
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
VMF
0
Canada

0
Australia

DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
Annual Reports
NA
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
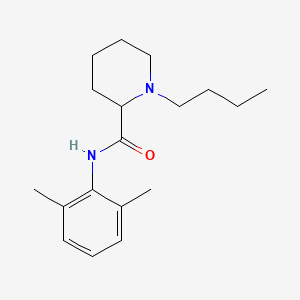

1. 1-butyl-n-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-piperidinecarboxamide
2. Bupivacain Janapharm
3. Bupivacain Rpr
4. Bupivacain-rpr
5. Bupivacaina Braun
6. Bupivacaine Anhydrous
7. Bupivacaine Carbonate
8. Bupivacaine Hydrochloride
9. Bupivacaine Monohydrochloride, Monohydrate
10. Buvacaina
11. Carbostesin
12. Dolanaest
13. Marcain
14. Marcaine
15. Sensorcaine
16. Svedocain Sin Vasoconstr
1. 1-butyl-n-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide
2. 2180-92-9
3. Dl-bupivacaine
4. 38396-39-3
5. Marcaine
6. Bupivacaina
7. Anekain
8. (+-)-bupivacaine
9. Bupivacainum
10. Sensorcaine
11. 1-butyl-2',6'-pipecoloxylidide
12. Exparel
13. Bupivacainum [inn-latin]
14. Bupivacaina [inn-spanish]
15. Dl-1-butyl-2',6'-pipecoloxylidide
16. Bucaine
17. 2-piperidinecarboxamide, 1-butyl-n-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-
18. Ah 250
19. Win 11318
20. Bloqueina
21. (+/-)-bupivacaine
22. 1-butyl-n-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-piperidinecarboxamide
23. Posimir
24. Sky0402
25. 2',6'-pipecoloxylidide, 1-butyl-
26. 1-butyl-n-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-piperidine-2-carboxamide
27. Marcain
28. Liq865
29. (1)-1-butyl-n-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide
30. Chebi:77431
31. Liq-865
32. Sky-0402
33. Xaracoll
34. Lac-43
35. Y8335394ro
36. Cbupivacaine
37. Bupivacaine Hcl Kit
38. Bupivacaine Base
39. (r)-bupivacaine Hcl
40. Bucaine (tn)
41. Dur-843
42. Einecs 218-553-3
43. Einecs 253-911-2
44. Bupivacaine [usan:inn:ban]
45. Unii-y8335394ro
46. Hsdb 7790
47. Racemic Bupivacaine
48. (rs)-bupivacaine
49. Bupivacaine Liposome
50. Sky 0402
51. Exparel (tn)
52. Liposomal Bupivacaine
53. Bupivacaine Free Base
54. Bupivacaine-[13c]
55. Spectrum_001524
56. Bupivacaine Liposome Injectable Suspension
57. Marcaine And Sensorcaine
58. Bupivacaine [mi]
59. Prestwick0_000305
60. Prestwick1_000305
61. Prestwick2_000305
62. Prestwick3_000305
63. Spectrum2_001589
64. Spectrum3_000974
65. Spectrum4_001098
66. Spectrum5_001483
67. Bupivacaine [inn]
68. (.+/-.)-1-butyl-2',6'-pipecoloxylidide
69. (.+/-.)-bupivacaine
70. Bupivacaine (usan/inn)
71. Bupivacaine [hsdb]
72. Bupivacaine [usan]
73. Lac-43 (salt/mix)
74. Epitope Id:122662
75. Bupivacaine [vandf]
76. Marcaine Spinal (salt/mix)
77. Chembl1098
78. Schembl25438
79. Bspbio_000270
80. Bspbio_002607
81. Bupivacaine [who-dd]
82. Kbiogr_001516
83. Kbioss_002004
84. Divk1c_000758
85. Spbio_001558
86. Spbio_002489
87. Bpbio1_000298
88. Chebi:3215
89. Gtpl2397
90. Bupivacaine [green Book]
91. Dtxsid2022703
92. Kbio1_000758
93. Kbio2_002004
94. Kbio2_004572
95. Kbio2_007140
96. Kbio3_001827
97. Bupivacaine [orange Book]
98. Dl-1-butyl-2,6-pipecoloxylidide
99. Ninds_000758
100. 1-butyl-n-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-piperidinecarboximidic Acid
101. Ah250
102. Hms2090f12
103. Hms3428p06
104. Marcaine Hydrochloride (salt/mix)
105. 1217442-06-2
106. 3-ethyl-2-methylbenzoxazoliumiodide
107. Bcp12242
108. Bcp21825
109. Hy-b0405
110. 2-piperidinecarboxamide, 1-butyl-n-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-, (+-)-
111. Ah-250
112. Bdbm50350790
113. Mfcd00243007
114. Stl484283
115. Zynrelef Component Bupivacaine
116. Akos001637202
117. Akos016842516
118. Ac-2096
119. Bs-5224
120. Cs-w023182
121. Db00297
122. Bupivacaine Component Of Zynrelef
123. Idi1_000758
124. Ncgc00178579-01
125. Ncgc00178579-02
126. Bb166160
127. Sbi-0051846.p002
128. Db-119016
129. Ab00053674
130. Ft-0623286
131. Ft-0660567
132. Ft-0699781
133. Ft-0771900
134. C07529
135. D07552
136. Ropivacaine Hydrochloride Impurity, Bupivacaine-
137. Ab00053674-08
138. Ab00053674-09
139. Ab00053674_10
140. Ab00053674_11
141. 180b929
142. A873847
143. L000695
144. Q422806
145. Q-100271
146. Brd-a01636364-003-05-2
147. Brd-a01636364-003-08-6
148. (plusmn)-1-butyl-n-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide
149. 2-piperidinecarboxamide, 1-butyl-n-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-, (+/-)-
150. 2-piperidinecarboxamide, 1-butyl-n-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-, (.+/-.)-
151. Ropivacaine Hydrochloride Impurity, Bupivacaine- [usp Impurity]
152. 119427-31-5
| Molecular Weight | 288.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H28N2O |
| XLogP3 | 3.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 288.220163521 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 288.220163521 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 32.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 321 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Exparel |
| PubMed Health | Bupivacaine Liposome (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Anesthetic, Local |
| Drug Label | EXPAREL is a sterile, non-pyrogenic white to off-white preservative-free aqueous suspension of multivesicular liposomes (DepoFoam drug delivery system) containing bupivacaine. Bupivacaine is present at a concentration of 13.3 mg/mL. After injection... |
| Active Ingredient | Bupivacaine |
| Dosage Form | Injectable, liposomal |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 266mg/20ml (13.3mg/ml) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pacira Pharms |
| 2 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Marcaine |
| PubMed Health | Bupivacaine/Epinephrine (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Anesthetic, Amino Amide Combination, Anesthetic, Local |
| Drug Label | MarcaineBupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection, USPMarcaineWith Epinephrine 1:200,000 (as bitartrate)Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection, USP Rx onlyBupivacaine hydrochloride is 2-Piperidinecarboxamide, 1-butyl-N-(2,6-dimethylpheny... |
| Active Ingredient | Bupivacaine hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Spinal |
| Strength | 0.75% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira |
| 3 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Sensorcaine |
| PubMed Health | Bupivacaine (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Anesthetic, Local |
| Drug Label | Sensorcaine (bupivacaine HCl) injections are sterile isotonic solutions that contain a local anesthetic agent with and without epinephrine (as bitartrate) 1:200,000 and are administered parenterally by injection. See INDICATIONS AND USAGE for spe... |
| Active Ingredient | Bupivacaine hydrochloride; epinephrine bitartrate |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Spinal; Injection |
| Strength | 0.5%; 0.0091mg/ml; 0.75%; 0.25% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Fresenius Kabi Usa |
| 4 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Exparel |
| PubMed Health | Bupivacaine Liposome (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Anesthetic, Local |
| Drug Label | EXPAREL is a sterile, non-pyrogenic white to off-white preservative-free aqueous suspension of multivesicular liposomes (DepoFoam drug delivery system) containing bupivacaine. Bupivacaine is present at a concentration of 13.3 mg/mL. After injection... |
| Active Ingredient | Bupivacaine |
| Dosage Form | Injectable, liposomal |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 266mg/20ml (13.3mg/ml) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Pacira Pharms |
| 5 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Marcaine |
| PubMed Health | Bupivacaine/Epinephrine (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Anesthetic, Amino Amide Combination, Anesthetic, Local |
| Drug Label | MarcaineBupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection, USPMarcaineWith Epinephrine 1:200,000 (as bitartrate)Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection, USP Rx onlyBupivacaine hydrochloride is 2-Piperidinecarboxamide, 1-butyl-N-(2,6-dimethylpheny... |
| Active Ingredient | Bupivacaine hydrochloride |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Spinal |
| Strength | 0.75% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira |
| 6 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Sensorcaine |
| PubMed Health | Bupivacaine (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Anesthetic, Local |
| Drug Label | Sensorcaine (bupivacaine HCl) injections are sterile isotonic solutions that contain a local anesthetic agent with and without epinephrine (as bitartrate) 1:200,000 and are administered parenterally by injection. See INDICATIONS AND USAGE for spe... |
| Active Ingredient | Bupivacaine hydrochloride; epinephrine bitartrate |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Spinal; Injection |
| Strength | 0.5%; 0.0091mg/ml; 0.75%; 0.25% |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Fresenius Kabi Usa |
Bupivacaine hydrochloride is used for infiltration anesthesia and for peripheral, sympathetic nerve, and epidural (including caudal) block anesthesia. A 0.75% solution of the drug in 8.25% dextrose is used for spinal anesthesia. Bupivacaine is not used for obstetric paracervical block or topical anesthesia. /Use Included in US product label/
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 3334
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride is indicated for the production of local or regional anesthesia or analgesia for surgery, dental and oral surgery procedures, diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, and for obstetrical procedures. Only the 0.25% and 0.5% concentrations are indicated for obstetrical anesthesia. /Use Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE, injection, solution; BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE WITH EPINEPHRINE, injection, solution (August 2008). Available from, as of February 22, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=8962
The 0.75% solution of bupivacaine hydrochloride is no longer recommended for obstetric anesthesia, since use of this concentration for epidural anesthesia in obstetric patients has been associated with cardiac arrest with difficult resuscitation or death. Cardiac arrest has occurred after seizures resulting from systemic toxicity, apparently following inadvertent intravascular injection.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 3335
Local anesthetics should only be employed by clinicians who are well versed in diagnosis and management of dose-related toxicity and other acute emergencies which might arise from the block to be employed, and then only after insuring the immediate availability of oxygen, other resuscitative drugs, cardiopulmonary resuscitative equipment, and the personnel resources needed for proper management of toxic reactions and related emergencies. delay in proper management of dose-related toxicity, under ventilation from any cause, and/or altered sensitivity may lead to the development of acidosis, cardiac arrest and, possibly, death. /Local anesthetics/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE, injection, solution; BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE WITH EPINEPHRINE, injection, solution (August 2008). Available from, as of February 22, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=8962
Pending accumulation of further data on the use of the drug in pediatric patients, bupivacaine hydrochloride solutions should not be used in children younger than 12 years of age and the solution for spinal anesthesia should not be used in children younger than 18 years of age.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 3335
Some commercially available formulations of bupivacaine hydrochloride contain sodium metabisulfite, a sulfite that may cause allergic-type reactions, including anaphylaxis and life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes, in certain susceptible individuals. The overall prevalence of sulfite sensitivity in the general population is unknown but probably low; such sensitivity appears to occur more frequently in asthmatic than in nonasthmatic individuals.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 3335
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Bupivacaine (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Bupivacaine is indicated for the production of local or regional anesthesia or analgesia for surgery, for oral surgery procedures, for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, and for obstetrical procedures. Bupivacaine is indicated to induce post-surgical analgesia in adults for up to 72 hours following arthroscopic subacromial decompression by administration into the subacromial space under direct arthroscopic visualization. Bupivacaine, together with the NSAID [meloxicam], is indicated for the production of postsurgical analgesia in adult patients for up to 72 hours following bunionectomy, open inguinal herniorrhaphy or total knee arthroplasty.
FDA Label
Exparel is indicated as a brachial plexus block or femoral nerve block for treatment of post-operative pain in adults, and as a field block for treatment of somatic post-operative pain from small- to medium-sized surgical wounds in adults.
Postsurgical analgesia
Bupivacaine is a widely used local anesthetic agent. Bupivacaine is often administered by spinal injection prior to total hip arthroplasty. It is also commonly injected into surgical wound sites to reduce pain for up to 20 hours after surgery. In comparison to other local anesthetics it has a long duration of action. It is also the most toxic to the heart when administered in large doses. This problem has led to the use of other long-acting local anaesthetics:ropivacaine and levobupivacaine. Levobupivacaine is a derivative, specifically an enantiomer, of bupivacaine. Systemic absorption of local anesthetics produces effects on the cardiovascular and central nervous systems. At blood concentrations achieved with therapeutic doses, changes in cardiac conduction, excitability, refractoriness, contractility, and peripheral vascular resistance are minimal. However, toxic blood concentrations depress cardiac conduction and excitability, which may lead to atrioventricular block, ventricular arrhythmias and to cardiac arrest, sometimes resulting in fatalities. In addition, myocardial contractility is depressed and peripheral vasodilation occurs, leading to decreased cardiac output and arterial blood pressure. Following systemic absorption, local anesthetics can produce central nervous system stimulation, depression or both.
Anesthetics, Local
Drugs that block nerve conduction when applied locally to nerve tissue in appropriate concentrations. They act on any part of the nervous system and on every type of nerve fiber. In contact with a nerve trunk, these anesthetics can cause both sensory and motor paralysis in the innervated area. Their action is completely reversible. (From Gilman AG, et. al., Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 8th ed) Nearly all local anesthetics act by reducing the tendency of voltage-dependent sodium channels to activate. (See all compounds classified as Anesthetics, Local.)
N01BB01
N01BB01
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
N - Nervous system
N01 - Anesthetics
N01B - Anesthetics, local
N01BB - Amides
N01BB01 - Bupivacaine
Absorption
Systemic absorption of local anesthetics is dose- and concentration-dependendent on the total drug administered. Other factors that affect the rate of systemic absorption include the route of administration, blood flow at the administration site, and the presence or absence of epinephrine in the anesthetic solution. Bupivacaine formulated for instillation with [meloxicam] produced varied systemic measures following a single dose of varying strength. In patients undergoing bunionectomy, 60 mg of bupivacaine produced a Cmax of 54 33 ng/mL, a median Tmax of 3 h, and an AUC of 1718 1211 ng\*h/mL. For a 300 mg dose used in herniorrhaphy, the corresponding values were 271 147 ng/mL, 18 h, and 15,524 8921 ng\*h/mL. Lastly, a 400 mg dose used in total knee arthroplasty produced values of 695 411 ng/mL, 21 h, and 38,173 29,400 ng\*h/mL.
Route of Elimination
Only 6% of bupivacaine is excreted unchanged in the urine.
After absorption into the blood, bupivacaine hydrochloride is more highly bound to plasma proteins than are any other local anesthetics; bupivacaine is reportedly 82-96% bound. Bupivacaine hydrochloride has the lowest degree of placental transmission of parenteral local anesthetics and may cause the least fetal depression.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 3335
Pregnant rats received an intravenous infusion of bupivacaine at a rate of 0.33 mg. kg-1. min-1 over a period of 15 min. The fetuses were delivered either at the end of infusion or at 2 or 4 hr after dosing. Maternal and fetal blood and tissue samples were obtained for the assays of bupivacaine and its metabolites using capillary gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The elimination half-life of bupivacaine was 37.7 min. The major metabolite was 3'-hydroxybupivacaine. Bupivacaine and 3'-hydroxybupivacaine were present in all samples at the end of administration. The fetal to maternal concentration ratio of bupivacaine in plasma was 0.29, and in the placenta was 0.63. The amnion contained the highest bupivacaine concentration: threefold higher in the maternal and 11-fold higher than in the fetal plasma. At 4 hr after dosing, bupivacaine was no longer detectable in any maternal and fetal samples, whereas 3'-hydroxybupivacaine was still present in all tissues except the fetal plasma and heart. These data indicate that a considerable amount of bupivacaine is taken up by both sides of the placenta, as well as the amnion and myometrium. 3'-Hydroxybupivacaine was present in all tissues except the fetal plasma and heart samples, even after the parent compound became no longer detectable.
PMID:11020763 Morishima HO et al; Anesthesiology. 93 (4): 1069-74 (2000).
After injection of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride for caudal, epidural, or peripheral nerve block in man, peak levels of bupivacaine in the blood are reached in 30 to 45 minutes, followed by a decline to insignificant levels during the next three to six hours.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE, injection, solution; BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE WITH EPINEPHRINE, injection, solution (August 2008). Available from, as of February 22, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=8962
Pharmacokinetic studies on the plasma profile of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride after direct intravenous injection suggest a three-compartment open model. The first compartment is represented by the rapid intravascular distribution of the drug. The second compartment represents the equilibration of the drug throughout the highly perfused organs such as the brain, myocardium, lungs, kidneys, and liver. The third compartment represents an equilibration of the drug with poorly perfused tissues, such as muscle and fat. The elimination of drug from tissue distribution depends largely upon the ability of binding sites in the circulation to carry it to the liver where it is metabolized.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE, injection, solution; BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE WITH EPINEPHRINE, injection, solution (August 2008). Available from, as of February 22, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=8962
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Bupivacaine (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Amide-type local anesthetics such as bupivacaine are metabolized primarily in the liver via conjugation with glucuronic acid. The major metabolite of bupivacaine is 2,6-pipecoloxylidine, which is mainly catalyzed via cytochrome P450 3A4.
Pregnant rats received an intravenous infusion of bupivacaine at a rate of 0.33 mg. kg-1. min-1 over a period of 15 min. The fetuses were delivered either at the end of infusion or at 2 or 4 hr after dosing. Maternal and fetal blood and tissue samples were obtained for the assays of bupivacaine and its metabolites using capillary gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The elimination half-life of bupivacaine was 37.7 min. The major metabolite was 3'-hydroxybupivacaine. Bupivacaine and 3'-hydroxybupivacaine were present in all samples at the end of administration. The fetal to maternal concentration ratio of bupivacaine in plasma was 0.29, and in the placenta was 0.63. The amnion contained the highest bupivacaine concentration: threefold higher in the maternal and 11-fold higher than in the fetal plasma. At 4 hr after dosing, bupivacaine was no longer detectable in any maternal and fetal samples, whereas 3'-hydroxybupivacaine was still present in all tissues except the fetal plasma and heart. These data indicate that a considerable amount of bupivacaine is taken up by both sides of the placenta, as well as the amnion and myometrium. 3'-Hydroxybupivacaine was present in all tissues except the fetal plasma and heart samples, even after the parent compound became no longer detectable.
PMID:11020763 Morishima HO et al; Anesthesiology. 93 (4): 1069-74 (2000).
Bupivacaine hydrochloride is principally metabolized to pipecolylxylidine (PPX) by N-dealkylation, probably in the liver. Bupivacaine is excreted in urine as small amounts of PPX, unchanged drug (5%), and other metabolites as yet unidentified.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 3335
2.7 hours in adults and 8.1 hours in neonates. Bupivacaine applied together with [meloxicam] for postsurgical analgesia had a median half-life of 15-17 hours, depending on dose and application site.
Pregnant rats received an intravenous infusion of bupivacaine at a rate of 0.33 mg. kg-1. min-1 over a period of 15 min. The fetuses were delivered either at the end of infusion or at 2 or 4 hr after dosing. Maternal and fetal blood and tissue samples were obtained for the assays of bupivacaine and its metabolites using capillary gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The elimination half-life of bupivacaine was 37.7 min.
PMID:11020763 Morishima HO et al; Anesthesiology. 93 (4): 1069-74 (2000).
The elimination half-life of bupivacaine hydrochloride is 1.5-5.5 hours in adults and 8.1 hours in neonates.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 3335
Local anesthetics such as bupivacaine block the generation and the conduction of nerve impulses, presumably by increasing the threshold for electrical excitation in the nerve, by slowing the propagation of the nerve impulse, and by reducing the rate of rise of the action potential. Bupivacaine prevents depolarization by bindng to the intracellular portion of sodium channels and blocking sodium ion influx into neurons. In general, the progression of anesthesia is related to the diameter, myelination and conduction velocity of affected nerve fibers. Clinically, the order of loss of nerve function is as follows: (1) pain, (2) temperature, (3) touch, (4) proprioception, and (5) skeletal muscle tone. The analgesic effects of Bupivicaine are thought to potentially be due to its binding to the prostaglandin E2 receptors, subtype EP1 (PGE2EP1), which inhibits the production of prostaglandins, thereby reducing fever, inflammation, and hyperalgesia.
Local anesthetics block the generation and the conduction of nerve impulses, presumably by increasing the threshold for electrical excitation in the nerve, by slowing the propagation of the nerve impulse, and by reducing the rate of rise of the action potential. In general, the progression of anesthesia is related to the diameter, myelination, and conduction velocity of affected nerve fibers. Clinically, the order of loss of nerve function is as follows: (1) pain, (2) temperature, (3) touch, (4) proprioception, and (5) skeletal muscle tone.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE, injection, solution; BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE WITH EPINEPHRINE, injection, solution (August 2008). Available from, as of February 22, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?id=8962

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
93
PharmaCompass offers a list of Bupivacaine API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Bupivacaine manufacturer or Bupivacaine supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Bupivacaine manufacturer or Bupivacaine supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Bupivacaine API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Bupivacaine API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Bupivacaine Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Bupivacaine Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Bupivacaine manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Bupivacaine, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Bupivacaine manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Bupivacaine API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Bupivacaine manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Bupivacaine supplier is an individual or a company that provides Bupivacaine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Bupivacaine finished formulations upon request. The Bupivacaine suppliers may include Bupivacaine API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Bupivacaine suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Bupivacaine DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Bupivacaine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Bupivacaine DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Bupivacaine USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Bupivacaine DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Bupivacaine USDMF includes data on Bupivacaine's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Bupivacaine USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Bupivacaine suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Bupivacaine Drug Master File in Korea (Bupivacaine KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Bupivacaine. The MFDS reviews the Bupivacaine KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Bupivacaine KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Bupivacaine KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Bupivacaine API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Bupivacaine suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Bupivacaine as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Bupivacaine API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Bupivacaine as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Bupivacaine and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Bupivacaine NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Bupivacaine suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Bupivacaine Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Bupivacaine GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Bupivacaine GMP manufacturer or Bupivacaine GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Bupivacaine CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Bupivacaine's compliance with Bupivacaine specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Bupivacaine CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Bupivacaine CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Bupivacaine may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Bupivacaine EP), Bupivacaine JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Bupivacaine USP).
