
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
KDMF
0
VMF
US Medicaid
NA
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
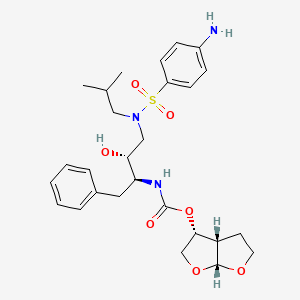

1. 114, Tmc
2. Darunavir Ethanolate
3. Ethanolate, Darunavir
4. Prezista
5. Tmc 114
6. Tmc-114
7. Tmc114
8. Uic 94017
9. Uic-94017
10. Uic94017
1. 206361-99-1
2. Tmc114
3. Tmc-114
4. Prezista
5. Uic-94017
6. Tmc 114
7. Darunavirum
8. Darunavirum [inn-latin]
9. Derunavir
10. (3r,3as,6ar)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl ((2s,3r)-4-(4-amino-n-isobutylphenylsulfonamido)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-yl)carbamate
11. Uic 94017
12. Chembl1323
13. (3r,3as,6ar)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl(1s,2r)-3-[[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](isobutyl)amino]-1-benzyl-2-hydroxypropylcarbamate
14. Chebi:367163
15. Tmc-41629
16. Yo603y8113
17. N-((1s,2r)-3-(((4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl)(2-methylpropyl)amino)-2-hydroxy-1-benzylpropyl)((1s,2r,5r)-4,6-dioxabicyclo(3.3.0)oct-2-yloxy)carboxamide
18. Darunavir [usan]
19. Ncgc00168773-01
20. (3r,3as,6ar)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl [(2s,3r)-4-{[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino}-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate
21. (3r,3as,6ar)-tetrahydro-2h-furo[2,3-b]furan-3-yl (2s,3r)-4-(4-amino-n-isobutylphenylsulfonamido)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-ylcarbamate
22. (3r,3as,6ar)-tetrahydro-2h-furo[2,3-b]furan-3-yl (2s,3r)-4-(4-amino-n-neopentylphenylsulfonamido)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-ylcarbamate
23. [(s)-3-[(4-amino-benzenesulfonyl)-isobutyl-amino]-2-hydroxy-1-((r)-phenylmethyl)-propyl]-carbamic Acid (3r,3as,6ar)-(hexahydro-furo[2,3-b]furan-3-yl) Ester
24. {(1s,2r)-3-[(4-amino-benzenesulfonyl)-isobutyl-amino]-1-benzyl-2-hydroxy-propyl}-carbamic Acid (3r,3as,6ar)-(hexahydro-furo[2,3-b]furan-3-yl) Ester
25. Drv
26. Prezista(tm)
27. Darunavir [inn]
28. (3r,3as,6ar)-hexahydrofuro(2,3-b)furan-3-yl N-((1s,2r)-1-benzyl-2-hydroxy-3-(n1-isobutylsulfanilamido)propyl)carbamate
29. (3r,3as,6ar)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl (2s,3r)-4-(4-amino-n-isobutylphenylsulfonamido)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-ylcarbamate
30. [(3as,4r,6ar)-2,3,3a,4,5,6a-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-4-yl] N-[(1s,2r)-3-[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl-isobutyl-amino]-1-benzyl-2-hydroxy-propyl]carbamate
31. Aids073035
32. [(3as,4r,6ar)-2,3,3a,4,5,6a-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-4-yl] N-[(2s,3r)-4-[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl-(2-methylpropyl)amino]-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate
33. Darunavir (usan/inn)
34. Darunavir [usan:inn:ban]
35. Prezista Naive
36. Unii-yo603y8113
37. Hsdb 7788
38. 2idw
39. 2ien
40. 3bvb
41. 3cyw
42. 3ekt
43. 3ggu
44. 3lzs
45. 3lzu
46. 3lzv
47. 3ogp
48. 3pwm
49. 3qoz
50. 3tkw
51. 3ttp
52. 4hla
53. Darunavir (drv)
54. (3r,3as,6ar)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl N-((1s,2r)-1-benzyl-2-hydroxy-3-(n1-isobutylsulfanilamido)propyl)carbamate
55. Tmc41629
56. Mfcd09260006
57. Tmc 41629
58. Uic-96017
59. 2f8g
60. 2hs1
61. 2hs2
62. 3d1z
63. 3so9
64. 3t3c
65. 3u7s
66. 4ll3
67. Darunavir [mi]
68. Darunavir [hsdb]
69. Darunavir [vandf]
70. (-)-darunavir
71. Darunavir [mart.]
72. Drv & Aag
73. Drv & Hsa
74. Darunavir [who-dd]
75. Dsstox_cid_26779
76. Dsstox_rid_81898
77. Dsstox_gsid_46779
78. Darunavir [ema Epar]
79. Schembl118546
80. Amy373
81. Bdbm8125
82. Uic-940t
83. Darunavir & Human Serum Albumin
84. Darunavir [orange Book]
85. Darunavir, >=98% (hplc)
86. Dtxsid0046779
87. Gtpl11243
88. 2f80
89. 2f81
90. 3d20
91. 3s53
92. 3s54
93. Hms3715i13
94. (3r,3as,6ar)-hexahydrofuro(2,3-b)furan-3-yl ((2s,3r)-4-((4-amino-n-isobutylphenyl)sulfonamido)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-yl)carbamate
95. Ex-a4009
96. Zinc3955219
97. Tox21_112634
98. Darunavir & Alpha1-acid Glycoprotein
99. Mc-114
100. S5250
101. 206361-99-1 (free)
102. Akos015966592
103. Bcp9000587
104. Ccg-269991
105. Cs-0749
106. Db01264
107. Ks-1469
108. Ncgc00388284-07
109. Ncgc00388284-08
110. Ncgc00388284-12
111. (3r,3as,6ar)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl N-((1s,2r)-1-benzyl-2-hydroxy-3-(n(1)-isobutylsulfanilamido)propyl)carbamate
112. Ac-26778
113. Carbamic Acid, [(1s,2r)-3-[[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino]-2-hydroxy-1-(phenylmethyl)propyl]-, (3r,3as,6ar)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl Ester
114. Hy-17040
115. Bcp0726000058
116. Cas-206361-99-1
117. D03656
118. Ab01565837_02
119. 361d991
120. J-013483
121. Q3765251
122. 3-(4-amino-phenoxy)-pyrrolidine-1-carboxylicacidtert-butylester
123. ((1s,2r)-3-(((4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl)(2-methylpropyl)amino)-2-hydroxy-1-(phenylmethyl)propyl)-carbamic Acid (3r,3as,6ar)-hexahydrofurano(2,3-b)furan-3-yl Ester
124. ((1s,2r)-3-(((4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl)(2-methylpropyl)amino)-2-hydroxy-1-(phenylmethyl)propyl)-carbamic Acid (3r,3as,6ar)-hexahydrofuro(2,3-b)furan-3-yl Ester
125. (3r,3as,6ar)-hexahydrofuro(2,3-b)furan-3-yl ((1s,2r)-3-(((4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl)(isobutyl)amino)-1-benzyl-2-hydroxypropyl)carbamate
126. (3r,3as,6ar)-hexahydrofuro(2,3-b)furan-3-yl N-((1s,2r)-1-benzyl-2-hydroxy-3-(n(sup 1)-isobutylsulfanilamido)propyl)carbamate
127. (3r,3as,6ar)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl N-[(1s,2r)-3-[[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino]-2-hydroxy-1-(phenylmethyl)propyl]carbamate
128. (3r,3as,6ar)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl N-[(2s,3r)-3-hydroxy-4-[n-(2-methylpropyl)(4-aminobenzene)sulfonamido]-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate
129. (3r,3as,6ar)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl N-[(2s,3r)-4-[(4-aminobenzene)(2-methylpropyl)sulfonamido]-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate
130. (3r,3as,6ar)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl((2s,3r)-4-(4-amino-n-isobutylphenylsulfonamido)-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-yl)carbamate
131. [(3r,3as,6ar)-2,3,3a,4,5,6a-hexahydrofuro[5,4-b]furan-3-yl] N-[(2s,3r)-4-[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl-(2-methylpropyl)amino]-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate
132. Carbamic Acid, ((1s,2r)-3-(((4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl)(2-methylpropyl)amino)-2-hydroxy-1-(phenylmethyl)propyl)-, (3r,3as,6ar)-hexahydrofurano(2,3-b)furan-3-yl Ester
| Molecular Weight | 547.7 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C27H37N3O7S |
| XLogP3 | 2.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 12 |
| Exact Mass | 547.23522170 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 547.23522170 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 149 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 38 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 853 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 5 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Darunavir |
| PubMed Health | Darunavir (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiretroviral Agent |
| Drug Label | PREZISTA (darunavir) is an inhibitor of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) protease.PREZISTA (darunavir), in the form of darunavir ethanolate, has the following chemical name: [(1S,2R)-3-[[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino]-2-hydrox... |
| Active Ingredient | Darunavir |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | oral |
| Strength | 300mg; 75mg; 150mg; 600mg; 400mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval |
| Company | Mylan Pharms |
| 2 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Prezista |
| PubMed Health | Darunavir (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiretroviral Agent |
| Drug Label | PREZISTA (darunavir) is an inhibitor of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) protease.PREZISTA (darunavir), in the form of darunavir ethanolate, has the following chemical name: [(1S,2R)-3-[[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino]-2-hydrox... |
| Active Ingredient | Darunavir ethanolate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Suspension |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 150mg base; eq 75mg base; eq 600mg base; eq 800mg base; eq 100mg base/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Janssen Prods |
| 3 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Darunavir |
| PubMed Health | Darunavir (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiretroviral Agent |
| Drug Label | PREZISTA (darunavir) is an inhibitor of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) protease.PREZISTA (darunavir), in the form of darunavir ethanolate, has the following chemical name: [(1S,2R)-3-[[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino]-2-hydrox... |
| Active Ingredient | Darunavir |
| Dosage Form | Tablet |
| Route | oral |
| Strength | 300mg; 75mg; 150mg; 600mg; 400mg |
| Market Status | Tentative Approval |
| Company | Mylan Pharms |
| 4 of 4 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Prezista |
| PubMed Health | Darunavir (By mouth) |
| Drug Classes | Antiretroviral Agent |
| Drug Label | PREZISTA (darunavir) is an inhibitor of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) protease.PREZISTA (darunavir), in the form of darunavir ethanolate, has the following chemical name: [(1S,2R)-3-[[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino]-2-hydrox... |
| Active Ingredient | Darunavir ethanolate |
| Dosage Form | Tablet; Suspension |
| Route | Oral |
| Strength | eq 150mg base; eq 75mg base; eq 600mg base; eq 800mg base; eq 100mg base/ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Janssen Prods |
Darunavir with low-dose ritonavir (ritonavir-boosted darunavir) is used in conjunction with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection in treatment-experienced (previously treated) adults, including those infected with HIV-1 strains resistant to multiple HIV protease inhibitors (PIs). This indication is based on surrogate marker data (plasma HIV-1 RNA levels, CD4+ T-cell counts) obtained from two 24-week controlled studies in treatment-experienced adults (previously treated with nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs, nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs), and PIs) with evidence of HIV-1 replication despite ongoing antiretroviral therapy. The manufacturer advises that the following factors be considered when initiating ritonavir-boosted darunavir. Use of ritonavir-boosted darunavir should be guided by results of baseline genotypic and phenotypic viral resistance testing and the individual's prior antiretroviral treatment. Administration of ritonavir-boosted darunavir in conjunction with other active antiretroviral agents is associated with a greater likelihood of treatment response. /Use Included in US product label/
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 646
Prezista is a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) protease inhibitor indicated for the treatment of HIV infection in adult patients. Prezista is also indicated for the treatment of HIV infection in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older. Prezista must be co-administered with ritonavir and with other antiretroviral agents. /Use Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for PREZISTA (darunavir ethanolate) tablet, film-coated (October 2009). Available from, as of February 17, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=darunavir
Safety and efficacy of darunavir/ritonavir and optimized background regimen in treatment-experienced patients (6-17 years) /was assessed in a/ forty-eight-week, open-label, two-part, phase II study. In part I, 44 patients were randomized (1: 1 ratio) to receive a body weight-adjusted, adult-equivalent dose (group A) or a 20-33% higher darunavir/ritonavir twice daily (b.i.d.) dose (group B). Pharmacokinetics, safety and efficacy were assessed following 2-week dosing (part I), which determined dosing for part II (evaluated 48-week safety and efficacy). In part I, both groups met the protocol-specified criteria for pharmacokinetics and showed favorable tolerability and efficacy. The following body-weight doses were selected: darunavir/ritonavir 375/50 mg b.i.d. (20-<30 kg), 450/60 mg b.i.d. (30-<40 kg) and 600/100 mg b.i.d. (> or =40 kg); these gave an AUC 24 hr, C0 hr and Cmax of 102, 114 and 112%, respectively, versus the corresponding mean adult pharmacokinetic parameter. In part II, 80 patients received darunavir/ritonavir (median age: 14 years, mean baseline HIV-1 RNA: 4.64 log(10)copies/ml). One patient (1%) discontinued (treatment-unrelated grade 3 anxiety). An abnormal mean baseline triglyceride level was normalized at 48 weeks (P < 0.01). At week 48, 65% had at least 1.0 log (10)HIV-1 RNA reduction; 59 and 48% achieved HIV-1 RNA less than 400 and less than 50 copies/mL, respectively (time-to-loss-of-virologic response). Mean age-adjusted weight z-score increased by 0.2 (P = 0.003). In treatment-experienced children and adolescents, darunavir/ritonavir showed comparable exposure to adults with appropriate dose selection, favorable safety and tolerability, improved body weight and significant virologic response. Darunavir/ritonavir is a valuable therapeutic option for this population.
PMID:19724191 Blanche S et al; AIDS 23 (15): 2005-13 (2009).
Acute hepatitis has occurred in patients receiving ritonavir-boosted darunavir in clinical studies. Liver injury (in some cases fatal) has been reported during postmarketing surveillance; liver injury generally has occurred in patients with advanced HIV infection who were receiving multiple concomitant drugs, were coinfected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) or hepatitis C virus (HCV), and/or were developing immune reconstitution syndrome. Appropriate laboratory tests should be performed to evaluate hepatic function prior to initiating ritonavir-boosted darunavir and periodically during treatment. Increased AST/ALT monitoring should be considered, especially during the first several months of therapy, in patients with hepatitis, cirrhosis, or elevated transaminase values prior to therapy. Interruption or discontinuance of ritonavir-boosted darunavir should be considered in patients who develop manifestations suggestive of hepatic impairment (e.g., fatigue, anorexia, nausea, jaundice, dark urine, liver tenderness, hepatomegaly, clinically important increases in hepatic enzyme concentrations).
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 647
The risks versus benefits of ritonavir-boosted darunavir have not been established in pediatric patients.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 646
Spontaneous bleeding has been reported in patients with hemophilia A or B receiving PIs; use caution in such patients. Increased hemostatic therapy (e.g., antihemophilic factor) may be needed.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 647
Darunavir contains a sulfonamide moiety, which may cause allergic-type reactions in certain susceptible individuals. Use darunavir with caution in patients with known hypersensitivity to sulfonamide-containing drugs.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 647
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Darunavir (19 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Darunavir, co-administered with ritonavir, and with other antiretroviral agents, is indicated for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in children age 3 or above and adults with HIV-1 infection.
FDA Label
PREZISTA, co administered with low dose ritonavir is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV 1) infection in adult and paediatric patients from the age of 3 years and at least 15 kg body weight.
PREZISTA, co administered with cobicistat is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV 1) infection in adults and adolescents (aged 12 years and older, weighing at least 40 kg).
In deciding to initiate treatment with PREZISTA co administered with cobicistat or low dose ritonavir, careful consideration should be given to the treatment history of the individual patient and the patterns of mutations associated with different agents. Genotypic or phenotypic testing (when available) and treatment history should guide the use of PREZISTA.
PREZISTA, co administered with low dose ritonavir is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV 1) infection.
PREZISTA 75 mg, 150 mg, and 600 mg tablets may be used to provide suitable dose regimens:
- For the treatment of HIV 1 infection in antiretroviral treatment (ART) experienced adult patients, including those that have been highly pre treated.
- For the treatment of HIV 1 infection in paediatric patients from the age of 3 years and at least 15 kg body weight.
In deciding to initiate treatment with PREZISTA co administered with low dose ritonavir, careful consideration should be given to the treatment history of the individual patient and the patterns of mutations associated with different agents. Genotypic or phenotypic testing (when available) and treatment history should guide the use of PREZISTA.
PREZISTA, co administered with low dose ritonavir is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV 1) infection.
PREZISTA, co administered with cobicistat is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV 1) infection in adults and adolescents (aged 12 years and older, weighing at least 40 kg).
PREZISTA 400 mg and 800 mg tablets may be used to provide suitable dose regimens for the treatment of HIV 1 infection in adult and paediatric patients from the age of 3 years and at least 40 kg body weight who are:
- antiretroviral therapy (ART) nave.
- ART experienced with no darunavir resistance associated mutations (DRV RAMs) and who have plasma HIV 1 RNA < 100,000 copies/ml and CD4+ cell count 100 cells x 106/L. In deciding to initiate treatment with PREZISTA in such ART experienced patients, genotypic testing should guide the use of PREZISTA.
* 400mg and 800 mg Film-coated Tablets:
Darunavir Krka d. d. , co-administered with low dose ritonavir is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection.
Darunavir Krka d. d. , co-administered with cobicistat is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection in adult patients (see section 4. 2).
Darunavir Krka d. d. 400 mg and 800 mg tablets may be used to provide suitable dose regimens for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adult and paediatric patients from the age of 3 years and at least 40 kg body weight who are:
- antiretroviral therapy (ART)-nave (see section 4. 2).
- ART-experienced with no darunavir resistance associated mutations (DRV-RAMs) and who have plasma HIV-1 RNA < 100,000 copies/ml and CD4+ cell count 100 cells x 106/l. In deciding to initiate treatment with darunavir in such ART-experienced patients, genotypic testing should guide the use of darunavir (see sections 4. 2, 4. 3, 4. 4 and 5. 1).
* 600mg Film-coated Tablets:
Darunavir Krka d. d. , co-administered with low dose ritonavir is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection.
Darunavir Krka d. d. 600 mg tablets may be used to provide suitable dose regimens (see section 4. 2):
- For the treatment of HIV-1 infection in antiretroviral treatment (ART)-experienced adult patients, including those that have been highly pre-treated.
- For the treatment of HIV-1 infection in paediatric patients from the age of 3 years and at least 15 kg body weight.
In deciding to initiate treatment with darunavir co-administered with low dose ritonavir, careful consideration should be given to the treatment history of the individual patient and the patterns of mutations associated with different agents. Genotypic or phenotypic testing (when available) and treatment history should guide the use of darunavir.
* 400 and 800 mg:
Darunavir Krka, co-administered with low dose ritonavir is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection.
Darunavir Krka 400 mg and 800 mg tablets may be used to provide suitable dose regimens for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adult and paediatric patients from the age of 3 years and at least 40 kg body weight who are:
- antiretroviral therapy (ART)-nave (see section 4. 2).
- ART-experienced with no darunavir resistance associated mutations (DRV-RAMs) and who have plasma HIV-1 RNA < 100,000 copies/ml and CD4+ cell count 100 cells x 106/l. In deciding to initiate treatment with darunavir in such ART-experienced patients, genotypic testing should guide the use of darunavir (see sections 4. 2, 4. 3, 4. 4 and 5. 1).
* 600 mg:
Darunavir Krka, co-administered with low dose ritonavir is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection.
Darunavir Krka 600 mg tablets may be used to provide suitable dose regimens (see section 4. 2):
- For the treatment of HIV-1 infection in antiretroviral treatment (ART)-experienced adult patients, including those that have been highly pre-treated.
- For the treatment of HIV-1 infection in paediatric patients from the age of 3 years and at least 15 kg body weight.
In deciding to initiate treatment with darunavir co-administered with low dose ritonavir, careful consideration should be given to the treatment history of the individual patient and the patterns of mutations associated with different agents. Genotypic or phenotypic testing (when available) and treatment history should guide the use of darunavir.
Darunavir, co-administered with low dose ritonavir is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection (see section 4. 2).
Darunavir Mylan 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg and 600 mg tablets may be used to provide suitable dose regimens (see section 4. 2):
- For the treatment of HIV-1 infection in antiretroviral treatment (ART)-experienced adult patients, including those that have been highly pre-treated.
- For the treatment of HIV-1 infection in paediatric patients from the age of 3 years and at least 15 kg body weight.
In deciding to initiate treatment with darunavir co-administered with low dose ritonavir, careful consideration should be given to the treatment history of the individual patient and the patterns of mutations associated with different agents. Genotypic or phenotypic testing (when available) and treatment history should guide the use of darunavir (see sections 4. 2, 4. 4 and 5. 1).
Darunavir co-administered with low dose ritonavir is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection.
Darunavir co-administered with cobicistat is indicated in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection in adults and adolescents (aged 12 years and older, weighing at least 40 kg) (see section 4. 2).
Darunavir Mylan 400 mg and 800 mg tablets may be used to provide suitable dose regimens for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adult and paediatric patients from the age of 3 years and at least 40 kg body weight who are:
- antiretroviral therapy (ART)-nave (see section 4. 2).
- ART-experienced with no darunavir resistance associated mutations (DRV-RAMs) and who have plasma HIV-1 RNA < 100,000 copies/ml and CD4+ cell count 100 cells x 10/L. In deciding to initiate treatment with darunavir in such ART-experienced patients, genotypic testing should guide the use of darunavir (see sections 4. 2, 4. 3, 4. 4 and 5. 1).
Treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection
Darunavir is an inhibitor of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) protease, which prevents HIV viral replication. When administered with ritonavir in combination antiretroviral therapy, darunavir significantly decreases viral load and increases CD4 cell counts, decreasing the morbidity and mortality of HIV infection.
HIV Protease Inhibitors
Inhibitors of HIV PROTEASE, an enzyme required for production of proteins needed for viral assembly. (See all compounds classified as HIV Protease Inhibitors.)
J05AE10
J05AE10
J05AE10
J05AE10
J - Antiinfectives for systemic use
J05 - Antivirals for systemic use
J05A - Direct acting antivirals
J05AE - Protease inhibitors
J05AE10 - Darunavir
Absorption
The absolute oral bioavailability of one single 600 mg dose of darunavir alone and with 100 mg of ritonavir twice a day was 37% and 82%, respectively. Exposure to darunavir in boosted patients has been found to be 11 times higher than in unboosted patients. Tmax is achieved approximately 2.4 to 4 hours after oral administration. When darunavir is taken with food, the Cmax and AUC of darunavir given with ritonavir increase by 30% when compared to the fasted state.
Route of Elimination
A mass balance study in healthy volunteers demonstrated that after single dose administration of 400 mg 14C-darunavir, given with 100 mg ritonavir, approximately 79.5% and 13.9% of the administered dose of radiolabeled darunavir was obtained in the feces and urine, respectively. Excretion of unchanged drug accounted for 8.0% of the darunavir dose in volunteers who were unboosted. In boosted darunavir administration, unchanged darunavir made up 48.8% of the excreted dose in boosted subjects due to inhibition of darunavir metabolism by ritonavir. Unchanged drug in the urine made up 1.2% of the administered dose in volunteers who where unboosted, and 7.7% in boosted volunteers.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of darunavir in one pharmacokinetic study in conjunction with ritonavir was 206.5 L (with a range of 161.0264.9) in healthy young adult volunteers. Another pharmacokinetic study revealed a volume of distribution of 220 L.
Clearance
Darunavir has a low renal clearance. After intravenous administration, the clearance darunavir administered alone and with 100 mg ritonavir twice daily, was 32.8 L/h and 5.9 L/h, respectively.
Darunavir is approximately 95% bound to plasma proteins. Darunavir binds primarily to plasma alpha 1-acid glycoprotein (AAG).
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for PREZISTA (darunavir ethanolate) tablet, film-coated (October 2009). Available from, as of February 17, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=darunavir
Darunavir, co-administered with 100 mg ritonavir twice daily, was absorbed following oral administration with a Tmax of approximately 2.5-4 hours. The absolute oral bioavailability of a single 600 mg dose of darunavir alone and after co-administration with 100 mg ritonavir twice daily was 37% and 82%, respectively.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for PREZISTA (darunavir ethanolate) tablet, film-coated (October 2009). Available from, as of February 17, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=darunavir
Darunavir is distributed into milk in rats; not known whether the drug is distributed into human milk.
American Society of Health System Pharmacists; AHFS Drug Information 2009. Bethesda, MD. (2009), p. 647
A mass balance study in healthy volunteers showed that after single dose administration of 400 mg (14)C-darunavir, co-administered with 100 mg ritonavir, approximately 79.5% and 13.9% of the administered dose of (14)C-darunavir was recovered in the feces and urine, respectively. Unchanged darunavir accounted for approximately 41.2% and 7.7% of the administered dose in feces and urine, respectively. The terminal elimination half-life of darunavir was approximately 15 hours when co-administered with ritonavir. After intravenous administration, the clearance of darunavir, administered alone and co-administered with 100 mg twice daily ritonavir, was 32.8 L/hr and 5.9 L/hr, respectively.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for PREZISTA (darunavir ethanolate) tablet, film-coated (October 2009). Available from, as of February 17, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=darunavir
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Darunavir (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Darunavir is heavily oxidized and metabolized by hepatic cytochrome enzymes, mainly CYP3A. Darunavir is extensively metabolized in subjects who do not receive a booster, primarily via carbamate hydrolysis, isobutyl aliphatic hydroxylation, and aniline aromatic hydroxylation, as well as both benzylic aromatic hydroxylation and glucuronidation.
In vitro experiments with human liver microsomes (HLMs) indicate that darunavir primarily undergoes oxidative metabolism. Darunavir is extensively metabolized by CYP enzymes, primarily by CYP3A. A mass balance study in healthy volunteers showed that after a single dose administration of 400 mg (14)C-darunavir, co-administered with 100 mg ritonavir, the majority of the radioactivity in the plasma was due to darunavir. At least 3 oxidative metabolites of darunavir have been identified in humans; all showed activity that was at least 90% less than the activity of darunavir against wild-type HIV.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for PREZISTA (darunavir ethanolate) tablet, film-coated (October 2009). Available from, as of February 17, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=darunavir
Absorption, metabolism, and excretion of darunavir, an inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus protease, was studied in eight healthy male subjects after a single oral dose of 400 mg of ((14)C)darunavir given alone (unboosted subjects) or with ritonavir (100 mg b.i.d. 2 days before and 7 days after darunavir administration (boosted subjects)). ... Darunavir was extensively metabolized in unboosted subjects, mainly by carbamate hydrolysis, isobutyl aliphatic hydroxylation, and aniline aromatic hydroxylation and to a lesser extent by benzylic aromatic hydroxylation and glucuronidation. Total excretion of unchanged darunavir accounted for 8.0% of the dose in unboosted subjects. Boosting with ritonavir resulted in significant inhibition of carbamate hydrolysis, isobutyl aliphatic hydroxylation, and aniline aromatic hydroxylation but had no effect on aromatic hydroxylation at the benzylic moiety, whereas excretion of glucuronide metabolites was markedly increased but still represented a minor pathway. Total excretion of unchanged darunavir accounted for 48.8% of the administered dose in boosted subjects as a result of the inhibition of darunavir metabolism by ritonavir. Unchanged darunavir in urine accounted for 1.2% of the administered dose in unboosted subjects and 7.7% in boosted subjects, indicating a low renal clearance.
PMID:19131522 Vermeir M et al; Drug Metab Dispos 37 (4): 809-20 (2009).
Darunavir is metabolized by Phase I and Phase II biotransformation mechanisms. A large number of metabolites were detected in vitro using animal and human hepatocytes and microsomal preparations. The metabolic pathway was qualitatively similar in rats, dogs and humans. The most prevalent pathway was the Phase I biotransformation including carbamate hydrolysis, aliphatic hydroxylation at the isobutyl moiety and aromatic hydroxylation at the aniline moiety. Dogs were most representatives of human with carbamate hydrolysis predominating in both species. Darunavir was mainly metabolized by CYP3A. In mice and rats darunavir treatment induced hepatic microsomal CYP3A4. UDP-GT activity was additionally induced in rats. In dogs, no induction effects were observed. Darunavir is presented as a single enantiomer but no chiral inversion occurs in vivo.
European Medicines Agency (EMEA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use; European Public Assessment Report (EPAR) (Scientific Discussion); PREZISTA (darunavir) (May 2009). Available from, as of February 18, 2010: https://www.ema.europa.eu/humandocs/PDFs/EPAR/prezista/0770707en6.pdf
The terminal elimination half-life of darunavir is approximately 15 hours when it is combined with ritonavir.
A mass balance study in healthy volunteers showed that after a single dose administration of 400 mg (14)C-darunavir, co-administered with 100 mg ritonavir ... The terminal elimination half-life of darunavir was approximately 15 hours when co-administered with ritonavir.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for PREZISTA (darunavir ethanolate) tablet, film-coated (October 2009). Available from, as of February 17, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=darunavir
The pharmacokinetics of darunavir has been evaluated in vitro and in several species (mice, rats, dogs and rabbits), that were also used in the non-clinical pharmacology and toxicology studies. ... Following oral administration, ... elimination half-life was ... rapid with half-lives generally less than 5 hr.
European Medicines Agency (EMEA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use; European Public Assessment Report (EPAR) (Scientific Discussion); PREZISTA (darunavir) (May 2009). Available from, as of February 18, 2010: https://www.ema.europa.eu/humandocs/PDFs/EPAR/prezista/0770707en6.pdf
The HIV-1 protease enzyme is necessary for viral precursor protein processing and viral maturation in preparation for infection, and is therefore a target for antiretroviral therapy for HIV. Protease inhibitors are used as a part of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) in patients diagnosed with HIV infection. It has been shown to effectively suppress the virus, leading to significantly decreased morbidity and mortality rates. Darunavir, a HIV protease inhibitor, prevents HIV replication through binding to the enzyme, stopping the dimerization and the catalytic activity of HIV-1 protease. In particular, it inhibits the cleavage of HIV encoded Gag-Pol proteins in cells that have been infected with the virus, halting the formation of mature virus particles, which spread the infection. The close contact that darunavir makes with the primary chains of the active site amino acids (Asp-29 and Asp-30) on the protease likely contributes to its potency and efficacy against resistant variants of HIV-1. Darunavir is known to bind to different sites on the enzyme: the active site cavity and the surface of one of the flexible flaps in the protease dimer. Darunavir can adapt to changes in the shape of a protease enzyme due to its molecular flexibility.
Darunavir as a protease inhibitor inhibits the cleavage of HIV encoded gag-pol polyproteins in virus infected cells, thereby preventing the formation of mature and infectious new virions. It was selected for its potency against wild type HIV-1 and HIV strains resistant to currently approved protease inhibitors.
European Medicines Agency (EMEA), Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use; European Public Assessment Report (EPAR) (Scientific Discussion); PREZISTA (darunavir) (May 2009). Available from, as of February 18, 2010: https://www.ema.europa.eu/humandocs/PDFs/EPAR/prezista/0770707en6.pdf
Darunavir is an inhibitor of the HIV-1 protease. It selectively inhibits the cleavage of HIV encoded Gag-Pol polyproteins in infected cells, thereby preventing the formation of mature virus particles.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for PREZISTA (darunavir ethanolate) tablet, film-coated (October 2009). Available from, as of February 17, 2010: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/search.cfm?startswith=darunavir

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS

Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ANALYTICAL

ABOUT THIS PAGE
27
PharmaCompass offers a list of Darunavir API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Darunavir manufacturer or Darunavir supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Darunavir manufacturer or Darunavir supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Darunavir API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Darunavir API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Darunavir Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Darunavir Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Darunavir manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Darunavir, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Darunavir manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Darunavir API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Darunavir manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Darunavir supplier is an individual or a company that provides Darunavir active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Darunavir finished formulations upon request. The Darunavir suppliers may include Darunavir API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Darunavir suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Darunavir DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Darunavir active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Darunavir DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Darunavir USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Darunavir DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Darunavir USDMF includes data on Darunavir's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Darunavir USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Darunavir suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Darunavir written confirmation (Darunavir WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Darunavir manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Darunavir active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Darunavir APIs or Darunavir finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Darunavir WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Darunavir suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Darunavir as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Darunavir API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Darunavir as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Darunavir and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Darunavir NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Darunavir suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Darunavir Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Darunavir GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Darunavir GMP manufacturer or Darunavir GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Darunavir CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Darunavir's compliance with Darunavir specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Darunavir CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Darunavir CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Darunavir may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Darunavir EP), Darunavir JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Darunavir USP).
