
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
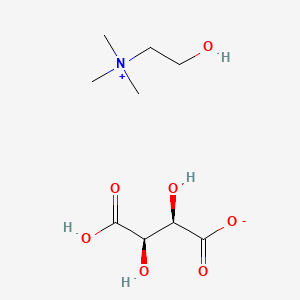

1. 2-hydroxy-n,n,n-trimethylethanaminium
2. Bitartrate, Choline
3. Bursine
4. Chloride, Choline
5. Choline
6. Choline Chloride
7. Choline Citrate
8. Choline Hydroxide
9. Choline O Sulfate
10. Choline O-sulfate
11. Citrate, Choline
12. Fagine
13. Hydroxide, Choline
14. O-sulfate, Choline
15. Vidine
1. 87-67-2
2. 6k2w7t9v6y
3. Choline Hydrogen L-(+)-tartrate
4. Choline Tartrate
5. (2-hydroxyethyl)trimethylammonium-l-(+)-tartrate Salt (1:1)
6. Choline Hydrogen Tartrate
7. 2-hydroxyethanaminium,-n,n,n-trimethyl-, (r-(r*,r*))-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate (1:1)
8. Ethanaminium, 2-hydroxy-n,n,n-trimethyl-, (2r,3r)-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate (1:1)
9. Choline, Tartrate (1:1)
10. Choline Bitartrate, Anhydrous
11. Hsdb 983
12. Choline, Tartrate (1:1) Salt
13. Tartaric Acid, Ion(1-), Choline
14. Einecs 201-763-4
15. Unii-6k2w7t9v6y
16. 2-hydroxy-n,n,n-trimethylethanaminium 2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate, (r-(r*,r*))-
17. 4-trihydroxy-4-oxobutanoate
18. Butanedioic Acid, 2,3-dihydroxy- (r-(r*,r*))-, Ion(1-), 2-hydroxy-n,n,n-trimethylethanaminium
19. Ethanaminium, 2-hydroxy-n,n,n-trimethyl-, Salt With (2r,3r)-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioic Acid (1:1)
20. Ethanaminium, 2-hydroxy-n,n,n-trimethyl-, Salt With (r-(r*,r*))-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioic Acid (1:1)
21. Schembl225594
22. Choline (as Bitartrate)
23. Choline Bitartrate [mi]
24. 2-hydroxyethyl(trimethyl)azanium;(2r,3r)-2,3,4-trihydroxy-4-oxobutanoate
25. Choline Bitartrate [fcc]
26. Choline Bitartrate [hsdb]
27. Dtxsid00889332
28. Choline Bitartrate [vandf]
29. 2-hydroxyethyl(trimethyl)azanium;2
30. Choline Bitartrate [mart.]
31. Choline Bitartrate [usp-rs]
32. Choline Bitartrate [who-dd]
33. S4703
34. Ccg-266986
35. Choline (as Bitartrate) [vandf]
36. Ethanaminium, 2-hydroxy-n,n,n-trimethyl-, Salt With (theta-(theta,theta))-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioic Acid (1:1)
37. Hy-101036
38. Cs-0020747
39. F71308
40. Q18324709
41. Choline Bitartrate, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
42. 2-hydroxy-n,n,n-trimethylethan-1-aminium (2r,3r)-3-carboxy-2,3-dihydroxypropanoate
| Molecular Weight | 253.25 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H19NO7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 253.11615195 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 253.11615195 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 138 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 193 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Some clinical improvement with choline treatment has also been reported in huntington's chorea...in gilles de la tourette's disease, in friedreich's ataxia, & in presenile dementia ... /Choline/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1575
A nutrient and/or dietary supplement food additive
Sax, N.I. Dangerous Properties of Industrial Materials. 5th ed. New York: Van Nostrand Rheinhold, 1979., p. 503
/EXPL THER/ Eight lithium-treated patients with DSM-IV bipolar disorder, rapid cycling type were randomly assigned to 50 mg/kg/day of choline bitartrate or placebo for 12 weeks. Brain purine, choline and lithium levels were assessed using 1H- and 7Li-MRS. Patients received four to six MRS scans, at baseline and weeks 2, 3, 5, 8, 10 and 12 of treatment (n = 40 scans). Patients were assessed using the Clinical Global Impression Scale (CGIS), the Young Mania Rating Scale (YRMS) and the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS) at each MRS scan. ... There were no significant differences in change-from-baseline measures of CGIS, YMRS, and HDRS, brain choline/creatine ratios, and brain lithium levels over a 12-week assessment period between the choline and placebo groups or within each group. However, the choline treatment group showed a significant decrease in purine metabolite ratios from baseline (purine/n-acetyl aspartate: coef = -0.08, z = -2.17, df = 22, p = 0.030; purine/choline: coef = -0.12, z = -1.97, df = 22, p = 0.049) compared to the placebo group, controlling for brain lithium level changes. Brain lithium level change was not a significant predictor of purine ratios. ... The current study reports that oral choline supplementation resulted in a significant decrease in brain purine levels over a 12-week treatment period in lithium-treated patients with DSM-IV bipolar disorder, rapid-cycling type, which may be related to the anti-manic effects of adjuvant choline. This result is consistent with mitochondrial dysfunction in bipolar disorder inadequately meeting the demand for increased ATP production as exogenous oral choline administration increases membrane phospholipid synthesis.
PMID:12895208 Lyoo IK et al; Bipolar Disord 5 (4): 300-6 (2003)
/EXPL THER/ ... Choline bitartrate was given openly to 6 consecutive lithium-treated outpatients with rapid-cycling bipolar disorder. Five patients also underwent brain proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Five of 6 rapid-cycling patients had a substantial reduction in manic symptoms, and 4 patients had a marked reduction in all mood symptoms during choline therapy. The patients who responded to choline all exhibited a substantial rise in the basal ganglia concentration of choline-containing compounds. Choline was well tolerated in all cases. Choline, in the presence of lithium, was a safe and effective treatment for 4 of 6 rapid-cycling patients in our series. A hypothesis is suggested to explain both lithium refractoriness in patients with bipolar disorder and the action of choline in mania, which involves the interaction between phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidylcholine second-messenger systems.
PMID:8874839 Stoll AL et al; Biol Psychiatry 40 (5): 382-8 (1996)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CHOLINE BITARTRATE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Oral LD50 for man is estimated to be of the order of 200-400 g. /CHOLINE/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1575
Nootropic Agents
Drugs used to specifically facilitate learning or memory, particularly to prevent the cognitive deficits associated with dementias. These drugs act by a variety of mechanisms. (See all compounds classified as Nootropic Agents.)
Lipotropic Agents
Endogenous factors or drugs that increase the transport and metabolism of LIPIDS including the synthesis of LIPOPROTEINS by the LIVER and their uptake by extrahepatic tissues. (See all compounds classified as Lipotropic Agents.)
Choline is absorbed from diet as such or as lecithin. Latter is hydrolyzed by intestinal mucosa to glycerophosphoryl choline, which either passes to liver to liberate choline or to peripheral tissues via intestinal lymphatics. /Choline/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1575
Choline are absorbed via the portal circulation ... The liver takes up the majority of choline and stores it in the form of phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin. Kidney and brain also accumulate choline ... Some free choline is excreted with urine ... A specific carrier is needed for the transport of free choline across the blood-brain barrier, and the capacity is especially high in neonates. /Choline/
Coates, P.M., Blackman, M.R., Cragg, G.M., Levine, M., Moss, J., White, J.D. (Ed), Encyclopedia of Dietary Supplements. Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, p. 106 (2005)
Free choline is transported across the blood-brain barrier at a rate that is proportional to serum choline level ... In advanced age ... brain choline uptake /is decr/ ... /Choline/
Coates, P.M., Blackman, M.R., Cragg, G.M., Levine, M., Moss, J., White, J.D. (Ed), Encyclopedia of Dietary Supplements. Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, p. 107 (2005)
During pregnancy, large amt of choline are delivered to the fetus across the placenta and this depletes maternal stores. Choline concn in amniotic fluid is 10-fold greater than that in maternal blood. At birth, humans and other mammals have plasma choline concn that are much higher than those in adults ... In rats, the liver choline concn in late pregnancy decr to less than one-third that of nonpregnant females ... /Choline/
Coates, P.M., Blackman, M.R., Cragg, G.M., Levine, M., Moss, J., White, J.D. (Ed), Encyclopedia of Dietary Supplements. Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, p. 108 (2005)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for CHOLINE BITARTRATE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Free choline is not fully absorbed, especially after large doses, and intestinal bacteria metabolize choline to trimethylamine. /Choline/
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1575
/The/ ability to form choline /de novo via the methylation of phosphatidylethanolamine using S-adenosylmethionine as the methyl donor, mostly in the liver,/ means that some of the demand for choline can ... be met using methyl groups derived from 1-carbon metabolism (via methyl-folate and methionine). Several vitamins (folate, vitamin B12, vitamin B6, and riboflavin) and the amino acid methionine interact with choline in 1-carbon metabolism ... Methionine, methyl-tetrahydrofolate (THF), and choline can be fungible sources of methyl groups. /Choline/
Coates, P.M., Blackman, M.R., Cragg, G.M., Levine, M., Moss, J., White, J.D. (Ed), Encyclopedia of Dietary Supplements. Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, p. 105 (2005)
Before choline can be absorbed in the gut, some is metabolized by bacteria to form betaine and methylamines (which are not methyl donors) ... Although some free choline is excreted with urine, most is oxidized in the kidney to form betaine ... /Choline/
Coates, P.M., Blackman, M.R., Cragg, G.M., Levine, M., Moss, J., White, J.D. (Ed), Encyclopedia of Dietary Supplements. Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, p. 106 (2005)
Acetylcholine is one of the most important neurotransmitters used by neurons in the memory centers of the brain (hippocampus and septum). Choline accelerates the synth and release of acetylcholine in nerve cells. Choline used by brain neurons is largely derived from membrane lecithin /(phosphatidylcholine)/, or from dietary intake of choline and lecithin ... Choline derived from lecithin may be especially important when extracellular choline is in short supply, as might be expected to occur in advanced age because of decr brain choline uptake ... /Choline/
Coates, P.M., Blackman, M.R., Cragg, G.M., Levine, M., Moss, J., White, J.D. (Ed), Encyclopedia of Dietary Supplements. Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, p. 107 (2005)
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for CHOLINE BITARTRATE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Several mechanisms are suggested for the cancer-promoting effect of a choline-devoid diet. These incl incr cell proliferation related to regeneration after parenchymal cell death occurs in the choline deficient liver, hypomethylation of DNA (alters expression of genes), reactive oxygen species leakage from mitochondria with incr lipid peroxidation in liver, activation of protein kinase C signaling due to accumulation of diacylglycerol in liver, mutation of the fragile histidine triad (FHIT) gene, which is a tumor suppressor gene, and defective cell-suicide (apoptosis) mechanisms. Loss of phposphatidylethanolamine N-methyl-transferase (PEMT) function may also contribute to malignant transformation of hepatocytes. /Choline/
Coates, P.M., Blackman, M.R., Cragg, G.M., Levine, M., Moss, J., White, J.D. (Ed), Encyclopedia of Dietary Supplements. Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, p. 107 (2005)
Acetylcholine is one of the most important neurotransmitters used by neurons in the memory centers of the brain (hippocampus and septum). Choline accelerates the synth and release of acetylcholine in nerve cells. /Choline/
Coates, P.M., Blackman, M.R., Cragg, G.M., Levine, M., Moss, J., White, J.D. (Ed), Encyclopedia of Dietary Supplements. Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, p. 107 (2005)
... Choline deficiency in cell culture causes apoptosis or programmed cell death. This appears to be due to abnormalities in cell membrane phosphatidylcholine content and an incr in ceramide, a precursor, as well as a metabolite of sphingomyelin. Ceramide accumulation, which is caused by choline deficiency, appears to activate a caspase, a type of enzyme that mediates apoptosis. /Choline/
Thomson Healthcare. PDR for Nutritional Supplements. Thomson Health Care Inc. Montvale, NJ. p.90 (2001)
Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
33
PharmaCompass offers a list of Choline Tartrate API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Choline Tartrate manufacturer or Choline Tartrate supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Choline Tartrate manufacturer or Choline Tartrate supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Choline Tartrate API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Choline Tartrate API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Choline Tartrate Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Choline Tartrate Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Choline Tartrate manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Choline Tartrate, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Choline Tartrate manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Choline Tartrate API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Choline Tartrate manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Choline Tartrate supplier is an individual or a company that provides Choline Tartrate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Choline Tartrate finished formulations upon request. The Choline Tartrate suppliers may include Choline Tartrate API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Choline Tartrate suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Choline Tartrate Drug Master File in Korea (Choline Tartrate KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Choline Tartrate. The MFDS reviews the Choline Tartrate KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Choline Tartrate KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Choline Tartrate KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Choline Tartrate API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Choline Tartrate suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Choline Tartrate written confirmation (Choline Tartrate WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Choline Tartrate manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Choline Tartrate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Choline Tartrate APIs or Choline Tartrate finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Choline Tartrate WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Choline Tartrate suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
Choline Tartrate Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Choline Tartrate GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Choline Tartrate GMP manufacturer or Choline Tartrate GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Choline Tartrate CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Choline Tartrate's compliance with Choline Tartrate specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Choline Tartrate CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Choline Tartrate CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Choline Tartrate may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Choline Tartrate EP), Choline Tartrate JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Choline Tartrate USP).
