
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
API
0
FDF
0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Finished Drug Prices
NA
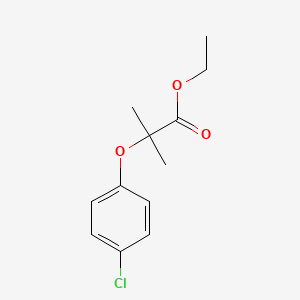

1. Athromidin
2. Atromid
3. Atromid S
4. Chlorophenoxyisobutyrate, Ethyl
5. Clofibric Acid, Ethyl Ester
6. Ethyl Chlorophenoxyisobutyrate
7. Miscleron
8. Miskleron
1. 637-07-0
2. Ethyl 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)-2-methylpropanoate
3. Ethyl Clofibrate
4. Atromid
5. Clofibratum
6. Atromid-s
7. Clofibrato
8. Liprin
9. Miscleron
10. Epib
11. Angiokapsul
12. Antilipid
13. Antilipide
14. Arterioflexin
15. Arterosol
16. Ateriosan
17. Athebrate
18. Atheromide
19. Atheropront
20. Chlorphenisate
21. Clofibate
22. Lipofacton
23. Ticlobran
24. Amotril
25. Anparton
26. Ateculon
27. Atrolen
28. Atromida
29. Lipavil
30. Lipavlon
31. Lipomid
32. Liprinal
33. Xyduril
34. Apolan
35. Amotril S
36. Ethyl Chlorophenoxyisobutyrate
37. Athranid-wirkstoff
38. Atromidin
39. Bioscleran
40. Cartagyl
41. Citiflus
42. Claripex
43. Clofibram
44. Clofibrat
45. Clofinit
46. Clofipront
47. Fibralem
48. Gerastop
49. Hyclorate
50. Klofibrat
51. Klofiran
52. Levatrom
53. Lipidsenker
54. Liponorm
55. Liporeduct
56. Lobetrin
57. Normalip
58. Persantinat
59. Regardin
60. Serotinex
61. Skleromexe
62. Atrovis
63. Azionyl
64. Bresit
65. Clobrat
66. Clofar
67. Delipid
68. Deliva
69. Lipamid
70. Liporil
71. Liposid
72. Normat
73. Regelan
74. Sklero
75. Dura Clofibrat
76. Sklero-tablinen
77. Neo-atomid
78. Neo-atromid
79. Atromid S
80. Claripex Cpib
81. Clobren-sf
82. Elpi
83. Cinnarizin
84. Cloberat
85. Misclerone
86. Normolipol
87. Robigram
88. Skerolip
89. Artevil
90. Negalip
91. Normet
92. Recolip
93. Scrobin
94. Yoclo
95. Sklero-tabuls
96. Regelan N
97. 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic Acid Ethyl Ester
98. Lipide 500
99. Chlorfenisate
100. Oxan 600
101. Propanoic Acid, 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)-2-methyl-, Ethyl Ester
102. Ethyl 2-(p-chlorophenoxy)isobutyrate
103. Ethyl P-chlorophenoxyisobutyrate
104. Nsc-79389
105. 2-(p-chlorophenoxy)-2-methylpropionic Acid Ethyl Ester
106. Ethyl Para-chlorophenoxyisobutyrate
107. Ethyl 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)-2-methylpropionate
108. Ici 28257
109. Ay-61123
110. Ay 61123
111. Alpha-p-chlorophenoxyisobutyryl Ethyl Ester
112. Ethyl 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)isobutyrate
113. Ethyl 2-(p-chlorophenoxy)-2-methylpropionate
114. Alpha-(p-chlorophenoxy)isobutyric Acid, Ethyl Ester
115. Ici-28257
116. 19 More Names Available
117. Propionic Acid, 2-(p-chlorophenoxy)-2-methyl-, Ethyl Ester
118. Chembl565
119. Hpn91k7fu3
120. Acetic Acid, (p-chlorophenoxy)dimethyl-, Ethyl Ester
121. Chebi:3750
122. Propanoic Acid, 2-(p-chlorophenoxy)-2-methyl-, Ethyl Ester
123. Propionic Acid, 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)-2-methyl-, Ethyl Ester
124. .alpha.-p-chlorophenoxyisobutyryl Ethyl Ester
125. 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)isobutyric Acid Ethyl Ester
126. Nsc79389
127. .alpha.-(p-chlorophenoxy)isobutyric Acid, Ethyl Ester
128. Ncgc00015257-08
129. Sklerepmexe
130. Serofinex
131. Sklerolip
132. Skleromex
133. Clofibrato [spanish]
134. Ethyl .alpha.-(4-chlorophenoxy)isobutyrate
135. Ethyl .alpha.-(p-chlorophenoxy)isobutyrate
136. Dsstox_cid_336
137. Sklero-tablinene
138. Clobren-5f
139. Dsstox_rid_75521
140. Vincamin Compositum
141. Clofibratum [inn-latin]
142. Dsstox_gsid_20336
143. Clofibrato [inn-spanish]
144. Ethyl 2-[(4-chlorophenyl)oxy]-2-methylpropanoate
145. Ethyl .alpha.-(p-chlorophenoxy)-.alpha.-methylpropionate
146. Ethyl .alpha.-(4-chlorophenoxy)-.alpha.-methylpropionate
147. Abitrate
148. Cas-637-07-0
149. Smr000058279
150. Ccris 177
151. Clofibrate (clof)
152. Ethyl-alpha-p-chlorophenoxy-isobutyrate
153. Ethyl Alpha-(4-chlorophenoxy)isobutyrate
154. Ethyl Alpha-(p-chlorophenoxy)isobutyrate
155. Hsdb 3038
156. Sr-01000075544
157. Einecs 211-277-4
158. Atromid-s (tn)
159. Nsc 79389
160. Unii-hpn91k7fu3
161. Brn 1913459
162. Bml2-f02
163. Clobren Sf
164. Clofibrate, Liquid
165. Ethyl Alpha-(4-chlorophenoxy)-alpha-methylpropionate
166. Ethyl Alpha-(p-chlorophenoxy)-alpha-methylpropionate
167. Mfcd00000615
168. Clofibrate [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
169. Isobutyric Acid, Alpha-(p-chlorophenoxy)-, Ethyl Ester
170. Ethyl 2-(para-chlorophenoxy)-2-methylpropionate (iupac)
171. Spectrum_001735
172. P-chlorophenoxyisobutyric Acid Ethyl Ester
173. Clofibrate [mi]
174. Clofibrate [inn]
175. Clofibrate [jan]
176. Spectrum2_001209
177. Spectrum4_000223
178. Spectrum5_001133
179. Clofibrate [hsdb]
180. Clofibrate [iarc]
181. Clofibrate [usan]
182. Lopac-c-6643
183. Clofibrate [vandf]
184. Upcmld-dp019
185. C 6643
186. Ethyl 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)-2-methyl-propanoate
187. Clofibrate [mart.]
188. Schembl2356
189. Clofibrate [who-dd]
190. Nciopen2_004739
191. Bidd:pxr0178
192. Cbiol_001860
193. Lopac0_000306
194. Bspbio_001577
195. Kbiogr_000297
196. Kbiogr_000885
197. Kbioss_000297
198. Kbioss_002215
199. Mls001336011
200. Mls001336012
201. Mls002153494
202. Bidd:gt0172
203. Divk1c_000822
204. Divk1c_000926
205. Spbio_000998
206. Clofibrate (jp17/usp/inn)
207. Gtpl2667
208. Clofibrate [orange Book]
209. Dtxsid3020336
210. Upcmld-dp019:001
211. Bcbcmap01_000104
212. Hms502j04
213. Hms502o08
214. Kbio1_000822
215. Kbio1_000926
216. Kbio2_000297
217. Kbio2_002215
218. Kbio2_002865
219. Kbio2_004783
220. Kbio2_005433
221. Kbio2_007351
222. Kbio3_000593
223. Kbio3_000594
224. Wln: Gr Dox1&1&vo2
225. Zinc56648
226. Clofibrate [ep Monograph]
227. Clofibrate [usp Impurity]
228. Clofibrate, >=98.0% (gc)
229. Ninds_000822
230. Ninds_000926
231. Bio1_000146
232. Bio1_000635
233. Bio1_001124
234. Bio2_000297
235. Bio2_000777
236. Hms1361o19
237. Hms1791o19
238. Hms1989o19
239. Hms2089p03
240. Hms2093g07
241. Hms2233c17
242. Hms3260n14
243. Hms3373c06
244. Hms3402o19
245. Hms3715j03
246. Pharmakon1600-01503429
247. Hy-b0287
248. Tox21_110116
249. Tox21_202414
250. Tox21_300277
251. Tox21_500306
252. Bdbm50085047
253. Ccg-40281
254. Nsc758474
255. Akos015889383
256. Tox21_110116_1
257. Db00636
258. Lp00306
259. Nsc-758474
260. Sdccgsbi-0050294.p004
261. Idi1_000822
262. Idi1_000926
263. Idi1_034047
264. Clofibrate, Analytical Reference Material
265. Ncgc00015257-01
266. Ncgc00015257-02
267. Ncgc00015257-03
268. Ncgc00015257-04
269. Ncgc00015257-05
270. Ncgc00015257-06
271. Ncgc00015257-07
272. Ncgc00015257-09
273. Ncgc00015257-10
274. Ncgc00015257-11
275. Ncgc00015257-12
276. Ncgc00015257-14
277. Ncgc00015257-22
278. Ncgc00093755-01
279. Ncgc00093755-03
280. Ncgc00093755-04
281. Ncgc00093755-05
282. Ncgc00093755-06
283. Ncgc00093755-07
284. Ncgc00093755-08
285. Ncgc00254073-01
286. Ncgc00259963-01
287. Ncgc00260991-01
288. Ac-33179
289. As-14127
290. Clofibrate 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
291. Nci60_041748
292. Ethyl .alpha.-p-(chlorophenoxy)isobutyrate
293. Sbi-0050294.p003
294. Db-054528
295. Ethyl2-(4-chlorophenoxy)-2-methylpropanoate
296. Eu-0100306
297. Ft-0625865
298. Ft-0665112
299. S1820
300. 2-(p-chlorophenoxy)isobutyric Acid Ethyl Ester
301. C06916
302. D00279
303. F20382
304. Ab00052358-07
305. Ab00052358-08
306. Ab00052358_09
307. Ab00052358_10
308. Ethyl 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)-2-methylpropanoate #
309. A834483
310. Ethyl 2-(4-chloranylphenoxy)-2-methyl-propanoate
311. Acetic Acid, (p-chlorophenoxy)dimethyl-, Ethyl Este
312. Ethyl 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)-2-methylpropionate, 99%
313. Q2701912
314. Sr-01000075544-1
315. Sr-01000075544-4
316. Sr-01000075544-5
317. Sr-01000075544-8
318. Z53835984
319. 2-(p-chlorophenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic Acid Ethyl Ester
320. 2-(4-chloro-phenoxy)-2-methyl-propionic Acid Ethyl Ester
321. Clofibrate, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
322. Isobutyric Acid, .alpha.-(p-chlorophenoxy)-, Ethyl Ester
323. Clofibrate, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
| Molecular Weight | 242.70 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C12H15ClO3 |
| XLogP3 | 3.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 242.0709720 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 242.0709720 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 35.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 16 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 232 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Anticholesteremic Agents; Antilipemic Agents
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
Clofibrate is indicated only in subjects with increased concentrations of VLDL and IDL (such as patients with familial type-III hyperlipoproteinemia) who have failed to respond adequately to gemfibrozil or nicotinic acid. Because clofibrate has only a modest effect on LDL and more effective agents are available for lowering the concentration of LDL, the drug is of limited utility for patients with either familial hypercholesterolemia or polygenic hypercholesterolemia.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 889
In a ... trial of primary prevention involving asymptomatic men with hypercholesterolemia, clofibrate lowered the plasma cholesterol concentration by only 6 to 11%. This very modest effect in unselected patients can be contrasted with that seen in patients with familial type-III hyperlipoproteinemia, in whom concentrations of cholesterol and triglycerides were lowered by approximately 50% and by as much as 80%, respectively. In such patients, administration of clofibrate results in the mobilization of deposits of cholesterol in tissues, accompanied by regression and disappearance of xanthomas. Clofibrate has no effect on hyperchylomicronemia, nor does it affect concentrations of HDL. Thus, clofibrate appears to have specific efficacy only in patients with familial type-III hyperlipoproteinemia.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 886
The clinical evidence for the efficacy of clofibrate in preventing deaths from coronary artery disease is not encouraging. A number of clinical trials have been completed, and none has shown a clear-cut beneficial effect. A double blind study ... compared clofibrate with placebo in 10,000 men in the upper third of the distribution of plasma cholesterol concentrations. Patients treated with clofibrate had a decrease in nonfatal myocardial infarctions. ... Clofibrate treated patients had a higher noncardiac mortality rate than did control subjects, owing mainly to an increased incidence of malignant neoplasms and complications of cholecystectomy.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 886
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CLOFIBRATE (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Impotence observed after clofibrate treatment was the fourth most frequently occurring side effect of more than 30 side effects recorded ... . Although the exact mechanism is not known ...
Thomas, J.A., K.S. Korach, J.A. McLachlan. Endocrine Toxicology. New York, NY: Raven Press, Ltd., 1985., p. 278
Response to clofibrate is variable, and serum cholesterol and triglyceride concn should be determined prior to and regularly during (eg, every 3-6 mo) clofibrate therapy. If possible, the LDL and HDL fractions should also be determined and the LDL fraction rechecked during the first few months of clofibrate therapy ...
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 1162
Liver function tests and complete blood cell counts should be performed periodically during clofibrate therapy ... some clinicians recommend serial determinations of plasma CK (CPK) concn during treatment with clofibrate ...
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 1162
...THE DRUG IS OF LIMITED UTILITY FOR PATIENTS WITH TYPE-II HYPERLIPOPROTEINEMIA. FURTHERMORE, SINCE CLOFIBRATE MAY INCREASE THE CONCN OF LOW DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN IN SOME PATIENTS WITH ELEVATIONS OF VERY LOW DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN /VLDL/, THE EFFECTS OF THE DRUG SHOULD BE MONITORED BY SEQUENTIAL MEASUREMENT OF PLASMA LIPOPROTEINS. A SHIFT FROM AN EXCESS OF VLDL TO ONE OF LDL /LOW DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN/ SUGGESTS THE NECESSITY TO DISCONTINUE THE DRUG.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 841
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for CLOFIBRATE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For Primary Dysbetalipoproteinemia (Type III hyperlipidemia) that does not respond adequately to diet. This helps control high cholesterol and high triglyceride levels.
Clofibrate is an antilipidemic agent similar to gemfibrozil. It acts to lower elevated serum lipids by reducing the very low-density lipoprotein fraction (Sf 20-400) rich in triglycerides. Serum cholesterol may be decreased, particularly in those patients whose cholesterol elevation is due to the presence of IDL as a result of Type III hyperlipoproteinemia. Several investigators have observed in their studies that clofibrate may produce a decrease in cholesterol linoleate but an increase in palmitoleate and oleate, the latter being considered atherogenic in experimental animals. The significance of this finding is unknown at this time. Reduction of triglycerides in some patients treated with clofibrate or certain of its chemically and clinically similar analogs may be associated with an increase in LDL cholesterol. Increase in LDL cholesterol has been observed in patients whose cholesterol is initially normal. Animal studies suggest that clofibrate interrupts cholesterol biosynthesis prior to mevalonate formation.
Anticholesteremic Agents
Substances used to lower plasma cholesterol levels. (See all compounds classified as Anticholesteremic Agents.)
Hypolipidemic Agents
Substances that lower the levels of certain LIPIDS in the BLOOD. They are used to treat HYPERLIPIDEMIAS. (See all compounds classified as Hypolipidemic Agents.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C10 - Lipid modifying agents
C10A - Lipid modifying agents, plain
C10AB - Fibrates
C10AB01 - Clofibrate
Absorption
Completely but slowly absorbed from the intestine. Between 95% and 99% of an oral dose of clofibrate is excreted in the urine as free and conjugated clofibric acid; thus, the absorption of clofibrate is virtually complete.
IN MAN, CLOFIBRATE IS COMPLETELY ABSORBED FROM INTESTINE & APPEARS IN PLASMA AS DEESTERIFIED P-CHLOROPHENOXYISOBUTYRIC ACID (CPIB); PEAK PLASMA CONCN OF THE ACID OCCUR WITHIN 4 HR AFTER ORAL ADMIN ... MAJOR FRACTION OF CPIB ... BOUND TO PLASMA ALBUMIN. ELIMINATION OF CPIB PROCEEDS IN 2 KINETIC PHASES, WITH SLOWER EXPONENTIAL PHASE HAVING MEAN HALF-LIFE OF NEARLY 15 HR. ESSENTIALLY ALL ACID ... EXCRETED IN URINE, ABOUT 60% AS GLUCURONIDE.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 841
TRANSFER ACROSS THE PLACENTA AND INTO THE MILK AND A POSTNATAL INCREASE IN LIVER ALPHA-GLYCEROPHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE HAS BEEN REPORTED IN NEWBORN RATS WHOSE MOTHERS WERE FED CLOFIBRATE.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V24 45 (1980)
CLOFIBRATE IS RAPIDLY AND COMPLETELY ABSORBED AFTER ORAL ADMINISTRATION. IN MAN, CLOFIBRIC ACID, A MAJOR METABOLITE OF CLOFIBRATE, IS EXCRETED IN THE URINE IN THE FORM OF THE GLUCURONIDE CONJUGATE; THE PLASMA ELIMINATION HALF-LIFE OF CLOFIBRIC ACID RANGES BETWEEN 12-25 HOURS.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V24 48 (1980)
Clofibrate is readily and reportedly almost completely absorbed from the GI tract; approx 95-99% of an orally admin dose ... is excreted in urine as free and conjugated clofibric acid. The drug is rapidly hydrolyzed by serum enzymes to the free acid, clofibric acid ... . Peak plasma clofibric acid concn 4-6 hr after oral admin of a single 500-mg, 1-g, or 2-g doses of clofibrate in healthy individuals average 49-53, 89, or 151 ug/ml, respectively.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 1160
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for CLOFIBRATE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Hepatic and gastrointestinal: rapid de-esterification occurs in the gastrointestinal tract and/or on first-pass metabolism to produce the active form, clofibric acid (chlorophenoxy isobutyric acid [CPIB]).
IN MAN, CLOFIBRATE ... APPEARS IN PLASMA AS DEESTERIFIED PARA-CHLOROPHENOXYISOBUTYRIC ACID ... ESSENTIALLY ALL ACID ... EXCRETED IN URINE, ABOUT 60% AS GLUCURONIDE.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 841
AN ACYL-LINKED ACID METABOLITE OF CLOFIBRATE HAS BEEN IDENTIFIED IN HUMAN URINE. THIS REPRESENTS THE FIRST ACYL-LINKED MERCAPTURATE FOUND IN MAN. AUTHORS PROPOSE THAT CLOFIBRATE ACYL GLUCURONIDE IS AN ELECTROPHILIC METABOLITE WHICH REACTS WITH SULFHYDRYL GROUPS & THEREFORE MAY BE RESPONSIBLE FOR THE HUMAN HEPATOTOXICITY OF CLOFIBRATE.
PMID:6130909 STOGNIEW W, FENSELAU C; DRUG METAB DISPOS 10 (6): 609-13 (1982)
Half-life in normal volunteers averages 18 to 22 hours (range 14 to 35 hours) but can vary by up to 7 hours in the same subject at different times.
THE PLASMA ELIMINATION HALF-LIFE OF CLOFIBRIC ACID RANGES BETWEEN 12-25 HOURS.
IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V24 48 (1980)
Clofibric acid has an elimination half-life of 12-35 hr (mean 12-22 hr) in healthy adults and 29-88 hr in patients with renal failure. /Clofibric acid/
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 1160
Clofibrate increases the activity of extrahepatic lipoprotein lipase (LL), thereby increasing lipoprotein triglyceride lipolysis. Chylomicrons are degraded, VLDLs are converted to LDLs, and LDLs are converted to HDL. This is accompanied by a slight increase in secretion of lipids into the bile and ultimately the intestine. Clofibrate also inhibits the synthesis and increases the clearance of apolipoprotein B, a carrier molecule for VLDL. Also, as a fibrate, Clofibrate is an agonist of the PPAR- receptor[4] in muscle, liver, and other tissues. This agonism ultimately leads to modification in gene expression resulting in increased beta-oxidation, decreased triglyceride secretion, increased HDL, increased lipoprotein lipase activity.
Clofibrate decreases serum very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) concn in healthy individuals and abnormal lipoproteins in patients with type III hyperlipoproteinemia. Serum triglyceride concn are usually reduced more than cholesterol concn.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 1160
The exact mechanism by which clofibrate lowers serum concn of triglycerides and cholesterol is unknown. Apparently, the drug has several antilipemic actions, including increasing triglyceride and VLDL clearance, inhibition of the biosynthesis of cholesterol before mevalonate formation, mobilization of cholesterol from tissues, increasing fecal excretion of neutral sterols, decreasing hepatic lipoprotein synthesis and/or secretion (particularly VLDL), decreasing free fatty acid release, and decreasing triglyceride synthesis.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 1160
Clofibrate induces changes in blood coagulation which are independent of the lipid-lowering action of the drug. The drug decreases platelet adhesiveness. Plasma fibrinogen concn decrease during the first 6 wk to 4 mo of therapy after which the concn return toward normal. Plasma fibrinolysis is usually increased.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 1160
Their primary effect is to increase the activity of lipoprotein lipase, which in turn promotes the catabolism of the triglyceride rich lipoproteins, VLDL and IDL. The drugs may also decrease the hepatic synthesis and secretion of VLDL. Fibric acids are believed to raise HDL cholesterol indirectly as a result of the decrease in the concentration of VLDL triglyceride. VLDL normally exchanges lipids with HDL, the triglycerides of VLDL moving to HDL and the cholesteryl esters of HDL moving to VLDL. When VLDL concentrations are reduced, this exchange is slowed. Cholesteryl esters remain in HDL and thus the concentration of HDL cholesterol increases. /Fibric Acids/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 888
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE


LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?