
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Canada

0
Australia

DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers

1. (mpa(1),d-tyr(et)2,thr(4),orn(8))oxytocin
2. (mpa(1)-d-tyr(et)(2)-thr(4)-orn(8))-oxytocin
3. 1-deamino-2-tyr(oet)-4-thr-8-orn-oxytocin
4. Orf 22164
5. Orf-22164
6. Oxytocin, 1-deamino-(o-et-tyr)(2)-thr(4)-orn(8)-
7. Oxytocin, 1-deamino-o-ethyltyrosyl(2)-threonyl(4)-ornithine(8)-
8. Rwj 22164
9. Rwj-22164
1. Tractocile
2. 90779-69-4
3. Antocin
4. Antocin Ii
5. Tractocil
6. Rwj 22164
7. Orf 22164
8. Antocile
9. Orf-22164
10. Rwj-22164
11. Cap-476
12. Chembl382301
13. F-314
14. Cap-449
15. Cap-581
16. 081d12si0z
17. Dtvt
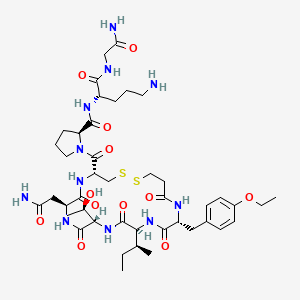
18. (2s)-n-[(2s)-5-amino-1-[(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)amino]-1-oxopentan-2-yl]-1-[(4r,7s,10s,13s,16r)-7-(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)-13-[(2s)-butan-2-yl]-16-[(4-ethoxyphenyl)methyl]-10-[(1r)-1-hydroxyethyl]-6,9,12,15,18-pentaoxo-1,2-dithia-5,8,11,14,17-pentazacycloicosane-4-carbonyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide
19. Ncgc00165718-01
20. Rw-22164
21. 1-(3-mercaptopropionic Acid)-2-(3-(p-ethoxyphenyl)-d-alanine)-4-l-threonine-8-l-ornithineoxytocin
22. Atosibanum
23. Oxytocin, 1-(3-mercaptopropanoic Acid)-2-(o-ethyl-d-tyrosine)-4-l-threonine-8-l-ornithine-
24. Atosibanum [inn-latin]
25. 1-deamino-2d-tyr-(oet)-4-thr-8-orn-oxytocin
26. Atosiban [usan:inn:ban]
27. Unii-081d12si0z
28. 1-(3-mercaptopropanoic Acid)-2-(o-ethyl-d-tyrosine)-4-l-threonine-8-l-ornithineoxytocin
29. Detvt
30. Atosiban [usan]
31. Atosiban [inn]
32. Atosiban [mi]
33. Atosiban [mart.]
34. Atosiban [who-dd]
35. Dsstox_cid_28917
36. Dsstox_rid_83184
37. Dsstox_gsid_48991
38. Schembl34316
39. D[d-tyr(et)2,thr4]ovt
40. Chembl_332615
41. Gtpl2213
42. Atosiban, >=98% (hplc)
43. Dtxsid8048991
44. Cap-440
45. Chebi:135899
46. Orf22164
47. Tox21_113474
48. Bdbm50177595
49. D[d-tyr(et)2,thr4,orn8]vasotocin
50. Akos015994643
51. Zinc169362009
52. Ccg-270604
53. Db09059
54. Hs-2003
55. Ncgc00165718-02
56. Cas-90779-69-4
57. Ft-0652583
58. 79a694
59. A14334
60. C77085
61. (2s)-5-amino-2-{[(2s)-1-{[(4r,7s,10s,13s,16r)-13-[(2s)-butan-2-yl]-7-(carbamoylmethyl)-16-[(4-ethoxyphenyl)methyl]-10-[(1r)-1-hydroxyethyl]-6,9,12,15,18-pentaoxo-1,2-dithia-5,8,11,14,17-pentaazacycloicosan-4-yl]carbonyl}pyrrolidin-2-yl]formamido}-n-(carbamoylmethyl)pentanamide
62. (2s)-n-[(2s)-5-amino-1-[(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)amino]-1-oxopentan-2-yl]-1-[(4r,7s,10s,13s,16r)-7-(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)-13-[(2s)-butan-2-yl]-16-[(4-ethoxyphenyl)methyl]-10-(1-hydroxyethyl)-6,9,12,15,18-pentaoxo1,2-dithia-5,8,11,14,17-pentazacycloicosane-4-carbonyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide
63. Glycinamide, O-ethyl-n-(3-mercapto-1-oxopropyl)-d-tyrosyl-l-isoleucyl-l-threonyl-l-asparaginyl-l-cysteinyl-l-prolyl-l-ornithyl-, Cyclic (1->5)-disulfide
| Molecular Weight | 994.2 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C43H67N11O12S2 |
| XLogP3 | -1.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 11 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 15 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 18 |
| Exact Mass | 993.44120896 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 993.44120896 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 416 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 68 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1770 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 9 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Atosiban is indicated for use in delaying imminent pre-term birth in pregnant adult women with: - regular uterine contractions of at least 30 s duration at a rate of at least 4 per 30 min - a cervical dilation of 1-3cm (0-3cm for nulliparas) and effacement of at least 50% - a gestational age of 24-33 weeks - a normal fetal heart rate
Tractotile is indicated to delay imminent pre-term birth in pregnant adult women with:
- regular uterine contractions of at least 30 seconds duration at a rate of 4 per 30 minutes;
- a cervical dilation of 1 to 3 cm (0-3 for nulliparas) and effacement of 50%;
- a gestational age from 24 until 33 completed weeks;
- a normal foetal heart rate.
Atosiban reduces the frequency of uterine contractions to delay pre-term birth in adult females and induces uterine quiescence.
Hormone Antagonists
Chemical substances which inhibit the function of the endocrine glands, the biosynthesis of their secreted hormones, or the action of hormones upon their specific sites. (See all compounds classified as Hormone Antagonists.)
Tocolytic Agents
Drugs that prevent preterm labor and immature birth by suppressing uterine contractions (TOCOLYSIS). Agents used to delay premature uterine activity include magnesium sulfate, beta-mimetics, oxytocin antagonists, calcium channel inhibitors, and adrenergic beta-receptor agonists. The use of intravenous alcohol as a tocolytic is now obsolete. (See all compounds classified as Tocolytic Agents.)
G02CX01
G02CX01
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
G - Genito urinary system and sex hormones
G02 - Other gynecologicals
G02C - Other gynecologicals
G02CX - Other gynecologicals
G02CX01 - Atosiban
Absorption
In women receiving 300 g/min by infusion for 6-12 h, average steady state concentrations of 442 ng/mL were reached within 1 h. Steady state concentrations increase proportionally to dosage.
Route of Elimination
Small amounts of atosiban are found in the urine with 50 times the amount appearing as the large fragment metabolite (des-(Orn, Gly-NH2)-[Mpa, D-Tyr(Et), Thr]-oxytocin. The amount of drug excreted in the feces is not known.
Volume of Distribution
Atosiban has a mean volume of distribution of 41.8 L. Atosiban crosses the placenta and, at a dose of 300 g/min, was found to have a 0.12 maternal/fetal concentration ratio.
Clearance
Atosiban has a mean clearance rate of 41.8 L/h.
There are two metabolites of atosiban created through the cleavage of the peptide bond between ornithine and proline which is thought to be facilitated by prior cleavage of the disulfide bridge. The larger fragment remains active as an antagonist of oxytocin receptors but is 10 times less potent than the parent molecule. At a dosage of 300 g/min the ratio of parent molecule to the main metabolite was observed to be 1.4 at the second hour and 2.8 at the end of infusion.
Atosiban does not conform to either 1-compartment or 2-compartment kinetics. It has been determined to have an initial half life (t) of 0.21 h and a terminal half life (t) of 1.7 h.
Atosiban is a synthetic peptide oxytocin antagonist. It resembles oxytocin with has modifications at the 1, 2, 4, and 8 positions. The N-terminus of the cysteine residue is deaminated to form 3-mercaptopropanic acid at position 1, at position 2 L-tyrosine is modified to D-tyrosine with an ethoxy group replacing the phenol , threonine replaces glutamine at postion 4, and ornithine replaces leucine at position 8. It binds to membrane bound oxytocin receptors on the myometrium and prevents oxytocin-stimulated increases in inositol triphosphate production. This ultimately prevents release of stored calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and subsequent opening of voltage gated calcium channels. This shutdown of cytosolic calcium increase prevents contractions of the uterine muscle, reducing the frequency of contractions and inducing uterine quiescence. Atosiban has more recently been found to act as a biased ligand at oxytocin receptors. It acts as an antagonist of Gq coupling, explaining the inhibition of the inositol triphosphate pathway thought to be responsible for the effect on uterine contraction, but acts as an agonist of Gi coupling. This agonism produces a pro-inflammatory effect in the human amnion, activating pro-inflammatory signal tranducer NF-B. It is thought that this reduces atosiban's effectiveness compared to agents which do not produce inflammation as inflammatory mediators are known to play a role in the induction of labour.
Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
19
PharmaCompass offers a list of Atosiban API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Atosiban manufacturer or Atosiban supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Atosiban manufacturer or Atosiban supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Atosiban API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Atosiban API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Atosiban Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Atosiban Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Atosiban manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Atosiban, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Atosiban manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Atosiban API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Atosiban manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Atosiban supplier is an individual or a company that provides Atosiban active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Atosiban finished formulations upon request. The Atosiban suppliers may include Atosiban API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Atosiban suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Atosiban DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Atosiban active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Atosiban DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Atosiban USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Atosiban DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Atosiban USDMF includes data on Atosiban's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Atosiban USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Atosiban suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Atosiban Drug Master File in Korea (Atosiban KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Atosiban. The MFDS reviews the Atosiban KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Atosiban KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Atosiban KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Atosiban API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Atosiban suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
Atosiban Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Atosiban GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Atosiban GMP manufacturer or Atosiban GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Atosiban CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Atosiban's compliance with Atosiban specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Atosiban CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Atosiban CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Atosiban may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Atosiban EP), Atosiban JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Atosiban USP).
