
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
VMF
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
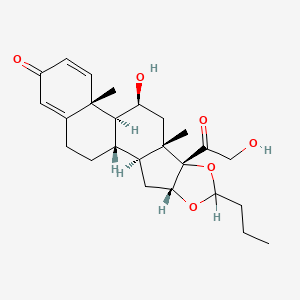

1. Budesonide, (r)-isomer
2. Budesonide, (s)-isomer
3. Horacort
4. Pulmicort
5. Rhinocort
6. Tarpeyo
1. Pulmicort
2. Entocort
3. Rhinocort
4. 51333-22-3
5. Preferid
6. Rhinocort Aqua
7. Entocort Ec
8. Uceris
9. Pulmicort Respules
10. Respules
11. Budeson
12. Pulmicort Flexhaler
13. Cortivent
14. Micronyl
15. Spirocort
16. Bidien
17. S-1320
18. Map-0010
19. Chebi:3207
20. Q3oks62q6x
21. 51372-29-3
22. Mls000028507
23. Budesonide Mmx
24. Budesonidum
25. Rhinocort Alpha
26. Map0010
27. R01ad05
28. (11beta,16alpha)-16,17-(butylidenebis(oxy))-11,21-dihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
29. 16a(r),17-(butylidenebis(oxy))-11b,21-dihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
30. Nsc-757788
31. Budenofalk
32. Budesonido
33. Smr000058337
34. Budecort Inhaler
35. Budesonidum [inn-latin]
36. Budesonido [inn-spanish]
37. (r)-budesonide
38. Inflammide
39. Budiair
40. Miflonide
41. Pulmaxan
42. Fvolir
43. 16,17-butylidenebis(oxy)-11,21-dihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
44. Budesonide [usan:inn:ban:jan]
45. Rhinocort Allergy
46. Pulmaxan Turbohaler
47. Pulmicort (tn)
48. Pulmicort Topinasal
49. Rhinocort (tn)
50. Pulmicort Turbuhaler
51. Budesonide Easyhaler
52. S 1320
53. Ccris 5230
54. Entocort Ec (tn)
55. Sr-01000000101
56. Einecs 257-139-7
57. Mfcd00083259
58. Unii-q3oks62q6x
59. Jorveza
60. Eltair
61. Ultesa
62. Noex
63. Giona Easyhaler
64. 16?,17-[(1rs)-butylidenebis(oxy)]-11?,21-dihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
65. Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 16,17-[butylidenebis(oxy)]-11,21-dihydroxy-, (11.beta.,16.alpha.)-
66. Prestwick_840
67. Uceris (tn)
68. Ortikos
69. (11-beta,16-alpha)-16,17-(butylidenebis(oxy))-11,21-dihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
70. 16-alpha,17-alpha-butylidenedioxy-11-beta,21-dihydroxy-1,4-pregnadiene-3,20-dione
71. (rs)-11beta,16alpha,17,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione Cyclic 16,17-acetal With Butyraldehyde
72. Budesonide, >=99%
73. Budesonide [mi]
74. Budesonide [inn]
75. Budesonide [jan]
76. Opera_id_1696
77. Prestwick0_000518
78. Prestwick1_000518
79. Prestwick2_000518
80. Prestwick3_000518
81. Budesonide [usan]
82. Budesonide [vandf]
83. Epitope Id:161750
84. B 7777
85. Schembl4096
86. (+)-16alpha,17alpha-butylidenedioxy-11beta,21-dihydroxy-1,4-pregnadiene-3,20-dione
87. Budesonide [usp-rs]
88. Budesonide [who-dd]
89. Chembl1370
90. Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione,16,17-(butylidenebis(oxy))-11,21-dihydroxy-, (11beta,16alpha)-
91. Lopac0_000174
92. Bspbio_000475
93. Budesonide (jan/usp/inn)
94. Mls001077323
95. Mls002207112
96. Spbio_002396
97. Bpbio1_000523
98. Gtpl7434
99. Budesonide [orange Book]
100. Dtxsid8020202
101. Hsdb 8279
102. Budesonide [ep Monograph]
103. Uceris Component Budesonide
104. Budesonide [usp Monograph]
105. Hms1569h17
106. Hms2096h17
107. Hms2232d17
108. Hms3259h07
109. Hms3260d09
110. Hms3413b08
111. Hms3413p17
112. Hms3677b08
113. Hms3677p17
114. Hms3713h17
115. Breztri Component Budesonide
116. (rs)-11.beta.,16.alpha.,17,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione Cyclic 16,17-acetal With Butyraldehyde
117. 5-hydroxy-6b-(hydroxyacetyl)-4a,6a-dimethyl-8-propyl-4a,4b,5,6,6a,6b,9a,10,10a,10b,11,12-dodecahydro-2h-naphtho[2',1':4,5]indeno[1,2-d][1,3]dioxol-2-one
118. Act03247
119. Bcp05589
120. Eohilia (budesonide Oral Suspension)
121. Tox21_500174
122. Bdbm50354850
123. Symbicort Component Budesonide
124. Budesonide Component Of Uceris
125. Akos015969655
126. Budesonide Component Of Breztri
127. Ac-4697
128. Ccg-204269
129. Cs-2063
130. Db01222
131. Ks-1162
132. Lp00174
133. Nc00626
134. Nsc 757788
135. Sdccgsbi-0050162.p002
136. 11beta,21-dihydroxy-16alpha,17alpha-(butane-1,1-diyldioxy)pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
137. Budesonide Component Of Symbicort
138. Ncgc00021318-05
139. Ncgc00021318-06
140. Ncgc00021318-08
141. Ncgc00021318-18
142. Ncgc00089747-04
143. Ncgc00260859-01
144. Bb164267
145. Budesonide 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
146. Cpd000058337
147. Hy-13580
148. Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 16,17-(butylidenebis(oxy))-11,21-dihydroxy-, (11-beta,16-alpha)-
149. Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 16,17-butylidenebis(oxy)-11,21-dihydroxy-, (11beta,16alpha(r))-, And 16alpha,17-((s)-butylidenebis(oxy))-11beta,21-dihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
150. B3909
151. Budesonide 100 Microg/ml In Methanol/water
152. Eu-0100174
153. D00246
154. T70986
155. 333b223
156. Q422212
157. J-504150
158. Q-101375
159. Sr-01000000101-2
160. Sr-01000000101-6
161. Brd-a34299591-001-03-4
162. Budesonide, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
163. Budesonide, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
164. Budesonide, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
165. (11?,16?)-16,17-[butylidenebis(oxy)]-11,21-dihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione
166. (1s,2s,4r,8s,9s,11s,12s,13r)-11-hydroxy-8-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-9,13-dimethyl-6-propyl-5,7-dioxapentacyclo[10.8.0.0^{2,9}.0^{4,8}.0^{13,18}]icosa-14,17-dien-16-one
167. (4ar,4bs,5s,6as,6bs,9ar,10as,10bs)-6b-glycoloyl-5-hydroxy-4a,6a-dimethyl-8-propyl-4a,4b,5,6,6a,6b,9a,10,10a,10b,11,12-dodecahydro-2h-naphtho[2',1':4,5]indeno[1,2-d][1,3]dioxol-2-one
168. (6ar,6bs,7s,8as,8bs,11ar,12as,12bs)-7-hydroxy-8b-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-6a,8a-dimethyl-10-propyl-1,2,6a,6b,7,8,8a,8b,11a,12,12a,12b-dodecahydro-4h-naphtho[2',1':4,5]indeno[1,2-d][1,3]dioxol-4-one
| Molecular Weight | 430.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C25H34O6 |
| XLogP3 | 2.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 430.23553880 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 430.23553880 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 93.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 862 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 8 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Budesonide |
| Drug Label | Budesonide, the active ingredient of ENTOCORT EC capsules, is a synthetic corticosteroid. It is designated chemically as (RS)-11, 16, 17,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione cyclic 16,17-acetal with butyraldehyde. Budesonide is provided a... |
| Active Ingredient | Budesonide |
| Dosage Form | Spray, metered; Capsule; Solution; Suspension |
| Route | Nasal; Inhalation; Topical foam; Oral |
| Strength | 0.032mg/inh; 1mg/2ml; 0.5mg/2ml; 2mg; 3mg; 0.25mg/2ml |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Watson Labs; Barr Labs Div Teva; Teva Pharms; Apotex; Salix Pharms; Sandoz; Mylan |
| 2 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Entocort ec |
| PubMed Health | Budesonide |
| Drug Classes | Anti-Inflammatory, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent, Gastrointestinal Agent |
| Drug Label | Budesonide, the active ingredient of ENTOCORT EC capsules, is a synthetic corticosteroid. It is designated chemically as (RS)-11, 16, 17,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione cyclic 16,17-acetal with butyraldehyde. Budesonide is provided a... |
| Active Ingredient | Budesonide |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 3mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astrazeneca |
| 3 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Pulmicort flexhaler |
| PubMed Health | Budesonide |
| Drug Classes | Anti-Inflammatory, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent, Gastrointestinal Agent |
| Drug Label | Budesonide, the active component of PULMICORT FLEXHALER, is a corticosteroid designated chemically as (RS)-11, 16, 17,21-Tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione cyclic 16,17-acetal with butyraldehyde. Budesonide is provided as a mixture of two ep... |
| Active Ingredient | Budesonide |
| Dosage Form | Powder, metered |
| Route | Inhalation |
| Strength | 0.16mg/inh; 0.08mg/inh |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astrazeneca |
| 4 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Pulmicort respules |
| Drug Label | Budesonide, the active component of PULMICORT RESPULES, is a corticosteroid designated chemically as (RS)-11, 16, 17, 21-tetrahydroxypregna-1, 4-diene-3, 20-dione cyclic 16, 17-acetal with butyraldehyde. Budesonide is provided as a mixture of t... |
| Active Ingredient | Budesonide |
| Dosage Form | Suspension |
| Route | Inhalation |
| Strength | 0.5mg/2ml; 0.25mg/2ml; 1mg/2ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astrazeneca |
| 5 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Rhinocort |
| PubMed Health | Budesonide/Formoterol (By breathing) |
| Drug Classes | Antiasthma, Anti-Inflammatory/Bronchodilator Combination, Respiratory Agent |
| Drug Label | Budesonide, the active ingredient of RHINOCORT AQUA Nasal Spray, is an anti-inflammatory synthetic corticosteroid.It is designated chemically as (RS)-11-beta, 16-alpha, 17, 21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione cyclic 16, 17-acetal with butyrald... |
| Active Ingredient | Budesonide |
| Dosage Form | Spray, metered |
| Route | Nasal |
| Strength | 0.032mg/inh |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astrazeneca |
| 6 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Symbicort |
| PubMed Health | Budesonide |
| Drug Classes | Anti-Inflammatory, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent, Gastrointestinal Agent |
| Active Ingredient | formoterol fumarate dihydrate; Budesonide |
| Dosage Form | Aerosol, metered |
| Route | Inhalation |
| Strength | 0.16mg/inh; 0.08mg/inh; 0.0045mg/inh |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astrazeneca |
| 7 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Uceris |
| PubMed Health | Budesonide |
| Drug Classes | Anti-Inflammatory, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent, Gastrointestinal Agent |
| Drug Label | UCERIS (budesonide) extended release tablets, for oral administration, contain budesonide, a synthetic corticosteroid, as the active ingredient. Budesonide is designated chemically as (RS)-11, 16, 17,21 tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione cyc... |
| Active Ingredient | Budesonide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 9mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Santarus |
| 8 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Budesonide |
| Drug Label | Budesonide, the active ingredient of ENTOCORT EC capsules, is a synthetic corticosteroid. It is designated chemically as (RS)-11, 16, 17,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione cyclic 16,17-acetal with butyraldehyde. Budesonide is provided a... |
| Active Ingredient | Budesonide |
| Dosage Form | Spray, metered; Capsule; Solution; Suspension |
| Route | Nasal; Inhalation; Topical foam; Oral |
| Strength | 0.032mg/inh; 1mg/2ml; 0.5mg/2ml; 2mg; 3mg; 0.25mg/2ml |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval; Prescription |
| Company | Watson Labs; Barr Labs Div Teva; Teva Pharms; Apotex; Salix Pharms; Sandoz; Mylan |
| 9 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Entocort ec |
| PubMed Health | Budesonide |
| Drug Classes | Anti-Inflammatory, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent, Gastrointestinal Agent |
| Drug Label | Budesonide, the active ingredient of ENTOCORT EC capsules, is a synthetic corticosteroid. It is designated chemically as (RS)-11, 16, 17,21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione cyclic 16,17-acetal with butyraldehyde. Budesonide is provided a... |
| Active Ingredient | Budesonide |
| Dosage Form | Capsule |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 3mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astrazeneca |
| 10 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Pulmicort flexhaler |
| PubMed Health | Budesonide |
| Drug Classes | Anti-Inflammatory, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent, Gastrointestinal Agent |
| Drug Label | Budesonide, the active component of PULMICORT FLEXHALER, is a corticosteroid designated chemically as (RS)-11, 16, 17,21-Tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione cyclic 16,17-acetal with butyraldehyde. Budesonide is provided as a mixture of two ep... |
| Active Ingredient | Budesonide |
| Dosage Form | Powder, metered |
| Route | Inhalation |
| Strength | 0.16mg/inh; 0.08mg/inh |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astrazeneca |
| 11 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Pulmicort respules |
| Drug Label | Budesonide, the active component of PULMICORT RESPULES, is a corticosteroid designated chemically as (RS)-11, 16, 17, 21-tetrahydroxypregna-1, 4-diene-3, 20-dione cyclic 16, 17-acetal with butyraldehyde. Budesonide is provided as a mixture of t... |
| Active Ingredient | Budesonide |
| Dosage Form | Suspension |
| Route | Inhalation |
| Strength | 0.5mg/2ml; 0.25mg/2ml; 1mg/2ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astrazeneca |
| 12 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Rhinocort |
| PubMed Health | Budesonide/Formoterol (By breathing) |
| Drug Classes | Antiasthma, Anti-Inflammatory/Bronchodilator Combination, Respiratory Agent |
| Drug Label | Budesonide, the active ingredient of RHINOCORT AQUA Nasal Spray, is an anti-inflammatory synthetic corticosteroid.It is designated chemically as (RS)-11-beta, 16-alpha, 17, 21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione cyclic 16, 17-acetal with butyrald... |
| Active Ingredient | Budesonide |
| Dosage Form | Spray, metered |
| Route | Nasal |
| Strength | 0.032mg/inh |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astrazeneca |
| 13 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Symbicort |
| PubMed Health | Budesonide |
| Drug Classes | Anti-Inflammatory, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent, Gastrointestinal Agent |
| Active Ingredient | formoterol fumarate dihydrate; Budesonide |
| Dosage Form | Aerosol, metered |
| Route | Inhalation |
| Strength | 0.16mg/inh; 0.08mg/inh; 0.0045mg/inh |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Astrazeneca |
| 14 of 14 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Uceris |
| PubMed Health | Budesonide |
| Drug Classes | Anti-Inflammatory, Endocrine-Metabolic Agent, Gastrointestinal Agent |
| Drug Label | UCERIS (budesonide) extended release tablets, for oral administration, contain budesonide, a synthetic corticosteroid, as the active ingredient. Budesonide is designated chemically as (RS)-11, 16, 17,21 tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione cyc... |
| Active Ingredient | Budesonide |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, extended release |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 9mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Santarus |
Anti-Inflammatory Agents; Bronchodilator Agents; Glucocorticoids
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Budesonide. Online file (MeSH, 2015). Available from, as of November 20, 2015: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/MBrowser.html
/CLINICAL TRIALS/ ClinicalTrials.gov is a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world. The Web site is maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Each ClinicalTrials.gov record presents summary information about a study protocol and includes the following: Disease or condition; Intervention (for example, the medical product, behavior, or procedure being studied); Title, description, and design of the study; Requirements for participation (eligibility criteria); Locations where the study is being conducted; Contact information for the study locations; and Links to relevant information on other health Web sites, such as NLM's MedlinePlus for patient health information and PubMed for citations and abstracts for scholarly articles in the field of medicine. Budesonide is included in the database.
NIH/NLM; ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available from, as of September 30, 2015: https://clinicaltrials.gov/search/intervention=budesonide
Budesonide capsules (enteric coated) are indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate active Crohn's disease involving the ileum and/or the ascending colon. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Budesonide (Budesonide) Capsule (Updated: March 2014). Available from, as of November 20, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=4a578d93-087e-42f7-a258-a49afef41dea
Budesonide capsules (enteric coated) are indicated for the maintenance of clinical remission of mild to moderate Crohn's disease involving the ileum and/or the ascending colon for up to 3 months. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Budesonide (Budesonide) Capsule (Updated: March 2014). Available from, as of November 20, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=4a578d93-087e-42f7-a258-a49afef41dea
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Budesonide (13 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Intranasal budesonide therapy should be used with caution, if at all, in patients with clinical or asymptomatic Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections of the respiratory tract, untreated fungal or bacterial infections, or ocular herpes simplex or untreated, systemic viral infections.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 2810
Localized candidal infections of the nose and/or pharynx have occurred rarely during intranasal budesonide therapy. When infection occurs, appropriate local or systemic treatment of the infection may be necessary, and/or discontinuance of intranasal budesonide therapy may be required. Patients receiving the drug for several months or longer should be examined periodically for candidal infections or changes in the nasal mucosa. Nasal septum perforation and increased intraocular pressure (IOP) have been reported rarely in patients receiving budesonide nasal spray. Because corticosteroid therapy may inhibit wound healing, patients with recent nasal septum ulcers, nasal surgery, or nasal trauma should not use nasal corticosteroids until healing has occurred.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 2810
Patients who are taking immunosuppressant drugs have increased susceptibility to infections compared with healthy individuals, and certain infections (e.g., varicella [chickenpox], measles) can have a more serious or even fatal outcome in such patients, particularly in children. In patients who have not had these diseases, particular care should be taken to avoid exposure. It is not known how the dosage, route, and duration of administration of a corticosteroid or the contribution of the underlying disease and/or prior corticosteroid therapy affect the risk of developing a disseminated infection. If exposure to varicella (chickenpox) or measles occurs in such individuals, administration of varicella zoster immune globulin (VZIG) or pooled IM immune globulin (IG) respectively, may be initiated. If varicella (chickenpox) develops, treatment with an antiviral agent may be considered.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 2810
Adverse effects of budesonide occurring in 2% or more of patients receiving budesonide nasal spray and with an incidence more frequent than that of placebo include epistaxis, pharyngitis, bronchospasm, cough, and nasal irritation.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 2810
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Budesonide (17 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Budesonide extended release capsules are indicated for the treatment and maintenance of mild to moderate Crohns disease. Various inhaled budesonide products are indicated for prophylactic therapy in asthma and reducing exacerbations of COPD. A budesonide nasal spray is available over the counter for symptoms of hay fever and upper respiratory allergies. Extended-release capsules are indicated to induce remission of mild to moderate ulcerative colitis and a rectal foam is used for mild to moderate distal ulcerative colitis. In addition, a delayed-release capsule formulation of budesonide is indicated to reduce proteinuria in adults with IgA nephropathy at risk of rapid disease progression.
FDA Label
Jorveza is indicated for the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) in adults (older than 18 years of age).
Treatment of asthma
Treatment of asthma
Prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Treatment of primary IgA nephropathy
Kinpeygo is indicated for the treatment of primary immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy (IgAN) in adults at risk of rapid disease progression with a urine protein-to-creatinine ratio (UPCR) 1. 5 g/gram.
Budesonide is a glucocorticoid used to treat respiratory and digestive conditions by reducing inflammation. It has a wide therapeutic index, as dosing varies highly from patient to patient. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of hypercorticism and adrenal axis suppression.
Bronchodilator Agents
Agents that cause an increase in the expansion of a bronchus or bronchial tubes. (See all compounds classified as Bronchodilator Agents.)
Anti-Inflammatory Agents
Substances that reduce or suppress INFLAMMATION. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Inflammatory Agents.)
Glucocorticoids
A group of CORTICOSTEROIDS that affect carbohydrate metabolism (GLUCONEOGENESIS, liver glycogen deposition, elevation of BLOOD SUGAR), inhibit ADRENOCORTICOTROPIC HORMONE secretion, and possess pronounced anti-inflammatory activity. They also play a role in fat and protein metabolism, maintenance of arterial blood pressure, alteration of the connective tissue response to injury, reduction in the number of circulating lymphocytes, and functioning of the central nervous system. (See all compounds classified as Glucocorticoids.)
A07EA06
A07EA06
A07EA06
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A07 - Antidiarrheals, intestinal antiinflammatory/antiinfective agents
A07E - Intestinal antiinflammatory agents
A07EA - Corticosteroids acting locally
A07EA06 - Budesonide
D - Dermatologicals
D07 - Corticosteroids, dermatological preparations
D07A - Corticosteroids, plain
D07AC - Corticosteroids, potent (group iii)
D07AC09 - Budesonide
R - Respiratory system
R01 - Nasal preparations
R01A - Decongestants and other nasal preparations for topical use
R01AD - Corticosteroids
R01AD05 - Budesonide
R - Respiratory system
R03 - Drugs for obstructive airway diseases
R03B - Other drugs for obstructive airway diseases, inhalants
R03BA - Glucocorticoids
R03BA02 - Budesonide
Absorption
Extended release oral capsules are 9-21% bioavailable. A 9mg dose reaches a Cmax of 1.500.79ng/mL with a Tmax of 2-8h and an AUC of 7.33ng\*hr/mL. A high fat meal increases the Tmax by 2.3h but otherwise does not affect the pharmacokinetics of budesonide. 180-360g metered inhaled doses of budesonide are 34% deposited in the lungs, 39% bioavailable, and reach a Cmax of 0.6-1.6nmol/L with a Tmax of 10 minutes. A 1mg nebulized dose is 6% bioavailable, reaching a Cmax of 2.6nmol/L with a Tmax of 20 minutes. A 9mg oral extended release tablet reaches a Cmax of 1.350.96ng/mL with a Tmax of 13.35.9h and an AUC of 16.4310.52ng\*hr/mL. Budesonide rectal foam 2mg twice daily has an AUC of 4.31ng\*hr/mL.
Route of Elimination
Approximately 60% of a budesonide dose is recovered in the urine as the major metabolites 6beta-hydroxybudesonide, 16alpha-hydroxyprednisolone, and their conjugates. No unchanged budesonide is recovered in urine.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of budesonide is 2.2-3.9L/kg.
Clearance
Budesonide has a plasma clearance of 0.9-1.8L/min. The 22R form has a clearance of 1.4L/min while the 22S form has a clearance of 1.0L/min. The clearance in asthmatic children 4-6 years old is 0.5L/min.
/MILK/ Not known whether budesonide is distributed in milk.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 2810
When budesonide is administered intranasally, approximately 34% of a dose reaches systemic circulation. Mean peak plasma budesonide concentrations are achieved in about 0.7 hours.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 2810
Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) are mainstay treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. However, highly lipophilic ICS accumulate in systemic tissues, which may lead to adverse systemic effects. The accumulation of a new, highly lipophilic ICS, ciclesonide and its active metabolite (des-CIC) has not yet been reported. Here, we have compared tissue accumulation of des-CIC and an ICS of a moderate lipophilicity, budesonide (BUD), after 14 days of once-daily treatment in mice. Single, three or 14 daily doses of [(3) H]-des-CIC or [(3) H]-BUD were administered subcutaneously to male CD1 albino mice, which were killed at 4 hrs, 24 hrs or 5 days after the last dose. Distribution of tissue concentration of radioactivity was studied by quantitative whole-body autoradiography. Pattern of radioactivity distribution across most tissues was similar for both corticosteroids after a single as well as after repeated dosing. However, tissue concentration of radioactivity differed between des-CIC and BUD. After a single dose, concentrations of radioactivity for both corticosteroids were low for most tissues but increased over 14 days of daily dosing. The tissue radioactivity of des-CIC at 24 hrs and 5 days after the 14th dose was 2-3 times higher than that of BUD in majority of tissues. Tissue accumulation, assessed as concentration of tissue radioactivity 5 days after the 14th versus 3rd dose, showed an average ratio of 5.2 for des-CIC and 2.7 for BUD (p < 0.0001). In conclusion, des-CIC accumulated significantly more than BUD. Systemic accumulation may lead to increased risk of adverse systemic side effects during long-term therapy.
PMID:23256845 Mars U et al; Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 112(6): 401-11 (2013).
Budesonide is 80-90% metabolized at first pass. Budesonide is metabolized by CYP3A to its 2 major metabolites, 6beta-hydroxybudesonide and 16alpha-hydroxyprednisolone. The glucocorticoid activity of these metabolites is negligible (<1/100) in relation to that of the parent compound. CYP3A4 is the strongest metabolizer of budesonide, followed by CYP3A5, and CYP3A7.
Budesonide is metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P-450 (CYP) isoenzyme 3A4; the 2 main metabolites have less than 1% of affinity for glucocorticoid receptors than the parent compound. Budesonide is excreted in urine and feces as metabolites.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 2810
Asthma is one of the most prevalent diseases in the world, for which the mainstay treatment has been inhaled glucocorticoids (GCs). Despite the widespread use of these drugs, approximately 30% of asthma sufferers exhibit some degree of steroid insensitivity or are refractory to inhaled GCs. One hypothesis to explain this phenomenon is interpatient variability in the clearance of these compounds. The objective of this research is to determine how metabolism of GCs by the CYP3A family of enzymes could affect their effectiveness in asthmatic patients. In this work, the metabolism of four frequently prescribed inhaled GCs, triamcinolone acetonide, flunisolide, budesonide, and fluticasone propionate, by the CYP3A family of enzymes was studied to identify differences in their rates of clearance and to identify their metabolites. Both interenzyme and interdrug variability in rates of metabolism and metabolic fate were observed. CYP3A4 was the most efficient metabolic catalyst for all the compounds, and CYP3A7 had the slowest rates. CYP3A5, which is particularly relevant to GC metabolism in the lungs, was also shown to efficiently metabolize triamcinolone acetonide, budesonide, and fluticasone propionate. In contrast, flunisolide was only metabolized via CYP3A4, with no significant turnover by CYP3A5 or CYP3A7. Common metabolites included 6 Beta-hydroxylation and Delta (6)-dehydrogenation for triamcinolone acetonide, budesonide, and flunisolide. The structure of Delta (6)-flunisolide was unambiguously established by NMR analysis. Metabolism also occurred on the D-ring substituents, including the 21-carboxy metabolites for triamcinolone acetonide and flunisolide. The novel metabolite 21-nortriamcinolone acetonide was also identified by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and NMR analysis.
PMID:23143891 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3558858 Moore CD et al; Drug Metab Dispos 41(2): 379-89 (2013).
Budesonide has a plasma elimination half life of 2-3.6h. The terminal elimination half life in asthmatic children 4-6 years old is 2.3h.
The short term effects of corticosteroids are decreased vasodilation and permeability of capillaries, as well as decreased leukocyte migration to sites of inflammation. Corticosteroids binding to the glucocorticoid receptor mediates changes in gene expression that lead to multiple downstream effects over hours to days. Glucocorticoids inhibit neutrophil apoptosis and demargination; they inhibit phospholipase A2, which decreases the formation of arachidonic acid derivatives; they inhibit NF-Kappa B and other inflammatory transcription factors; they promote anti-inflammatory genes like interleukin-10. Lower doses of corticosteroids provide an anti-inflammatory effect, while higher doses are immunosuppressive. High doses of glucocorticoids for an extended period bind to the mineralocorticoid receptor, raising sodium levels and decreasing potassium levels.
To investigate the roles of signal transduction and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) and orosomucoid 1-like 3 (ORMDL3) in airway remodeling among asthmatic mice and to observe the effects of budesonide (BUD) on their expression, thirty mice were randomly divided into control, asthma, and BUD intervention group. The mice were sensitized and challenged with ovalbumin (OVA) to establish a mouse model of asthma. The BUD intervention group received aerosol inhalation of BUD dissolved in normal saline 30 minutes before each OVA challenge, while normal saline was used instead of OVA solution in the control group. The pathological changes in the airway were observed by hematoxylin-eosin staining and Masson staining. The interleukin-13 (IL-13) level in lung homogenate was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The mRNA expression of STAT6 and ORMDL3 was measured by RT-PCR. The asthma group showed more pathological changes in the airway than the control and BUD intervention groups, and the BUD intervention group had reduced pathological changes in the airway compared with the asthma group. The asthma and BUD intervention groups had significantly higher IL-13 levels and mRNA expression of STAT6 and ORMDL3 than the control group (P<0.05), and these indices were significantly higher in the asthma group than in the BUD intervention group (P<0.05). The Pearson correlation analysis showed that STAT6 mRNA expression was positively correlated with ORMDL3 mRNA expression (r=0.676, P=0.032). STAT6 and ORMDL3 may be involved in the airway remodeling of mice, and BUD can reduce airway remodeling in asthmatic mice, possibly by down-regulating mRNA expression of STAT6 and ORMDL3.
PMID:24568918 Zou LP et al; Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 16(2): 198-202 (2014).
Mucus hypersecretion from airway epithelium is a characteristic feature of severe asthma. Glucocorticoids (GCs) may suppress mucus production and diminish the harmful airway obstruction. We investigated the ability of GCs to suppress mRNA expression and protein synthesis of a gene encoding mucin, MUC5AC, induced by transforming growth factor (TGF)-alpha in human mucoepidermoid carcinoma (NCI-H292) cells and the molecular mechanisms underlying the suppression. We determined if GCs such as dexamethasone (DEX), budesonide (BUD), and fluticasone (FP) could suppress MUC5AC production induced by a combination of TGF-alpha and double-strand RNA, polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid (polyI:C). MUC5AC mRNA expression and MUC5AC protein production were evaluated. The signaling pathways activated by TGF-alpha and their inhibition by GCs were tested using a phosphoprotein assay and MUC5AC promoter assay. DEX significantly suppressed the expression of MUC5AC mRNA and MUC5AC protein induced by TGF-alpha. The activation of the MUC5AC promoter by TGF-alpha was significantly inhibited by DEX. DEX did not affect activation of downstream pathways of the EGF receptor or mRNA stability of MUC5AC transcripts. DEX, BUD, and FP suppressed MUC5AC protein expression induced by a combination of TGF-alpha and polyI:C in a dose-dependent manner. GCs inhibited MUC5AC production induced by TGF-alpha alone or a combination of TGF-alpha and polyI:C; the repression may be mediated at the transcriptional but not post-transcriptional level.
PMID:22824974 Takami S et al; Allergol Int 61(3): 451-9 (2012).

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS

Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ANALYTICAL

ABOUT THIS PAGE
50
PharmaCompass offers a list of Budesonide API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Budesonide manufacturer or Budesonide supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Budesonide manufacturer or Budesonide supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Budesonide API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Budesonide API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Budesonide Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Budesonide Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Budesonide manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Budesonide, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Budesonide manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Budesonide API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Budesonide manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Budesonide supplier is an individual or a company that provides Budesonide active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Budesonide finished formulations upon request. The Budesonide suppliers may include Budesonide API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Budesonide suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Budesonide DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Budesonide active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Budesonide DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Budesonide USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Budesonide DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Budesonide USDMF includes data on Budesonide's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Budesonide USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Budesonide suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Budesonide Drug Master File in Japan (Budesonide JDMF) empowers Budesonide API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Budesonide JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Budesonide JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Budesonide suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Budesonide Drug Master File in Korea (Budesonide KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Budesonide. The MFDS reviews the Budesonide KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Budesonide KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Budesonide KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Budesonide API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Budesonide suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Budesonide CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Budesonide Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Budesonide CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Budesonide EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Budesonide to their clients by showing that a Budesonide CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Budesonide CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Budesonide CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Budesonide CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Budesonide DMF.
A Budesonide CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Budesonide CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Budesonide suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
A Budesonide written confirmation (Budesonide WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Budesonide manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Budesonide active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Budesonide APIs or Budesonide finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Budesonide WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Budesonide suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Budesonide as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Budesonide API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Budesonide as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Budesonide and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Budesonide NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Budesonide suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Budesonide Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Budesonide GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Budesonide GMP manufacturer or Budesonide GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Budesonide CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Budesonide's compliance with Budesonide specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Budesonide CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Budesonide CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Budesonide may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Budesonide EP), Budesonide JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Budesonide USP).
