
1. Anhydrous, Atropine Sulfate
2. Atropen
3. Atropin Augenl
4. Atropine Sulfate
5. Atropine Sulfate Anhydrous
6. Atropinol
7. Augenl, Atropin
8. Sulfate Anhydrous, Atropine
9. Sulfate, Atropine
1. Dl-hyoscyamine
2. Tropine Tropate
3. Atropen
4. Atropin
5. 51-55-8
6. Dl-tropyltropate
7. Atropinol
8. Eyesules
9. Isopto-atropine
10. Troyl Tropate
11. Hyoscyamine
12. Atropina
13. Atropin-flexiolen
14. (+,-)-tropyl Tropate
15. Atropin [german]
16. Atropina [italian]
17. (+-)-hyoscyamine
18. Tropine, Tropate (ester)
19. (+-)-atropine
20. Tropic Acid, Ester With Tropine
21. (+/-)-atropine
22. (+/-)-hyoscyamine
23. Ccris 3080
24. Atropine (usp)
25. Tropic Acid, 3-alpha-tropanyl Ester
26. Atropinum
27. Hsdb 2199
28. Dl-tropanyl 2-hydroxy-1-phenylpropionate
29. 2-phenylhydracrylic Acid 3-alpha-tropanyl Ester
30. (3-endo)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl Tropate
31. Ai3-60219
32. Beta-phenyl-gamma-oxypropionsaure-tropyl-ester [german]
33. Dl-tropyl Tropate
34. (3-endo)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl 3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoate
35. 1alphah,5alphah-tropan-3alpha-ol (+-)-tropate (ester)
36. Beta-phenyl-gamma-oxypropionsaeure-tropyl-ester [german]
37. Tropan-3alpha-yl 3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoate
38. 8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl Tropate
39. Mls000069795
40. Chebi:16684
41. 7c0697dr9i
42. 8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl 3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoate
43. [(1s,5r)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl] 3-hydroxy-2-phenyl-propanoate
44. Alpha-(hydroxymethyl)benzeneacetic Acid 8-methyl-8-azabicyclo(3.2.1)oct-3-yl Ester
45. Endo-(+/-)-alpha-(hydroxymethyl)benzeneacetic Acid 8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl Ester
46. Benzeneacetic Acid, Alpha-(hydroxymethyl)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo(3,2,1)oct-3-yl Ester, Endo-(+-)-
47. Ncgc00017333-03
48. Smr000058248
49. Dsstox_cid_113
50. Ab00694549-11
51. Dsstox_rid_75375
52. Dsstox_gsid_20113
53. Benzeneacetic Acid, Alpha-(hydroxymethyl)-, 8-methyl-8-azabicyclo(3.2.1)oct-3-yl Ester, Endo-(+-)-
54. Cas-51-55-8
55. Atropen (tn)
56. Protamine & Atropine
57. Atropine [usp:ban]
58. Einecs 200-104-8
59. Tropine (+/-)-tropate
60. Ropine Tropate
61. Unii-7c0697dr9i
62. (3-endo)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo(3.2.1)oct-3-yl Tropate
63. Atropine Solution
64. (1r,3r,5s)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-yl 3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoate
65. Ncgc00159345-02
66. 3-tropoyloxytropane
67. 1-alpha-h,5-alpha-h-tropan-3-alpha-ol (+-)-tropate (ester)
68. Atropine [mi]
69. Atropine [vandf]
70. Atropinum [hpus]
71. Opera_id_1088
72. Atropine [mart.]
73. Beta-phenyl-gamma-oxypropionsaure-tropyl-ester
74. Atropine [usp-rs]
75. Atropine [who-dd]
76. Bmse000649
77. Beta-phenyl-gamma-oxypropionsaeure-tropyl-ester
78. Schembl2812
79. [(1r,5s)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-yl] 3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoate
80. Atropine, Analytical Standard
81. Gtpl320
82. Benzeneacetic Acid, Alpha-(hydroxymethyl)-, (3-endo)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo(3.2.1)oct-3-yl Ester
83. Mls001148094
84. Mls002695888
85. Atropine [green Book]
86. Atnaa Component Atropine
87. Atropine [ep Impurity]
88. Atropine [orange Book]
89. Chembl254656
90. Chembl475124
91. Chembl517712
92. Cid_174174
93. Megxp0_001878
94. Atropine [ep Monograph]
95. Atropine ((+/-))
96. Atropine [usp Monograph]
97. Atropine, (+/-)-
98. Dtxsid4020113
99. Acon1_000046
100. Chebi:78734
101. Duodote Component Atropine
102. Atropine, >=95.0% (nt)
103. Atropine Component Of Atnaa
104. Bdbm200229
105. Dtxsid601141720
106. Hms2089a16
107. Hms2231g17
108. Hms3259m13
109. Bcp15060
110. Hy-b1205
111. Atropine Component Of Duodote
112. Atropine, >=99% (tlc), Powder
113. Tox21_110816
114. Tox21_111590
115. Tox21_200487
116. 1-alpha-h,5-alpha-h-tropan-3-alpha-ol (+-)-tropate (ester) (8ci)
117. Bdbm50403547
118. S4713
119. Akos015955538
120. Cs-4834
121. Db00572
122. Nc00493
123. Ncgc00017333-02
124. Ncgc00017333-04
125. Ncgc00017333-05
126. Ncgc00017333-06
127. Ncgc00142514-01
128. Ncgc00142514-03
129. Ncgc00258041-01
130. Ncgc00385525-01
131. As-56020
132. Benzeneacetic Acid, Alpha-(hydroxymethyl)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo(3.2.1)oct-3-yl Ester, Endo-(+-)-
133. Atropine, Meets Usp Testing Specifications
134. C1504
135. Ft-0627165
136. C01479
137. D00113
138. Q26272
139. Ab00694549-12
140. Ab00694549_14
141. Rac-tropan-3alpha-yl 3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoate
142. Brd-a27290375-001-01-8
143. Brd-a27290375-330-01-1
144. Atropine, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
145. Homatropine Hydrobromide Impurity D [ep Impurity]
146. 1.alpha.h,5.alpha.h-tropan-3.alpha.-ol (+/-)-tropate (ester)
147. (3-exo)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl Alpha-(hydroxymethyl)benzeneacetate
148. [(1r,5s)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-yl] 3-hydroxy-2-phenyl-propanoate
149. [(1s,5r)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-yl] 3-hydroxy-2-phenyl-propanoate
150. Alpha-hydroxymethylphenylacetic Acid (1r,5s)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane-3-yl Ester
151. Atropine For Peak Identification, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
152. Rac-(3-endo)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl 3-hydroxy-2-phenylpropanoate
153. (1beta,3alpha,5beta)-3-[(3-hydroxy-1-oxo-2-phenylpropyl)oxy]-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane
154. 16175-85-2
155. Benzeneacetic Acid, .alpha.-(hydroxymethyl)-(3-endo)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo(3.2.1)oct-3-yl Ester
156. Benzeneacetic Acid, .alpha.-(hydroxymethyl)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo(3.2.1)oct-3-yl Ester, Endo-(+/-)-
157. Benzeneacetic Acid, Alpha-(hydroxymethyl)- (3-endo)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo(3.2.1)oct-3-yl Ester
158. Benzeneacetic Acid, Alpha-(hydroxymethyl)-, 8-methyl-8-azabicyclo(3.2.1)oct-3-yl Ester, Endo-(+/-)-
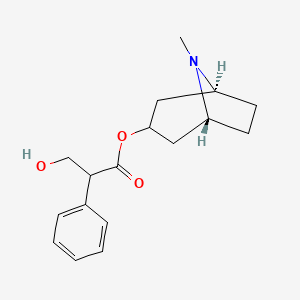
| Molecular Weight | 289.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H23NO3 |
| XLogP3 | 1.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 289.16779360 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 289.16779360 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 49.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 353 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Atropen |
| PubMed Health | Atropine (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Anesthetic Adjunct, Cholinergic Antagonist, Gastrointestinal Agent, Nerve Gas Antidote, Urinary Antispasmodic |
| Drug Label | Each prefilled auto-injector provides a dose of the antidote atropine in a self-contained unit, specially designed for self or caregiver administration. Four strengths of AtroPen are available; they are AtroPen 0.25 mg, AtroPen 0.5 mg, AtroPen... |
| Active Ingredient | Atropine |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | eq 0.25mg sulfate/0.3ml; eq 1mg sulfate/0.7ml; eq 0.5mg sulfate/0.7ml; eq 2mg sulfate/0.7ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Meridian Medcl |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Atropen |
| PubMed Health | Atropine (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Anesthetic Adjunct, Cholinergic Antagonist, Gastrointestinal Agent, Nerve Gas Antidote, Urinary Antispasmodic |
| Drug Label | Each prefilled auto-injector provides a dose of the antidote atropine in a self-contained unit, specially designed for self or caregiver administration. Four strengths of AtroPen are available; they are AtroPen 0.25 mg, AtroPen 0.5 mg, AtroPen... |
| Active Ingredient | Atropine |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | eq 0.25mg sulfate/0.3ml; eq 1mg sulfate/0.7ml; eq 0.5mg sulfate/0.7ml; eq 2mg sulfate/0.7ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Meridian Medcl |
Adjuvants, Anesthesia; Anti-Arrhythmia Agents; Antidotes; Bronchodilator Agents; Muscarinic Antagonists; Mydriatics; Parasympatholytics
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
... people poisoned by anticholinesterase organic phosphorus compounds have an increased tolerance for atropine sulfate.
Hayes, W.J., Jr., E.R. Laws, Jr., (eds.). Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. Volume 2. Classes of Pesticides. New York, NY: Academic Press, Inc., 1991., p. 951
MEDICATION (VET): ...USED ROUTINELY AS ADJUNCT TO GENERAL ANESTHESIA...TO DECR SALIVARY & AIRWAY SECRETIONS. ... USED TO FACILITATE OPHTHALMOSCOPIC EXAM OF INTERNAL OCULAR STRUCTURES & FUNCTIONS &...FOR TREATMENT OF VARIOUS OCULAR DISORDERS. ... ATROPINE IS ESSENTIAL ANTIDOTE TO ANTICHOLINESTERASE OVERDOSAGE & POISONING.
Jones, L.M., et al. Veterinary Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 4th ed. Ames: Iowa State University Press, 1977., p. 159
Adequate doses of atropine can abolish many types of reflex vagal cardiac slowing or asystole--for example, from inhalation of irritant vapors, stimulation of the carotid sinus, pressure on the eyeballs, peritoneal stimulation, or injection of contrast dye during cardiac catheterization. It also prevents or abruptly abolishes bradycardia or asystole caused by choline esters, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, or other parasympathomimetic drugs, as well as cardiac arrest from electrical stimulation of the vagus.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 165
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for ATROPINE (24 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
FATALITIES FROM ATROPINE...ARE RARE, BUT SOMETIMES OCCUR IN CHILDREN. OF ALL POTENT ALKALOIDS, ATROPINE HAS ONE OF WIDEST MARGINS OF SAFETY. FATAL DOSE... NOT KNOWN; 200-MG DOSE..USED THERAPEUTICALLY FOR MENTAL ILLNESS, &...1000 MG HAVE BEEN SURVIVED. IN CHILDREN, 10 MG OR LESS MAY BE LETHAL.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 522
DRY MOUTH, BLURRED VISION, PHOTOPHOBIA, ANHIDROSIS, & CONSTIPATION ARE UNAVOIDABLE SIDE EFFECTS...
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 840
...CONTRAINDICATED IN PERSONS WHOSE INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE IS...ELEVATED...IN PRESENCE OF PROSTATIC HYPERTROPHY OR ORGANIC PYLORIC STENOSIS. ...USED CAUTIOUSLY IN PT WITH PROSTATISM, URINARY RETENTION, DIABETES, HYPERTHYROIDISM, TACHYCARDIA, IN ELDERLY PERSONS, & CHILDREN UNDER 6 YR OF AGE.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 840
ATROPINE IS OF NO VALUE IN DELAYED TYPE OF MUSHROOM POISONING DUE TO TOXINS OF A PHALLOIDES & CERTAIN OTHER SPECIES OF SAME GENUS.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 531
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for ATROPINE (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of poisoning by susceptible organophosphorous nerve agents having anti-cholinesterase activity (cholinesterase inhibitors) as well as organophosphorous or carbamate insecticides.
FDA Label
Atropine, a naturally occurring belladonna alkaloid, is a racemic mixture of equal parts of d- and l-hyoscyamine, whose activity is due almost entirely to the levo isomer of the drug. Atropine is commonly classified as an anticholinergic or antiparasympathetic (parasympatholytic) drug. More precisely, however, it is termed an antimuscarinic agent since it antagonizes the muscarine-like actions of acetylcholine and other choline esters. Adequate doses of atropine abolish various types of reflex vagal cardiac slowing or asystole. The drug also prevents or abolishes bradycardia or asystole produced by injection of choline esters, anticholinesterase agents or other parasympathomimetic drugs, and cardiac arrest produced by stimulation of the vagus. Atropine may also lessen the degree of partial heart block when vagal activity is an etiologic factor. Atropine in clinical doses counteracts the peripheral dilatation and abrupt decrease in blood pressure produced by choline esters. However, when given by itself, atropine does not exert a striking or uniform effect on blood vessels or blood pressure.
Adjuvants, Anesthesia
Agents that are administered in association with anesthetics to increase effectiveness, improve delivery, or decrease required dosage. (See all compounds classified as Adjuvants, Anesthesia.)
Anti-Arrhythmia Agents
Agents used for the treatment or prevention of cardiac arrhythmias. They may affect the polarization-repolarization phase of the action potential, its excitability or refractoriness, or impulse conduction or membrane responsiveness within cardiac fibers. Anti-arrhythmia agents are often classed into four main groups according to their mechanism of action: sodium channel blockade, beta-adrenergic blockade, repolarization prolongation, or calcium channel blockade. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Arrhythmia Agents.)
Muscarinic Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate MUSCARINIC RECEPTORS, thereby blocking the actions of endogenous ACETYLCHOLINE or exogenous agonists. Muscarinic antagonists have widespread effects including actions on the iris and ciliary muscle of the eye, the heart and blood vessels, secretions of the respiratory tract, GI system, and salivary glands, GI motility, urinary bladder tone, and the central nervous system. (See all compounds classified as Muscarinic Antagonists.)
Bronchodilator Agents
Agents that cause an increase in the expansion of a bronchus or bronchial tubes. (See all compounds classified as Bronchodilator Agents.)
Mydriatics
Agents that dilate the pupil. They may be either sympathomimetics or parasympatholytics. (See all compounds classified as Mydriatics.)
Parasympatholytics
Agents that inhibit the actions of the parasympathetic nervous system. The major group of drugs used therapeutically for this purpose is the MUSCARINIC ANTAGONISTS. (See all compounds classified as Parasympatholytics.)
A03BA01
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A03 - Drugs for functional gastrointestinal disorders
A03B - Belladonna and derivatives, plain
A03BA - Belladonna alkaloids, tertiary amines
A03BA01 - Atropine
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A03 - Drugs for functional gastrointestinal disorders
A03B - Belladonna and derivatives, plain
A03BA - Belladonna alkaloids, tertiary amines
A03BA03 - Hyoscyamine
S - Sensory organs
S01 - Ophthalmologicals
S01F - Mydriatics and cycloplegics
S01FA - Anticholinergics
S01FA01 - Atropine
Absorption
Atropine is rapidly and well absorbed after intramuscular administration. Atropine disappears rapidly from the blood and is distributed throughout the various body tissues and fluids.
Route of Elimination
Much of the drug is destroyed by enzymatic hydrolysis, particularly in the liver; from 13 to 50% is excreted unchanged in the urine.
BELLADONNA ALKALOIDS...ARE ABSORBED RAPIDLY FROM THE GI TRACT. THEY ALSO ENTER CIRCULATION WHEN APPLIED...TO MUCOSAL SURFACES OF THE BODY. ABSORPTION FROM INTACT SKIN IS LIMITED, ALTHOUGH EFFICIENT ABSORPTION DOES OCCUR IN THE POSTAURICULAR REGION. ... ATROPINE HAS A HALF-LIFE OF APPROX 4 HR; HEPATIC METAB ACCOUNTS FOR THE ELIMINATION OF ABOUT HALF OF A DOSE, & THE REMAINDER IS EXCRETED UNCHANGED IN THE URINE.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 167
...WHEN ADMIN TO MOTHER PASS RAPIDLY INTO FETAL BLOOD.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals Volume 3. London: The Chemical Society, 1975., p. 634
IN DOG, 27% OF SC DOSE OF (3)H-ATROPINE WAS EXCRETED IN 2-HR URINE MOSTLY UNCHANGED. 50%...WAS EXCRETED WITHIN 6-HR, & RENAL EXCRETION OF ATROPINE OCCURRED BY GLOMERULAR FILTRATION & TUBULAR SECRETION.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 1: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1960 and 1969. London: The Chemical Society, 1970., p. 69
AFTER IM ADMIN OF RADIOACTIVELY LABELED ATROPINE TO MAN, DISAPPEARANCE OF RADIOACTIVITY FROM PLASMA WAS BIPHASIC, WITH...HALF-LIVES OF 2 HR & 13-28 HR... BETWEEN 77 & 94% OF TOTAL RADIOACTIVITY WAS EXCRETED IN URINE... CHROMATOGRAPHIC EVIDENCE SUGGESTED THAT RELATIVE PROPORTIONS OF METABOLITIES VARIED WITH TIME.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 2: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1970 and 1971. London: The Chemical Society, 1972., p. 455
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ATROPINE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Much of the drug is destroyed by enzymatic hydrolysis, particularly in the liver. From 13 to 50% is excreted unchanged in the urine.
... HEPATIC METAB ACCOUNTS FOR THE ELIMINATION OF ABOUT HALF OF A DOSE, & THE REMAINDER IS EXCRETED UNCHANGED IN THE URINE.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 167
WITH (14)C RESTRICTED TO ALPHA-CARBON...ON TROPIC ACID PORTION...10 RADIOACTIVE...PRODUCTS...IN MOUSE & RAT URINE, PRINCIPAL METABOLITES WERE GLUCURONIDE CONJUGATES OF HYDROXYATROPINES FORMED IN VIVO BY METABOLIC HYDROXYLATION OF AROMATIC RING...GLUCURONIDES OF ATROPINE COULD NOT BE DETECTED IN HUMAN URINE...
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. III-44
3.0 ± 0.9 hours in adults. The half-life of atropine is slightly shorter (approximately 20 minutes) in females than males.
AFTER IM ADMIN OF RADIOACTIVELY LABELED ATROPINE TO MAN, DISAPPEARANCE OF RADIOACTIVITY FROM PLASMA WAS BIPHASIC, WITH...HALF-LIVES OF 2 HR & 13-28 HR...
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 2: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1970 and 1971. London: The Chemical Society, 1972., p. 455
Atropine binds to and inhibit muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, producing a wide range of anticholinergic effects.
Atropine... competes with ACh & other muscarinic agonists for a common binding site on the muscarinic receptor. The binding site for competitive antagonists & acetylcholine is in a cleft predicted to be formed by several of the receptor's 7 transmembrane helices, as shown recently for the position of retinol in the mammalian rhodopsin structure. An aspartic acid present in the N-terminal portion of the third transmembrane helix of all 5 muscarinic receptor subtypes is believed to form an ionic bond with the cationic quaternary nitrogen in acetylcholine & the tertiary or quaternary nitrogen of the antagonists.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 164
ATROPINE...(IS A) SELECTIVE ANTAGONIST OF MUSCARINIC AGENTS AT CORRESPONDING RECEPTORS OF SMOOTH & CARDIAC MUSCLE & EXOCRINE GLAND CELLS. THIS ANTAGONISM IS SO SELECTIVE THAT ATROPINE BLOCKADE OF ACTIONS OF NONCHOLINOMIMETIC DRUG... TAKEN AS EVIDENCE THAT DRUG ACTS INDIRECTLY THROUGH ACH RELEASE OR SOME OTHER CHOLINERGIC MECHANISM.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 516
...The site of action of atropine, a non-selective muscarinic receptor antagonist, in reducing increased muscle rigidity ...induced by the selective dopamine D2 receptor antagonist, raclopride /was investigated/. Atropine significantly reduced raclopride-induced EMG increases in rat hindlimb muscles, when injected into the ventral striatum, but not the dorsal striatum or the substantia nigra. Atropine's site of action was localized to a small area of muscarinic receptors within the ventral part of the striatum... These findings provide new information about the regulation of motor control by muscarinic receptor antagonists & additional evidence about the functional heterogeneity of the striatum.
PMID:11779574 Hemsley KM, Crocker AD; Eur J Pharmacol 434(3): 117-123 (2002)