
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
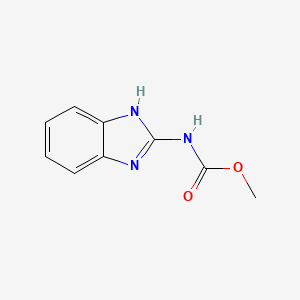

1. 1h-benzimidazole-2-carbamic Acid, Methyl Ester
2. 2-(methoxycarbonylamino)benzimidazole
3. Bavistan
4. Bavistin
5. Benzimidazolecarbamate Methyl Ester
6. Carbendazim Phosphate
7. Carbendazin
8. Carbendazine
9. Carbendazole
10. Carbendazyme
11. Fb-642
12. Fb642
13. G-665
14. Ipo-1250
15. Mecarzole
16. Mecarzole Monohydrochloride
17. Mecarzole Mononitrate
18. Mecarzole Monophosphate
19. Mecarzole Monophosphinate
20. Mecarzole Monosodium Salt
21. Mecarzole Monosulfate
22. Mecarzole Triphosphinate
23. Medamine
24. Mekarzole
25. Methoxybenzimidazole-2-carbamic Acid
26. Methyl 2-benzimidazil Carbamate
27. Methyl-2-benzimidazole Carbamate
28. Methyl-n-(2-benzimidazolyl)carbamate
29. Methylbenzimidazole-2-ylcarbamate
1. 10605-21-7
2. Carbendazole
3. Bavistin
4. Mecarzole
5. Thicoper
6. Carbendazime
7. Derosal
8. Carbendazol
9. Bavistan
10. Medamine
11. Funaben
12. Methyl 2-benzimidazolecarbamate
13. Bmk (fungicide)
14. Carbendazym
15. Equitdazin
16. Garbenda
17. Kemdazin
18. Supercarb
19. Agrizim
20. Battal
21. Bengard
22. Bitosen
23. Custos
24. Delsene
25. Karben
26. Kolfugo
27. Stempor
28. Myco
29. Methyl Benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamate
30. Bavistin 3460
31. Carbendazine
32. Falicarben
33. Pillarstin
34. Fungisol
35. Triticol
36. Stein
37. Spin
38. Bercema-bitosen
39. Carbamic Acid, 1h-benzimidazol-2-yl-, Methyl Ester
40. Kolfugo Extra
41. Methyl 1h-benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamate
42. Methyl 1h-benzo[d]imidazol-2-ylcarbamate
43. Preventol Bcm
44. Antibac Mf
45. Carben Vl
46. Funaben 3
47. Bcm (fungicide)
48. 2-mbc
49. Ipo Y
50. Methyl Benzimidazolylcarbamate
51. Benzimidazolecarbamic
52. Funaben 50
53. Methyl N-(1h-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamate
54. Jkatein
55. Preparation G 665
56. 2-(methoxycarbamoyl)benzimidazole
57. A 118 (pesticide)
58. 2-(carbomethoxyamino)benzimidazole
59. Methyl 1h-benzimidazole-2-carbamate
60. 1h-benzimidazole-2-carbamic Acid, Methyl Ester
61. Kolfugo 25 Fw
62. Lignasan
63. Mercarzole
64. 2-(methoxycarbonylamino)-benzimidazole
65. Methyl Benzimidazolecarbamate
66. Bas 67054f
67. 2-(methoxycarbonylamino)benzimidazole
68. 2-benzimidazolecarbamic Acid, Methyl Ester
69. Carbendazim [bsi:iso]
70. Bmk (van)
71. Methyl N-2-benzimidazolecarbamate
72. 1h-benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamic Acid Methyl Ester
73. Bas-3460
74. Ctr 6669
75. Benzimidazole-2-carbamic Acid, Methyl Ester
76. Ek 578
77. Hoe 17411
78. G 665
79. Derroprene
80. Zhiweiling
81. Bavistine
82. Ccris 1553
83. Fungoxan
84. Jkstein
85. Protek
86. Sarfun
87. Subeej
88. 2-(methoxy-carbonylamino)-benzimidazol
89. Hsdb 6581
90. U 32104
91. Bavistin Fl
92. Spin (pesticide)
93. Karben Flo Stefes
94. Karben Stefes Flo
95. Olgin (fungicide)
96. Ba 67054f
97. Bavistin 25sd
98. Bavistin 50sd
99. Delsene 10
100. Derosal 60pm
101. Kolfugo 25fw
102. 2-[(methoxycarbonyl)amino]benzimidazole
103. Methyl 2-benzimidazolylcarbamate
104. Bmk
105. Bas 3460f
106. Methyl 1h-benzimidazolylcarbamate
107. Benzimidazole Carbamate De Methyle
108. Ipo 1250
109. Bas-67054
110. Fb-642
111. 1h-benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamic Acid, Methyl Ester
112. Nsc-109874
113. U-32.104
114. Carbamic Acid, N-1h-benzimidazol-2-yl-, Methyl Ester
115. Chembl70971
116. 2-methyl Benzimidazolecarbamate
117. Mls002701961
118. Chebi:3392
119. 105268-95-9
120. A 118
121. Methyl 1h-benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamate (9ci)
122. 2-(methoxy-carbonylamino)-benzimidazol [german]
123. Bas-67054f
124. Carbamic Acid, 1h-benzimidazolyl-, Methyl Ester
125. H75j14aa89
126. 2-(methoxycarboxamido)benzimidazole
127. Bas 3460
128. Ek-578
129. 2-bezimidazolecarbamic Acid Methyl Ester
130. Carbendazin
131. Carbendazyme
132. Mekarzole
133. Dsstox_cid_4729
134. Dsstox_rid_77513
135. 1h-benzimidazol-2-yl-carbamic Acid, Methyl Ester
136. Dsstox_gsid_24729
137. 37953-07-4
138. Mbc (van)
139. Carbendazime [iso-french]
140. Ipo-1250
141. Carbamic Acid, N-1h-benzimidazol-2-yl-, Methyl Ester;methyl 1h-benzo[d]imidazol-2-ylcarbamate
142. Carbendazim [iso]
143. Cas-10605-21-7
144. Methyl 2-benzimidazil Carbamate
145. Methyl-2-benzimidazole Carbamate
146. Methylbenzimidazole-2-ylcarbamate
147. 2-(methoxy-carbonylamino)-benzimidazol (german)
148. Benzimidazolecarbamate Methyl Ester
149. Bas 3460 F
150. Methoxybenzimidazole-2-carbamic Acid
151. Einecs 234-232-0
152. Methyl-n-(2-benzimidazolyl)carbamate
153. Rcra Waste No. U372
154. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 115001
155. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 128872
156. Nsc 109874
157. 2-benzimidazolecarbamic Acid Methyl Ester
158. Carbate
159. Unii-h75j14aa89
160. Benzimidazole Carbamate De Methyle [french]
161. Carbendazim-d3
162. Carbendazol, Jmaf
163. Ctr-6669
164. Tripart Defensor Fl
165. N-benzimidazol-2-ylmethoxycarboxamide
166. Carbendazim, 97%
167. Turfclear (salt/mix)
168. Bmc?
169. Carbendazim [mi]
170. Chemdivam_000201
171. Chemdiv1_000052
172. 1h-benzimidazole-2-carbamic Acid Methyl Ester
173. Carbendazim [hsdb]
174. Schembl21051
175. Carbendazim [who-dd]
176. N-1h-benzimidazol-2-yl-carbamic Acid Methyl Ester
177. Bidd:er0282
178. Fenbendazole Related Compound A
179. Carbendazim, Analytical Standard
180. 2-carbomethoxyamino-benzimidazole
181. Dtxsid4024729
182. Methyl Benzimidazole-2-carbamate
183. Schembl19926051
184. Hms587c08
185. Methyl 2-benzimidazolyl-carbamate
186. Zinc43475
187. Kid Pest Project (carbendazim) (see Also Carbendazim)
188. Amy22465
189. Tox21_202295
190. Tox21_300478
191. 2-(carbomethoxy-amino)-benzimidazole
192. Bdbm50116313
193. Hoe-17411
194. Methyl 1h-2-benzimidazolecarbaminate
195. Methyl N-benzimidazol-2-yl-carbamate
196. Mfcd00055390
197. Nsc109874
198. Akos002384358
199. Carbendazim 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
200. Ccg-101273
201. Cs-8030
202. Db13009
203. Ks-5360
204. 2-(methoxy-carbonylamino)-benzimidazole
205. Ncgc00090706-01
206. Ncgc00090706-02
207. Ncgc00090706-03
208. Ncgc00090706-04
209. Ncgc00254328-01
210. Ncgc00259844-01
211. A118
212. Ac-10590
213. Bp-21318
214. Hy-13582
215. Nci60_000240
216. Smr000304463
217. 1h-benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamicacidmethylester
218. Db-040676
219. Methyl 1h-benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamate, 9ci
220. Albendazole Impurity E [ep Impurity]
221. Ft-0602933
222. Ft-0664246
223. S3676
224. Carbendazim, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
225. E78626
226. Methyl N-(1h-1,3-benzodiazol-2-yl)carbamate
227. Methyl N-1h-benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamate
228. Fenbendazole Related Compound A [usp-rs]
229. 605c217
230. A801368
231. Af-962/00515023
232. Q418607
233. Sr-01000390861
234. (1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-carbamic Acid Methyl Ester
235. J-001536
236. Sr-01000390861-1
237. Carbendazim, Certified Reference Material, Tracecert(r)
238. F0266-0908
239. Fenbendazole Impurity A, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
240. Fenbendazole Related Compound A, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
241. 102040-01-7
242. 110342-67-1
243. 212384-28-6
244. 39413-19-9
| Molecular Weight | 191.19 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H9N3O2 |
| XLogP3 | 1.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 191.069476538 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 191.069476538 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 67 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 222 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
/EXPL THER/ The benzimidazoles, benomyl and carbendazim, are fungicides suggested to target microtubules. Benomyl is metabolized to carbendazim, which has already been explored as an anticancer drug in phase 1 clinical trials. We further characterized the cytotoxic properties of benomyl and carbendazim in 12 human cell lines and in primary cultures of patient tumor cells with the overall aims of elucidating mechanisms of action and anticancer activity spectrum. Cytotoxicity was assessed in the short-term fluorometric microculture cytotoxicity assay and was correlated with the activity of other anticancer drugs and gene expression assessed by cDNA microarray analysis. Benomyl was generally more potent than its metabolite, carbendazim. Both showed high drug activity correlations with several established and experimental anticancer drugs, but modest association with established mechanisms of drug resistance. Furthermore, these benzimidazoles showed high correlations with genes considered relevant for the activity of several mechanistically different standard and experimental anticancer drugs, indicating multiple and broad mechanisms of action. In patient tumor samples, benomyl tended to be more active in hematological compared with solid tumor malignancies, whereas the opposite was observed for carbendazim. In conclusion, benomyl and carbendazim show interesting and diverse cytotoxic mechanisms of action and seem suitable as lead compounds for the development of new anticancer drugs.
PMID:19786863 Laryea D et al; Anticancer Drugs 21 (1): 33-42 (2010)
/EXPL THER/ Carbendazim inhibits microtubule assembly, thus blocking mitosis and inhibiting cancer cell proliferation. Accordingly, carbendazim is being explored as an anticancer drug. Data show that carbendazim increased mRNA and protein expressions and promoter activity of CYP1A1. In addition, carbendazim activated transcriptional activity of the aryl hydrocarbon response element, and induced nuclear translocation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), a sign the AhR is activated. Carbendazim-induced CYP1A1 expression was blocked by AhR antagonists, and was abolished in AhR signal-deficient cells. Results demonstrated that carbendazim activated the AhR, thereby stimulating CYP1A1 expression. In order to understand whether AhR-induced metabolic enzymes turn carbendazim into less-toxic metabolites, Hoechst 33,342 staining to reveal carbendazim-induced nuclear changes and flow cytometry to reveal the subG0/G1 population were applied to monitor carbendazim-induced cell apoptosis. Carbendazim induced less apoptosis in Hepa-1c1c7 cells than in AhR signal-deficient Hepa-1c1c7 mutant cells. Pretreatment with beta-NF, an AhR agonist that highly induces CYP1A1 expression, decreased carbendazim-induced cell death. In addition, the lower the level of AhR was, the lower the vitality present in carbendazim-treated cells, including hepatoma cells and their derivatives with AhR RNA interference, also embryonic kidney cells, bladder carcinoma cells, and AhR signal-deficient Hepa-1c1c7 cells. In summary, carbendazim is an AhR agonist. The toxicity of carbendazim was lower in cells with the AhR signal. This report provides clues indicating that carbendazim is more potent at inducing cell death in tissues without than in those with the AhR signal, an important reference for applying carbendazim in cancer chemotherapy.
PMID:27286660 Wei KL et al; Toxicol Appl Pharmacol pii: S0041-008X(16)30138-7 doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2016.06.004 (2016) (Epub ahead of print)
/EXPL THER/ ... The results of this present study indicate that FB642 /carbendazim/ increases the degree of apoptosis in all examined tumor cell lines, may induce G2/M uncoupling, may selectively kill p53 abnormal cells, and exhibits antitumor activity in drug- and multidrug-resistant cell lines. The induction of apoptosis by FB642, particularly in p53-deficient cells, its impressive in vivo activity against a broad spectrum of murine and human tumors, as well as an acceptable toxicity profile in animals, make FB642 an excellent candidate for further evaluation in clinical trials in cancer patients. /FB642/
PMID:11355145 Hammond LA et al; J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 127 (5): 301-13 (2001)
Antinematodal Agents
Substances used in the treatment or control of nematode infestations. They are used also in veterinary practice. (See all compounds classified as Antinematodal Agents.)
Mutagens
Chemical agents that increase the rate of genetic mutation by interfering with the function of nucleic acids. A clastogen is a specific mutagen that causes breaks in chromosomes. (See all compounds classified as Mutagens.)
Fungicides, Industrial
Chemicals that kill or inhibit the growth of fungi in agricultural applications, on wood, plastics, or other materials, in swimming pools, etc. (See all compounds classified as Fungicides, Industrial.)
In male rats, following a single oral admin of 3 mg/kg, 66% was eliminated in the urine within 6 hr.
Tomlin, C.D.S. (ed.). The Pesticide Manual - World Compendium. 10th ed. Surrey, UK: The British Crop Protection Council, 1994., p. 150
Readily absorbed by plants. One degradation product is 2-aminobenzimidazole.
Tomlin, C.D.S. (ed.). The Pesticide Manual - World Compendium. 10th ed. Surrey, UK: The British Crop Protection Council, 1994., p. 150
... Two metabolites: methyl 5-hydroxy-2-benzimidazolecarbamate (5-HBC) and 2-aminobenzimidazole (2-AB) were formed very rapidly /in rats admin 12 mg/kg iv/. Their peak concentrations in liver and kidney were 15 min after i.v. injection. Unchanged carbendazim was found in highest concentrations in blood. 5-HBC prevails in organs. 2-AB was present only in minor amounts. The extent of bioavailability in orally administered 14C-carbendazim (12 mg/kg) was about 85%. The disposition of radioactivity in subcellular fractions was not uniform, its highest concentration was in cytosol, the lowest in microsomes. ...
PMID:3765661 Krechniak J, Klosowska B; Xenobiotica 16 (9): 809-15 (1986)
The disappearance of (14)C-carbendazim in rat (i.v. 12 mg/kg) followed the kinetics of a two-compartment open-system model. Half-lives of the alpha-phase were 0.16 hr (liver), 0.25 hr (kidney), and of the beta-phase: 2.15 hr, 6.15 hr, respectively. Two metabolites: methyl 5-hydroxy-2-benzimidazolecarbamate (5-HBC) and 2-aminobenzimidazole (2-AB) were formed very rapidly. Their peak concentrations in liver and kidney were 15 min after i.v. injection. Unchanged carbendazim was found in highest concentrations in blood. 5-HBC prevails in organs. 2-AB was present only in minor amounts. The extent of bioavailability in orally administered 14C-carbendazim (12 mg/kg) was about 85%. The disposition of radioactivity in subcellular fractions was not uniform, its highest concentration was in cytosol, the lowest in microsomes. The elimination of (14)C-carbendazim in urine is biphasic. Half-lives of the alpha-phase were 1.4 hr (i.v.) and 2.5 hr (oral), and of the beta-phase 11.2 hr and 12.1 hr, respectively. Irrespective of the route of administration, 95% of the radioactivity in urine was composed of 5-HBC. The concentration of unchanged carbendazim in blood and of 5-HBC in urine may be of diagnostic value in acute poisoning with carbendazim.
PMID:3765661 Krechniak J, Klosowska B; Xenobiotica 16 (9): 809-15 (1986)
... Previous studies indicate that FB642 /carbendazim/ may interfere with mitosis and thus may disrupt or inhibit microtubule function resulting in apoptosis. ...
PMID:11355145 Hammond LA et al; J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 127 (5): 301-13 (2001)
Carbendazim inhibits microtubule assembly, thus blocking mitosis and inhibiting cancer cell proliferation. Accordingly, carbendazim is being explored as an anticancer drug. Data show that carbendazim increased mRNA and protein expressions and promoter activity of CYP1A1. In addition, carbendazim activated transcriptional activity of the aryl hydrocarbon response element, and induced nuclear translocation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), a sign the AhR is activated. Carbendazim-induced CYP1A1 expression was blocked by AhR antagonists, and was abolished in AhR signal-deficient cells. Results demonstrated that carbendazim activated the AhR, thereby stimulating CYP1A1 expression. In order to understand whether AhR-induced metabolic enzymes turn carbendazim into less-toxic metabolites, Hoechst 33,342 staining to reveal carbendazim-induced nuclear changes and flow cytometry to reveal the subG0/G1 population were applied to monitor carbendazim-induced cell apoptosis. Carbendazim induced less apoptosis in Hepa-1c1c7 cells than in AhR signal-deficient Hepa-1c1c7 mutant cells. Pretreatment with beta-NF, an AhR agonist that highly induces CYP1A1 expression, decreased carbendazim-induced cell death. In addition, the lower the level of AhR was, the lower the vitality present in carbendazim-treated cells, including hepatoma cells and their derivatives with AhR RNA interference, also embryonic kidney cells, bladder carcinoma cells, and AhR signal-deficient Hepa-1c1c7 cells. In summary, carbendazim is an AhR agonist. The toxicity of carbendazim was lower in cells with the AhR signal. This report provides clues indicating that carbendazim is more potent at inducing cell death in tissues without than in those with the AhR signal, an important reference for applying carbendazim in cancer chemotherapy.
PMID:27286660 Wei KL et al; Toxicol Appl Pharmacol pii: S0041-008X(16)30138-7 doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2016.06.004 (2016) (Epub ahead of print)
ABOUT THIS PAGE
34
PharmaCompass offers a list of Carbendazim API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Carbendazim manufacturer or Carbendazim supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Carbendazim manufacturer or Carbendazim supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Carbendazim API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Carbendazim API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Carbendazim Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Carbendazim Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Carbendazim manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Carbendazim, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Carbendazim manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Carbendazim API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Carbendazim supplier is an individual or a company that provides Carbendazim active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Carbendazim finished formulations upon request. The Carbendazim suppliers may include Carbendazim API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
Carbendazim Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Carbendazim GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Carbendazim GMP manufacturer or Carbendazim GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Carbendazim CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Carbendazim's compliance with Carbendazim specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Carbendazim CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Carbendazim CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Carbendazim may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Carbendazim EP), Carbendazim JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Carbendazim USP).

