
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
Australia

DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers

1. Aragonite
2. Calcite
3. Calcium Milk
4. Carbonate, Calcium
5. Chalk
6. Limestone
7. Marble
8. Milk Of Calcium
9. Vaterite
1. Aragonite
2. 471-34-1
3. Limestone
4. Calcite
5. Chalk
6. Carbonic Acid Calcium Salt (1:1)
7. Aeromatt
8. Calciumcarbonate
9. Calcium Carbonate (1:1)
10. Calofort U
11. Calcite (ca(co3))
12. Precipitated Calcium Carbonate
13. 1317-65-3
14. Marble Dust
15. Caco3
16. Calciumcarbonat
17. Glauberitum
18. Kalziumkarbonat
19. Calcitum
20. Calcium Carbonate Slurry
21. Hydrolyzed Pearl
22. Calcium Carbonate, Powder
23. Ci 77220
24. Han Shui Shi
25. Kohlensaurer Kalk
26. Limestone, Ground
27. Carbonato De Calcio
28. Chalk, Precipitated
29. Carbonate De Calcium
30. Phx Cal-carb Buffer
31. Calcium (as Carbonate)
32. Calcium Trioxidocarbonate
33. Calcium Carbonate [usp]
34. Carbonate (calcium)
35. Marble
36. Precpitated Calcium Carbonate
37. Kalkspar
38. Calcium (as Calcium Carbonate)
39. Chebi:3311
40. H0g9379fgk
41. Ins No.170(i)
42. Ins-170(i)
43. Mfcd00010906
44. Akadama
45. Albacar
46. Albafil
47. Albaglos
48. Atomite
49. Calcicoll
50. Calibrite
51. Calmote
52. Calseeds
53. Calwhite
54. Carbium
55. Chemcarb
56. Clefnon
57. Duramite
58. E-170(i)
59. Hydrocarb
60. Kotamite
61. Microcarb
62. Micromya
63. Neoanticid
64. Atomit
65. Calmos
66. Caltec
67. Dacote
68. Marfil
69. Levigated Chalk
70. Allied Whiting
71. Tums
72. Marble White
73. Calcium Carbonate (usp)
74. Camel-carb
75. Camel-wite
76. Camel-tex
77. Britomya M
78. Britomya S
79. Calofort S
80. Calofort T
81. Calopake F
82. Calopake H
83. Hakuenka O
84. Multiflex Mm
85. Multiflex Sc
86. Albaglos Sf
87. Calopake Fs
88. Calopake Pc
89. Carusis P
90. Garolite Sa
91. Gilder's Whiting
92. Hakuenka Cc
93. Hakuenka Dd
94. Hakuenka Px
95. Hakuenka Pz
96. Homocal D
97. Multifex Mm
98. Neolite F
99. Calcene Co
100. Calcene Nc
101. Calcene Tm
102. Carbium Mm
103. Hakuenka Ccr
104. Neolite Sp
105. Crystic Prefil S
106. Neolite Tps
107. Calcilit 8
108. Carborex 2
109. Cal-sup
110. Microwhite 25
111. R Jutan
112. Calcium Carbonate Nanopowder
113. Hakuenka T-dd
114. Brilliant 15
115. Filtex White Base
116. Hydrocarb 60
117. Hydrocarb 65
118. Marblewhite 325
119. Cal-light Sa
120. Calcidar 40
121. Carbital 90
122. Durcal 2nh
123. Non-fer-al
124. Ccc G-white
125. Kredafil Rm 5
126. Brilliant Br 15
127. Calofil A 4
128. Calofil B 1
129. Calofil E 2
130. C.i. Pigment White 18
131. Calcilit 100
132. Hakuenka R 06
133. Micromic Cr 16
134. Calcium Monocarbonate
135. Durcal 10
136. Durcal 40
137. Monocalcium Carbonate
138. Brilliant 1500
139. Calofor U 50
140. Calopake High Opacity
141. Ccc No.aa Oolitic
142. Eskalon 100
143. Eskalon 200
144. Eskalon 400
145. Eskalon 800
146. Finncarb 6002
147. C 50 (carbonate)
148. Kredafil 150 Extra
149. Albacar 5970
150. Caswell No. 139
151. Eskalon 1500
152. Msk-po
153. Msk-c
154. Msk-g
155. Msk-k
156. Msk-p
157. Msk-v
158. Ncc-p
159. Slaker Rejects
160. Mylanta Soothing Lozenges
161. Natural Calcium Carbonate
162. Oyster Shell
163. Ground Limestone
164. Mc-t
165. Calcium, Reference Standard Solution
166. Durcal C 640305
167. P-lite 500
168. P-lite 700
169. Di-gel Tablets
170. Carbonic Acid Calcium Salt
171. Precipitated Chalk
172. Egri M 5
173. Pigment White 18
174. Kulu 40
175. Calcium Carbonate, Precipitated
176. Brt 30
177. Ccris 1333
178. Hsdb 927
179. Ncc 45
180. Tylenol Headache Plus
181. Bs 32
182. Vaterite (ca(co3))
183. Brt 1500
184. Carbonic Acid, Calcium Salt (1:1)
185. Einecs 207-439-9
186. Ax 363
187. Bf 200
188. Ks 500
189. Ns 100
190. Ns 200
191. Ns 400
192. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 073502
193. Ks 1300
194. Ks 1500
195. Ks 1800
196. Ks 2100
197. Ns 2500
198. Unii-h0g9379fgk
199. N 34
200. N 43
201. Caltan
202. Calcii Carbonas
203. Kalk
204. Chalk Powder
205. Coral Calcium
206. Marble Chips
207. Carbonate Calcium
208. C.i. 77220
209. K 250
210. Calcium Carb Onate
211. Copper Nickel Foil
212. Marble, Cp
213. T 130-2500
214. Cal-sup (tn)
215. Calcium(ii) Carbonate
216. Calcium Carbonate, Cp
217. Calcium Carbonate,(s)
218. Acid Controller Complete
219. Calcite [inci]
220. Calcium Carbonate (as)
221. Chalk [inci]
222. Chalk [who-dd]
223. Ec 207-439-9
224. Schembl3261
225. Calcium Carbonate Dispersion
226. Calcium Carbonate Granular Dc
227. Calcium Carbonate Precipitated
228. Ca (c O3)
229. Calcium Carbonate [ii]
230. Calcium Carbonate [mi]
231. Calcium Carbonate Nanoparticles
232. Ndi 443 [fdms]
233. Calcium Carbonate [fcc]
234. Calcium Carbonate Microparticles
235. Hydrolyzed Pearl [inci]
236. Calcium Carbonate [hsdb]
237. Calcium Carbonate [inci]
238. Chembl1200539
239. Dtxsid3036238
240. Limestone, Ground [fcc]
241. Calcium Carbonate [vandf]
242. Ndi 443
243. Calcium Carbonate [mart.]
244. Calcium Carbonate, Reagentplus(r)
245. Calcium Carbonate,puratronic Powder
246. Ci 77220 [inci]
247. Calcium Carbonate [usp-rs]
248. Calcium Carbonate [who-dd]
249. Calcium Carbonate [who-ip]
250. Calcium Carbonate, Ar, >=98.5%
251. Calcium Carbonate, Lr, >=98.5%
252. Akos015903256
253. Calcium Carbonate, Precipitated (jan)
254. Calcii Carbonas [who-ip Latin]
255. Calcium Carbonate [orange Book]
256. Calcium Carbonate, Chelometric Standard
257. Children's Mylanta Upset Stomach Relief
258. Db06724
259. Precipitated Calcium Carbonate (jp17)
260. Calcium (as Carbonate) [vandf]
261. Calcium Carbonate [ep Monograph]
262. Calcium Carbonate, Bioxtra, >=99.0%
263. Calcium Carbonate, Monocalcium Carbonate
264. Calcium Carbonate [usp Monograph]
265. 13701-58-1
266. Calcium Carbonate, Powder A.c.s. Reagent
267. E170
268. Precpitated Calcium Carbonate [jan]
269. Calcium Carbonate, Puriss. P.a., >=99%
270. Calcium Carbonate, Usp, 98.0-100.5%
271. Calcium Carbonate, Nist(r) Srm(r) 915b
272. E 170
273. Ft-0623383
274. Calcium Carbonate (99.999%-ca) Puratrem
275. C08129
276. Calcium (as Calcium Carbonate) [vandf]
277. Calcium Carbonate, Saj First Grade, >=98.0%
278. Calcium Carbonate, Tested According To Ph.eur.
279. D00932
280. Q23767
281. Calcium Carbonate, 99.999% Trace Metals Basis
282. Calcium Carbonate, Jis Special Grade, >=99.5%
283. Calcium Carbonate, P.a., 99.0%, Acs Reagent
284. Calcium Carbonate Dc (spray Dried) [ndi]
285. Calcium Carbonate, >=99.995% Trace Metals Basis
286. Calcium Carbonate, Vetec(tm) Reagent Grade, 99%
287. Pepcid Complete Component Calcium Carbonate
288. Calcium Carbonate, Acs Reagent, >=99.0%, Powder
289. Calcium Carbonate Component Of Pepcid Complete
290. Calcium Carbonate, Bioultra, Precipitated, >=99.0% (kt)
291. Calcium Carbonate, Powder, <=30 Mum Particle Size, 98%
292. Calcium Carbonate, Primary Reference Standard, 99.95-100.05%
293. Nbs 18 (carbon Isotopes In Carbonatite), Nist(r) Rm 8543
294. Calcium Carbonate, Trace Metals Grade 99.99% Trace Metals Basis
295. Calcium Carbonate (as), United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
296. Calcium Carbonate, Bioreagent, Suitable For Insect Cell Culture, >=99.0%
297. Calcium, Ion Chromatography Standard Solution, Specpure?, Ca2+ 1000?g/ml
298. Calcium Carbonate, Acs Reagent, Chelometric Standard, 99.95-100.05% Dry Basis
299. Calcium Carbonate, Anhydrous, Free-flowing, Redi-dri(tm), Acs Reagent, >=99%
300. Calcium Carbonate, Anhydrous, Free-flowing, Redi-dri(tm), Reagentplus(r), >=99%
301. Calcium Carbonate, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
302. Calcium Carbonate, Certified Reference Material For Titrimetry, Certified By Bam, According To Iso 17025, >=99.5%
303. Calcium Carbonate, Puriss., Meets Analytical Specification Of Ph. Eur., Bp, Usp, Fcc, E170, Precipitated, 98.5-100.5% (based On Anhydrous Substance)
| Molecular Weight | 100.09 g/mol |
|---|---|
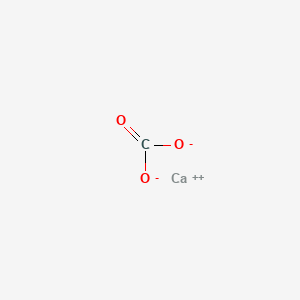
| Molecular Formula | CCaO3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 99.9473347 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 99.9473347 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 63.2 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 5 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 18.8 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Mesh Heading: Antacids
National Library of Medicine, SIS; ChemIDplus Record for Calcium Carbonate (471-34-1).>> Available from, as of April 17, 2006: https://chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/chemidlite.jsp
/EXPL THER/ The aim of the present study was to test the hypothesis that a fibrin matrix enhances the osteogenic differentiation and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) by human bone marrow stromal cells (hBMSCs) seeded into mineralised scaffolds. Porous calcium carbonate scaffolds were droplet seeded with hBMSCs using a matrix containing 3 % fibrinogen and cultured for 3 weeks. Seeded scaffolds without the fibrin matrix served as controls. The scaffolds were evaluated, using undecalcified thick sections, for fluorescence staining for nuclei, osteocalcin (OC) and VEGF. The sections were systematically scanned using optical sectioning and three dimensional distributions of cells and positive staining indicating expression of OC and VEGF were reconstructed from the z-stacks. The fibrin matrix maintained a significantly higher level of cell numbers after 2 d and 1 week and delayed the onset of osteogenic differentiation while sustaining a significantly higher level of OC and VEGF expression after 2 and 3 weeks, starting from the periphery of the scaffolds. There was a decrease in cell density from the periphery to the centre of the scaffolds in both groups. The percentage of cells expressing OC and VEGF was significantly different between the centre and the periphery of the scaffolds in the fibrin(+) group but not in the controls. It is concluded that the fibrin matrix used appears to be a useful adjunct for supporting and sustaining osteogenic and angiogenic activity of hBMSCs in tissue engineered constructs. This could help to improve their performance in a clinical setting.
PMID:22665163 Lohse N et al; Eur Cell Mater. 23: 413-23 (2012)
/EXPL THER/ Thirty coral-derived calcium carbonate-based macroporous constructs with limited hydrothermal conversion to hydroxyapatite (7% HA/CC) were implanted in the rectus abdominis of three adult non-human primate Papio ursinus to investigate the intrinsic induction of bone formation. Macroporous constructs with 125 ug human recombinant osteogenic protein-1 (hOP-1) or 125 ug human recombinant transforming growth factor-beta(3) (hTGF-beta(3)) were also implanted. The potential synergistic interaction between morphogens was tested by implanting binary applications of hOP-1 and hTGF-beta(3) 5:1 by weight, respectively. To evaluate the role of osteoclastic activity on the implanted macroporous surfaces, coral-derived constructs were pre-loaded with 0.24 mg of bisphosphonate zoledronate (Zometa). To correlate the morphology of tissue induction with osteogenic gene expression and activation, harvested specimens on day 90 were analyzed for changes in OP-1 and TGF-beta(3) mRNA synthesis by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The induction of bone formation in 7% HA/CC solo correlated with OP-1 expression. Massive bone induction formed by binary applications of the recombinant morphogens. Single applications of hOP-1 and hTGF-beta(3) also resulted in substantial bone formation, not comparable however to synergistic binary applications. Zoledronate-treated macroporous constructs showed limited bone formation and in two specimens bone formation was altogether absent; qRT-PCR showed a prominent reduction of OP-1 gene expression whilst TGF-beta(3) expression was far greater than OP-1. The lack of bone formation by zoledronate-treated specimens indicates that osteoclastic activity on the implanted coral-derived constructs is critical for the spontaneous induction of bone formation. Indirectly, zoledronate-treated samples showing lack of OP-1 gene expression and absent or very limited bone formation by induction confirm that the spontaneous induction of bone formation by coral-derived macroporous constructs is initiated by secreted BMPs/OPs, in context the OP-1 isoform.
PMID:20493522 Ripamonti U et al; Biomaterials. 31 (25): 6400-10 (2010)
/EXPL THER/ Calcium is an essential cotherapy in osteoporosis treatment. The relative effectiveness of various calcium salts for this purpose is uncertain. Many older women with osteoporosis have phosphorus intakes of <70% of the Recommended Dietary Allowance. /The study's/ objective was to test the hypothesis that calcium phosphate would better support anabolic bone building than would calcium carbonate. This study was a 12-mo, randomized, positive-comparator, 2-arm, single-blind clinical trial in 211 patients treated with teriparatide who consumed <1000 mg phosphorus/d. Participants were randomly assigned to receive, in addition to teriparatide and 1000 IU cholecalciferol, 1800 mg calcium/d as either tricalcium phosphate or calcium carbonate. The primary endpoints were changes in lumbar spine and total hip bone mineral densities (BMDs); secondary endpoints were changes in bone resorption biomarkers and serum and urine calcium and phosphorus concentrations. In the combined group, the lumbar spine BMD increased by 7.2%, and total hip BMD increased by 2.1% (P < 0.01 for both). However, there was no significant difference between calcium-treatment groups, and there were no significant between-group differences in serum calcium and phosphorus concentrations or in urine calcium concentrations. Bone resorption biomarkers increased in both groups, as expected with teriparatide, but the increases in the 2 calcium groups did not differ significantly.Tricalcium phosphate and calcium carbonate appear to be approximately equally effective in supporting bone building with a potent anabolic agent; phosphate salt may be preferable in patients with restricted phosphorus intakes.
PMID:20484446 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2884321 Heaney RP et al; Am J Clin Nutr. 92 (1): 101-5 (2010)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CALCIUM CARBONATE (20 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Large doses of calcium carbonate (above 2 g) increase gastric secretion for a period of time that considerably outlasts elevation of pH. ... With single doses below 2 g, this effect is negligible.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 733
After ingestion /of CaCO3 tablets/, it is converted to sol calcium salts in bowel, and calcium is thereby made available for absorption. Patients with achlorhydria may not solubilize calcium from ... preparation.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1528
Gastric hypersecretory action is counter productive and may possibly account for various reports that calcium carbonate is less efficacious than other antacids. Calcium carbonate has been known to cause fecal concretions.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 993
Constipating effects and chalky taste of calcium carbonate are clinically disadvantageous.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 993
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for CALCIUM CARBONATE (23 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For relief of heartburn and acid indigestion. May also be used as a nutritional supplement or to treat hypocalcemia.
Gastric-peptic disease occurs as a result of an imbalance between protective factors, such as mucus, bicarbonate, and prostaglandin secretion, and aggressive factors, such as hydrochloric acid, pepsin, and Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori). Antacids work by restoring acid-base balance, attenuating the pepsin activity and increasing bicarbonate and prostaglandin secretion. The acid-neutralizing capacity of calcium carbonate is 58 mEq/15 ml. When used as a nutritional supplement, calcium carbonate acts by directly increasing calcium stores within the body.
Antacids
Substances that counteract or neutralize acidity of the GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. (See all compounds classified as Antacids.)
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A02 - Drugs for acid related disorders
A02A - Antacids
A02AC - Calcium compounds
A02AC01 - Calcium carbonate
A - Alimentary tract and metabolism
A12 - Mineral supplements
A12A - Calcium
A12AA - Calcium
A12AA04 - Calcium carbonate
Absorption
Maximal absorption occurs at doses of 500 mg or less taken with food. Oral bioavailability depends on intestinal pH, the presence of food and dosage.
Route of Elimination
Excreted mainly in the feces. The majority of renally filtered calcium is reabsorbed in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle and the proximal and distal convoluted tubules. Also secreted by sweat glands.
Volume of Distribution
Calcium is rapidly distributed taken up by skeletal tissues following absorption and distribution into extracellular fluids. Bone contains 99% of the body's calcium and the remaining 1% is approximately equally distributed between intracellular and extracellular fluids.
Calcium absorption is best when a person consumes no more than 500 mg at one time. So a person who takes 1,000 mg/day of calcium from supplements, for example, should split the dose rather than take it all at once.
NIH Office of Dietary Supplements. Dietary Supplement Fact Sheet for Calcium. Available from, as of August 26, 2013: https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Calcium-QuickFacts/
Amount of calcium absorbed from calcium carbonate is usually stated to be 10%, but ... depends upon amount of gastric acid; in 1 study, 0-2% of single 2 g dose was ... absorbed in achlorhydric persons, 9-16% in normal subjects, and 11-37% in patients with peptic ulcer ...
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 992
Fraction absorbed seems to be nearly the same when CaCO3 is given chronically in daily doses of 20 g /as when it is given in single 2 g dose/. ... Amount absorbed probably reaches a plateau at a dose of about 20 g.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 992
... Increased calcium excretion almost always follows admin of antacid doses of calcium carbonate ...
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 992
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for CALCIUM CARBONATE (15 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
None.
After ingestion /of CaCO3 tablets/, it is converted to sol calcium salts in stomach, and calcium is thereby made available for absorption.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1528
Calcium carbonate is a basic inorganic salt that acts by neutralizing hydrochloric acid in gastric secretions. It also inhibits the action of pepsin by increasing the pH and via adsorption. Cytoprotective effects may occur through increases in bicarbonate ion (HCO3-) and prostaglandins. Neutralization of hydrochloric acid results in the formation of calcium chloride, carbon dioxide and water. Approximately 90% of calcium chloride is converted to insoluble calcium salts (e.g. calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate).

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
65
PharmaCompass offers a list of Calcium Carbonate API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Calcium Carbonate manufacturer or Calcium Carbonate supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Calcium Carbonate manufacturer or Calcium Carbonate supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Calcium Carbonate API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Calcium Carbonate API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Calcium Carbonate Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Calcium Carbonate Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Calcium Carbonate manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Calcium Carbonate, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Calcium Carbonate manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Calcium Carbonate API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Calcium Carbonate manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Calcium Carbonate supplier is an individual or a company that provides Calcium Carbonate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Calcium Carbonate finished formulations upon request. The Calcium Carbonate suppliers may include Calcium Carbonate API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Calcium Carbonate suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Calcium Carbonate DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Calcium Carbonate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Calcium Carbonate DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Calcium Carbonate USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Calcium Carbonate DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Calcium Carbonate USDMF includes data on Calcium Carbonate's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Calcium Carbonate USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Calcium Carbonate suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Calcium Carbonate Drug Master File in Japan (Calcium Carbonate JDMF) empowers Calcium Carbonate API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Calcium Carbonate JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Calcium Carbonate JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Calcium Carbonate suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Calcium Carbonate CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Calcium Carbonate Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Calcium Carbonate CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Calcium Carbonate EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Calcium Carbonate to their clients by showing that a Calcium Carbonate CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Calcium Carbonate CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Calcium Carbonate CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Calcium Carbonate CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Calcium Carbonate DMF.
A Calcium Carbonate CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Calcium Carbonate CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Calcium Carbonate suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
A Calcium Carbonate written confirmation (Calcium Carbonate WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Calcium Carbonate manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Calcium Carbonate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Calcium Carbonate APIs or Calcium Carbonate finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Calcium Carbonate WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Calcium Carbonate suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Calcium Carbonate as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Calcium Carbonate API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Calcium Carbonate as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Calcium Carbonate and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Calcium Carbonate NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Calcium Carbonate suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Calcium Carbonate Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Calcium Carbonate GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Calcium Carbonate GMP manufacturer or Calcium Carbonate GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Calcium Carbonate CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Calcium Carbonate's compliance with Calcium Carbonate specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Calcium Carbonate CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Calcium Carbonate CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Calcium Carbonate may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Calcium Carbonate EP), Calcium Carbonate JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Calcium Carbonate USP).
