
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
FDF
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Finished Drug Prices
NA

1. Aspartylphenylalanine Methyl Ester
2. Aspartylphenylalanine, Methyl
3. Canderel
4. Gold, Hermesetas
5. Goldswite
6. Hermesetas Gold
7. Methyl Aspartylphenylalanine
8. Methyl Ester, Aspartylphenylalanine
9. Milisucre
10. Nozucar
11. Nutrasweet
12. Sc 18862
13. Sc-18862
14. Sc18862
15. Tri Sweet
16. Tri-sweet
17. Trisweet
1. 22839-47-0
2. Nutrasweet
3. Asp-phe-ome
4. Asp-phe Methyl Ester
5. Aspartam
6. Canderel
7. L-aspartyl-l-phenylalanine Methyl Ester
8. Aspartamo
9. Aspartamum
10. Aspartylphenylalanine Methyl Ester
11. Equal
12. Sweet Dipeptide
13. Methyl Aspartylphenylalanate
14. Dipeptide Sweetener
15. Pal Sweet
16. H-asp-phe-ome
17. 1-methyl N-l-alpha-aspartyl-l-phenylalanate
18. Tri-sweet
19. Sladex
20. Zero-cal
21. Methyl L-alpha-aspartyl-l-phenylalaninate
22. Sc-18862
23. 3-amino-n-(alpha-methoxycarbonylphenethyl) Succinamic Acid
24. (s)-3-amino-4-(((s)-1-methoxy-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl)amino)-4-oxobutanoic Acid
25. Chebi:2877
26. N-l-alpha-aspartyl-l-phenylalanine 1-methyl Ester
27. 3-amino-n-(alpha-carboxyphenethyl)succinamic Acid N-methyl Ester
28. Aspartame (e951)
29. Ins No.951
30. (3s)-3-amino-4-[[(2s)-1-methoxy-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]amino]-4-oxobutanoic Acid
31. N-l-alpha-aspartyl-l-phenylalanine Methyl Ester
32. Nsc-758953
33. Ins-951
34. Z0h242bbr1
35. (s)-3-amino-4-((s)-1-methoxy-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-ylamino)-4-oxobutanoic Acid
36. L-aspartyl-l-phenylalanyl Methyl Ester
37. Aspartame 1000 Microg/ml In Methanol
38. N-l-alpha-aspartyl L-phenylalanine 1-methyl Ester
39. Ncgc00091104-02
40. Dsstox_cid_107
41. E 951
42. E-951
43. Mfcd00002724
44. Dsstox_rid_75371
45. Dsstox_gsid_20107
46. Sanecta
47. Aspartam [inn-french]
48. Aspartame, L,l-alpha-
49. Aspartamum [inn-latin]
50. Aspartamo [inn-spanish]
51. Smr000471870
52. Cas-22839-47-0
53. Ccris 5456
54. Sc 18862
55. Hsdb 3915
56. Methyl L-aspartyl-l-phenylalanine
57. Einecs 245-261-3
58. L-phenylalanine, N-l-.alpha.-aspartyl-, 1-methyl Ester
59. Methyl L-alpha-aspartyl-l-phenylalanate
60. Unii-z0h242bbr1
61. Aminosweet
62. L-phenylalanine, N-l-alpha-aspartyl-, 1-methyl Ester
63. Palsweet Diet
64. Methyl N-l-alpha-aspartyl-l-phenylalaninate
65. 1-methyl N-l-alpha-aspartyl-l-phenylalanine
66. Aspartame [usan:inn:ban:nf]
67. L-alpha-aspartyl-l-phenylalanine 2-methyl Ester
68. Ncgc00095160-01
69. Df-ome
70. Aspartame (nf/inn)
71. N-(l-a-aspartyl)-l-phenylalanine Methyl Ester
72. Aspartame [fcc]
73. Aspartame [inn]
74. Aspartame [ii]
75. Aspartame [mi]
76. Aspartame [fhfi]
77. Aspartame [hsdb]
78. Aspartame [inci]
79. Aspartame [usan]
80. Spectrum2_001706
81. Spectrum3_001949
82. Aspartame [vandf]
83. Aspartame [mart.]
84. Epitope Id:164026
85. 3-amino-n-(alpha-carboxyphenethyl)succinamic Acid N-methyl Ester, Stereoisomer
86. Aspartame [usp-rs]
87. Aspartame [who-dd]
88. Schembl3636
89. Succinamic Acid, 3-amino-n-(alpha-carboxyphenethyl)-, N-methyl Ester, Stereoisomer
90. Bspbio_003549
91. Mls001066421
92. Mls001306461
93. Aspartame, Analytical Standard
94. Spectrum1505306
95. L-phenylalanine, L-alpha-aspartyl-, 2-methyl Ester
96. Spbio_001692
97. 3-amino-n-(.alpha.-carboxyphenethyl)succinamic Acid N-methyl Ester
98. Chembl171679
99. Aspartame [ep Monograph]
100. Dtxsid0020107
101. Asp-phe Methyl Ester, >=98%
102. Kbio3_002839
103. Aspartyl-phenylalanine Methyl Ester
104. Hms1922b16
105. Hms2093b05
106. Hms2233d15
107. Pharmakon1600-01505306
108. Hy-b0361
109. Zinc1532132
110. Tox21_111080
111. Tox21_111459
112. Tox21_202315
113. Tox21_302965
114. Aspartame 1000 Microg/ml In Water
115. Ccg-39444
116. Nsc758953
117. S2036
118. Akos015920055
119. Tert-butyln-(3-formylphenyl)carbamate
120. Tox21_111080_1
121. Am84801
122. Db00168
123. Nsc 758953
124. Alpha-aspartyl-phenylalanine Methyl Ester
125. L-aspartyl-l-phenyl-alanine Methyl Ester
126. Ncgc00091104-01
127. Ncgc00091104-03
128. Ncgc00091104-04
129. Ncgc00091104-05
130. Ncgc00095160-03
131. Ncgc00256407-01
132. Ncgc00259864-01
133. 7421-84-3
134. Ac-12293
135. As-13889
136. E951
137. L-aspartyl-l-3-phenylalanine Methyl Ester
138. Sbi-0206757.p001
139. Asp-phe Methyl Ester, >=99.0% (hplc)
140. A0997
141. Am20060556
142. Sw219179-1
143. Alpha-l-aspartyl-l-phenylalanine Methyl Ester
144. L-aspartyl-l-phenylalanine Methyl Ester, 96%
145. 39a470
146. D02381
147. Ab00376622_08
148. Ab00376622_09
149. A816383
150. Q182040
151. Sr-05000001682
152. J-502447
153. Sr-05000001682-1
154. Brd-k78841970-001-06-2
155. Aspartame, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
156. Aspartame, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
157. (s)-3-amino-n-((s)-1-methoxycarbonyl-2-phenyl-ethyl)-succinamic Acid
158. Aspartame, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
159. (3s)-3-amino-3-{[(2s)-1-methoxy-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]carbamoyl}propanoic Acid
160. (s)-3-amino-4-(((s)-1-methoxy-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl)amino)-4-oxobutanoicacid
161. 3-amino-4-[(1-carboxy-2-phenyl-ethyl)-methyl-amino]-4-oxo-butanoic Acid;n-l-alpha-aspartyl-l-phenylalanine Methyl Ester
| Molecular Weight | 294.30 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H18N2O5 |
| XLogP3 | -2.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 294.12157168 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 294.12157168 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 119 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 380 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Aspartame is used as an intense sweetening agent ... in pharmaceutical preparations including tablets, powder mixes, and vitamin preparations. It enhances flavor systems and can be used to mask some unpleasant taste characteristics; the approximate sweetening power is 80-200 times that of sucrose.
Rowe, R.C., Sheskey, P.J., Quinn, M.E.; (Eds.), Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients 6th edition Pharmaceutical Press, London, England 2009, p. 48
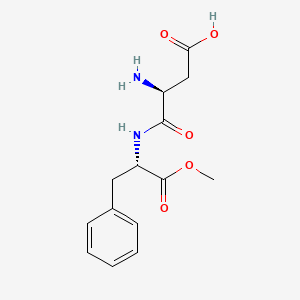
Aspartame is the methylester of a dipeptide composed of two amino acids, phenylalanine and aspartic acid. ... Persons with phenylketonuria, who must restrict carefully their phenylalanine intake, must be alerted to the presence of phenylalanine in the drug product and the amount of the ingredient in each dosage unit.
21 CFR 201.21 (USFDA); Declaration of presence of phenylalanine as a component of aspartame in over-the-counter and prescrpition drugs for human use
Excessive use of aspartame should be avoided by patients with phenylketonuria.
Reynolds, J.E.F., Prasad, A.B. (eds.) Martindale-The Extra Pharmacopoeia. 28th ed. London: The Pharmaceutical Press, 1982., p. 425
Aspartic acid and sodium glutamate were both neuroexcitatory amino acids which had an additive toxic effect on hypothalamic neurones. As this might be specially damaging to young children, who already receive sodium glutamate in gram quantities in their diet, aspartame should not generally be added to children's food.
Reynolds, J.E.F., Prasad, A.B. (eds.) Martindale-The Extra Pharmacopoeia. 28th ed. London: The Pharmaceutical Press, 1982., p. 425
Reported adverse effects include: headaches; grand mal seizure; memory loss; gastrointestinal symptoms; and dermatological symptoms. However, scientifically controlled peer-reviewed studies have consistently failed to produce evidence of a causal effect between aspartame consumption and adverse health events ...
Rowe, R.C., Sheskey, P.J., Quinn, M.E.; (Eds.), Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients 6th edition Pharmaceutical Press, London, England 2009, p. 49
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Aspartame (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Used as a diet supplement and sugar substitute.
Aspartame (L-alpha-aspartyl-L-phenylalanine methyl ester) is a low-calorie sweetener used to sweeten a wide variety of low- and reduced-calorie foods and beverages, including low-calorie tabletop sweeteners. Aspartame is composed of two amino acids, aspartic acid and phenylalanine, as the methyl ester. Aspartic acid and phenylalanine are also found naturally in protein containing foods, including meats, grains and dairy products. Methyl esters are also found naturally in many foods such as fruits and vegetable and their juices. Upon digestion, aspartame breaks down into three components (aspartic acid, phenylalanine and methanol), which are then absorbed into the blood and used in normal body processes. Neither aspartame nor its components accumulates in the body. These components are used in the body in the same ways as when they are derived from common foods.
Sweetening Agents
Substances that sweeten food, beverages, medications, etc., such as sugar, saccharine or other low-calorie synthetic products. (From Random House Unabridged Dictionary, 2d ed) (See all compounds classified as Sweetening Agents.)
Absorption
Absorbed in the small intestine, aspartame is metabolized and absorbed very quickly.
Approximately 10% of aspartame (by weight) is broken down into methanol in the small intestine. Most of the methanol is absorbed and quickly converted into formaldehyde. Approximately 50% of aspartame (by weight) is broken down into phenylalanine. Approximately 40% of aspartame (by mass) is broken down into aspartic acid.
Unlike some other intense sweeteners, aspartame is metabolized in the body and consequently has some nutritive value: 1 g provides approx 17 kJ (4 kcal). However, in practice, the small quantity of aspartame consumed provides a minimal nutritive effect.
Rowe, R.C., Sheskey, P.J., Quinn, M.E.; (Eds.), Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients 6th edition Pharmaceutical Press, London, England 2009, p. 48
The use of aspartame has been of some concern owing to the formation of the potentially toxic metabolites methanol, aspartic acid, and phenylalanine. Of these materials, only phenylalanine is produced in sufficient quantities, at normal aspartame intake levels, to cause concern.
Rowe, R.C., Sheskey, P.J., Quinn, M.E.; (Eds.), Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients 6th edition Pharmaceutical Press, London, England 2009, p. 49
Aspartame [SC-18862; 3-amino-N-(alpha-carboxyphenethyl) succinamic acid, methyl ester, the methyl ester of aspartylphenylalanine] is a sweetening agent that organoleptically has about 180 times the sweetness of sugar. The metabolism of aspartame has been studied in mice, rats, rabbits, dogs, monkeys, and humans. The compound was digested in all species in the same way as are natural constituents of the diet. Hydrolysis of the methyl group by intestinal esterases yielded methanol, which was oxidized in the one-carbon metabolic pool to CO2. The resultant dipeptide was split at the mucosal surface by dipeptidases and the free amino acids were absorbed. The aspartic acid moiety was transformed in large part to CO2 through its entry into the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Phenylalanine was primarily incorporated into body protein either unchanged or as its major metabolite, tyrosine.
PMID:827618 Ranney RE, et al; J Toxicol Environ Health 2 (2): 441-51 (1976).
Although aspartame was hydrolyzed in the gut of the monkey to its constituent moieties, methanol, aspartic acid, and phenylalanine, the ingestion of 15 or 60 mg/kg doses for 10 days did not modify phenylalanine metabolism. Aspartame had little effect on the disappearance of iv admin (14)C-phenylalanine from the plasma, it did not substantially affect the conversion of phenylalanine into tyrosine or carbon dioxide, and it did not alter the rate of incorporation of label into protein. The majority of phenylalanine derived from aspartame was incorporated into body protein, with only 20-25% of the compound being excreted. 60-80% of the derived methanol and aspartic acid was oxidized to carbon dioxide.
PMID:4200873 Oppermann JA et al; J Nutr 103 (10): 1460-6 (1973)
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for Aspartame (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
At room temperature, aspartame is most stable at pH 4.3, where its half-life is nearly 300 days. At pH 7, its half-life is shortened to only a few days.
180 to 200 times sweeter than sucrose, it is metabolized as a protein and its subsequent amino-acids used up in there respective mechanisms.

API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ANALYTICAL

ABOUT THIS PAGE


LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?