
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
VMF
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
Annual Reports
NA
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
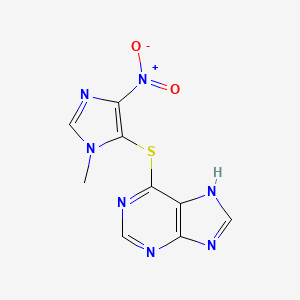

1. Azathioprine Sodium
2. Azathioprine Sodium Salt
3. Azathioprine Sulfate
4. Azothioprine
5. Immuran
6. Imuran
7. Imurel
8. Sodium, Azathioprine
1. 446-86-6
2. Imuran
3. Azothioprine
4. Azathioprin
5. Azatioprin
6. Azamun
7. Azanin
8. Azasan
9. Imurel
10. Azathiopurine
11. Ccucol
12. Imurek
13. Muran
14. Rorasul
15. Bw 57-322
16. Azathioprinum
17. Nsc-39084
18. Bw-57-322
19. 6-(1-methyl-4-nitroimidazol-5-yl)thiopurine
20. Nci-c03474
21. 6-[(1-methyl-4-nitro-1h-imidazol-5-yl)sulfanyl]-7h-purine
22. Imuran (tn)
23. Nsc 39084
24. 6-(1-methyl-p-nitro-5-imidazolyl)-thiopurine
25. 6-((1-methyl-4-nitroimidazol-5-yl)thio)purine
26. 6-((1-methyl-4-nitro-1h-imidazol-5-yl)thio)-1h-purine
27. 6-(1'-methyl-4'-nitro-5'-imidazolyl)-mercaptopurine
28. 6-((1-methyl-4-nitro-1h-imidazol-5-yl)thio)-9h-purine
29. Azathioprine (azasan, Imuran)
30. 1h-purine, 6-((1-methyl-4-nitro-1h-imidazol-5-yl)thio)-
31. Purine, 6-(1-methyl-4-nitro-5-imidazolylthio)-
32. 6-(3-methyl-5-nitroimidazol-4-yl)sulfanyl-7h-purine
33. 6-(methyl-p-nitro-5-imidazolyl)-thiopurine
34. 1h-purine, 6-[(1-methyl-4-nitro-1h-imidazol-5-yl)thio]-
35. Mrk240iy2l
36. Bw 57322
37. Azamun [czech]
38. 6-((1-methyl-4-nitro-1h-imidazol-5-yl)thio)-7h-purine
39. Chebi:2948
40. B. W. 57-322
41. Nsc39084
42. 6-(1'-methyl-4'-nitro-5'-imidazolyl)mercaptopurine
43. Purine, 6-((1-methyl-4-nitroimidazol-5-yl)thio)-
44. 6-[(1-methyl-4-nitro-1h-imidazol-5-yl)thio]-7h-purine
45. 6-[(1-methyl-4-nitro-1h-imidazol-5-yl)thio]-9h-purine
46. Ncgc00015060-06
47. Ncgc00015060-14
48. Azatioprina
49. Cas-446-86-6
50. Dsstox_cid_119
51. 6-[(1-methyl-4-nitroimidazol-5-yl)thio]purine
52. Dsstox_rid_75381
53. Dsstox_gsid_20119
54. Azathioprinum [inn-latin]
55. Azatioprina [inn-spanish]
56. Azamune
57. Methylnitroimidazolylmercaptopurine
58. Ccris 62
59. Azasan (tn)
60. Hsdb 7084
61. Sr-01000075537
62. Purine, 6-[(1-methyl-4-nitroimidazol-5-yl)thio]-
63. Einecs 207-175-4
64. Mfcd00069203
65. Unii-mrk240iy2l
66. 6-(1-methyl-4-nitro-1h-imidazol-5-ylthio)-9h-purine
67. 6-1'-methyl,4'-nitro,5'-imidazolyl Mercaptopurine
68. Azanine
69. 6-(1-methyl-4-nitroimidazol-5-ylthio)purin [czech]
70. Azothioprin
71. Jayempi
72. Azoran
73. Ai3-50290
74. 6-(1-methyl-4-nitroimidazol-5-ylthio)purin
75. Prestwick_41
76. Azathiopurine,(s)
77. [methyl(nitroimidazolyl)mercaptopurine]
78. Azathioprine [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
79. Spectrum_000064
80. Azathioprine, >=98%
81. 6-(methyl-p-nitro-5-imidazolyl)thiopurine
82. Prestwick0_000094
83. Prestwick1_000094
84. Prestwick2_000094
85. Prestwick3_000094
86. Spectrum2_000068
87. Spectrum3_000308
88. Spectrum4_000243
89. Spectrum5_000848
90. Azathioprine [mi]
91. Lopac-a-4638
92. Chemdiv1_002659
93. 6-(1-methyl-p-nitro-5-imidazolyl)thiopurine
94. Azathioprine [inn]
95. Azathioprine [jan]
96. A 4638
97. Azathioprine [hsdb]
98. Azathioprine [iarc]
99. Azathioprine [usan]
100. Thiopurine 6-(1-methyl-4-nitroimidazol-5-yl)
101. Schembl4278
102. Azathioprine [vandf]
103. Chembl1542
104. Lopac0_000027
105. Oprea1_375441
106. Oprea1_533384
107. Oprea1_633462
108. Azathioprine [mart.]
109. Bspbio_000048
110. Bspbio_001876
111. Cbdive_013132
112. Kbiogr_000646
113. Kbiogr_002427
114. Kbioss_000464
115. Kbioss_002433
116. Ai-981/34845012
117. Mls001049307
118. Azathioprine [usp-rs]
119. Azathioprine [who-dd]
120. Azathioprine [who-ip]
121. Divk1c_000586
122. Spectrum1500133
123. Spbio_000255
124. Spbio_001987
125. Bpbio1_000054
126. Gtpl7120
127. Dtxsid4020119
128. Azathioprine (jp17/usp/inn)
129. Hms501n08
130. Hms594i19
131. Kbio1_000586
132. Kbio2_000464
133. Kbio2_002427
134. Kbio2_003032
135. Kbio2_004995
136. Kbio2_005600
137. Kbio2_007563
138. Kbio3_001376
139. Kbio3_002906
140. Cmap_000046
141. Ninds_000586
142. 6-({4-nitro-1-methyl-1h-imidazol-5-yl}sulfanyl)-7h-purine
143. 6-[(1-methyl-4-nitro-1h-imidazol-5-yl)sulfanyl]-1h-purine
144. Azathioprine [ep Impurity]
145. Azathioprine [orange Book]
146. Hms1568c10
147. Hms1920e17
148. Hms2091k19
149. Hms2095c10
150. Hms2802j03
151. Hms3259p03
152. Hms3260e15
153. Hms3655m04
154. Hms3712c10
155. Pharmakon1600-01500133
156. Azathioprine [ep Monograph]
157. Act02232
158. Bcp09492
159. Hy-b0256
160. Zinc4258316
161. Azathioprine [usp Monograph]
162. Tox21_110074
163. Tox21_400024
164. Tox21_500027
165. Azathioprinum [who-ip Latin]
166. Bdbm50373919
167. Ccg-16168
168. Ccg-39877
169. Nsc755900
170. S1721
171. Stk831906
172. Akos005609209
173. Akos028108935
174. Tox21_110074_1
175. Ac-4230
176. Ccg-220094
177. Db00993
178. Ks-1146
179. Lp00027
180. Nc00614
181. Nsc-755900
182. Sdccgmls-0065415.p001
183. Sdccgsbi-0050016.p005
184. Idi1_000586
185. Ncgc00015060-01
186. Ncgc00015060-02
187. Ncgc00015060-03
188. Ncgc00015060-04
189. Ncgc00015060-05
190. Ncgc00015060-07
191. Ncgc00015060-08
192. Ncgc00015060-09
193. Ncgc00015060-10
194. Ncgc00015060-11
195. Ncgc00015060-12
196. Ncgc00015060-13
197. Ncgc00015060-15
198. Ncgc00015060-16
199. Ncgc00015060-18
200. Ncgc00015060-19
201. Ncgc00015060-29
202. Ncgc00090836-01
203. Ncgc00090836-02
204. Ncgc00090836-03
205. Ncgc00090836-04
206. Ncgc00090836-05
207. Ncgc00090836-06
208. Ncgc00094593-01
209. Ncgc00094593-02
210. Ncgc00094593-03
211. Ncgc00260712-01
212. Ba166065
213. Smr000427366
214. 6-1'-methyl,5'-imidazolyl Mercaptopurine
215. Sbi-0050016.p003
216. Azathioprine 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
217. 6-(1-methyl-4-nitromidazol-5-ylthio)purine
218. Ab00443544
219. Eu-0100027
220. Ft-0602904
221. Ft-0662375
222. Sw198560-2
223. 6-(1-methyl-4-nitroimidazol-5-ylthio)purine
224. Azathioprine, Meets Usp Testing Specifications
225. C06837
226. D00238
227. D70170
228. Q18939
229. Ab00443544-03
230. Ab00443544-11
231. Ab00443544_12
232. Ab00443544_13
233. 055a974
234. 446a866
235. A826664
236. Sr-01000762955
237. 6-(1-methyl-4-nitro-5-imidazolythio)-9h-pur-ine
238. Sr-01000075537-1
239. Sr-01000075537-4
240. Sr-01000762955-2
241. Brd-k32821942-001-05-6
242. Brd-k32821942-001-10-6
243. Brd-k60324116-001-01-5
244. Wln: T56 Bm Dn Fn Hnj Is- Et5n Cnj A1 Dnw
245. Z57063156
246. 6-((1-methyl-4-nitro-1h-imidazol-5-yl)thio)-1h-purin
247. 6-(3-methyl-5-nitro-imidazol-4-yl)sulfanyl-9h-purine
248. 6-[(1-methyl-4-nitro-1h-imidazol-5-yl)sulfanyl]-9h-purine
249. 9h-purine, 6-[(1-methyl-4-nitro-1h-imidazol-5-yl)thio]-
250. Azathioprine, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
251. 1h-purine, 6-((1-methyl-4-nitro-1h-imidazol-5-yl)thio)
252. 6-[(1-methyl-4-nitro-1h-imidazol-5-yl)sulfanyl]-1h-purine #
253. Azathioprine, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
254. Azathioprine, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
255. 6-((1-methyl-4-nitroimidazol-5-yl)thio)purine6-((1-methyl-4-nitro-1h-imidazol-5-yl)thio)-1h-purine
| Molecular Weight | 277.27 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H7N7O2S |
| XLogP3 | 0.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 277.03819367 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 277.03819367 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 143 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 354 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Azasan |
| PubMed Health | Azathioprine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antirheumatic, Cytotoxic, Gastrointestinal Agent |
| Drug Label | AZASAN, an immunosuppressive antimetabolite, is available in tablet form for oral administration. Each scored tablet contains75mg or 100 mg azathioprine and the inactive ingredients lactose monohydrate, pregelatinized starch,povidone, corn st... |
| Active Ingredient | Azathioprine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 75mg; 100mg; 25mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Aaipharma |
| 2 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Azathioprine |
| PubMed Health | Azathioprine |
| Drug Classes | Antirheumatic, Cytotoxic, Gastrointestinal Agent |
| Drug Label | Azathioprine is an immunosuppressive antimetabolite. Each uncoated azathioprine tablet intended for oral administration contains 50 mg of azathioprine. In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, lacto... |
| Active Ingredient | Azathioprine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 75mg; 100mg; 25mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Zydus Pharms Usa; Mylan; Roxane |
| 3 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Azathioprine sodium |
| PubMed Health | Azathioprine |
| Drug Classes | Antirheumatic, Cytotoxic, Gastrointestinal Agent |
| Drug Label | IMURAN (azathioprine), an immunosuppressive antimetabolite, is available in tablet form for oral administration. Each scored tablet contains 50mg azathioprine and the inactive ingredients lactose, magnesium stearate, potato starch, povidone, and st... |
| Active Ingredient | Azathioprine sodium |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | eq 100mg base/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Eurohlth Intl |
| 4 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Imuran |
| Active Ingredient | Azathioprine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Prometheus Labs |
| 5 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Azasan |
| PubMed Health | Azathioprine (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antirheumatic, Cytotoxic, Gastrointestinal Agent |
| Drug Label | AZASAN, an immunosuppressive antimetabolite, is available in tablet form for oral administration. Each scored tablet contains75mg or 100 mg azathioprine and the inactive ingredients lactose monohydrate, pregelatinized starch,povidone, corn st... |
| Active Ingredient | Azathioprine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 75mg; 100mg; 25mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Aaipharma |
| 6 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Azathioprine |
| PubMed Health | Azathioprine |
| Drug Classes | Antirheumatic, Cytotoxic, Gastrointestinal Agent |
| Drug Label | Azathioprine is an immunosuppressive antimetabolite. Each uncoated azathioprine tablet intended for oral administration contains 50 mg of azathioprine. In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, lacto... |
| Active Ingredient | Azathioprine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 75mg; 100mg; 25mg; 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Zydus Pharms Usa; Mylan; Roxane |
| 7 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Azathioprine sodium |
| PubMed Health | Azathioprine |
| Drug Classes | Antirheumatic, Cytotoxic, Gastrointestinal Agent |
| Drug Label | IMURAN (azathioprine), an immunosuppressive antimetabolite, is available in tablet form for oral administration. Each scored tablet contains 50mg azathioprine and the inactive ingredients lactose, magnesium stearate, potato starch, povidone, and st... |
| Active Ingredient | Azathioprine sodium |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | eq 100mg base/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Eurohlth Intl |
| 8 of 8 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Imuran |
| Active Ingredient | Azathioprine |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 50mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Prometheus Labs |
Azathioprine also is indicated in the treatment of other immunological diseases including regional and ulcerative colitis, biliary cirrhosis, systemic dermatomyositis (polymyositis), glomerulonephritis, chronic active hepatitis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), inflammatory myopathy, myasthenia gravis, nephrotic syndrome, pemphigus and pemphigoid. /NOT included in US product labeling/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 509
Azathioprine is indicated for the management of severe, active, and erosive rheumatoid arthritis unresponsive to rest or conventional medications. /Included in US product labeling/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 509
It /azathioprine/ is also also indicated in the prevention of rejection in cardiac, hepatic, and pancreatic transplantation. /NOT included in US product labeling/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 509
Azathioprine is indicated as an adjunct for prevention of rejection in renal homotransplantation. /Included in US product labeling/
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 509
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for AZATHIOPRINE (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Azathioprine is a toxic drug and must be used only under close medical supervision. Other immunosuppressive therapy given concomitantly with azathioprine therapy may increase the toxic potential of the drug.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 3592
Azathioprine may also cause rash, infection, drug fever, serum sickness, alopecia, arthralgia, retinopathy, Raynaud's disease, and pulmonary edema. Some of these adverse effects can occur as manifestations of rare hypersensitivity reactions. Azathioprine-induced hypersensitivity reactions are often characterized by a combination of symptoms, including fever, rigors, musculuskeletal symptoms (arthralgias, myalgias), and/or cutaneous effects (generalized erythematous or maculopapular rash with nonspecific inflammatory changes demonstrated on biopsy); pulmonary manifestations (eg, cough and/or dyspnea) and hypotension (which may be severe and, in the presence of fever, mimic septic shock) may also occur.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 3591
Hepatotoxicity manifested by increased serum alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, and/or aminotransferase concentrations may occur in patients receiving azathioprine, principally in allograft recipients. Azathioprine-induced hepatotoxicity following transplantation occurs most frequently within 6 months of transplantation and is generally reversible following discontinuance of the drug. Rare, but life-threatening hepatic veno-occlusive disease has occurred during chronic azathioprine therapy in several renal allograft recipients and in a patient with panuveitis; serious complications, including progressive portal hypertension, progressive liver failure requiring a portacaval shunt, progressive chronic liver failure with portal hypertension and esophageal varices, and/or rapid deterioration resulting in death, occurred in most of these patients. Veno-occlusive disease was associated with cytomegalovirus infection in some of these patients and with use of azathioprine but not with dosage of the drug, type or duration of renal allograft, or type of underlying renal disease. Reports to date suggest that the onset of hepatic veno-occlusive disease generally occurs after 1-2 years of therapy and that the disease occur principally in males. The clinical syndrome is usually manifested initially by jaundice, often followed by the development of ascites and other signs of partal hypertension. Serum alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin concentrations are usually elevated. Prognosis is poor. Because hepatic veno-occlusive disease may result in rapid clincial deterioration, prompt diagnosis and therapeutic intervention are necessary. Many clinicians suggest that liver biopsy to diagnose veno-occlusive disease should be performed in renal allograft recipients receiving azathioprine at the first sign of mild hepatic dysfunction. If veno-occlusive disease is evident, azathioprine therapy should be promptly and permanently discontinued; alternative immunosuppressive therapy should be considered and, if liver failure is progressive anticoagulation, a partacaval shunt, or hepatic allotransplantation should be considered. Hepatotoxicity occurs in less than 1% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis who receive azathioprine.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 3591
Nausea, vomiting, anorexia, and diarrhea may occur in patients receiving large doses of azathioprine. Adverse GI effects may be minimized by giving the drug in divided doses and/or after meals. Vomiting with abdominal pain may occur rarely with a hypersensitivity pancreatitis. A GI hypersensitivity reaction characterized by severe nausea and vomiting has been reported. This reaction also may be accompanied by diarrhea, rash, fever, malaise, myalgias, elevations in liver enzymes, and, occasionally, hypotension. Symptoms of GI toxicity most often develop within the first several weeks of azathioprine therapy and are reversible upon discontinuance of the drug. The reaction can occur within several hours after rechallange with a single dose of the drug. Other adverse GI effects include ulceration of the mucous membranes of the mouth, esophagitis with possible ulceration, and steatorrhea.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service- Drug Information 2002. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 2002 (Plus Supplements)., p. 3591
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for AZATHIOPRINE (33 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Azathioprine is indicated to treat rheumatoid arthritis and prevent renal transplant rejection.
FDA Label
Jayempi is indicated in combination with other immunosuppressive agents for the prophylaxis of transplant rejection in patients receiving allogenic kidney, liver, heart, lung or pancreas transplants. Azathioprine is indicated in immunosuppressive regimens as an adjunct to immunosuppressive agents that form the mainstay of treatment (basis immunosuppression).
Jayempi is used as an immunosuppressant antimetabolite either alone or, more commonly, in combination with other agents (usually corticosteroids) and/ or procedures which influence the immune response.
Jayempi is indicated in patients who are intolerant to glucocorticosteroids or if the therapeutic response is inadequate despite treatment with high doses of glucocorticosteroids, in the following diseases:
- severe active rheumatoid arthritis (chronic polyarthritis ) that cannot be kept under control by less toxic agents (disease-modifying anti-rheumatic -medicinal products DMARDs)
- auto-immune hepatitis
- systemic lupus erythematosus
- dermatomyositis
- polyarteritis nodosa
- pemphigus vulgaris and bullous pemphigoid
- Behets disease
- refractory auto-immune haemolytic anaemia, caused by warm IgG antibodies
- chronic refractory idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
Jayempi is used for the treatment of moderately severe to severe forms of chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) (Crohns disease or ulcerative colitis) in patients in whom glucocorticosteroid therapy is necessary, but where glucocorticosteroids are not tolerated, or in whom the disease is untreatable with other common means of first choice.
It is also indicated in adult patients in relapsing multiple sclerosis, if an immunomodulatory therapy is indicated but beta interferon therapy is not possible, or a stable course has been achieved with previous treatment with azathioprine. 3
Jayempi is indicated for the treatment of generalised myasthenia gravis. Depending on the severity of the disease, Jayempi should be given in combination with glucocorticosteroids because of slow onset of action at the beginning of treatment and the glucocorticosteroid dose should be gradually reduced after several months of treatment.
Azathioprine is an immunosuppressive agent which functions through modulation of rac1 to induce T cell apoptosis, as well as other unknown immunosuppressive functions. It has a long duration of action as it is given daily, and has a narrow therapeutic index. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of malignancies of the skin and lymphomas.
Antimetabolites
Drugs that are chemically similar to naturally occurring metabolites, but differ enough to interfere with normal metabolic pathways. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p2033) (See all compounds classified as Antimetabolites.)
Antirheumatic Agents
Drugs that are used to treat RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. (See all compounds classified as Antirheumatic Agents.)
Antimetabolites, Antineoplastic
Antimetabolites that are useful in cancer chemotherapy. (See all compounds classified as Antimetabolites, Antineoplastic.)
Immunosuppressive Agents
Agents that suppress immune function by one of several mechanisms of action. Classical cytotoxic immunosuppressants act by inhibiting DNA synthesis. Others may act through activation of T-CELLS or by inhibiting the activation of HELPER CELLS. While immunosuppression has been brought about in the past primarily to prevent rejection of transplanted organs, new applications involving mediation of the effects of INTERLEUKINS and other CYTOKINES are emerging. (See all compounds classified as Immunosuppressive Agents.)
L04AX01
L04AX01
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L04 - Immunosuppressants
L04A - Immunosuppressants
L04AX - Other immunosuppressants
L04AX01 - Azathioprine
Absorption
Oral azathioprine is well absorbed, with a Tmax of 1-2h. Further data regarding the absorption of azathioprine is not readily available.
Route of Elimination
Azathioprine and mercaptopurine are not detectable in urine after 8 hours. Further data regarding the route of elimination of azathioprine are not available.
Volume of Distribution
Data regarding the volume of distribution of azathioprine is not readily available.
Clearance
Data regarding the clearance of azathioprine is not readily available.
Azathioprine and mercaptopurine are moderately bound to plasma proteins and are partially dialyzable. They are rapidly removed from the blood by oxidation or methylation in the liver and/or erythrocytes. Renal clearance is of little impact in biological effectiveness or toxicity, but dose reduction is practiced in patients with renal failure.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1471
Azathioprine is well absorbed orally and reaches maximum blood levels within 1 to 2 hours after administration.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1471
Azathioprine is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and has an oral bioavailibility of approximately 60%.
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 778
Azathioprine is rapidly cleared from the blood; both azathioprine and mercaptopurine are approximately 30% bound to serum proteins, both appear dialyzable, and both appear to cross the placenta.
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 778
The metabolites are excreted in the urine, largely as 6-mercaptopurine. Less than 2% of azathioprine and 20 to 40% of 6-mercaptopurine are excreted as unchanged drugs in the urine.
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 778
Azathioprine is converted to 6-mercaptopurine nonenzymatically. 6-mercaptopurine is then metabolized to 6-methylmercaptopurine by thiopurine methyltransferase, 6-thiouric acid by xanthine oxidase, or 6-thiosine-5'-monophosphate by hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. 6-thiosine-5'-monophosphate is metabolized to 6-methylthiosine-5'-monophosphate by thiopurine methyltransferase or 6-thioxanthylic acid by inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase. 6-thioxanthylic acid is metabolized by guanosine monophosphate synthetase to 6-thioguanine monophosphate, the first of the 6-thioguanine nucleotides. 6-thioguanine monophosphate is phosphorylated to produce the remaining 6-thioguanine nucleotides, 6-thioguanine diphosphate and 6-thioguanine triphosphate.
Orally administered azathioprine is rapidly divided in vivo to form 6-mercaptopurine.
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 778
Metabolized in vivo to 6-mercaptopurine, q.v.
O'Neil, M.J. (ed.). The Merck Index - An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals. 13th Edition, Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck and Co., Inc., 2001., p. 157
Azathioprine is metabolized to 6-mercaptopurine.
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 777
The half life of azathioprine is approximately 5 hours.
The elimination half-life of azathioprine is approximately 12 to 15 minutes, and that of 6-mercaptopurine is approximately 30 minutes to 4 hours. The total boby clearance of azathioprine is 60 ml/min/kg, and that of 6-mercaptopurine, 10 ml/min/kg.
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 778
The half-life of azathioprine itself is about 10 minutes, and that for mercaptopurine is about an hour.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1471
Azathioprine's mechanism of action is not entirely understood but it may be related to inhibition of purine synthesis, along with inhibition of B and T cells. 6-thioguanine triphosphate, a metabolite of azathioprine, modulates activation of rac1 when costimulated with CD28, inducing T cell apoptosis. This may be mediated through rac1's action on mitogen-activated protein kinase, NF-kappaB.
Following exposure to nucleophiles ... azathioprine is cleaved to 6-mercaptopurine which, in turn, is converted to additional metabolites that inhibit de novo purine synthesis. 6-Thio-IMP, a fraudulent nucleotide, is converted to 6-thio-GMP and finally to 6-thio-GTP, which is incorporated into DNA and gene translation is inhibited. Cell proliferation is prevented, inhibiting a variety of lymphocyte functions.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1471
Azathioprine (AZA), one of the antimetabolite drugs, is a purine analog that is more potent than the prototype 6-mercaptopurine, as an inhibitor of cell replication. Immunosuppression likely occurs because of the ability of the drug to inhibit purine biosynthesis. ... Although T-cell functions are the primary targets for this drug, inhibition of /(natural killer cells)/ NK function and macrophage activities has also been reported.
Klaassen, C.D. (ed). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. The Basic Science of Poisons. 6th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 447
Azathioprine inhibits DNA synthesis and, as a purine antimetabolite, exerts its effect on activated lymphocytes, which requires purines during their proliferative phase. It inhibits both cellular and humoral responses, but does not interfere with phagocytosis or interferon production. It is a nonspecific cytotoxic agent. Its immunosuppressive effect is believed to be due to mercaptopurine, to which it is metabolized.
Ellenhorn, M.J., S. Schonwald, G. Ordog, J. Wasserberger. Ellenhorn's Medical Toxicology: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1997., p. 778
The exact mechanism of immunosuppressive action is unknown since the exact mechanism of the immune response itself is complex and not completely understood. The immunosuppressive effects of azathioprine involve a greater suppression of delayed hypersensitivity and cellular cytotoxicity tests than of antibody responses. Azathioprine antagonizes purine metabolism and may inhibit synthesis of DNA, RNA, and proteins; it may also interfere with cellular metabolism and inhibit mitosis.
MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care, Greenwood Village, CO. 2002. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., p. 509
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for AZATHIOPRINE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
39
PharmaCompass offers a list of Azathioprine API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Azathioprine manufacturer or Azathioprine supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Azathioprine manufacturer or Azathioprine supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Azathioprine API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Azathioprine API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Azathioprine Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Azathioprine Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Azathioprine manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Azathioprine, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Azathioprine manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Azathioprine API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Azathioprine manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Azathioprine supplier is an individual or a company that provides Azathioprine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Azathioprine finished formulations upon request. The Azathioprine suppliers may include Azathioprine API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Azathioprine suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Azathioprine DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Azathioprine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Azathioprine DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Azathioprine USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Azathioprine DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Azathioprine USDMF includes data on Azathioprine's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Azathioprine USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Azathioprine suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Azathioprine Drug Master File in Japan (Azathioprine JDMF) empowers Azathioprine API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Azathioprine JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Azathioprine JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Azathioprine suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Azathioprine Drug Master File in Korea (Azathioprine KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Azathioprine. The MFDS reviews the Azathioprine KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Azathioprine KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Azathioprine KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Azathioprine API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Azathioprine suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Azathioprine CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Azathioprine Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Azathioprine CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Azathioprine EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Azathioprine to their clients by showing that a Azathioprine CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Azathioprine CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Azathioprine CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Azathioprine CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Azathioprine DMF.
A Azathioprine CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Azathioprine CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Azathioprine suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
A Azathioprine written confirmation (Azathioprine WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Azathioprine manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Azathioprine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Azathioprine APIs or Azathioprine finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Azathioprine WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Azathioprine suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Azathioprine as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Azathioprine API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Azathioprine as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Azathioprine and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Azathioprine NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Azathioprine suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Azathioprine Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Azathioprine GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Azathioprine GMP manufacturer or Azathioprine GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Azathioprine CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Azathioprine's compliance with Azathioprine specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Azathioprine CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Azathioprine CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Azathioprine may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Azathioprine EP), Azathioprine JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Azathioprine USP).
