
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
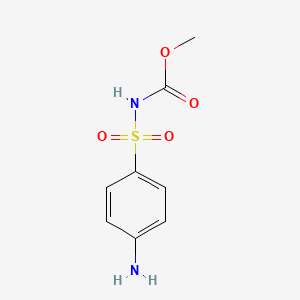

1. Asulam Monohydrobromide
2. Asulam Monohydrochloride
3. Asulam, Calcium Salt
4. Asulam, Magnesium Salt
5. Asulam, Monoacetate
6. Asulam, Mononitrate
7. Asulam, Monosodium Salt
8. Asulam, Monosulfamate
9. Asulam, Oxalate (1:1)
10. Asulam, Phosphate (1:1)
11. Asulam, Potassium Salt
12. Asulam, Sulfate (1:1)
13. Methyl N-(4-aminobenzenesulfonyl)carbamate
1. 3337-71-1
2. Asulox
3. Asilan
4. Jonnix
5. Asulox F
6. Plakin
7. Asulox 40
8. Methyl Sulphanilylcarbamate
9. Methyl Sulfanilylcarbamate
10. M And B 9057
11. Mb 9057
12. Methyl N-(4-aminobenzenesulfonyl)carbamate
13. Methyl Sulfanilyl Carbamate
14. Asulame
15. Asulame [iso-french]
16. Carbamic Acid, [(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl]-, Methyl Ester
17. Carbamic Acid, Sulfanilyl-, Methyl Ester
18. Methyl ((4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl)carbamate
19. Methyl 4-aminobenzenesulphonyl Carbamate
20. Methyl N-(4-aminophenyl)sulfonylcarbamate
21. 4-amino-benzolsulfonyl-methylcarbamat
22. Methyl 4-aminophenylsulphonylcarbamate
23. Methyl 4-aminobenzenesulphonylcarbamate
24. Methyl 4-aminophenylsulphonyl Carbamate
25. Ai3-52723
26. Methyl P-aminobenzenesulfonylcarbamate
27. Methyl 4-aminobenzenesulfonyl Carbamate
28. 0y5asm7p5s
29. Methyl [(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl]carbamate
30. Methyl N-(4-aminophenylsulfonyl)carbamate
31. Chebi:81696
32. Methyl 4-aminophenylsulfonylcarbamate
33. Carbamic Acid, ((4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl)-, Methyl Ester
34. Dsstox_cid_3890
35. Dsstox_rid_77220
36. Dsstox_gsid_23890
37. Caswell No. 062a
38. Asulox F; M And B 9057; Mb 9057;methyl P-aminobenzenesulfonylcarbamate;
39. Asulam [ansi:bsi:iso]
40. Cas-3337-71-1
41. Asulam [iso]
42. N1-methoxycarbonylsulfanilamide
43. Einecs 222-077-1
44. N(sup 1)-methoxycarbonylsulfanilamide
45. Unii-0y5asm7p5s
46. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 106901
47. Brn 2697523
48. Asulfox F
49. 4-amino-benzolsulfonyl-methylcarbamat [german]
50. Sodium [(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](methoxycarbonyl)azanide
51. Sulfanilylcarbamic Acid Methyl Ester
52. Methyl 4-aminobenzenesulfonylcarbamate
53. Methyl (4-aminophenylsulfonyl)carbamate
54. Carbamicacid, N-[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl]-, Methyl Ester
55. Asulam [mi]
56. Methyl Sulfanilyl Carbamate.
57. Schembl64856
58. 3-14-00-01967 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
59. Carbamic Acid, Sulfanilyl-, Methyl Ester (7ci)(8ci)
60. Chembl2137678
61. Dtxsid8023890
62. Hsdb 6556
63. N(1)-methoxycarbonylsulfanilamide
64. Act03339
65. Zinc2019346
66. Tox21_201642
67. Tox21_300851
68. Asulam 10 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
69. C1263
70. Mfcd00055534
71. Akos015891065
72. Methyl 4-aminophenyl Sulphonylcarbamate
73. Ks-5377
74. Cid 6433598
75. Ncgc00160637-01
76. Ncgc00160637-02
77. Ncgc00160637-03
78. Ncgc00160637-04
79. Ncgc00160637-05
80. Ncgc00160637-06
81. Ncgc00254754-01
82. Ncgc00259191-01
83. Ac-12057
84. Asulam, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
85. Ft-0603635
86. M & B 9057
87. C18350
88. 337a711
89. Carbamic Acid, 4-aminobenzenesulfonyl-, Methyl Ester
90. J-019170
91. Methyl N-((4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl)carbamate
92. Q2868667
93. N-((4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl)carbamic Acid Methyl Ester
| Molecular Weight | 230.24 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H10N2O4S |
| XLogP3 | -0.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 230.03612798 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 230.03612798 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 107 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 15 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 314 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
... Two goats were dosed with ring-labeled (14)C-asulam at 20 ppm in the diet for 7 consecutive days. The total radioactive residues were nondetectable (<0.005 ppm) in fat and muscle, 0.162 ppm in kidneys, 0.090 ppm in liver, and up to 0.021 ppm in milk. The parent compound, asulam, constituted the majority of the residues in milk (81% of total reactive reside (TRR)) and kidneys (100% of TRR) and its metabolite N4-acetylsulfanilamide constitutes the majority of residues in liver (58% of TRR). The parent was not identified in liver samples. In a previous study, sulfanilamide was found in ruminant liver and muscle, and N4-acetylasulam was found in liver, kidney, milk, muscle, and fat.
USEPA/Office of Pesticide Programs; Reregistration Eligibility Decision Document - Asulam p.14-5 EPA 738-R-95-024 (September 1995). Available from, as of June 25, 2018: https://www.epa.gov/pesticides/reregistration/status.htm
... Laying hens were dosed with ring-labeled (14)C-asulam at 22.5 ppm in the diet for 7 consecutive days. The maximum total radioactive residues were 0.027 ppm in egg yolks, 0.062 ppm in egg whites, 0.011 ppm in fat, 0.074 ppm in muscle, 0.444 ppm in kidneys, and 0.086 ppm in liver. The parent compound asulam, and its metabolite N4-acetylsulfanilamide constituted the majority of the residues in poultry, comprising 63 and 44% of the total reactive reside (TRR), respectively, in egg yolks, 21 and 52% of the TRR, respectively, in egg whites, 35 and 51% of the TRR, respectively, in muscle, and 83 and 14% of the TRR, respectively, in kidney. The parent was not identified in liver samples; N4-acetyl sulfanilamide represented 81% of the TRR in liver samples.
USEPA/Office of Pesticide Programs; Reregistration Eligibility Decision Document - Asulam p.14 EPA 738-R-95-024 (September 1995). Available from, as of June 25, 2018: https://www.epa.gov/pesticides/reregistration/status.htm
Metabolism studies were conducted in male and female Sprague- Dawley rats. The tests used a single oral or iv dose, or repeated i.v. doses for 14 days. The pharmacokinetics of asulam were similar after all dose regimens in both sexes. Peak blood levels were attained at 0.5 hours. No unusual localization of asulam occurred in tissues and all tissue levels were low at 72 hours. Asulam was rapidly eliminated, mostly within 24 hours. 76.5% to 101.5% of the administered dose was eliminated in the urine, and 1.4% to 25.3% of the dose in feces. The major excretory product was unchanged parent compound (70% to 80%), with acetylasulam (3% to 8%) and acetylsulphanilamide (<3%) being the two major metabolites.
USEPA/Office of Pesticide Programs; Reregistration Eligibility Decision Document - Asulam p.10 EPA 738-R-95-024 (September 1995). Available from, as of June 25, 2018: https://www.epa.gov/pesticides/reregistration/status.htm
The metabolism of [ring-(14)C]asulam, a systemic herbicide highly effective against bracken, has been studied in rats. Most of the radioactivity (76-100% dose) administered orally or intravenously is excreted in the urine in 24 hr as unchanged asulam (61-74% dose), N4-acetylasulam (8-14%) and N4-acetylsulphanilamide (0.1-2.6%). Small amounts of radioactivity (0.3-7.4% dose) were present in the feces, only traces (0.2-0.3%) were excreted in the bile, and no significant (14)CO2 was detected. Perfusion of rat liver with (14)C-asulam resulted in more extensive metabolism. Total amounts present in perfusate (81% total), bile (1%) plus liver (14%) were 23.1% for unchanged asulam, 25.7% for acetylasulam, less than 1% for acetylsulphanilamide, and 4.5% as conjugates of asulam and acetylasulam, together with several other unidentified metabolites. Asulam is acetylated more readily than sulphanilamide, by rat-liver homogenate, and the highest enzyme activity was associated with the mitochondrial fraction (2.4 pmol/mg protein per min). Although not hydroxylated by rats in vivo, evidence was obtained for the hydroxylation of asulam by rat-liver microsomal preparations in vitro.
PMID:6711013 Heijbroek WM et al; Xenobiotica 14 (3): 235-47 (1984)
... Two goats were dosed with ring-labeled (14)C-asulam at 20 ppm in the diet for 7 consecutive days. The total radioactive residues were nondetectable (<0.005 ppm) in fat and muscle, 0.162 ppm in kidneys, 0.090 ppm in liver, and up to 0.021 ppm in milk. The parent compound, asulam, constituted the majority of the residues in milk (81% of total reactive reside (TRR)) and kidneys (100% of TRR) and its metabolite N4-acetylsulfanilamide constitutes the majority of residues in liver (58% of TRR). The parent was not identified in liver samples. In a previous study, sulfanilamide was found in ruminant liver and muscle, and N4-acetylasulam was found in liver, kidney, milk, muscle, and fat.
USEPA/Office of Pesticide Programs; Reregistration Eligibility Decision Document - Asulam p.14-5 EPA 738-R-95-024 (September 1995). Available from, as of June 25, 2018: https://www.epa.gov/pesticides/reregistration/status.htm
... Laying hens were dosed with ring-labeled (14)C-asulam at 22.5 ppm in the diet for 7 consecutive days. The maximum total radioactive residues were 0.027 ppm in egg yolks, 0.062 ppm in egg whites, 0.011 ppm in fat, 0.074 ppm in muscle, 0.444 ppm in kidneys, and 0.086 ppm in liver. The parent compound asulam, and its metabolite N4-acetylsulfanilamide constituted the majority of the residues in poultry, comprising 63 and 44% of the total reactive reside (TRR), respectively, in egg yolks, 21 and 52% of the TRR, respectively, in egg whites, 35 and 51% of the TRR, respectively, in muscle, and 83 and 14% of the TRR, respectively, in kidney. The parent was not identified in liver samples; N4-acetyl sulfanilamide represented 81% of the TRR in liver samples.
USEPA/Office of Pesticide Programs; Reregistration Eligibility Decision Document - Asulam p.14 EPA 738-R-95-024 (September 1995). Available from, as of June 25, 2018: https://www.epa.gov/pesticides/reregistration/status.htm
Metabolism studies were conducted in male and female Sprague- Dawley rats. The tests used a single oral or iv dose, or repeated i.v. doses for 14 days. The pharmacokinetics of asulam were similar after all dose regimens in both sexes. Peak blood levels were attained at 0.5 hours. No unusual localization of asulam occurred in tissues and all tissue levels were low at 72 hours. Asulam was rapidly eliminated, mostly within 24 hours. 76.5% to 101.5% of the administered dose was eliminated in the urine, and 1.4% to 25.3% of the dose in feces. The major excretory product was unchanged parent compound (70% to 80%), with acetylasulam (3% to 8%) and acetylsulphanilamide (<3%) being the two major metabolites.
USEPA/Office of Pesticide Programs; Reregistration Eligibility Decision Document - Asulam p.10 EPA 738-R-95-024 (September 1995). Available from, as of June 25, 2018: https://www.epa.gov/pesticides/reregistration/status.htm
The metabolism of [ring-(14)C]asulam, a systemic herbicide highly effective against bracken, has been studied in rats. Most of the radioactivity (76-100% dose) administered orally or intravenously is excreted in the urine in 24 hr as unchanged asulam (61-74% dose), N4-acetylasulam (8-14%) and N4-acetylsulphanilamide (0.1-2.6%). Small amounts of radioactivity (0.3-7.4% dose) were present in the feces, only traces (0.2-0.3%) were excreted in the bile, and no significant (14)CO2 was detected. Perfusion of rat liver with (14)C-asulam resulted in more extensive metabolism. Total amounts present in perfusate (81% total), bile (1%) plus liver (14%) were 23.1% for unchanged asulam, 25.7% for acetylasulam, less than 1% for acetylsulphanilamide, and 4.5% as conjugates of asulam and acetylasulam, together with several other unidentified metabolites. Asulam is acetylated more readily than sulphanilamide, by rat-liver homogenate, and the highest enzyme activity was associated with the mitochondrial fraction (2.4 pmol/mg protein per min). Although not hydroxylated by rats in vivo, evidence was obtained for the hydroxylation of asulam by rat-liver microsomal preparations in vitro.
PMID:6711013 Heijbroek WM et al; Xenobiotica 14 (3): 235-47 (1984)
ANALYTICAL

ABOUT THIS PAGE
57
PharmaCompass offers a list of Asulam API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Asulam manufacturer or Asulam supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Asulam manufacturer or Asulam supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Asulam API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Asulam API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Asulam Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Asulam Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Asulox 40 manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Asulox 40, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Asulox 40 manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Asulox 40 API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Asulox 40 supplier is an individual or a company that provides Asulox 40 active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Asulox 40 finished formulations upon request. The Asulox 40 suppliers may include Asulox 40 API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
Asulox 40 Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Asulox 40 GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Asulox 40 GMP manufacturer or Asulox 40 GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Asulox 40 CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Asulox 40's compliance with Asulox 40 specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Asulox 40 CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Asulox 40 CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Asulox 40 may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Asulox 40 EP), Asulox 40 JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Asulox 40 USP).
