
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
EU WC
0
VMF
0
Australia

0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers

1. Biodermatin
2. Biokur
3. Biotin Gelfert
4. Biotin Hermes
5. Biotin Ratiopharm
6. Biotin-ratiopharm
7. Biotine Roche
8. Deacura
9. Gabunat
10. Gelfert, Biotin
11. Hermes, Biotin
12. Medebiotin
13. Medobiotin
14. Roche, Biotine
15. Rombellin
16. Vitamin H
1. D-biotin
2. 58-85-5
3. Vitamin H
4. Vitamin B7
5. Coenzyme R
6. Bioepiderm
7. Bios Ii
8. Factor S
9. D(+)-biotin
10. Biodermatin
11. D-(+)-biotin
12. Medebiotin
13. (+)-biotin
14. Biotinum
15. Biotine
16. Meribin
17. Factor S (vitamin)
18. Lutavit H2
19. Biotina
20. 3h-biotin
21. Nsc 63865
22. Ccris 3932
23. Hsdb 346
24. Ritatin
25. Injacom H
26. 5-((3as,4s,6ar)-2-oxohexahydro-1h-thieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl)pentanoic Acid
27. Cis-hexahydro-2-oxo-1h-thieno(3,4)imidazole-4-valeric Acid
28. Cis-tetrahydro-2-oxothieno(3,4-d)imidazoline-4-valeric Acid
29. L-biotin
30. 1swk
31. 1swn
32. 1swr
33. Mfcd00005541
34. Rovimix H 2
35. D-biotin Factor S
36. 5-[(3as,4s,6ar)-2-oxo-hexahydro-1h-thieno[3,4-d]imidazolidin-4-yl]pentanoic Acid
37. Ai3-51198
38. 5-[(3as,4s,6ar)-2-oxohexahydro-1h-thieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl]pentanoic Acid
39. 5-[(3as,4s,6ar)-2-oxo-1,3,3a,4,6,6a-hexahydrothieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl]pentanoic Acid
40. Cis-(+)-tetrahydro-2-oxothieno[3,4]imidazoline-4-valeric Acid
41. (+)-cis-hexahydro-2-oxo-1h-thieno[3,4]imidazole-4-valeric Acid
42. (3as,4s,6ar)-hexahydro-2-oxo-1h-thieno(3,4-d)imidazole-4-valeric Acid
43. 1h-thieno(3,4-d)imidazole-4-pentanoic Acid, Hexahydro-2-oxo-, (3as-(3aalpha,4beta,6aalpha))-
44. 2'-keto-3,4-imidazolido-2-tetrahydrothiophene-n-valeric Acid
45. Chebi:15956
46. 6so6u10h04
47. 1h-thieno[3,4-d]imidazole-4-pentanoic Acid, Hexahydro-2-oxo-, (3as,4s,6ar)-
48. Nsc-63865
49. Hexahydro-2-oxo-1h-thieno(3,4-d)imidazole-4-pentanoic Acid, (3as-(3aalpha,4beta,6aalpha))-
50. 22377-59-9
51. D-biotin 10 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
52. Md-1003
53. Beta-biotin
54. Biotin Impurity D - Mixture Of Diastereomers
55. Dsstox_cid_2679
56. Vitamin Bw
57. (3as,4s,6ar)-hexahydro-2-oxo-1h-thieno[3,4-d]imidazole-4-valeric Acid
58. (3as-(3aalpha,4b,6aalpha))-hexahydro-2-oxo-1h-thieno(3,4-d)imidaz- Ole-4-pentanoic Acid
59. Dsstox_rid_76688
60. Dsstox_gsid_22679
61. Medobiotin
62. Deacura
63. Gabunat
64. Hexahydro-2-oxo-1h-thieno(3,4-d)imidazole-4-pentanoic Acid
65. Rombellin
66. Biokur
67. Biotine [inn-french]
68. Biotinum [inn-latin]
69. Biotina [inn-spanish]
70. Biotin Gelfert
71. Biotin Hermes
72. Biotine Roche
73. Gelfert, Biotin
74. Biotin Ratiopharm
75. Biotin-ratiopharm
76. Hermes, Biotin
77. Roche, Biotine
78. 1h-thieno(3,4-d)imidazole-4-pentanoic Acid, Hexahydro-2-oxo-, (3as,4s,6ar)-
79. 5-((3as,4s,6ar)-rel-2-oxohexahydro-1h-thieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl)pentanoic Acid
80. Smr000112255
81. D(+)biotin
82. 5-(2-oxohexahydro-1h-thieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl)pentanoic Acid
83. Einecs 200-399-3
84. Biotin [usp:inn:jan]
85. Hexahydro-2-oxo-1h-thieno[3,4-d]imidazole-4-pentanoic Acid
86. Unii-6so6u10h04
87. Delta-biotin
88. Vitamin-h
89. 1avd
90. 1ndj
91. 1stp
92. 1swg
93. 1swp
94. 2avi
95. 4bcs
96. 4ggz
97. 4jnj
98. Bioepiderm (tn)
99. Cas-58-85-5
100. Bios H
101. Ncgc00094984-04
102. 1h-thieno[3,4-d]imidazole-4-pentanoic Acid, Hexahydro-2-oxo-, [3as-(3aalpha,4beta,6aalpha)]-
103. Biotin111in
104. Delta-(+)-biotin
105. Biotin (8ci)
106. Delta-biotin Factor S
107. 1df8
108. 1n9m
109. 2gh7
110. 3t2w
111. 4bj8
112. Biotin [vandf]
113. Biotin [hsdb]
114. Biotin [inci]
115. Biotin [fcc]
116. Biotin [inn]
117. Biotin [jan]
118. Biotin [usp-rs]
119. Biotin [who-dd]
120. Prestwick0_000418
121. Prestwick1_000418
122. Prestwick2_000418
123. Prestwick3_000418
124. Biotin [mi]
125. Biotin [mart.]
126. Cid_253
127. D-biotin [vandf]
128. Bdbm12
129. Biotin Silver Nanoparticles
130. Bmse000227
131. Chembl857
132. Probes2_000006
133. Schembl8763
134. Biotin [ep Impurity]
135. Biotin [orange Book]
136. Biotin For System Suitability
137. Bspbio_000376
138. 22879-79-4
139. Biotin (jp17/usp/inn)
140. Mls001066402
141. Mls001074888
142. Mls001331736
143. Mls001333089
144. Biotin [ep Monograph]
145. D-biotin, Analytical Standard
146. Spbio_002315
147. Biotin [usp Monograph]
148. Bpbio1_000414
149. Cid_171548
150. Gtpl4787
151. Amf0005
152. 1n43
153. 2f01
154. Biotin, >=99.0% (t)
155. Hms1569c18
156. Hms2096c18
157. Hms2271o06
158. Hms3713c18
159. Hy-b0511
160. Tox21_113050
161. Tox21_302161
162. Ac8089
163. Bbl028095
164. Biotin, Tested According To Ph.eur.
165. S3130
166. Stk801941
167. Zinc35024346
168. Akos001287669
169. Tox21_113050_1
170. Ccg-220418
171. Db00121
172. 1h-thieno(3,4-d)imidazole-4-pentanoic Acid, Hexahydro-2-oxo-, (3as-(3aalpha,4b,6aalpha))-
173. Biotin, Meets Usp Testing Specifications
174. Biotin, Saj Special Grade, >=98.0%
175. Ncgc00179580-01
176. Ncgc00179580-02
177. Ncgc00179580-04
178. Ncgc00255377-01
179. 56846-45-8
180. Ac-19998
181. Bp-20441
182. Biotin, >=99% (tlc), Lyophilized Powder
183. Biotin, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, >=99%
184. Ab00374191
185. B0463
186. 58b855
187. C00120
188. D00029
189. M02926
190. Ab00374191-08
191. Ab00374191_11
192. A929752
193. Biotin, Plant Cell Culture Tested, >=99% (tlc)
194. Q181354
195. Sr-01000765521
196. Biotin, Certified Reference Material, Tracecert(r)
197. Q-200929
198. Sr-01000765521-2
199. Brd-k89210380-001-03-8
200. Brd-k89210380-001-13-7
201. 6ae43aa3-bc3d-4c49-9db9-5913a2401eb6
202. Biotin, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
203. F2173-0855
204. Hexahydro-2-oxo-1h-thieno(3,4-d)imidazole-4-pentanoate
205. Z210803762
206. Biotin, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
207. Cis-(+)-tetrahydro-2-oxothieno[3,4]imidazoline-4-valerate
208. (+)-cis-hexahydro-2-oxo-1h-thieno[3,4]imidazole-4-valerate
209. 5-(2-oxohexahydro-1h-thieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl)pentanoate
210. Daunorubicin Hydrochloride, Antibiotic For Culture Media Use Only
211. (3as,4s,6ar)-hexahydro-2-oxo-1h-thieno[3,4-d]imidazole-4-valerate
212. Biotin, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
213. 1h-thieno[3,4-d]imidazole-4-pentanoic Acid, Hexahydro-2-oxo-, (3as,4s,6ar)- (9ci)
214. 5-((3ar,6s,6as)-2-oxo-hexahydro-thieno[3,4-d]imidazol-6-yl)-pentanoic Acid
215. 5-[(3ar,6s,6as)-2-oxo-1,3,3a,4,6,6a-hexahydrothieno[3,4-d]imidazol-6-yl]pentanoic Acid
216. Biotin For System Suitability, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
217. Hexahydro-2-oxo-[3as-(3aa,4b,6aa)]-1h-thieno[3,4-d]imidazole-4-pentanoate
218. Hexahydro-2-oxo-[3as-(3aa,4b,6aa)]-1h-thieno[3,4-d]imidazole-4-pentanoic Acid
219. Hexahydro-2-oxo-[3as-(3alpha,4beta,6alpha)]-1h-thieno[3,4-d]imidazole-4-pentanoate
220. Hexahydro-2-oxo-[3as-(3alpha,4beta,6alpha)]-1h-thieno[3,4-d]imidazole-4-pentanoic Acid
221. Biotin, Pharmagrade, Usp, Meets Fcc Testing Specifications, Manufactured Under Appropriate Gmp Controls For Pharma Or Biopharmaceutical Production.
222. Biotin, Powder, Bioreagent, Suitable For Cell Culture, Suitable For Insect Cell Culture, Suitable For Plant Cell Culture, >=99%
| Molecular Weight | 244.31 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H16N2O3S |
| XLogP3 | 0.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 244.08816355 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 244.08816355 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 104 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 16 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 298 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
The B vitamins are indicated for prevention and treatment of vitamin B deficiency. Vitamin B deficiency may occur as a result of inadequate nutrition or intestinal malabsorption but does not occur in healthy individuals receiving an adequate balanced diet. Simple nutritional deficiency of individual B vitamins is rare since dietary inadequacy usually results in multiple deficiencies. For prophylaxis of biotin deficiency, dietary improvement, rather than supplementatin, is advisable. For teatment of biotin deficiency, supplementation is preferred. /Included in US product labeling/
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007.
Large doses of biotin ... are administered to babies with infantile seborrhea and to individuals with genetic alterations of biotin-dependent enzymes. patients who receive long-term parenteral nutrition should be given vitamin formulations that contain biotin.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1763
(VET): Biotin is used as a feed additive for poultry and swine.
Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. 3rd ed., Volumes 1-26. New York, NY: John Wiley and Sons, 1978-1984., p. V24 41
Biotin is used to treat the biotin-responsive inborn errors of metabolism holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency and biotinidase deficiency. Holocarboxylase deficiency is the most common cause of neonatal multiple carboxylase deficiency. Biotinidase deficiency is the most common cause of late-onset multiple carboxylase deficiency.
Physicians Desk Reference (PDR) for Nutritional Supplements 1st ed, Medical Economics, Thomson Healthcare; Montvale, NJ p.52 (2001)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for BIOTIN (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Biotin deficiency, which can occur by the feeding of uncooked egg whites or by the omission of biotin from the diet, can cause alopecia and a characteristic scaly, erythematous dermatitis around body orifices in infants, children, and adults. For adults, prolonged biotin deficiency can result in depression, lethargy, hallucinations, and paresthesias of the extremities.
PMID:11800048 Fiume MZ, Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel; Int J Toxicol 20 (Suppl 4):1-12 (2001)
Biotin has not been proven effective in the treatment of acne, seborrheic eczema, or alopecia.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007.
For nutritional supplementation, also for treating dietary shortage or imbalance.
Treatment of multiple sclerosis
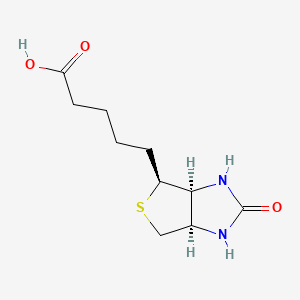
Biotin is a water-soluble B-complex vitamin which is composed of an ureido ring fused with a tetrahydrothiophene ring, which attaches a valeric acid substituent at one of its carbon atoms. Biotin is used in cell growth, the production of fatty acids, metabolism of fats, and amino acids. It plays a role in the Kreb cycle, which is the process in which energy is released from food. Biotin not only assists in various metabolic chemical conversions, but also helps with the transfer of carbon dioxide. Biotin is also helpful in maintaining a steady blood sugar level. Biotin is often recommended for strengthening hair and nails. Consequenty, it is found in many cosmetic and health products for the hair and skin. Biotin deficiency is a rare nutritional disorder caused by a deficiency of biotin. Initial symptoms of biotin deficiency include: Dry skin, Seborrheic dermatitis, Fungal infections, rashes including erythematous periorofacial macular rash, fine and brittle hair, and hair loss or total alopecia. If left untreated, neurological symptoms can develop, including mild depression, which may progress to profound lassitude and, eventually, to somnolence; changes in mental status, generalized muscular pains (myalgias), hyperesthesias and paresthesias. The treatment for biotin deficiency is to simply start taking some biotin supplements. A lack of biotin in infants will lead to a condition called seborrheic dermatitis or "cradle cap". Biotin deficiencies are extremely rare in adults but if it does occur, it will lead to anemia, depression, hair loss, high blood sugar levels, muscle pain, nausea, loss of appetite and inflamed mucous membranes.
Vitamin B Complex
A group of water-soluble vitamins, some of which are COENZYMES. (See all compounds classified as Vitamin B Complex.)
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A11 - Vitamins
A11H - Other plain vitamin preparations
A11HA - Other plain vitamin preparations
A11HA05 - Biotin
Absorption
Systemic - approximately 50%
The intestine is exposed to biotin from a few sources: the diet, biotin supplements and biotin synthesized by bacteria in the large intestine. Dietary biotin exists in free and protein-bound forms. Protein-bound biotin is digested by proteases and peptidases to biotin-containing oligopeptides and biocytin (epsilon-N-biotinyl-L-lysine). Biocytin and the biotin-containing oligopeptides are converted to biotin via the enzyme biotinidase. Biotin - both dietary-derived biotin and supplementary biotin - is efficiently absorbed from the small intestine. At doses of biotin derived from food, biotin appears to be transported into enterocytes by a sodium -dependent carrier. At higher doses of biotin,absorption appears to occur by passive diffusion. Absorption of the biotin produced by the colonic microflora, appears to occur by a carrier mediated process in the proximal large intestine.
Physicians Desk Reference (PDR) for Nutritional Supplements 1st ed, Medical Economics, Thomson Healthcare; Montvale, NJ p.52 (2001)
Elimination: Primarily in urine.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2007.
Protein binding: Primarily to plasma proteins.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006.
Absorption: approximately 50%.
Thomson/Micromedex. Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. Volume 1, Greenwood Village, CO. 2006.
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for BIOTIN (32 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Biotin is excreted in the urine as biotin, bisnorbiotin, biotin sulfoxide, biotin sulfone, bisnorbiotin methyl ketone and tetranobiotin-1-sulfoxide.
Physicians Desk Reference (PDR) for Nutritional Supplements 1st ed, Medical Economics, Thomson Healthcare; Montvale, NJ p.52 (2001)
Biotin is catabolized to a number of different metabolites, including bisnorbiotin, biotin sulfoxide, biotin sulfone, bisonorbiotin methylketone and tetranorbiotin-1-sulfoxide.
Physicians Desk Reference (PDR) for Nutritional Supplements 1st ed, Medical Economics, Thomson Healthcare; Montvale, NJ p.52 (2001)
More than 95% of the biotin is free in the skim fraction of human milk. The concentration of biotin varies substantially in some women and exceeds that in serum by one to two order of magnitude, suggesting that there is a transport system into milk. The biotin metabolite bisnorbiotin accounts for approximately 50%. In early and transitional human milk, the biotin metabolite biotin sulfoxide accounts for about 10% of the total biotin plus metabolites. With postpartum maturation, the biotin concentration increases, but the bisnorbiotin and biotin sulfoxide concentrations still account for 25% and 8% at 5 weeks postpartum. Current studies provide no evidence for a soluble biotin-binding protein or any other mechanism that traps biotin in human milk.
Coates, P.M., Blackman, M.R., Cragg, G.M., Levine, M., Moss, J., White, J.D. (Ed), Encyclopedia of Dietary Supplements. Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, p. 35 (2005)
On a molar basis, biotin accounts for approximately half of the total avidin-binding substances in human serum and urine. Biocytin, bisnorbiotin, bisnorbiotin methylketone, biotin sulfoxide, and biotin sulfone form most of the balance. Biotin metabolism is accelerated in some individuals by anticonvulsants and during pregnancy, thereby increasing the ratio of biotin metabolites to biotin excreted in urine.
Coates, P.M., Blackman, M.R., Cragg, G.M., Levine, M., Moss, J., White, J.D. (Ed), Encyclopedia of Dietary Supplements. Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, p. 35 (2005)
An alternate fate to being incorporated into carboxylases or unchanged excretion is catabolism to an inactive metabolite before excretion in urine. About half of biotin undergoes metabolism before excretion. Two principal pathways of biotin catabolism have been identified in mammals. In the first pathway, the valeric acid side chain of biotin is degraded by beta oxidation. This leads to the formation of bisnorbiotin, tetranorbiotin, and related intermediates that are known to result from beta-oxidation of fatty acids. The cellular site of this beta-oxidation of biotin is uncertain. Nonenzymatic decarboxylation of the unstable beta-ketobiotin and beta-keto-bisnorbiotin leads to formation of bisnorbiotin methylketone and tetranorbiotin methylketone, which appear in urine. In the second pathway, the sulfur in the thiophane ring of biotin is oxidized, leading to the formation of biotin L-sulfoxide, biotin D-sulfoxide, and biotin sulfone. Combined oxidation of the ring sulfur and beta-oxidation of the side chain lead to metabolites such as bisnorbiotin sulfone. In mammals, degradation of the biotin ring to release carbon dioxide and urea is quantitatively minor.
Coates, P.M., Blackman, M.R., Cragg, G.M., Levine, M., Moss, J., White, J.D. (Ed), Encyclopedia of Dietary Supplements. Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, p. 35 (2005)
Biotin is necessary for the proper functioning of enzymes that transport carboxyl units and fix carbon dioxide, and is required for various metabolic functions, including gluconeogenesis, lipogenesis, fatty acid biosynthesis, propionate metabolism, and catabolism of branched-chain amino acids.
In human tissues biotin is a cofactor for the enzymatic carboxylation of four substrates: pyruvate, acetyl coenzyme A (CoA), propionyl CoA, and beta-methylcrotonyl CoA. As such, it plays an important role in both carbohydrate and fat metabolism. Carbon dioxide fixation occurs in a two-step reaction, the first involving binding of carbon dioxide to the biotin moiety of the holoenzyme, and the second involving transfer of the biotin-bound carbon dioxide to an appropriate acceptor.
Hardman, J.G., L.E. Limbird, P.B., A.G. Gilman. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 10th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2001., p. 1763
Biotin functions in carbon dioxide fixation reactions in intermediate metabolism, transferring the carboxyl group to acceptor molecules. It acts similarly in decarboxylation reactions. Biotin is essential in human metabolism for its part in the previously described enzymatic steps, in catalyzing deamination of amino acids, and in oleic acid synthesis. Biotin is a cofactor for the enzymatic carboxylation of pyruvate, acetyl coenzyme A (CoA), propionyl CoA, and beta-methylcrotonyl CoA, and, therefore, plays an important role in carbohydrate and fat metabolism.
PMID:11800048 Fiume MZ, Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel; Int J Toxicol 20 (Suppl 4):1-12 (2001)
Protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) depends on Ca2+; uptake of Ca2+ into the ER is mediated by sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase 3 (SERCA3). The 5'-flanking region of the SERCA3 gene (ATP2A3) contains numerous binding sites for the transcription factors Sp1 and Sp3. Biotin affects the nuclear abundance of Sp1 and Sp3, which may act as transcriptional activators or repressors. Here we determined whether biotin affects the expression of the SERCA3 gene and, thus, protein folding in human lymphoid cells. Jurkat cells were cultured in media containing 0.025 nmol/L biotin (denoted "deficient") or 10 nmol/L biotin ("supplemented"). The transcriptional activity of the full-length human SERCA3 promoter was 50% lower in biotin-supplemented cells compared to biotin-deficient cells. Biotin-dependent repressors bind to elements located 731 to 1312 bp upstream from the transcription start site in the SERCA3 gene. The following suggest that low expression of SERCA3 in biotin-supplemented cells impaired folding of secretory proteins in the ER, triggering unfolded protein response: (i) sequestration of Ca2+ in the ER decreased by 14 to 24% in response to biotin supplementation; (ii) secretion of interleukin-2 into the extracellular space decreased by 75% in response to biotin supplementation; (iii) the nuclear abundance of stress-induced transcription factors increased in response to biotin supplementation; and (iv) the abundance of stress-related proteins such ubiquitin activating enzyme 1, growth arrest and DNA damage 153 gene, X-box binding protein 1 and phosphorylated eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2alpha increased in response to biotin supplementation. Collectively, this study suggests that supplements containing pharmacological doses of biotin may cause cell stress by impairing protein folding in the ER.
PMID:16109482 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1473219 Griffin JB et al; J Nutr Biochem 17(4):272-81 (2006)
Evidence is emerging that biotin participates in processes other than classical carboxylation reactions. Specifically, novel roles for biotin in cell signaling, gene expression, and chromatin structure have been identified in recent years. Human cells accumulate biotin by using both the sodium-dependent multivitamin transporter and monocarboxylate transporter 1. These transporters and other biotin-binding proteins partition biotin to compartments involved in biotin signaling: cytoplasm, mitochondria, and nuclei. The activity of cell signals such as biotinyl-AMP, Sp1 and Sp3, nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB, and receptor tyrosine kinases depends on biotin supply. Consistent with a role for biotin and its catabolites in modulating these cell signals, greater than 2000 biotin-dependent genes have been identified in various human tissues. Many biotin-dependent gene products play roles in signal transduction and localize to the cell nucleus, consistent with a role for biotin in cell signaling. Posttranscriptional events related to ribosomal activity and protein folding may further contribute to effects of biotin on gene expression. Finally, research has shown that biotinidase and holocarboxylase synthetase mediate covalent binding of biotin to histones (DNA-binding proteins), affecting chromatin structure; at least seven biotinylation sites have been identified in human histones. Biotinylation of histones appears to play a role in cell proliferation, gene silencing, and the cellular response to DNA repair. Roles for biotin in cell signaling and chromatin structure are consistent with the notion that biotin has a unique significance in cell biology.
PMID:16011464 Zempleni J; Annu Rev Nutr 25:175-96 (2005)

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS

Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
92
PharmaCompass offers a list of Biotin API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Biotin manufacturer or Biotin supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Biotin manufacturer or Biotin supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Biotin API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Biotin API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Biotin Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Biotin Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Biotin manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Biotin, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Biotin manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Biotin API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Biotin manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Biotin supplier is an individual or a company that provides Biotin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Biotin finished formulations upon request. The Biotin suppliers may include Biotin API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Biotin suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Biotin DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Biotin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Biotin DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Biotin USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Biotin DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Biotin USDMF includes data on Biotin's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Biotin USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Biotin suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Biotin Drug Master File in Japan (Biotin JDMF) empowers Biotin API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Biotin JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Biotin JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Biotin suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Biotin Drug Master File in Korea (Biotin KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Biotin. The MFDS reviews the Biotin KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Biotin KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Biotin KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Biotin API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Biotin suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Biotin CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Biotin Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Biotin CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Biotin EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Biotin to their clients by showing that a Biotin CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Biotin CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Biotin CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Biotin CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Biotin DMF.
A Biotin CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Biotin CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Biotin suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Biotin as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Biotin API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Biotin as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Biotin and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Biotin NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Biotin suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Biotin Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Biotin GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Biotin GMP manufacturer or Biotin GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Biotin CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Biotin's compliance with Biotin specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Biotin CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Biotin CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Biotin may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Biotin EP), Biotin JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Biotin USP).
