Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel; Int J Toxicol 24 (Suppl 2): 51-111 (2005).
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for L-Ascorbic Acid (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Ascorbic acid has known human metabolites that include Ascorbic acid-2-sulfate.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
16 days (3.4 hours in people who have excess levels of vitamin C)
The plasma half-life is reported to be 16 days in humans. This is different in people who have excess levels of vitamin C where the half-life is 3.4 hours
IPCS; Poisons Information Monograph 046: Ascorbic acid (2006). Available from, as of March 9, 2010: https://www.inchem.org/pages/pims.html
Vitamin C has a 96 hr half-life in guinea pigs.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 651
Due to homeostatic regulation, the biological half-life of ascorbate varies widely from 8 to 40 days and is inversely related to the ascorbate body pool.
NAS, Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine; Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Carotenoids. National Academy Press, Washington, D.C., pg. 100, 2000. Available from, as of March 4, 2010: https://www.nap.edu/catalog/9810.html
In humans, an exogenous source of ascorbic acid is required for collagen formation and tissue repair by acting as a cofactor in the posttranslational formation of 4-hydroxyproline in -Xaa-Pro-Gly- sequences in collagens and other proteins. Ascorbic acid is reversibly oxidized to dehydroascorbic acid in the body. These two forms of the vitamin are believed to be important in oxidation-reduction reactions. The vitamin is involved in tyrosine metabolism, conversion of folic acid to folinic acid, carbohydrate metabolism, synthesis of lipids and proteins, iron metabolism, resistance to infections, and cellular respiration.
Ascorbic Acid reducing potential and conversion to AFR (ascorbate free radical) are key to its biological activity, including its free radical scavenging and its relationship to the oxidation of transition metals such as iron and copper at enzyme active sites and in food.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel; Int J Toxicol 24 (Suppl 2): 51-111 (2005).
Vitamin C is known to be an electron donor for eight human enzymes. Three participate in collagen hydroxylation; two in carnitine biosynthesis; and three in hormone and amino acid biosynthesis. The three enzymes that participate in hormone and amino acid biosynthesis are dopamine-beta-hydroxylase, necessary for the biosynthesis of the catecholamines norepinephrine and epinephrine; peptidyl-glycine monooxygenase, necessary for amidation of peptide hormones; and 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvatedioxygenase, involved in tyrosine metabolism. Ascorbate's action with these enzymes involves either monooxygenase or dioxygenase activities.
NAS, Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine; Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Carotenoids. National Academy Press, Washington, D.C., pg. 96-97, 2000. Available from, as of March 4, 2010: https://www.nap.edu/catalog/9810.html
As a cofactor for hydroxylase and oxygenase metalloenzymes, ascorbic acid is believed to work by reducing the active metal site, resulting in reactivation of the metal-enzyme complex, or by acting as a co-substrate involved in the reduction of molecular oxygen. The best known of these reactions is the posttranslational hydroxylation of peptide-bound proline and lysine residues during formation of mature collagen. In these reactions, ascorbate is believed to reactivate the enzymes by reducing the metal sites of prolyl (iron) and lysyl (copper) hydroxylases.
NAS, Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine; Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Carotenoids. National Academy Press, Washington, D.C., pg. 97-98, 2000. Available from, as of March 4, 2010: https://www.nap.edu/catalog/9810.html
Evidence also suggests that ascorbate plays a role in or influences collagen gene expression, cellular procollagen secretion, and the biosynthesis of other connective tissue components besides collagen, including elastin, fibronectin, proteoglycans, bone matrix, and elastin-associated fibrillin. The primary physical symptoms of ascorbic acid's clinical deficiency disease, scurvy, which involves deterioration of elastic tissue, illustrate the important role of ascorbate in connective tissue synthesis.
NAS, Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine; Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Carotenoids. National Academy Press, Washington, D.C., pg. 98, 2000. Available from, as of March 4, 2010: https://www.nap.edu/catalog/9810.html
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for L-Ascorbic Acid (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
 Rochem, your partner in developing, sourcing, and supplying pharmaceutical & animal health ingredients of Chinese origin.
Rochem, your partner in developing, sourcing, and supplying pharmaceutical & animal health ingredients of Chinese origin.
 Faran Shimi: Leading producer of high-quality APIs & alkaloid opiates, serving major pharmaceutical companies across the Middle East.
Faran Shimi: Leading producer of high-quality APIs & alkaloid opiates, serving major pharmaceutical companies across the Middle East.

GDUFA
DMF Review : Reviewed
Rev. Date : 2017-08-01
Pay. Date : 2017-01-10
DMF Number : 30618
Submission : 2016-07-05
Status : Active
Type : II

Certificate Number : R1-CEP 1996-078 - Rev 05
Issue Date : 2022-09-29
Type : Chemical
Substance Number : 253
Status : Valid

Registration Number : 225MF10007
Registrant's Address : Wurmisweg 576, CH-4303, Kaiseraugst, Switzerland
Initial Date of Registration : 2013-01-18
Latest Date of Registration :

NDC Package Code : 63238-3000
Start Marketing Date : 2022-12-28
End Marketing Date : 2026-12-31
Dosage Form (Strength) : POWDER (1kg/kg)
Marketing Category : BULK INGREDIENT


GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 32619
Submission : 2018-04-06
Status : Active
Type : II


GDUFA
DMF Review : Reviewed
Rev. Date : 2018-04-19
Pay. Date : 2018-03-22
DMF Number : 23162
Submission : 2009-10-07
Status : Active
Type : II

Certificate Number : R1-CEP 2004-019 - Rev 06
Issue Date : 2022-09-21
Type : Chemical
Substance Number : 253
Status : Valid

Registration Number : 218MF10950
Registrant's Address : No. 898, Hongshan East Road, High-Tech Industrial Development Zone, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, P. R. China
Initial Date of Registration : 2006-11-24
Latest Date of Registration :

NDC Package Code : 72783-1001
Start Marketing Date : 2020-04-22
End Marketing Date : 2025-12-31
Dosage Form (Strength) : POWDER (1kg/kg)
Marketing Category : BULK INGREDIENT

Registrant Name : Green Cross Wellbeing Co., Ltd.
Registration Date : 2022-01-12
Registration Number : 20210427-211-J-802(3)
Manufacturer Name : CSPC WEISHENG PHARMACEUTICAL(SHIJIAZHUANG) CO., LTD.
Manufacturer Address : No. 898 Zhongshan East Road, High-Tech Industrial Development Zone, Shijiazhuang, Hebei Province, China. Post Code: 050035


GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 23235
Submission : 2009-10-30
Status : Active
Type : II


GDUFA
DMF Review : Reviewed
Rev. Date : 2013-12-05
Pay. Date : 2013-06-28
DMF Number : 27209
Submission : 2013-07-01
Status : Active
Type : II

Registration Number : 219MF10309
Registrant's Address : Jiangshan Road, Jingjiang, Jiangsu Province, P. R. China
Initial Date of Registration : 2007-10-05
Latest Date of Registration :


GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 38717
Submission : 2024-01-04
Status : Active
Type : II

Registration Number : 230MF10117
Registrant's Address : South of Anshun Street and West of Xingyuan Road, Gucheng Subdistrict office, Shouguang, Shandong Province, 262711, P. R. China
Initial Date of Registration : 2018-08-22
Latest Date of Registration :

GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 4372
Submission : 1981-11-25
Status : Inactive
Type : II
Certificate Number : R0-CEP 2003-002 - Rev 01
Issue Date : 2005-07-25
Type : Chemical
Substance Number : 253
Status : Expired

 FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS

Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ANALYTICAL

ABOUT THIS PAGE
72
PharmaCompass offers a list of Ascorbic Acid API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Ascorbic Acid manufacturer or Ascorbic Acid supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Ascorbic Acid manufacturer or Ascorbic Acid supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Ascorbic Acid API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Ascorbic Acid API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Ascorbic Acid Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Ascorbic Acid Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Ascorbic Acid manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Ascorbic Acid, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Ascorbic Acid manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Ascorbic Acid API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Ascorbic Acid manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Ascorbic Acid supplier is an individual or a company that provides Ascorbic Acid active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Ascorbic Acid finished formulations upon request. The Ascorbic Acid suppliers may include Ascorbic Acid API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Ascorbic Acid suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Ascorbic Acid DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Ascorbic Acid active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Ascorbic Acid DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Ascorbic Acid USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Ascorbic Acid DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Ascorbic Acid USDMF includes data on Ascorbic Acid's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Ascorbic Acid USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Ascorbic Acid suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Ascorbic Acid Drug Master File in Japan (Ascorbic Acid JDMF) empowers Ascorbic Acid API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Ascorbic Acid JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Ascorbic Acid JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Ascorbic Acid suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Ascorbic Acid Drug Master File in Korea (Ascorbic Acid KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Ascorbic Acid. The MFDS reviews the Ascorbic Acid KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Ascorbic Acid KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Ascorbic Acid KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Ascorbic Acid API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Ascorbic Acid suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Ascorbic Acid CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Ascorbic Acid Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Ascorbic Acid CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Ascorbic Acid EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Ascorbic Acid to their clients by showing that a Ascorbic Acid CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Ascorbic Acid CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Ascorbic Acid CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Ascorbic Acid CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Ascorbic Acid DMF.
A Ascorbic Acid CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Ascorbic Acid CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Ascorbic Acid suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
A Ascorbic Acid written confirmation (Ascorbic Acid WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Ascorbic Acid manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Ascorbic Acid active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Ascorbic Acid APIs or Ascorbic Acid finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Ascorbic Acid WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Ascorbic Acid suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Ascorbic Acid as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Ascorbic Acid API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Ascorbic Acid as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Ascorbic Acid and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Ascorbic Acid NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Ascorbic Acid suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Ascorbic Acid Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Ascorbic Acid GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Ascorbic Acid GMP manufacturer or Ascorbic Acid GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Ascorbic Acid CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Ascorbic Acid's compliance with Ascorbic Acid specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Ascorbic Acid CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Ascorbic Acid CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Ascorbic Acid may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Ascorbic Acid EP), Ascorbic Acid JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Ascorbic Acid USP).
