

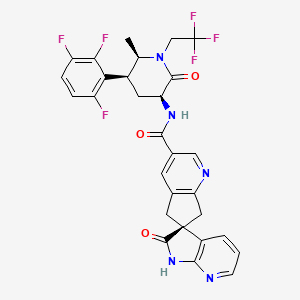

1. (3s)-n-((3s,5s,6r)-6-methyl-2-oxo-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-5-(2,3,6-trifluorophenyl)piperidin-3-yl)-2-oxospiro(1h-pyrrolo(2,3-b)pyridine-3,6'-5,7-dihydrocyclopenta(b)pyridine)-3'-carboxamide
1. Qulipta
2. Mk-8031
3. 1374248-81-3
4. Agn-241689
5. Atogepant [inn]
6. Atogepant [who-dd]
7. 7crv8rr151
8. Atogepant (usan)
9. Atogepant [usan]
10. (3's)-1',2',5,7-tetrahydro-n-((3s,5s,6r)-6-methyl-2-oxo-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-5-(2,3,6-trifluorophenyl)-3-piperidinyl)-2'-oxospiro(6h-cyclopenta(b)pyridine-6,3'-(3h)pyrrolo(2,3-b)pyridine)-3-carboxamide
11. (3's)-n-[(3s,5s,6r)-6-methyl-2-oxo-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-5-(2,3,6-trifluorophenyl)piperidin-3-yl]-2'-oxo-1',2',5,7-tetrahydrospiro[cyclopenta[b]pyridine-6,3'-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine]-3-carboxamide
12. (3s)-n-[(3s,5s,6r)-6-methyl-2-oxo-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-5-(2,3,6-trifluorophenyl)piperidin-3-yl]-2-oxospiro[1h-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine-3,6'-5,7-dihydrocyclopenta[b]pyridine]-3'-carboxamide
13. Spiro(6h-cyclopenta(b)pyridine-6,3'-(3h)pyrrolo(2,3-b)pyridine)-3-carboxamide, 1',2',5,7-tetrahydro-n-((3s,5s,6r)-6-methyl-2-oxo-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-5-(2,3,6-trifluorophenyl)-3-piperidinyl)-2'-oxo-, (3's)-
14. Atogepant [usan:inn]
15. Unii-7crv8rr151
16. Gtpl9730
17. Schembl4570348
18. Atogepant [orange Book]
19. Chembl3991065
20. Dtxsid901337079
21. Bcp29018
22. Ex-a6847
23. Mk 8031; Mk8031; Atogepant
24. Example 4 [us20120122911]
25. Hy-109022
26. Cs-0030524
27. D11313
| Molecular Weight | 603.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C29H23F6N5O3 |
| XLogP3 | 3.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 603.17050859 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 603.17050859 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 104 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 43 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1110 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Atogepant is indicated for the prevention of episodic migraine in adults.
Prevention of migraine headaches
Atogepant helps to prevent migraine headaches by antagonizing the activity of a pronociceptive molecule (CGRP) which has been implicated in migraine pathophysiology. Intended for preventative use, rather than abortive migraine therapy, atogepant is administered once daily. While no dose adjustments are required for patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment, atogepant should be avoided in patients with severe hepatic impairment. Similarly, no dose adjustments are required for patients with mild or moderate renal impairment, but patients with severe renal impairment should be limited to a maximum daily dose of 10mg.
N - Nervous system
N02 - Analgesics
N02C - Antimigraine preparations
N02CD - Calcitonin gene-related peptide (cgrp) antagonists
N02CD07 - Atogepant
Absorption
The time to peak plasma concentration following oral administration is approximately 2-3 hours. Atogepant displays dose-proportional pharmacokinetics up to approximately 3-fold its recommended maximum dosage, and its pharmacokinetics are not significantly influenced by co-administration with food.
Route of Elimination
The elimination of atogepant occurs primarily via metabolism by CYP3A4. Following a single oral dose of radiolabeled atogepant to healthy male subjects, 42% of the administered dose was recovered as unchanged parent drug in the feces and 5% as unchanged parent drug in the urine. In total, approximately 81% of the radioactivity was recovered in the feces, with only 8% recovered in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
The mean apparent volume of distribution of atogepant is 292 L.
Clearance
The mean apparent oral clearance of atogepant is approximately 19 L/h.
The metabolism of atogepant is mediated primarily via CYP3A4. The most prevalent circulating compounds in plasma are atogepant itself and a glucuronide conjugate metabolite (M23), comprising approximately 75% and 15% of the administered dose, respectively, with at least 10 other metabolites detected in feces representing <10% of the administered dose.
The elimination half-life of atogepant following oral administration is approximately 11 hours.
The currently accepted theory of migraine pathophysiology considers dysfunction of the central nervous system, in particular the trigeminal ganglion, to be the root cause behind the condition. Activation of the trigeminal ganglion triggers the stimulation of trigeminal afferents that project to the spinal cord and synapse on various pain-sensing intra- and extracranial structures, such as the dura mater. Pain signals are then further transmitted via second-order ascending neurons to the brainstem, hypothalamus, and thalamic nuclei, and from there to several cortical regions (e.g. auditory, visual, motor cortices). The trigeminal ganglion appears to amplify and perpetuate the migraine headache pain through the activation of perivascular fibers and the release of molecules involved in pain generation, such as calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP). The -isoform of CGRP, expressed in primary sensory neurons, is a potent vasodilator and has been implicated in migraine pathogenesis - CGRP levels are acutely elevated during migraine attacks, return to normal following treatment with triptan medications, and intravenous infusions of CGRP have been shown to trigger migraine-like headaches in migraine patients. In addition to its vasodilatory properties, CGRP appears to be a pronociceptive factor that modulates neuronal excitability to facilitate pain responses. Atogepant is an antagonist of the calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor - it competes with CGRP for occupancy at these receptors, preventing the actions of CGRP and its ability to induce and perpetuate migraine headache pain.

LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?