
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
Annual Reports
NA
0
FDF
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
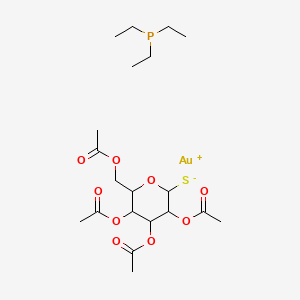

1. Auranofin
2. Crisinor
3. Ridaura
4. Ridauran
5. Sk And F 39162
6. Sk And F D 39162
7. Sk And F-39162
8. Sk And F39162
1. Auranofin
2. 34031-32-8
3. Bcp08217
4. Mfcd00080759
5. Mmv688978
6. Skf 39162
7. Akos026750078
8. Ft-0662343
9. D78135
10. A937040
11. 1-thio-
12. A-d-glucopyranosatotriethylphosphine Gold-2,3,4,6-tetraacetate
13. 1-thio-beta-d-glucopyranosatotriethyl Phosphine Gold-2,3,4,6-tetraacetate
14. 3,4,5-triacetyloxy-6-(acetyloxymethyl) Oxane-2-thiolate Triethylphosphanium
15. Gold(1+);3,4,5-triacetyloxy-6-(acetyloxymethyl)oxane-2-thiolate;triethylphosphane
16. Skf-39162; Skf-d-39162; Skf 39162; Skf D 39162; Skfd-39162; Skfd39162
| Molecular Weight | 678.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C20H34AuO9PS |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 12 |
| Exact Mass | 678.132686 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 678.132686 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 115 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 32 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 532 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 5 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
Auranofin is indicated in the treatment of adult rheumatoid arthritis and is used in the treatment of (juvenile arthritis /NOT included in US product labeling/). ... Gold compounds may induce remission or suppression of rheumatoid arthritis. In chronic advanced rheumatoid arthritis, they may prevent further damage to affected joints; however, they do not reverse existing damage. /Included in US product labeling/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 23rd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2003. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1586
Auranofin appears to be less toxic and better tolerated than currently available parenteral gold compounds, generally resulting in substantially fewer withdrawals from therapy because of adverse reactions (about 15-20% of patients); however, additional experience is needed to more fully characterize the adverse effect profile of auranofin, particularly with long-term therapy. Auranofin produces more adverse GI effects, including those severe enough to require discontinuance of therapy, than parenteral gold compounds, but fewer and substantially less severe adverse mucocutaneous (and possibly renal) effects than parenteral gold compounds. The overall difference in toxicity-related rates of withdrawal from therapy between auranofin and parenteral gold compounds results principally from the decreased frequency and severity of adverse mucocutaneous effects associated with auranofin. The incidence and severity of other auranofin-induced adverse effects appear to be generally comparable to those of parenteral gold compounds.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2841
The most common adverse effects of auranofin are changes in bowel habits, ranging from more frequent or loose stools to diarrhea, which occur in about 45-50% of patients. Auranofin-induced changes in bowel habits are most likely to occur within the first 3 months of therapy, appear to be dose related, and may be accompanied by abdominal cramping, with the effects often occurring principally within the first several hours after ingestion of a dose. The mechanism of GI toxicity has not been established, but may involve a direct effect of the drug on intestinal water and electrolyte absorption. Auranofin-induced changes in bowel habits may be self-limiting and subside with continued therapy or can generally be managed by dosage reduction or temporary discontinuance of the drug (e.g., for 3-7 days). Changes in bowel habits have also been controlled in some patients by temporary concomitant administration of an antidiarrhea agent (e.g., diphenoxylate hydrochloride), by concomitant administration of an oral iron preparation (in patients with iron deficiency anemia), or by increasing the amount of dietary fiber. Auranofin-induced changes in bowel habits have been severe enough to require discontinuance of the drug in about 4-6% of patients. Some patients, particularly geriatric patients, may consider the changes in bowel habits beneficial.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2841
Abdominal cramping or pain has occurred in about 14% of patients receiving auranofin and required discontinuance in about 1% of patients. Nausea, with or without vomiting, has occurred in about 10% of patients and required discontinuance in about 1% of patients. Other adverse GI effects have occurred in about 13% of patients and required discontinuance in about 1% of patients. Adverse GI effects occurring in 3-9% of patients include anorexia, dyspepsia, and flatulence; those occurring in 1-3% of patients include constipation and dysgeusia; those occurring in less than 1% of patients include GI bleeding, melena, and positive stool for occult blood; and those occurring in less than 0.1% of patients include dysphagia and ulcerative enterocolitis. Enterocolitis accompanied by eosinophilia has been reported. ... Epigastric pain and erosive gastritis have been reported rarely in patients receiving auranofin.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2841
Adverse effects involving the skin and mucous membranes are the second most common adverse reactions of auranofin. Rash has occurred in about 24% of patients receiving the drug and required discontinuance in about 3% of patients, and pruritus has occurred in about 17% of patients and required discontinuance in about 1% of patients. Pruritus often occurs before rash becomes apparent and should be considered a warning signal of an impending cutaneous reaction. Although not reported to date with auranofin, the most severe form of cutaneous reaction reported with parenteral gold compounds is generalized exfoliative dermatitis. Gold-induced dermatitis may be aggravated by exposure to sunlight or an actinic rash may develop. Urticaria has occurred in about 1-3% of patients receiving auranofin, hair loss or alopecia in about 2.5% of patients, and angioedema in less than 0.1% of patients.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2841
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for AURANOFIN (13 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Antirheumatic Agents
Drugs that are used to treat RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. (See all compounds classified as Antirheumatic Agents.)
M - Musculo-skeletal system
M01 - Antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products
M01C - Specific antirheumatic agents
M01CB - Gold preparations
M01CB03 - Auranofin
In vivo, gold from auranofin is approximately 60% bound to serum proteins. Of the gold bound to serum proteins, 82% is bound to albumin and the remainder to alpha1-, alpha2-, and beta-globulins and possibly to IgG. Less than 1-2% of gold from auranofin in serum is present as free gold; serum concentrations of free gold attained with auranofin appear to be similar to those attained with gold sodium thiomalate.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2844
Following oral administration of multiple doses of auranofin in animals, gold is distributed in highest concentrations into the kidneys; gold is also distributed into the spleen, lungs, adrenals, and liver, with lower concentrations being distributed into the heart, testes, GI tract, muscle, eyes, fat, and brain. In animals (and possibly in humans), small amounts of gold from auranofin are distributed into bile. Synovial fluid gold concentrations in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving auranofin are much lower than those in patients receiving therapy with parenteral gold compounds, but the ratio of blood-to-synovial fluid gold concentrations during auranofin therapy is similar to that during parenteral gold therapy (approximately 1.7:1). Preliminary data suggest that little or no gold cumulates in skin during auranofin therapy, in contrast to the accumulation that occurs during therapy with parenteral gold compounds. Little or no gold accumulation occurs in hair or nails during auranofin therapy, and accumulation of gold in the cornea or lens during therapy with the drug has not been detected to date with total cumulative doses as high as 6.1 g.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2844
Following oral administration of a single 6-mg dose of auranofin in healthy adults, mean peak blood gold concentrations of 0.025 ug/mL (range: 0.014-0.046 ug/mL) occurred at 2 hours. Following oral administration of multiple doses of the drug in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, steady-state blood gold concentrations are usually attained after 8-12 weeks, although periods of 13-16 weeks may be necessary in some patients. While there appears to be considerable interindividual variation, once steady-state blood gold concentrations are attained during auranofin therapy, there appears to be minimal intraindividual variation in blood gold concentration with continued dosing.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2844
Results of animal studies indicate that the ligands of auranofin are almost completely absorbed; since a much smaller fraction of the gold is absorbed, the drug is believed to undergo extensive disruption at its coordination bonds within the GI tract. Some experimental data suggest that auranofin is loosely and reversibly adsorbed onto GI mucosa. Other experimental data suggest that gold-containing forms of auranofin may undergo transmucosal absorption, possibly with the initial metabolic process being deacetylation within the GI mucosa.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2844
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for AURANOFIN (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Metabolized so rapidly that the intact molecule has not been detected in blood.
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 23rd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2003. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 1587
For a patient receiving gold sodium thiomalate the principal gold species in the urine is [Au(CN)2]-, which is also seen in a low molecular weight infiltrate of the blood. The same compound is also identified in the urine and blood of a patient taking auranofin
PMID:8474063 Elder R et al; J Rheumatol. 20 (2): 268-72 (1993)
Auranofin, 2,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-1-thio-beta-D-glucopyranosato-S-(triethylphosphine)- gold(I), ...metabolized in contact with hamster or rat gut wall to yield the deacetylated form of the drug. This product, 1-thio-beta-D-glucopyranosato-S-(triethylphosphine)-gold(I), passed through hamster or rat intestinal wall in an everted gut experiment...
PMID:6429854 Tepperman K et al; Science 225 (4660): 430-2 (1984)
The efflux of gold from red blood cells (RBCs) exposed to 10-100 microM auranofin, triethylphosphine(2,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl- 1-beta-D-gludopyranosato-S-)gold(I) was studied. RBCs in whole blood were allowed to accumulate gold, and then were place in fresh plasma or buffered saline solution. ...[14C]Glutathione, generated by in situ labeling, also effluxed and associated with the albumin and gold, providing the first direct evidence that the albumin-gold-glutathione complex (AlbSAuSG) may be a circulating metabolite of auranofin formed after both of the original ligands of auranofin are displaced.
PMID:2403377 Shaw C et al; Biochem Pharmacol 40(6): 1227-34 (1990)
The mean terminal plasma half-life of auranofin gold at steady state was 26 days (range 21 to 31 days; n = 5). The mean terminal body half-life was 80 days (range 42 to 128; n= 5)
Medical Economics Co; Physicians Desk Reference 50th ed p.2513 (1996)
In patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving an auranofin dosage of 6 mg daily, the terminal plasma and biologic half-lives of gold following the initial dose of the drug averaged 17 days (range: 11-23 days) and 58 days (range: 30-78 days), respectively; after 6 months of therapy with the same dosage, the terminal plasma and biologic gold half-lives averaged 26 days (range: 21-31 days) and 81 days (range: 42-128 days), respectively. ...
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 2003. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2003 (Plus Supplements)., p. 2844
The mechanism of action of anti-rheumatic gold compounds on 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA)-induced prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) production in rat peritoneal macrophages were examined. Auranofin (AF) at 3-10 muM inhibited TPA-induced PGE(2) production in concentration-dependent manner. In the pharmacological experiments, prostaglandin G/H synthase (PGHS)-2-dependent PGE(2) production was inhibited by 10 muM of AF. The enzyme activities of both PGHS-1 and PGHS-2 were not affectecd by the 10 muM AF. ...AF decreased the PGHS-2 protein content, but had no effect on the PGHS-1 protein content. AF at 3-10 muM decrease the PGHS-2 messenger RNA (mRNA) level by RT-PCR determination. Then the effect of AF on nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB), one of the transcription factors known to regulate transcription of a group of proinflammatory proteins, was determined. AF at 1-10 muM inhibited nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB in a concentration-dependent manner. AF ...did not affect the binding of NF-kappaB to its specific DNA. These observations may suggest that the effects of gold compounds on the inhibition of NF-kappaB nuclear translocation plays one of the major role in its anti-inflammatory effects in rat peritoneal macrophages.
Yamashita M et al; Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy (3): 216-23.
...The effect of AF /auranofin/ on PMN activated by two stimulates (PMA, ConA) added sequentially. AF (0.1-10 microM) caused a dose-dependent inhibition of lucigenin-dependent chemiluminescence regardless of the activator (FMLP, ConA, A23 187, PMA) when AF was added before the activator. In contrast, when AF was added to PMN after stimulation, it inhibited only the chemiluminescence of PMN stimulated by PMA. Furthermore, the chemiluminescence was largely unaffected by AF in sequentially activated PMN. The relative sensitivity to AF of the various processes studied indicate that blockade of the activation signal appears to be responsible for inhibition of the respiratory burst of PMN.
PMID:1645553 Rudkowski R et al; Biochem Pharmacol 41(12): 1921-9 (1991)
GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 15803
Submission : 2002-01-10
Status : Active
Type : II
GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 9748
Submission : 1992-06-29
Status : Inactive
Type : II

GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 8292
Submission : 1989-11-16
Status : Inactive
Type : II

GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 4212
Submission : 1981-07-17
Status : Inactive
Type : II

 FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
15
PharmaCompass offers a list of Auranofin API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Auranofin manufacturer or Auranofin supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Auranofin manufacturer or Auranofin supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Auranofin API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Auranofin API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Auranofin Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Auranofin Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Auranofin manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Auranofin, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Auranofin manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Auranofin API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Auranofin manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Auranofin supplier is an individual or a company that provides Auranofin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Auranofin finished formulations upon request. The Auranofin suppliers may include Auranofin API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Auranofin suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Auranofin DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Auranofin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Auranofin DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Auranofin USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Auranofin DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Auranofin USDMF includes data on Auranofin's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Auranofin USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Auranofin suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Auranofin as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Auranofin API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Auranofin as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Auranofin and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Auranofin NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Auranofin suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Auranofin Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Auranofin GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Auranofin GMP manufacturer or Auranofin GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Auranofin CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Auranofin's compliance with Auranofin specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Auranofin CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Auranofin CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Auranofin may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Auranofin EP), Auranofin JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Auranofin USP).
