
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
Annual Reports
NA
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
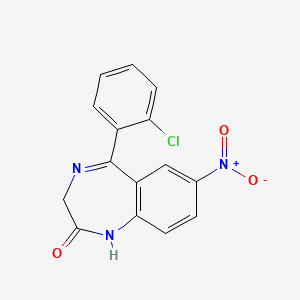

1. 2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one, 5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-7-nitro-
2. Antelepsin
3. Klonopin
4. Rivotril
5. Ro 5-4023
6. Ro 54023
1. Klonopin
2. Rivotril
3. 1622-61-3
4. Chlonazepam
5. Antelepsin
6. Cloazepam
7. Iktorivil
8. Clonazepamum
9. Clonopin
10. Landsen
11. Antilepsin
12. Lonazep
13. Kenoket
14. Ravotril
15. Rivatril
16. Clonex
17. Paxam
18. Ro 5-4023
19. Ro 4-8180
20. 5-(2-chlorophenyl)-7-nitro-1,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
21. 2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one, 5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-7-nitro-
22. Clonazepam Civ
23. 1,3-dihydro-7-nitro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-2h-1,4.benzodiazepin-2-one
24. 5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-7-nitro-2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
25. 5-(o-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-7-nitro-2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
26. Nsc 179913
27. Ro-5-4023
28. 7-nitro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-3h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2(1h)-one
29. Ro-54023
30. 5pe9fde8gb
31. Chembl452
32. Nsc-179913
33. 5-(2-chlorophenyl)-7-nitro-1,3-dihydro-2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
34. 2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one, 5-(o-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-7-nitro-
35. Chebi:3756
36. Lktorivil
37. Solfidin
38. Alti-clonazepam
39. 5-(o-chlorophenyl)-7-nitro-1,3-dihydro-2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
40. 5-(2-chloro-phenyl)-7-nitro-1,3-dihydro-benzo[e][1,4]diazepin-2-one
41. Nsc179913
42. Melzap
43. 2-h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one, 5-(o-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-7-nitro-
44. Klonopin Rapidly Disintegrating
45. Clonazepamum [inn-latin]
46. Apetryl
47. 5-(2-chlorophenyl)-7-nitro-1h-benzo[e][1,4]diazepin-2(3h)-one
48. Klonopin (tn)
49. Ro 54023
50. Ro 5-4023/b-7
51. Hsdb 3265
52. Einecs 216-596-2
53. Unii-5pe9fde8gb
54. Brn 0759557
55. Dea No. 2737
56. 5-(o-chlorophenyl)-7-nitro-1h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2(3h)-one
57. Clonazepam, Powder
58. Ro 4023
59. Ro4023
60. Clonazepam [usan:usp:inn:ban:jan]
61. Clonazepam [mi]
62. Clonazepam [inn]
63. Clonazepam [jan]
64. Clonazepam [hsdb]
65. Clonazepam [usan]
66. 1,4.benzodiazepin-2-one
67. Clonazepam [vandf]
68. Clonazepam [mart.]
69. Clonazepam [who-dd]
70. Bidd:pxr0144
71. Oprea1_168772
72. Schembl38899
73. 5-24-04-00351 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
74. Mls003899214
75. Divk1c_000973
76. Clonazepam (jp17/usp/inn)
77. Gtpl6963
78. Clonazepam [orange Book]
79. Clonazepam Civ [usp-rs]
80. Dtxsid1022845
81. Niosh/df2374250
82. Clonazepam--dea Schedule Iv Item
83. Hms503c07
84. Kbio1_000973
85. Clonazepam [ep Monograph]
86. Ninds_000973
87. Clonazepam [usp Monograph]
88. Hms2093h22
89. Clonazepam 0.1 Mg/ml In Methanol
90. Clonazepam 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol
91. Zinc3813003
92. 1,3-dihydro-5-(o-chlorophenyl)-7-nitro-3h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
93. Bdbm50019213
94. Akos015902192
95. Ccg-213669
96. Db01068
97. Idi1_000973
98. Wln: T67 Gmv Jn Ihj Cnw Kr Bg
99. 106955-87-7
100. Ac-15733
101. Smr000058982
102. Sbi-0206863.p001
103. Df23742500
104. 5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
105. 5-(o-chlorophenyl)-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
106. D00280
107. Ab01563349_01
108. 622c613
109. A810362
110. Q407988
111. Sr-01000937610
112. 2-h-1, 5-(o-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-7-nitro-
113. 2h-1, 5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-7-nitro-
114. 2h-1, 5-(o-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-7-nitro-
115. Sr-01000937610-2
116. Clonazepam Solution, Drug Standard, 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol
117. Clonazepam, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
118. 3h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one, 1,3-dihydro-5-(o-chlorophenyl)-7-nitro-
119. 5-(2-chlorophenyl)-7-nitro-1,3-dihydro-2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one #
120. 5-(2-chlorophenyl)-7-nitro-2,3-dihydro-1h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
121. 7-nitro-1,3-dihydro-5-(o-chlorophenyl)-2h-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
122. Clonazepam Solution, 1.0 Mg/ml In Methanol, Ampule Of 1 Ml, Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 315.71 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C15H10ClN3O3 |
| XLogP3 | 2.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Exact Mass | 315.0410689 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 315.0410689 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 87.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 491 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Clonazepam |
| PubMed Health | Clonazepam (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianxiety, Anticonvulsant |
| Drug Label | Clonazepam, USP a benzodiazepine, is available for oral administration as scored tablets containing 0.5 mg, 1 mg or 2 mg of clonazepam. In addition, each tablet also contains the following inactive ingredients: corn starch, lactose monohydrate, magne... |
| Active Ingredient | Clonazepam |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, orally disintegrating; Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 0.5mg; 2mg; 1mg; 0.25mg; 0.125mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Watson Labs; Vintage Pharms; Mylan Pharms; Actavis Elizabeth; Teva; Accord Hlthcare; Sun Pharm Inds; Sandoz; Par Pharm; Mylan; Barr |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Klonopin |
| PubMed Health | Clonazepam (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianxiety, Anticonvulsant |
| Drug Label | Klonopin, a benzodiazepine, is available as scored tablets with a K-shaped perforation containing 0.5 mg of clonazepam and unscored tablets with a K-shaped perforation containing 1 mg or 2 mg of clonazepam. Each tablet also contains lactose, magnesiu... |
| Active Ingredient | Clonazepam |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 0.5mg; 1mg; 2mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Roche |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Clonazepam |
| PubMed Health | Clonazepam (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianxiety, Anticonvulsant |
| Drug Label | Clonazepam, USP a benzodiazepine, is available for oral administration as scored tablets containing 0.5 mg, 1 mg or 2 mg of clonazepam. In addition, each tablet also contains the following inactive ingredients: corn starch, lactose monohydrate, magne... |
| Active Ingredient | Clonazepam |
| Dosage Form | Tablet, orally disintegrating; Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 0.5mg; 2mg; 1mg; 0.25mg; 0.125mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Watson Labs; Vintage Pharms; Mylan Pharms; Actavis Elizabeth; Teva; Accord Hlthcare; Sun Pharm Inds; Sandoz; Par Pharm; Mylan; Barr |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Klonopin |
| PubMed Health | Clonazepam (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antianxiety, Anticonvulsant |
| Drug Label | Klonopin, a benzodiazepine, is available as scored tablets with a K-shaped perforation containing 0.5 mg of clonazepam and unscored tablets with a K-shaped perforation containing 1 mg or 2 mg of clonazepam. Each tablet also contains lactose, magnesiu... |
| Active Ingredient | Clonazepam |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | 0.5mg; 1mg; 2mg |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Roche |
Anticonvulsants; GABA Modulators
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Clonazepam. Online file (MeSH, 2017). Available from, as of October 2, 2017: https://meshb.nlm.nih.gov/search
/CLINICAL TRIALS/ ClinicalTrials.gov is a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world. The Web site is maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Each ClinicalTrials.gov record presents summary information about a study protocol and includes the following: Disease or condition; Intervention (for example, the medical product, behavior, or procedure being studied); Title, description, and design of the study; Requirements for participation (eligibility criteria); Locations where the study is being conducted; Contact information for the study locations; and Links to relevant information on other health Web sites, such as NLM's MedlinePlus for patient health information and PubMed for citations and abstracts for scholarly articles in the field of medicine. Clonazepam is included in the database.
NIH/NLM; ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available from, as of October 2, 2017: https://clinicaltrials.gov/
Klonopin is useful alone or as an adjunct in the treatment of the Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (petit mal variant), akinetic and myoclonic seizures. In patients with absence seizures (petit mal) who have failed to respond to succinimides, Klonopin may be useful. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Klonopin (Clonazepam) Tablet (July 2017). Available from, as of October 9, 2017: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=542f22e8-dad2-47a8-93b6-30936715d73b
Klonopin is indicated for the treatment of panic disorder, with or without agoraphobia, as defined in DSM-IV. Panic disorder is characterized by the occurrence of unexpected panic attacks and associated concern about having additional attacks, worry about the implications or consequences of the attacks, and/or a significant change in behavior related to the attacks. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Klonopin (Clonazepam) Tablet (July 2017). Available from, as of October 9, 2017: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=542f22e8-dad2-47a8-93b6-30936715d73b
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Clonazepam (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: RISKS FROM CONCOMITANT USE WITH OPIOIDS. Concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate. Limit dosages and durations to the minimum required. Follow patients for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Klonopin (Clonazepam) Tablet (July 2017). Available from, as of October 9, 2017: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=542f22e8-dad2-47a8-93b6-30936715d73b
Klonopin should not be used in patients with a history of sensitivity to benzodiazepines, nor in patients with clinical or biochemical evidence of significant liver disease. It may be used in patients with open angle glaucoma who are receiving appropriate therapy but is contraindicated in acute narrow angle glaucoma.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Klonopin (Clonazepam) Tablet (July 2017). Available from, as of October 9, 2017: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=542f22e8-dad2-47a8-93b6-30936715d73b
Benzodiazepines have the potential to impair judgment, thinking, or motor skills. Therefore, patients receiving clonazepam should be cautioned that the drug may impair their ability to perform activities requiring mental alertness or physical coordination (e.g., operating machinery, driving a motor vehicle) and to avoid such activities until they experience how the drug affects them.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2017; Drug Information 2017. Bethesda, MD. 2017, p. 2339
Clinical studies of Klonopin did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy. Because clonazepam undergoes hepatic metabolism, it is possible that liver disease will impair clonazepam elimination. Metabolites of Klonopin are excreted by the kidneys; to avoid their excess accumulation, caution should be exercised in the administration of the drug to patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased hepatic and/or renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to assess hepatic and/or renal function at the time of dose selection. Sedating drugs may cause confusion and over-sedation in the elderly; elderly patients generally should be started on low doses of Klonopin and observed closely.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Klonopin (Clonazepam) Tablet (July 2017). Available from, as of October 9, 2017: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=542f22e8-dad2-47a8-93b6-30936715d73b
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Clonazepam (30 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Clonazepam is indicated as monotherapy or as an adjunct in the treatment of Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (petit mal variant), akinetic, and myoclonic seizures. Furthermore, clonazepam may also be of some value in patients with absence spells (petit mal) who have failed to respond to succinimides. Additionally, clonazepam is also indicated for the treatment of panic disorder, with or without agoraphobia, as defined in the DSM-V. Alternatively, some regional prescribing information note that clonazepam is indicated for all clinical forms of epileptic disease and seizures in adults, especially absence seizures (petit mal) including atypical absence; primary or secondarily generalised tonic-clonic (grand mal), tonic or clonic seizures; partial (focal) seizures with elementary or complex symptomatology; various forms of myoclonic seizures, myoclonus and associated abnormal movements. Such regional label data also has clonazepam indicated for most types of epilepsy in infants and children, especially absences (petit mal), myoclonic seizures and tonic-clonic fits, whether due to primary generalized epilepsy or to secondary generalization of partial epilepsy.
FDA Label
The pharmacodynamic properties of clonazepam are common among benzodiazepines and include anticonvulsive, sedative, muscle relaxing and anxiolytic effects. Animal data and electroencephalographic investigations in man have shown that clonazepam rapidly suppresses many types of paroxysmal activity including the spike and wave discharge in absence seizures (petit mal), slow spike wave, generalized spike wave, spikes with temporal or other locations, as well as irregular spikes and waves. Moreover, the agent can also decrease the frequency, amplitude, duration, and spread of discharge in minor motor seizures. Generalized EEG abnormalities are more readily suppressed by clonazepam than are focal EEG abnormalities such as focal spikes. Clonazepam has beneficial effects in generalized and focal epilepsies.
Anticonvulsants
Drugs used to prevent SEIZURES or reduce their severity. (See all compounds classified as Anticonvulsants.)
GABA Modulators
Substances that do not act as agonists or antagonists but do affect the GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID receptor-ionophore complex. GABA-A receptors (RECEPTORS, GABA-A) appear to have at least three allosteric sites at which modulators act: a site at which BENZODIAZEPINES act by increasing the opening frequency of GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID-activated chloride channels; a site at which BARBITURATES act to prolong the duration of channel opening; and a site at which some steroids may act. GENERAL ANESTHETICS probably act at least partly by potentiating GABAergic responses, but they are not included here. (See all compounds classified as GABA Modulators.)
N03AE01
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
N - Nervous system
N03 - Antiepileptics
N03A - Antiepileptics
N03AE - Benzodiazepine derivatives
N03AE01 - Clonazepam
Absorption
Clonazepam is rapidly and almost entirely absorbed after oral administration as tablets. Peak plasma concentrations of clonazepam administered by the oral route are reached within 1-4 hours and the associated absorption half-life is about 25 minutes. The absolute bioavailability is approximately 90% - but with substantially large differences between individuals.
Route of Elimination
Approximately 50-70% of a clonazepam dose is excreted in the urine and 10-30% is excreted in the feces as metabolites. The excretion of unchanged clonazepam in the urine is typically less than 2% of the administered dose. Metabolites of clonazepam are present in urine as both free and conjugated (glucuronide and sulfate) compounds.
Volume of Distribution
Clonazepam distributes very rapidly to various organs and body tissues with preferential uptake by brain structures. The apparent volume of distribution has been documented as approximately 3 L/kg.
Clearance
The documented clearance for clonazepam is approximately 55 ml/min regardless of gender. Nevertheless, clearance values normalized by weight decline with increasing body weight.
/MILK/ A 2750-g female infant was born at 36 weeks' gestation to a 40-year-old woman treated with clonazepam throughout her pregnancy. The infant developed apnea, cyanosis, and hypotonia within a few hours of birth. The mother's serum clonazepam level at delivery was 32 ng/mL; the cord blood level was 19 ng/mL. The infant had no congenital malformations, evidence of infection, or seizures. Clinical episodes ceased by ten days of age. The woman elected to breastfeed; breast milk clonazepam levels were between 11 and 13 ng/mL. She was discharged with a cardiorespiratory monitor. The authors suggest that infants of mothers receiving this agent during pregnancy or while nursing have serum levels measured. Additionally, these infants should be monitored for central nervous system depression or apnea.
PMID:4022513 Fisher JB et al; Obstet Gynecol 66 (3 Suppl): 34S-35S (1985)
Clonazepam is rapidly and well absorbed from the GI tract. The absolute bioavailability is approximately 90%. In one study, peak blood concentrations of 6.5-13.5 ng/mL were usually reached within 1-2 hours following a single 2 mg oral dose of micronized clonazepam in healthy adults. In some individuals, however, peak blood concentrations were reached at 4-8 hours. Although the plasma concentration of clonazepam required for anticonvulsant effects has not been definitely established, some studies indicate it may be 20-80 ng/mL. Plasma concentrations in this range have been reported to be maintained in adults receiving 6 mg of clonazepam daily in 3 divided doses and in children 6-13 years of age receiving 1.5-4 mg of the drug daily in 3 divided doses. The onset of anticonvulsant action usually occurs within 20-60 minutes, and the duration of action usually is 6-8 hours in infants and young children and up to 12 hours in adults.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2017; Drug Information 2017. Bethesda, MD. 2017, p. 2340
There is little information on the distribution of clonazepam. Clonazepam is approximately 85% bound to plasma proteins. Like other benzodiazepines, the drug apparently crosses the blood-brain barrier and the placenta.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2017; Drug Information 2017. Bethesda, MD. 2017, p. 2340
Clonazepam is extensively metabolized in the liver to several metabolites ... . Only very small amounts of the drug (less than 2%) are excreted unchanged.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2017; Drug Information 2017. Bethesda, MD. 2017, p. 2340
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Clonazepam (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Clonazepam is metabolized principally in the liver. The metabolic pathways include hydroxylation, reduction of the nitro groups to amine groups, and the addition of acetate to the amino grouping. In particular, clonazepam is extensively metabolized by reduction to 7-amino-clonazepam and by N-acetylation to 7-acetamido-clonazepam. Hydroxylation at the C-3 position also occurs. Hepatic cytochrome P450 3A4 is implicated in the nitroreduction of clonazepam to pharmacologically inactive metabolites.
The shortcomings of clonazepam therapy include tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, and adverse effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, and confusion leading to increased risk of falls. Inter-individual variability in the incidence of adverse events in patients partly originates from the differences in clonazepam metabolism due to genetic and nongenetic factors. Since the prominent role in clonazepam nitro-reduction and acetylation of 7-amino-clonazepam is assigned to CYP3A and N-acetyl transferase 2 enzymes, respectively, the association between the patients' CYP3A status (CYP3A5 genotype, CYP3A4 expression) or N-acetyl transferase 2 acetylator phenotype and clonazepam metabolism (plasma concentrations of clonazepam and 7-amino-clonazepam) was evaluated in 98 psychiatric patients suffering from schizophrenia or bipolar disorders. The patients' CYP3A4 expression was found to be the major determinant of clonazepam plasma concentrations normalized by the dose and bodyweight (1263.5 +/- 482.9 and 558.5 +/- 202.4 ng/mL per mg/kg bodyweight in low and normal expressers, respectively, P<0.0001). Consequently, the dose requirement for the therapeutic concentration of clonazepam was substantially lower in low-CYP3A4 expresser patients than in normal expressers (0.029 +/- 0.011 vs 0.058 +/- 0.024 mg/kg bodyweight, P<0.0001). Furthermore, significantly higher (about 2-fold) plasma concentration ratio of 7-amino-clonazepam and clonazepam was observed in the patients displaying normal CYP3A4 expression and slower N-acetylation than all the others. Prospective assaying of CYP3A4 expression and N-acetyl transferase 2 acetylator phenotype can better identify the patients with higher risk of adverse reactions and can facilitate the improvement of personalized clonazepam therapy and withdrawal regimen.
PMID:27639091 Full text: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5203763 Toth K et al; Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016 Dec 30;19(12). pii: pyw083. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyw083.
Clonazepam is extensively metabolized in the liver to several metabolites including 7-aminoclonazepam, 7-acetaminoclonazepam, and 3-hydroxy derivatives of these metabolites and clonazepam. Clonazepam metabolites are excreted in urine by first-order kinetics, principally as their glucuronide and/or sulfate conjugates.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2017; Drug Information 2017. Bethesda, MD. 2017, p. 2340
The mean elimination half-life determined for clonazepam is independent of the dose given and has been documented as being about 30-40 hours.
Elimination half-life ... 18.7 to 39 hr.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2017; Drug Information 2017. Bethesda, MD. 2017, p. 2340
Gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) is considered the principal inhibitory neurotransmitter in the human body. When GABA binds to GABA(a) receptors found in neuron synapses, chloride ions are conducted across neuron cell membranes via an ion channel in the receptors. With enough chloride ions conducted, the local, associated neuron membrane potentials are hyperpolarized - making it more difficult or less likely for action potentials to fire, ultimately resulting in less excitation of the neurons. Subsequently, benzodiazepines like clonazepam can bind to benzodiazepine receptors that are components of various varieties of GABA(a) receptors. This binding acts to enhance the effects of GABA by increasing GABA affinity for the GABA(a) receptor, which ultimately enhances GABA ligand binding at the receptors. This enhanced ligand binding of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA to the receptors increases the aforementioned chloride ion conduction (perhaps reportedly via an increase in the frequency of the chloride channel opening), resulting in a hyperpolarized cell membrane that prevents further excitation of the associated neuron cells. Combined with the notion that such benzodiazepine receptor associated GABA(a) receptors exist both peripherally and in the CNS, this activity consequently facilitates various effects like sedation, hypnosis, skeletal muscle relaxation, anticonvulsant activity, and anxiolytic action. In particular, when out of the ordinary rapid and repetitive electrical signals are released in the CNS, it is proposed that the brain can become over-stimulated and ordinary functions are disrupted - resulting in seizure activity. By enhancing the neuro-inhibitory activity of GABA, it is believed that clonazepam can facilitate in decreasing any excessive electrical nerve activity in the CNS that might be contributing to seizures. Concurrently, it is also believed that clonazepam's actions in enhancing GABA effects may inhibit neuronal activity proposed to occur in amygdala-centered fear circuits - therefore assisting in the management of anxiety or panic.

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS

Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ANALYTICAL

ABOUT THIS PAGE
54
PharmaCompass offers a list of Clonazepam API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Clonazepam manufacturer or Clonazepam supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Clonazepam manufacturer or Clonazepam supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Clonazepam API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Clonazepam API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Clonazepam Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Clonazepam Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Clonazepam manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Clonazepam, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Clonazepam manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Clonazepam API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Clonazepam manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Clonazepam supplier is an individual or a company that provides Clonazepam active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Clonazepam finished formulations upon request. The Clonazepam suppliers may include Clonazepam API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Clonazepam suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Clonazepam DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Clonazepam active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Clonazepam DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Clonazepam USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Clonazepam DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Clonazepam USDMF includes data on Clonazepam's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Clonazepam USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Clonazepam suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Clonazepam Drug Master File in Japan (Clonazepam JDMF) empowers Clonazepam API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Clonazepam JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Clonazepam JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Clonazepam suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Clonazepam CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Clonazepam Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Clonazepam CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Clonazepam EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Clonazepam to their clients by showing that a Clonazepam CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Clonazepam CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Clonazepam CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Clonazepam CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Clonazepam DMF.
A Clonazepam CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Clonazepam CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Clonazepam suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
A Clonazepam written confirmation (Clonazepam WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Clonazepam manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Clonazepam active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Clonazepam APIs or Clonazepam finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Clonazepam WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Clonazepam suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Clonazepam as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Clonazepam API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Clonazepam as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Clonazepam and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Clonazepam NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Clonazepam suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Clonazepam Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Clonazepam GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Clonazepam GMP manufacturer or Clonazepam GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Clonazepam CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Clonazepam's compliance with Clonazepam specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Clonazepam CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Clonazepam CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Clonazepam may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Clonazepam EP), Clonazepam JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Clonazepam USP).

