


1. Bms-790052
2. Bms-790052-05
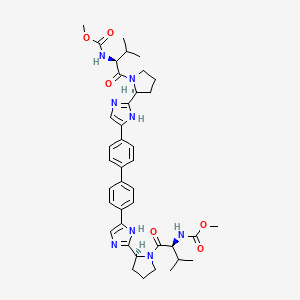
3. Carbamic Acid, N,n'-((1,1'-biphenyl)-4,4'-diylbis(1h-imidazole-5,2-diyl-(2s)-2,1-pyrrolidinediyl((1s)-1-(1-methylethyl)-2-oxo-2,1-ethanediyl)))bis-, C,c'-dimethyl Ester
4. Daclatasvir Dihydrochloride
5. Daklinza
1. 1009119-64-5
2. Daclatasvir (bms-790052)
3. Bms-790052
4. Daklinza
5. 1214735-16-6
6. Ebp 883
7. Bms790052
8. Bms 790052
9. Daclatasvir [usan]
10. Methyl N-[(2s)-1-[(2s)-2-[5-[4-[4-[2-[(2s)-1-[(2s)-2-(methoxycarbonylamino)-3-methylbutanoyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl]-1h-imidazol-5-yl]phenyl]phenyl]-1h-imidazol-2-yl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate
11. Chebi:82977
12. Ebp-883
13. Daclatasvir (usan)
14. Carbamic Acid, N,n'-[[1,1'-biphenyl]-4,4'-diylbis[1h-imidazole-5,2-diyl-(2s)-2,1-pyrrolidinediyl[(1s)-1-(1-methylethyl)-2-oxo-2,1-ethanediyl]]]bis-, C,c'-dimethyl Ester
15. Carbamic Acid, N,n'-((1,1'-biphenyl)-4,4'-diylbis(1h-imidazole-5,2-diyl-(2s)-2,1-pyrrolidinediyl((1s)-1-(1-methylethyl)-2-oxo-2,1-ethanediyl)))bis-, C,c'-dimethyl Ester
16. Dimethyl ((2s,2's)-((2s,2's)-2,2'-(5,5'-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4,4'-diyl)bis(1h-imidazole-5,2-diyl))bis(pyrrolidine-2,1-diyl))bis(3-methyl-1-oxobutane-2,1-diyl))dica
17. 1009119-65-6
18. Li2427f9ci
19. Methyl N-[(1s)-1-[(2s)-2-[5-[4-[4-[2-[(2s)-1-[(2s)-2-(methoxycarbonylamino)-3-methyl-butanoyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl]-1h-imidazol-5-yl]phenyl]phenyl]-1h-imidazol-2-yl]pyrrolidine-1-carbonyl]-2-methyl-propyl]carbamate
20. Daclatasvir [mi]
21. Daclatasvir [inn]
22. Daclatasvir [who-dd]
23. Dimethyl (2s,2's)-1,1'-((2s,2's)-2,2'-(4,4'-(biphenyl-4,4'-diyl)bis(1h-imidazole-4,2-diyl))bis(pyrrolidine-2,1-diyl))bis(3-methyl-1-oxobutane-2,1-diyl)dicarbamate
24. Mls006011140
25. Ebp883
26. Schembl2756027
27. Chembl2023898
28. Schembl17897804
29. Gtpl11266
30. Ex-a410
31. Dtxsid901026404
32. Amy36655
33. Dimethyl ((2s,2's)-((2s,2's)-2,2'-(5,5'-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4,4'-diyl)bis(1h-imidazole-5,2-diyl))bis(pyrrolidine-2,1-diyl))bis(3-methyl-1-oxobutane-2,1-diyl))dicarbamate
34. Dimethyl N,n'-(biphenyl-4,4'-diylbis{1h-imidazole-5,2-diyl-((2s)-pyrrolidine-2,1- Diyl)((1s)-1-(1-methylethyl)-2-oxoethane-2,1-diyl)})dicarbamate
35. Bdbm50387084
36. Mfcd17129086
37. S1482
38. Zinc68204830
39. Ccg-270425
40. Cs-0588
41. Db09102
42. Ncgc00346533-07
43. Ncgc00346533-09
44. Ac-28958
45. As-75298
46. Hy-10466
47. Smr004702917
48. Sw219754-1
49. D10065
50. J-520204
51. Q5207712
52. Dimethyl N,n'-((1,1'-biphenyl)-4,4'-diylbis(1h-imidazole-5,2-diyl-((2s)-pyrrolidine-2,1-diyl)((1s)-3-methyl-1-oxobutane-1,2-diyl)))dicarbamate
53. Methyl ((s)-1-((s)-2-(5-(4'-(2-((s)-1-((methoxycarbonyl)-l-valyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl)-1h-imidazol-5-yl)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-1h-imidazol-2-yl)pyrrolidin-1-yl)-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)carbamate
54. Methyl [(2s)-1-{(2s)-2-[4-(4'-{2-[(2s)-1-{(2s)-2-[(methoxycarbonyl)amino]-3-methylbutanoyl}-2-pyrrolidinyl]-1h-imidazol-4-yl}-4-biphenylyl)-1h-imidazol-2-yl]-1-pyrrolidinyl}-3-methyl-1-oxo-2-butanyl]carbamate
55. Methyl [(2s)-1-{(2s)-2-[4-(4'-{2-[(2s)-1-{(2s)-2-[(methoxycarbonyl)amino]-3-methylbutanoyl}pyrrolidin-2-yl]-1h-imidazol-4-yl}biphenyl-4-yl)-1h-imidazol-2-yl]pyrrolidin-1-yl}-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate
56. Methyl [(2s)-1-{(2s)-2-[5-(4'-{2-[(2s)-1-{(2s)-2-[(methoxycarbonyl)amino]-3-methylbutanoyl}pyrrolidin-2-yl]-1h-imidazol-5-yl}biphenyl-4-yl)-1h-imidazol-2-yl]pyrrolidin-1-yl}-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate
57. Methyl N-[(2s)-1-[(2s)-2-[5-(4'-{2-[(2s)-1-[(2s)-2-[(methoxycarbonyl)amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl]-1h-imidazol-5-yl}-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-1h-imidazol-2-yl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate
58. Methyl-n-[(2s)-1-[(2s)-2-[5-[4-[4-[2-[(2s)-1-[(2s)-2-(methoxycarbonylamino)-3-methylbutanoyl] Pyrrolidin-2-yl]-1h-imidazol-5-yl]phenyl]phenyl]-1himidazol-2-yl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate
| Molecular Weight | 738.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C40H50N8O6 |
| XLogP3 | 5.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 13 |
| Exact Mass | 738.38533134 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 738.38533134 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 175 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 54 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1190 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Indicated for use with sofosbuvir, with or without ribavirin, for the treatment of chronic HCV genotype 1a/b or 3 infection. The dosing regimen of 60mg daclatasvir 60 mg with 400mg sofosbuvir once a day is recommended for both genontypes. Resistance: Reduced susceptibility to daclatasvir was associated with the polymorphisms at NS5A amino acid positions M28, Q30, L31, and Y93 in genotypes 1a, 1b, and 3a patients. NS5A Resistance Testing is recommended for HCV genotype 1a-infected patients with cirrhosis prior to the initiaition of the treatment, as the risk of resistance development is higher in genotype 1a patients.
FDA Label
Daklinza is indicated in combination with other medicinal products for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection in adults (see sections 4. 2, 4. 4 and 5. 1).
For HCV genotype specific activity, see sections 4. 4 and 5. 1.
Daclatasvir is a direct-acting antiviral agent that targets the NS5A and causes a decrease in serum HCV RNA levels. It disrupts HCV replication by specifically inhibiting the critical functions of an NS5A protein in the replication complex. It is shown to cause downregulation of the hyperphosphorylation of NS5A. It does not appear to prolong the QT interval even when given at 3 times the maximum recommended dose.
J05AP07
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J05 - Antivirals for systemic use
J05A - Direct acting antivirals
J05AP - Antivirals for treatment of hcv infections
J05AP07 - Daclatasvir
Absorption
Studies demonstrated that peak plasma concentrations typically occurred within 2 hours after administration of multiple oral doses ranging from 1 - 100 mg once daily. Steady state is reached after approximately 4 days of once-daily daclatasvir administration. The absolute bioavailability of the tablet formulation is 67%.
Route of Elimination
Approximately 88% of total dose of daclatasvir is eliminated into bile and feces in which 53% remains as unchanged form, while 6.6% of the total dose is eliminated primarily unchanged in the urine.
Volume of Distribution
The approximate volume of distribution of daclatasvir is 47 L in patients who was orally administered 60 mg tablet followed by 100 g [13C,15N]-daclatasvir intravenously.
Clearance
In subjects who received daclatasvir 60 mg tablet orally followed by 100 g radiolabeled daclatasvir intravenously, the total clearance was 4.2 L/h.
Daclastavir is a substrate of CYP3A enzymes where its metabolism is predominantly mediated by CYP3A4 isoform. Oxidative pathways included -oxidation of the pyrrolidine moiety, resulting in ring opening to an aminoaldehyde intermediate followed by an intramolecular reaction between the aldehyde and the proximal imidazole nitrogen atom. High proportion of the drug in the plasma (greater than 97%) is in the unchanged form.
Following multiple dose administration of daclatasvir in HCV-infected subjects, with doses ranging from 1 mg to 100 mg once daily, the terminal elimination half-life of daclatasvir ranged from approximately 12 to 15 hours.
NS5A is a viral nonstructural phospoprotein that is part of a functional replication complex in charge of viral RNA genome amplification on endoplasmic reticulum membranes. It has the ability to bind to HCV RNA. It is shown to have two distinct functions in HCV RNA replication based on phosphorylated states. Maintaining the HCV replication complex is mediated by the cis-acting function of basally phosphorylated NS5A and the trans-acting function of hyperphosphorylated NS5A modulates HCV assembly and infectious particle formation. Daclatasvir is shown to disrupt hyperphosphorylated NS5A proteins thus interfere with the function of new HCV replication complexes. It is also reported that daclatasvir also blocks both intracellular viral RNA synthesis and virion assembly/secretion in vivo.

LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?