

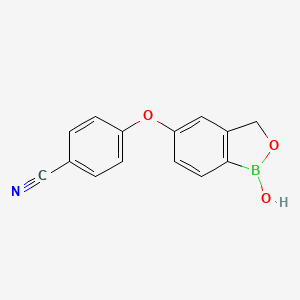

1. 5-(4-cyanophenoxy)-2,3-dihydro-1-hydroxy-2,1-benzoxaborole
2. An-2728
3. An2728
4. Eucrisa
1. 906673-24-3
2. An-2728
3. An2728
4. 4-((1-hydroxy-1,3-dihydrobenzo[c][1,2]oxaborol-5-yl)oxy)benzonitrile
5. Eucrisa
6. An 2728
7. Crisaborole (an2728)
8. 5-(4-cyanophenoxy)-2,3-dihydro-1-hydroxy-2,1-benzoxaborole
9. 4-[(1-hydroxy-3h-2,1-benzoxaborol-5-yl)oxy]benzonitrile
10. Crisaborole Topical Ointment 2%
11. Q2r47hgr7p
12. 4-((1-hydroxy-1,3-dihydrobenzo-[c][1,2]oxaborol-5-yl)oxy)benzonitrile
13. Chembl484785
14. Mfcd17169940
15. 4-((1-hydroxy-1,3-dihydrobenzo(c)(1,2)oxaborol-6-yl)oxy)benzonitrile
16. 906673-25-4
17. Staquis
18. 4-(1-hydroxy-1,3-dihydrobenzo[c][1,2]oxaborol-5-yloxy)benzonitrile
19. 4-[(1,3-dihydro-1-hydroxy-2,1-benzoxaborol-5-yl)oxy]benzonitrile
20. 4-[(1-hydroxy-1,3-dihydro-2,1-benzoxaborol-5-yl)oxy]benzonitrile
21. Benzonitrile, 4-((1,3-dihydro-1-hydroxy-2,1-benzoxaborol-5-yl)oxy)-
22. 4-[(1-hydroxy-1,3-dihydrobenzo[c][1,2]oxaborol-5-yl)oxy]benzonitrile
23. Crisaborole [usan]
24. Unii-q2r47hgr7p
25. Crisaborole [inn]
26. Eucrisa (tn)
27. Crisaborole [mi]
28. Crisaborole (usan/inn)
29. Crisaborole [usan:inn]
30. Crisaborole(an-2728)
31. Crisaborole [who-dd]
32. Schembl595261
33. Gtpl9151
34. Crisaborole, >=98% (hplc)
35. Crisaborole [orange Book]
36. Dtxsid10238231
37. Tqp0866
38. Chebi:134677
39. Bcp08677
40. Ex-a1087
41. Bdbm50277665
42. Akos016005425
43. Zinc169748244
44. Ccg-266972
45. Cs-1057
46. Db05219
47. Sb16802
48. Compound 5b [pmid: 19303290]
49. Ncgc00345792-01
50. Ncgc00345792-02
51. Ncgc00345792-04
52. Ac-30331
53. As-70551
54. Hy-10978
55. Sy113089
56. Db-078771
57. Ft-0767999
58. S5014
59. Pf-06930164
60. C90571
61. C90670
62. D10873
63. F51164
64. 5-(4-cyanophenoxy)-1-hydroxy-2,1-benzoxaborole
65. Q21098894
66. Crisaborole;4-(1-hydroxy-1,3-dihydrobenzo[c][1,2]oxaborol-5-yloxy)benzonitrile;an-2728
67. 1073669-75-6
| Molecular Weight | 251.05 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H10BNO3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 251.0753733 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 251.0753733 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 62.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 361 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Intended for the topical treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients 2 years of age and older.
FDA Label
Staquis is indicated for treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in adults and paediatric patients from 2 years of age with 40% body surface area (BSA) affected.
Crisaborole has broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory activity by mainly targeting phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) enzyme that is a key regulator of inflammatory cytokine production. As this enzyme is expressed in keratinocytes and immune cells, crisaborole mediates an anti-inflammatory effect on almost all inflammatory cells. Topical application of this drug is useful as it potentiates the localization of this drug in the skin and this anti-inflammatory activity is in the low micromolar range.
D11AH06
D - Dermatologicals
D11 - Other dermatological preparations
D11A - Other dermatological preparations
D11AH - Agents for dermatitis, excluding corticosteroids
D11AH06 - Crisaborole
Absorption
Systemic concentrations of crisaborole were reached by 8 days of twice-daily topical administration. It has low systemic absorption thus poses less risk for developing systemic side effects.
Route of Elimination
Renal excretion of metabolites is the major route of elimination.
Crisaborole is substantially metabolized into inactive metabolites. The major metabolite 5-(4-cyanophenoxy)-2-hydroxyl benzylalcohol (metabolite 1), is formed via hydrolysis; this metabolite is further metabolized into downstream metabolites, among which 5-(4-cyanophenoxy)-2-hydroxyl benzoic acid (metabolite 2), formed via oxidation, is also a major metabolite.
Inhibition of PDE4 by crisaborole leads to elevated levels of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). Increased intracellular levels of cAMP inhibit the NF-kB pathway and suppress the release of pro-inflammatory mediators such as TNF-alfa and various interleukins that play a causative role in psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. Suppression of downstream effects in different cell types may explain the therapeutic role of crisaborole in immune-mediated skin diseases.

