
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Canada

0
Australia

DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
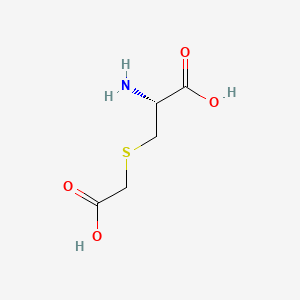

1. 3-(carboxymethylthio)alanine
2. Carbocysteine, L Isomer
3. Carbocysteine, L-isomer
4. L-isomer Carbocysteine
5. Mucodine
6. Mucodyne
7. Mukodin
8. Rhinathiol
9. S Carboxymethylcysteine
10. S-(carboxymethyl)-l-cysteine
11. S-carboxymethylcysteine
12. Thiodril
1. 638-23-3
2. S-carboxymethyl-l-cysteine
3. Carbocisteine
4. Carbocistein
5. S-(carboxymethyl)-l-cysteine
6. Mucodyne
7. Reomucil
8. Rhinathiol
9. Transbronchin
10. Lisomucil
11. Muciclar
12. Mucolase
13. Mucocis
14. Siroxyl
15. Loviscol
16. Mucofan
17. Bronchokod
18. Carbocit
19. Mucopront
20. Mucotab
21. Pectox
22. Lisil
23. Pectdrill
24. L-carbocisteine
25. H-cys(carboxymethyl)-oh
26. (r)-s-(carboxymethyl)cysteine
27. 186537-58-6
28. Carbocisteina
29. Carbocisteinum
30. Mucolex
31. Pulmoclase
32. Rinatiol
33. L-carbocysteine
34. S-(carboxymethyl)-(r)-cysteine
35. L-3-((carboxymethyl)thio)alanine
36. Superthiol Sirup
37. Thiodril
38. Lj 206
39. Methista
40. (l)-2-amino-3-(carboxymethylthio)propionic Acid
41. S-carboxymethylcysteine
42. Carbocisteine [inn]
43. 3-(carboxymethylthio)-l-alanine
44. R05cb03
45. Ahr 3053
46. Ahr-3053
47. Df 1794y
48. Nsc 14156
49. (2r)-2-amino-3-(carboxymethylsulfanyl)propanoic Acid
50. (2r)-2-amino-3-[(carboxymethyl)sulfanyl]propanoic Acid
51. L-cysteine, S-(carboxymethyl)-
52. Chembl396416
53. Chebi:16163
54. 740j2qx53r
55. Lj-206
56. Nsc-14156
57. Carbocysteine [usan]
58. Alanine, 3-((carboxymethyl)thio)-, L-
59. Chilvax
60. Mucosol
61. Carboxymethylated Cysteine
62. S-carboxylmethyl-l-cysteine
63. Broncodeterge
64. 1391068-19-1
65. Mucotron
66. Mukinyl
67. 3-((carboxymethyl)thio)-l-alanine
68. Mucojet Sirup
69. Mucolex Sirup
70. L-(carboxymethyl)cysteine
71. Scmc
72. (r)-2-amino-3-(carboxymethylthio)propanoic Acid
73. 3-((carboxymethyl)thio)alanine
74. 3-[(carboxymethyl)thio]alanine
75. Carbocisteinum [inn-latin]
76. Carbocisteina [inn-spanish]
77. Unii-740j2qx53r
78. Carbocysteine [usan:inn:ban]
79. L.j.206
80. (2r)-2-azaniumyl-3-(carboxylatomethylsulfanyl)propanoate
81. Mucodyne (tn)
82. Einecs 211-327-5
83. Carbocistein [jan]
84. Mfcd00002614
85. Carbocysteine Dl-form
86. Brn 1725012
87. L.j. 206
88. Carbocysteine [mi]
89. L-carbocisteine (jp17)
90. Carbocisteine [jan]
91. Carbocysteine [inci]
92. Schembl20854
93. (2r)-2-amino-3-(carboxymethylthio)propanoic Acid
94. Carbocisteine [mart.]
95. L-carbocisteine [jan]
96. Hy-d0205a
97. (carboxymethyl)cysteine-, (l)-
98. Dtxsid30110060
99. L-carbocisteine [who-dd]
100. 3-(carboxymethylthio)alanine, L-
101. S-carboxymethyl-l-cysteine, 98%
102. Zinc1529732
103. Carbocisteine [ep Monograph]
104. Bdbm50213735
105. S5216
106. Akos015922826
107. 5-amino-3-thiadihexanoic Acid, (l)-
108. Db04339
109. Ac-11146
110. As-57938
111. Cs-0017457
112. C-1850
113. C03727
114. D00175
115. H11928
116. (2r)-2-amino-3-(carboxymethylthio)propionic Acid
117. A813055
118. A816956
119. A834542
120. Q423408
121. 2-amino-3-(carboxymethylthio)propionic Acid, (l)-
122. Q-200796
123. (2r)-3-(carboxythio)-2-(methylamino)propanoic Acid
124. (2r)-2-amino-3-((carboxymethyl)thio)propionic Acid
125. (2r)-2-azanyl-3-(2-hydroxy-2-oxoethylsulfanyl)propanoic Acid
126. Carbocisteine, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
127. (2r)-2-amino-3-[(carboxymethyl)sulfanyl]propanoic Acids-(carboxymethyl)-l-cysteine
| Molecular Weight | 179.20 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C5H9NO4S |
| XLogP3 | -3.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 179.02522894 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 179.02522894 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 126 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 11 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 161 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Carbocisteine is indicated over the counter and in prescription formulas to clear airway secretions in conditions associated with increased mucus.
Due to its mucolytic effects, carbocisteine significantly reduces sputum viscosity, cough, dyspnea and fatigue. Additionally, it prevents pulmonary infections by decreasing accumulated mucus in the respiratory tract; this is especially beneficial in preventing exacerbations of COPD caused by bacteria and viruses. It has in-vitro anti-inflammatory activity with some demonstrated action against free radicals.
Anti-Infective Agents, Local
Substances used on humans and other animals that destroy harmful microorganisms or inhibit their activity. They are distinguished from DISINFECTANTS, which are used on inanimate objects. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Infective Agents, Local.)
Expectorants
Agents that increase mucous excretion. Mucolytic agents, that is drugs that liquefy mucous secretions, are also included here. (See all compounds classified as Expectorants.)
R05CB03
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
R - Respiratory system
R05 - Cough and cold preparations
R05C - Expectorants, excl. combinations with cough suppressants
R05CB - Mucolytics
R05CB03 - Carbocisteine
Absorption
Carbocisteine is rapidly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract when taken orally with peak serum concentrations achieved within 1 to 1.7 hours.
Route of Elimination
About 30% to 60% of an orally administered dose is detected unchanged in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
Carbocisteine penetrates well into the lung and bronchial secretions.
Clearance
Clearance information for carbocisteine is not readily available in the literature.
Metabolic pathways for carbocisteine include acetylation, decarboxylation, and sulfoxidation, leading to the formation of pharmacologically inactive carbocisteine derivatives. Significant variability exists in metabolism due to genetic polymorphism in sulfoxidation capacity. Two cytosolic enzymes are responsible for the metabolism of carbocisteine: cysteine dioxygenase and phenylalanine 4-hydroxylase. Reduced metabolism can cause increased exposure to carbocisteine, explaining variable clinical response between patients who may polymorphisms affecting the enzymes responsible for carbocisteine metabolism. It is generally accepted that sulfodixation is the main metabolic pathway of carbocisteine, however, one group of researchers found a novel urinary metabolite, S-(carboxymethylthio)-L-cysteine (CMTC). No cysteinyl sulfoxide metabolites were found in the urine of patients taking carbocisteine in this study.
The plasma half-life of carbicostine is 1.33 hours.
The hypersecretion of mucus characterizes serious respiratory conditions including asthma, cystic fibrosis (CF), and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It blocks bacterial adherence to cells, preventing pulmonary infections. Glycoproteins (fucomucins, sialomucins and sulfomucins) regulate the viscoelastic properties of bronchial mucus. Increased fucomucins can be found in the mucus of patients with COPD. Carbocisteine serves to restore equilibrium between sialomucins and fucomucins, likely by intracellular stimulation of sialyl transferase enzyme, thus reducing mucus viscosity. A study found that L-carbocisteine can inhibit damage to cells by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) by activating protein kinase B (Akt) phosphorylation, suggesting that carbocisteine may have antioxidant effects and prevent apoptosis of lung cells. There is some evidence that carbocisteine suppresses NF-B and ERK1/2 MAPK signalling pathways, reducing TNF-alpha induced inflammation in the lungs, as well as other inflammatory pathways. An in-vitro study found that L-carbocisteine reduces intracellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), inhibiting rhinovirus 14 infection, thereby reducing airway inflammation.

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Global Sales Information

Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
51
PharmaCompass offers a list of Carbocisteine API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Carbocisteine manufacturer or Carbocisteine supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Carbocisteine manufacturer or Carbocisteine supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Carbocisteine API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Carbocisteine API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Carbocisteine Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Carbocisteine Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Carbocisteine manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Carbocisteine, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Carbocisteine manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Carbocisteine API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Carbocisteine manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Carbocisteine supplier is an individual or a company that provides Carbocisteine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Carbocisteine finished formulations upon request. The Carbocisteine suppliers may include Carbocisteine API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Carbocisteine suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Carbocisteine DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Carbocisteine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Carbocisteine DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Carbocisteine USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Carbocisteine DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Carbocisteine USDMF includes data on Carbocisteine's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Carbocisteine USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Carbocisteine suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Carbocisteine Drug Master File in Japan (Carbocisteine JDMF) empowers Carbocisteine API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Carbocisteine JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Carbocisteine JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Carbocisteine suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Carbocisteine CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Carbocisteine Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Carbocisteine CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Carbocisteine EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Carbocisteine to their clients by showing that a Carbocisteine CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Carbocisteine CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Carbocisteine CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Carbocisteine CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Carbocisteine DMF.
A Carbocisteine CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Carbocisteine CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Carbocisteine suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
A Carbocisteine written confirmation (Carbocisteine WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Carbocisteine manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Carbocisteine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Carbocisteine APIs or Carbocisteine finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Carbocisteine WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Carbocisteine suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Carbocisteine as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Carbocisteine API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Carbocisteine as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Carbocisteine and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Carbocisteine NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Carbocisteine suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Carbocisteine Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Carbocisteine GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Carbocisteine GMP manufacturer or Carbocisteine GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Carbocisteine CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Carbocisteine's compliance with Carbocisteine specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Carbocisteine CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Carbocisteine CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Carbocisteine may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Carbocisteine EP), Carbocisteine JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Carbocisteine USP).
