
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
US Medicaid
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers

1. Bms 650032
2. Bms-650032
1. 630420-16-5
2. Bms-650032
3. Sunvepra
4. Bms 650032
5. Bms650032
6. S9x0krj00s
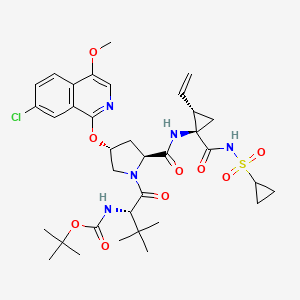
7. 1,1-dimethylethyl ((1s)-1-{((2s,4r)-4-(7-chloro-4-methoxyisoquinolin-1-yloxy)-2-({(1r,2s)-1-((cyclopropylsulfonyl)carbamoyl)-2-ethenylcyclopropyl}carbamoyl) Pyrrolidin-1-yl)carbonyl}-2,2-dimethylpropyl)carbamate
8. Tert-butyl N-[(2s)-1-[(2s,4r)-4-(7-chloro-4-methoxyisoquinolin-1-yl)oxy-2-[[(1r,2s)-1-(cyclopropylsulfonylcarbamoyl)-2-ethenylcyclopropyl]carbamoyl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate
9. Asunaprevir (bms-650032)
10. Cyclopropanecarboxamide, N-((1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl)-3-methyl-l-valyl-(4r)-4-((7-chloro-4-methoxy-1-isoquinolinyl)oxy)-l-prolyl-1-amino-n-(cyclopropylsulfonyl)-2-ethenyl-, (1r,2s)-
11. N-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-3-methyl-l-valyl-(4r)-4-[(7-chloro-4-methoxyisoquinolin-1-yl)oxy]-n-{(1r,2s)-1-[(cyclopropylsulfonyl)carbamoyl]-2-ethenylcyclopropyl}-l-prolinamide
12. Tert-butyl ((s)-1-((2s,4r)-4-((7-chloro-4-methoxyisoquinolin-1-yl)oxy)-2-(((1r,2s)-1-((cyclopropylsulfonyl)carbamoyl)-2-vinylcyclopropyl)carbamoyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)carbamate
13. Asunaprevir [usan]
14. Asunaprevir (jan/usan)
15. Asunaprevir [usan:inn]
16. Unii-s9x0krj00s
17. Sunvepratrade
18. Sunvepra (tn)
19. 2r9
20. Tert-butyl N-[(1s)-1-[(2s,4r)-4-[(7-chloro-4-methoxy-1-isoquinolyl)oxy]-2-[[(1r,2s)-1-(cyclopropylsulfonylcarbamoyl)-2-vinyl-cyclopropyl]carbamoyl]pyrrolidine-1-carbonyl]-2,2-dimethyl-propyl]carbamate
21. Asunaprevir [mi]
22. Asunaprevir [inn]
23. Asunaprevir [jan]
24. Asunaprevir [who-dd]
25. Asunaprevir; Bms-650032
26. Schembl2630655
27. Chembl2105735
28. Gtpl10882
29. Ex-a386
30. Chebi:134723
31. Dtxsid201026065
32. (1r,2s)-n-[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]-3-methyl-l-valyl-(4r)-4-[(7-chloro-4-methoxy-1-isoquinolinyl)oxy]-l-prolyl-1-amino-n-(cyclopropylsulfonyl)-2-ethenylcyclopropanecarboxamide
33. Amy38775
34. Bcp08230
35. Bdbm50287594
36. Mfcd27987900
37. Zinc85540202
38. Akos037515831
39. Cs-0674
40. Db11586
41. Compound 24 [pmid: 24564672]
42. Ncgc00378691-02
43. Ncgc00378691-05
44. Hy-14434
45. Asunaprevir;bms650032;bms-650032
46. D10093
47. A857563
48. Q4811881
49. 1,1-dimethylethyl ((1s)-1-(((2s,4r)-4-(7-chloro-4methoxyisoquinolin-1-yloxy)-2- (((1r,2s)-1-((cyclopropylsulfonyl)carbamoyl)-2-ethenylcyclopropyl)carbamoyl) Pyrrolidin-1-yl)carbonyl)-2,2-dimethylpropyl)carbamate
50. Bms650032;(1r,2s)-n-[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]-3-methyl-l-valyl-(4r)-4-[(7-chloro-4-methoxy-1-isoquinolinyl)oxy]-l-prolyl-1-amino-n-(cyclopropylsulfonyl)-2-ethenylcyclopropanecarboxamide
51. Carbamic Acid, [(1s)-1-[[(2s,4r)-4-[(7-chloro-4-methoxy-1-isoquinolinyl)oxy]-2-[[[(1r,2s)-1-[[(cyclopropylsulfonyl)amino]carbonyl]-2-ethenylcyclopropyl]amino]carbonyl]-1-pyrrolidinyl]carbonyl]-2,2-dimethylpropyl]-, 1,1-dimethylethyl Ester
52. Cyclopropanecarboxamide, N-((1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl)-3-methyl-l-valyl-(4r)-4- ((7-chloro-4-methoxy-1-isoquinolinyl)oxy)-l-prolyl-1-amino-n-(cyclopropylsulfonyl)-2- Ethenyl-, (1r,2s)-
53. Tert-butyl ((2s)-1-((2s,4r)-4-((7-chloro-4-methoxyisoquinolin-1-yl)oxy)-2-(((1r,2s)-1-((cyclopropanesulfonyl)carbamoyl)-2-ethenylcyclopropyl)carbamoyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)carbamate
| Molecular Weight | 748.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C35H46ClN5O9S |
| XLogP3 | 4.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 14 |
| Exact Mass | 747.2704769 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 747.2704769 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 191 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 51 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1470 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 5 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Asunaprevir is indicated in combination with other agents for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C in adult patients with hepatitis C virus genotypes 1 or 4 and compensated liver cirrhosis. Hepatitis C is a liver disease caused by the hepatitis C virus. The chronic state of this condition accounts for 60-80% of the cases from which the risk of cirrhosis of the liver within 20 years is of around 15-30%. The genotype 1 is the most common type of hepatitis C in the United States and the most difficult to treat.
Treatment of chronic hepatitis C
Studies in vitro demonstrated a significant antiviral activity in HCV replicon cell systems with an EC50 of 4nm and 1nm against the HCV genotype 1a and 1b respectively. These studies showed a limited activity against the genotypes 2 and 3. This property makes asunaprevir a highly selective anti-HCV agent that is not effective against HCV closely related virus. Asunaprevir produce robust declines in HCV RNA levels in patients with HCV genotype 1 infection.In clinical studies, it has been shown that asunaprevir is well-tolerated and the mean maximum HCV RNA level reduction from baseline was of approximately 2.87 log10 IU/ml. Monotherapy clinical studies with asunaprevir showed a mean maximum decline of HCV RNA in the range of 0.28-2.87 log10 IU/ml when administered in increasing doses from 10-600 mg. When asunaprevir was used as a combination product, it was possible to obtain a sustained virological response (aviremia 24 weeks after completion of therapy) in 83-92% of the patients.
Protease Inhibitors
Compounds which inhibit or antagonize biosynthesis or actions of proteases (ENDOPEPTIDASES). (See all compounds classified as Protease Inhibitors.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J05 - Antivirals for systemic use
J05A - Direct acting antivirals
J05AP - Antivirals for treatment of hcv infections
J05AP06 - Asunaprevir
Absorption
In preclinical studies, asunaprevir showed a high liver-to-plasma AUC ratio. It is rapidly absorbed within 30 minutes of administration. Clinical pharmacokinetic studies showed a Tmax of 2-4 hours. The pharmacokinetic profile act in a dose-proportional manner and in a dose of 100 mg the steady-state Cmax and AUC was 572 ng/ml and 1887 ng x h/mL. The absolute bioavailability is reported to be 9.3%. The absorption of asunaprevir is increased with food.
Route of Elimination
Asunaprevir is primarily eliminated via the feces. From the administered dose, 84% is excreted by feces mainly as metabolites and less than 1% of the dose is recovered as metabolites in the urine. The proportion of unchanged asunaprevir recovered in feces represents only 7.5% of the dose.
Volume of Distribution
The registered volume of distribution at steady state is 194 L.
Clearance
Clinical pharmacokinetic studies showed a mean oral clearance of 302-491 L/h.
Asunaprevir is metabolized by the liver. The metabolism is mainly marked by oxidative reactions mediated by the activity of CYP3A. Asunaprevir seems to weakly induce its own metabolism and from the circulating dose, just about 5% of the administered dose is formed by metabolites. The metabolites of asunaprevir are formed after mono- and bis-oxidation, N-dealkylation, loss of isoquinoline ring and O-demethylation. All the metabolic reactions form about 15 metabolites and studies have reported that the main metabolic activity is performed by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 with some minor activity from CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and CYP2D6.
Clinical pharmacokinetic studies showed a mean terminal half-life of 15-20 hours.
Asunaprevir is a highly active HCV NS3 protease inhibitor. The genome of HCV has a positive polarity which allows it to be translated into a protein in the host cell without further transformation steps. However, the resultant protein needs to be divided by the enzyme NS3 protease into single proteins in order to be able to exert its enzymatic activity or structural role. Therefore, due to NS3 vital importance for viral replication, the inhibiting action of asunaprevir causes a robust antiviral activity.
Global Sales Information

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
ABOUT THIS PAGE
84
PharmaCompass offers a list of Asunaprevir API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Asunaprevir manufacturer or Asunaprevir supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Asunaprevir manufacturer or Asunaprevir supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Asunaprevir API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Asunaprevir API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Asunaprevir Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Asunaprevir Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Asunaprevir manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Asunaprevir, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Asunaprevir manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Asunaprevir API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Asunaprevir supplier is an individual or a company that provides Asunaprevir active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Asunaprevir finished formulations upon request. The Asunaprevir suppliers may include Asunaprevir API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
Asunaprevir Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Asunaprevir GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Asunaprevir GMP manufacturer or Asunaprevir GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Asunaprevir CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Asunaprevir's compliance with Asunaprevir specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Asunaprevir CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Asunaprevir CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Asunaprevir may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Asunaprevir EP), Asunaprevir JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Asunaprevir USP).

