Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
API
0
FDF
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Finished Drug Prices
NA
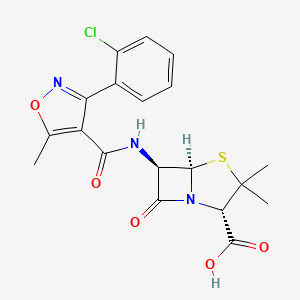

1. Chloroxacillin
2. Cloxacillin Sodium
3. Cloxacillin, Sodium
4. Sodium Cloxacillin
5. Sodium, Cloxacillin
6. Syntarpen
7. Tegopen
1. 61-72-3
2. Cloxacillinum
3. Cloxacilina
4. Cloxacilline
5. Syntarpen
6. Methocillin S
7. Cloxacillin Sodium
8. Tegopen
9. Clossacillina [dcit]
10. (3-(o-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolyl)penicillin
11. Cloxacillin (inn)
12. Chebi:49566
13. 6-(3-(o-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolecarboxamido)penicillanic Acid
14. O6x5qgc2vb
15. (2s,5r,6r)-6-[[3-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-oxazole-4-carbonyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
16. Chembl891
17. 6-(((3-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolyl)carbonyl)amino)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
18. Chloroxacillin
19. Clossacillina
20. (2s,5r,6r)-6-({[3-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazol-4-yl]carbonyl}amino)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
21. Cloxacillin [inn]
22. Cloxacillin [inn:ban]
23. Cloxacilina [inn-spanish]
24. Cloxacilline [inn-french]
25. Cloxacillinum [inn-latin]
26. Brl 1621
27. Methylchlorphenylisoxazoryl-penicillin
28. Tegopen (sodium Monohydrate)
29. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 6-[[[3-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolyl]carbonyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-, (2s,5r,6r)-
30. Orbenin (tn)
31. Mcipc
32. Hsdb 3042
33. Einecs 200-514-7
34. Unii-o6x5qgc2vb
35. P-25 (sodium Monohydrate)
36. Cloxacillinna
37. Cloxapen (sodium Monohydrate)
38. Brl-1621 (sodium Monohydrate)
39. (2s,5r,6r)-6-(3-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazole-4-carboxamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
40. Cloxacillin ,(s)
41. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 6-(((3-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolyl)carbonyl)amino)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-, (2s-(2alpha,5alpha,6beta))-
42. Spectrum_001345
43. Cloxacillin, Antibiotic For Culture Media Use Only
44. Cloxacillin [mi]
45. Prestwick0_000186
46. Prestwick1_000186
47. Prestwick2_000186
48. Prestwick3_000186
49. Spectrum2_001143
50. Spectrum3_000360
51. Spectrum4_000296
52. Spectrum5_000783
53. Cloxacillin [hsdb]
54. Epitope Id:120363
55. Cloxacillin [vandf]
56. Schembl2953
57. Cloxacillin [mart.]
58. Bspbio_000111
59. Bspbio_002059
60. Cloxacillin [who-dd]
61. Kbiogr_000852
62. Kbioss_001825
63. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 6-(3-(o-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-4-isoxazolecarboxamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-
64. Divk1c_000736
65. Spbio_001065
66. Spbio_002032
67. Bpbio1_000123
68. Dtxsid5022853
69. Gtpl11126
70. Hy-b0466a
71. Kbio1_000736
72. Kbio2_001825
73. Kbio2_004393
74. Kbio2_006961
75. Kbio3_001279
76. Brl1621
77. Ninds_000736
78. Bcp24144
79. Zinc3875417
80. Bdbm50022788
81. Db01147
82. Idi1_000736
83. (2s,5r,6r)-6-[[3-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-isoxazole-4-carbonyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
84. (2s,5r,6r)-6-[3-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-oxazole-4-amido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
85. 4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic Acid, 6-(3-(o-chlorophenyl)-s-methyl-4-isoxazolecarboxamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-
86. Sbi-0051319.p003
87. Cs-0028411
88. C06923
89. D07733
90. 242c583
91. Q422219
92. W-105105
93. Brd-k01244426-236-05-5
94. Brd-k01244426-236-08-9
95. Oxacillin Sodium Monohydrate Impurity E [ep Impurity]
96. 6-(3-o-chlorophenyl-5-methylisoxazol-4-ylamido) Penicillanic Acid
97. 6-(3-o-chlorophenyl-5-methylisoxazol-4-ylamido)penicillanic Acid
98. (2s,5r,6r)-6-(3-(2-chlorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazole-4-carboxamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-aza-bicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
99. (2s,5r,6r)-6-{[3-(2-chloro-phenyl)-5-methyl-isoxazole-4-carbonyl]-amino}-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-aza-bicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
100. 6-{[3-(2-chloro-phenyl)-5-methyl-isoxazole-4-carbonyl]-amino}-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-aza-bicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic Acid
| Molecular Weight | 435.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H18ClN3O5S |
| XLogP3 | 2.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 435.0655696 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 435.0655696 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 138 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 29 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 722 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Penicillins
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
...ITS USE SHOULD BE LIMITED TO TREATING INFECTIONS CAUSED BY PENICILLINASE-PRODUCING SUSCEPTIBLE MICROORGANISMS WHICH ARE RESISTANT TO PENICILLIN G. ...CAN BE USED IN COMBINATION WITH AMPICILLIN IN TREATMENT OF URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS CAUSED BY GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI. /MONOHYDRATE/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1129
METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCI ARE ALSO SENSITIVE TO CLOXACILLIN, SO THAT DRUG IS USEFUL IN TREATING INFECTIONS WHICH HAVE BECOME RESISTANT TO METHICILLIN. /MONOHYDRATE/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1129
IN FEW INSTANCES, IT IS NECESSARY TO INTERDICT FUTURE USE OF PENICILLIN BECAUSE OF RISK OF DEATH, & PT SHOULD BE SO WARNED. IT MUST AGAIN BE STRESSED THAT FATAL EPISODES OF ANAPHYLAXIS HAVE FOLLOWED INGESTION OF VERY SMALL DOSES OF THIS ANTIBIOTIC. /PENICILLINS/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1082
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CLOXACILLIN (19 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Penicillins are distributed into breast milk, some in low concentrations. Although significant problems in humans have not been documented, the use of penicillins by nursing mothers may lead to sensitization, diarrhea, candidiasis, and skin rash in the infant. /Penicillins/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 2151
Many penicillins have been used in pediatric patients and no pediatrics-specific problems have been documented to date. However, the incompletely developed renal function of neonates and young infants may delay the excretion of renally eliminated penicillins. /Penicillins/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 2151
Penicillins have been used in geriatric patients and no geriatrics-specific problems have been documented to date. However, elderly patients are more likely to have age-related renal function impairment, which may require an adjustment in dosage in patients receiving penicillins. /Penicillins/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 2151
Prolonged use of penicillins may lead to the development of oral candidiasis. /Penicillins/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 2151
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for CLOXACILLIN (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
...PENICILLIN G LIES ON BORDERLINE BETWEEN TOXICITY CLASSES 2 & 3. 2= SLIGHTLY TOXIC: PROBABLE ORAL LETHAL DOSE (HUMAN) 5-15 G/KG, BETWEEN 1 PINT & 1 QUART FOR 70 KG PERSON (150 LB). 3= MODERATELY TOXIC; PROBABLE ORAL LETHAL DOSE (HUMAN) 0.5-5 G/KG, BETWEEN 1 OZ & 1 PINT (OR 1 LB) FOR 70 KG PERSON (150 LB). /PENICILLINS/
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-171
Cloxacillin is indicated for the treatment of beta-hemolytic streptococcal, pneumococcal, and staphylococcal infections (including beta-lactamase producing organisms).
Cloxacillin is a semisynthetic antibiotic in the same class as penicillin. Cloxacillin is for use against staphylococci that produce beta-lactamase.
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Substances that inhibit the growth or reproduction of BACTERIA. (See all compounds classified as Anti-Bacterial Agents.)
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J01 - Antibacterials for systemic use
J01C - Beta-lactam antibacterials, penicillins
J01CF - Beta-lactamase resistant penicillins
J01CF02 - Cloxacillin
Absorption
Well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
.../ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS/ ARE RAPIDLY BUT INCOMPLETELY (30-80%) ABSORBED FROM GI TRACT. ABSORPTION OF DRUGS IS MORE EFFICIENT WHEN THEY ARE TAKEN ON AN EMPTY STOMACH. PEAK PLASMA CONCN ARE ATTAINED BY 1 HR & APPROX 5-10 UG/ML AFTER INGESTION OF 1 G OF OXACILLIN, & SIMILAR VALUES ARE OBTAINED WITH CLOXACILLIN.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1077
SINCE ABSORPTION IS LESS THAN COMPLETE, HIGHER PLASMA CONCN ARE ACHIEVED FOLLOWING IM INJECTION, & LARGER QUANTITIES OF DRUGS ARE RECOVERABLE IN URINE. ...BOUND TO PLASMA ALBUMIN TO GREAT EXTENT (APPROX 90-95%); NONE IS REMOVED FROM CIRCULATION TO SIGNIFICANT DEGREE BY HEMODIALYSIS.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1077
NORMALLY, ABOUT ONE HALF OF.../DRUG/ IS EXCRETED IN URINE IN FIRST 6 HR AFTER CONVENTIONAL ORAL DOSE. THERE IS ALSO SIGNIFICANT HEPATIC ELIMINATION...IN BILE.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1077
ISOXAZOLYL PENICILLINS ARE RAPIDLY EXCRETED BY KIDNEY, & CONCURRENT ADMIN OF PROBENECID RESULTS IN HIGHER & MORE PERSISTENT PLASMA CONCN. /PENICILLINS/
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1077
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for CLOXACILLIN (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Cloxacillin, like other penicillins, appears to be metabolized via breakage of the beta-lactam ring to form an inactive penicilloic acid metabolite.
PENICILLIN CAN UNDERGO SLOW CONVERSION IN VIVO TO INTERMEDIATES, SUCH AS PENICILLENIC ACID, WHICH CAN REACT WITH APPROPRIATE CONSTITUENTS OF TISSUES. /PENICILLINS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1147
Cloxacillin is partially metabolized to active and inactive metabolites. In one study following administration of a single 500-mg oral cloxacillin dose, 22% of the absorbed dose was hydrolyzed to penicilloic acids which are microbiologically inactive. Cloxacillin is also hydroxylated to a small extent to a microbiologically active metabolite which appears to be as active as cloxacillin.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 264
HALF-LIVES...BETWEEN 30 AND 60 MINUTES.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 1078
IN CHILDREN BEING TREATED FOR STAPHYLOCOCCAL INFECTIONS, MEAN ELIMINATION HALF-LIFE WAS 71 MIN.
PMID:707507 BURCKART GJ ET AL; AM J HOSP PHARM 35 (11): 1380-2 (1978)
The serum half-life of cloxacillin in adults with normal renal function is 0.4-0.8 hr.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 264
The serum half-life of cloxacillin is slightly prolonged in patients with impaired renal function and has been reported to range from 0.8-2.3 hr in patients with severe renal impairment.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 264
In one study in children 1 week to 2 years of age, the serum elimination half-life of cloxacillin was 0.8-1.5 hr. Serum concentrations of cloxacillin are generally higher and the serum half-life more prolonged in neonates than in older children.
McEvoy, G.K. (ed.). American Hospital Formulary Service - Drug Information 95. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Inc., 1995 (Plus Supplements 1995)., p. 264
By binding to specific penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located inside the bacterial cell wall, cloxacillin inhibits the third and last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cell lysis is then mediated by bacterial cell wall autolytic enzymes such as autolysins; it is possible that cloxacillin interferes with an autolysin inhibitor.
...ITS ANTIBACTERIAL SPECTRUM AGAINST GRAM-POSITIVE BACTERIA IS LIKE THAT OF PENICILLIN EXCEPT IT IS BROADER BY MARGIN OF THOSE STRAINS OR SPECIES THAT PRODUCE PENICILLINASE. ...IT IS LESS ACTIVE THAN PENICILLIN G AGAINST NON-PENICILLINASE-PRODUCING BACTERIA, ESPECIALLY STREPTOCOCCI. /CLOXACILLIN MONOHYDRATE/
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1129
SINCE PENICILLIN HAS NO EFFECT ON EXISTING CELL WALLS, BACTERIA MUST BE MULTIPLYING FOR BACTERIAL ACTION OF PENICILLIN TO BE MANIFEST. /PENICILLINS/
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 1135
The penicillins and their metabolites are potent immunogens because of their ability to combine with proteins and act as haptens for acute antibody-mediated reactions. The most frequent (about 95 percent) or "major" determinant of penicillin allergy is the penicilloyl determinant produced by opening the beta-lactam ring of the penicillin. This allows linkage of the penicillin to protein at the amide group. "Minor" determinants (less frequent) are the other metabolites formed, including native penicillin and penicilloic acids. /Penicillins/
Haddad, L.M., Clinical Management of Poisoning and Drug Overdose. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders Co., 1990., p. 953
Bactericidal; inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis. Action is dependent on the ability of penicillins to reach and bind penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located on the inner membrane of the bacterial cell wall. Penicillin-binding proteins (which include transpeptidases, carboxypeptidases, and endopeptidases) are enzymes that are involved in the terminal stages of assembling the bacterial cell wall and in reshaping the cell wall during growth and division. Penicillins bind to, and inactivate, penicillin-binding proteins, resulting in the weakening of the bacterial cell wall and lysis. /Penicillins/
USP Convention. USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 15 th ed. Volume 1. Rockville, MD: United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc., 1995. (Plus updates.), p. 2150
TOLERANCE DEVELOPED TO MULTIPLE DOSING. /PENICILLINS/
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-171
ABOUT THIS PAGE


LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?