
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
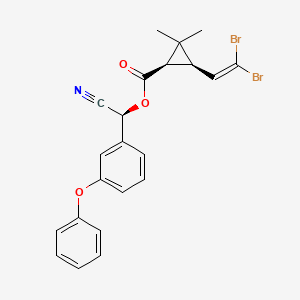

1. Alpha-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (1r,3r)-cis-3-(2,2-dibromovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
2. Butox
3. Decamethrin
4. Decamethrin, (1r-(1alpha(r*),3alpha))-isomer
5. Decamethrin, (1r-(1alpha(r*),3beta))-isomer
6. Decamethrin, (1r-(1alpha(s*),3beta))-isomer
7. Decamethrin, (1s-(1alpha(r*),3alpha))-isomer
8. Decamethrin, (1s-(1alpha(s*),3alpha))-isomer
9. Decis
10. Difexon
11. K-othrin
12. Nrdc 161
13. Oms 1998
1. Decamethrin
2. 52918-63-5
3. Decamethrine
4. Decis
5. K-othrin
6. Esbecythrin
7. Butox
8. Deltagard
9. Deltamethrine
10. Crackdown
11. Deltagran
12. Butoss
13. Cislin
14. Suspend
15. Zorcis
16. New Musigie
17. K-othrine
18. K-obiol
19. Phagase 1
20. Glossinex 200
21. Decis 0.5ulv
22. Decis 1.5ulv
23. Decis 2.5ulv
24. Nrdc 161
25. Ru 22974
26. 2jts8r821g
27. Chebi:4388
28. Deltamethrin (ban)
29. Deltamethrin [ban]
30. (s)-alpha-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (1r)-cis-3-(2,2-dibromovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
31. Rup 987
32. Deltacide
33. Deltamethrin 10 Microg/ml In Cyclohexane
34. Stricker
35. Deltamethrin 100 Microg/ml In Cyclohexane
36. Ipo 8831
37. Oms 1988
38. Dsstox_cid_381
39. Fmc 45498
40. Dsstox_rid_75555
41. Dekametrin
42. Dsstox_gsid_20381
43. (s)-cyano(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl (1r,3r)-3-(2,2-dibromoethenyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropane-1-carboxylate
44. (s)-cyano(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl (1r,3r)-3-(2,2-dibromoethenyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
45. Deltamethrin, Analytical Standard
46. Deltametryna [polish]
47. Dekametrin (hungarian)
48. Deltametryna
49. Deltamethrin [bsi:iso]
50. Deltamethrine [iso-french]
51. (s)-alpha-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (1r,3r)-3-(2,2-dibromovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
52. (s)-cyano[3-(phenyloxy)phenyl]methyl (1r,3r)-3-(2,2-dibromoethenyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
53. [(s)-cyano-(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl] (1r,3r)-3-(2,2-dibromoethenyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropane-1-carboxylate
54. Cas-52918-63-5
55. Ccris 3704
56. Hsdb 6604
57. Cyclopropanecarboxylic Acid, 3-(2,2-dibromoethenyl)-2,2-dimethyl-, (s)-cyano(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl Ester, (1r,3r)-
58. Einecs 258-256-6
59. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 978051
60. Unii-2jts8r821g
61. Deltashield
62. Ballistic
63. Scalibor
64. Delta-methrin
65. Ai3-29279
66. Decis Options
67. Cropro D-sect
68. Deltamethrin Formulations
69. Deltamethrin, >=98%
70. Deltamethrin [mi]
71. Deltamethrin [iso]
72. Deltamethrin [hsdb]
73. Deltamethrin [iarc]
74. Deltamethrin [inci]
75. Scalibor [veterinary] (tn)
76. Schembl22196
77. Deltamethrin [mart.]
78. Deltamethrin Impurity Standard
79. (1r-(1alpha(s*),3alpha))-cyano(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl 3-(2,2-dibromoethenyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
80. (s)-alpha-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (1r,3r)-3-(2,2-dibromovinyl)-2,2-dimethyl-cyclopropan-1-carboxylate
81. (s)-alpha-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl-(1r)-cis-3-(2,2-dibromovinyl)-2,2-dimethyl-cyclopropane Carboxyate
82. 3-(2,2-dibromoethenyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylic Acid, Cyano(3-phenoxy-phenyl)-, Methyl Ester
83. Bidd:er0143
84. Deltamethrin [who-dd]
85. Chembl1593566
86. Dtxsid8020381
87. Owzreifadzcyqd-nshgmrrfsa-
88. Hy-b1971
89. Zinc1532094
90. Tox21_201432
91. Tox21_303009
92. Mfcd00870122
93. Akos015895185
94. Db13600
95. Ks-5078
96. Deltamethrin 1000 Microg/ml In Hexane
97. Deltamethrin 100 Microg/ml In N-hexane
98. Ncgc00163904-01
99. Ncgc00163904-02
100. Ncgc00163904-03
101. Ncgc00256465-01
102. Ncgc00258983-01
103. (s)-alpha-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (1r,3s)-3-(2,2-dibromovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
104. Alpha-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (1r-(1alpha(s*),3alpha))-3-(2,2-dibromovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
105. Cyclopropanecarboxylic Acid, 3-(2,2-dibromoethenyl)-2,2-dimethyl-, Cyano(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl Ester, (1r-(1-alpha(s*),3-alpha))-
106. Ru-22974
107. Cs-0014071
108. D4775
109. Deltamethrin 1000 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
110. D07785
111. D90330
112. Deltamethrin, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
113. 918m635
114. A829307
115. Q422257
116. Deltamethrin, Certified Reference Material, Tracecert(r)
117. [(s)-cyano-[3-(phenoxy)phenyl]methyl] (1r,3r)-3-(2,2-dibromoethenyl)-2,2-dimethy
118. Deltamethrin Solution, 100 Ng/mul In Cyclohexane, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
119. (1r,3r)-((s)-cyano(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl) 3-(2,2-dibromovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
120. (1r,3r)-3-(2,2-dibromoethenyl)-2,2-dimethyl-1-cyclopropanecarboxylic Acid [(s)-cyano-(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl] Ester
121. (1r,3r)-3-(2,2-dibromovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylic Acid (s)-alpha-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl Ester
122. (s)-.alpha.-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (1r,3r)-3-(2,2-dibromovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
123. (s)-.alpha.-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (1r,3s)-3-(2,2-dibromovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
124. (s)-i+/--cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl (1r)-cis-3-(2,2-dibromovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropane Carboxylate
125. [(s)-cyano-(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl] (1r,3r)-3-[2,2-bis(bromanyl)ethenyl]-2,2-dimethyl-cyclopropane-1-carboxylate
126. Cyclopropanecarboxylic Acid, 3-(2,2-dibromoethenyl)-2,2-dimethyl-,(s)-cyano(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl Ester, (1r,3r)-
| Molecular Weight | 505.2 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C22H19Br2NO3 |
| XLogP3 | 6.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 504.97112 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 502.97317 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 59.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 643 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Insecticides
Pesticides designed to control insects that are harmful to man. The insects may be directly harmful, as those acting as disease vectors, or indirectly harmful, as destroyers of crops, food products, or textile fabrics. (See all compounds classified as Insecticides.)
P - Antiparasitic products, insecticides and repellents
P03 - Ectoparasiticides, incl. scabicides, insecticides and repellents
P03B - Insecticides and repellents
P03BA - Pyrethrines
P03BA03 - Decamethrin
In rats, following oral administration, elimination occurs within 2-4 days. The phenyl ring is hydroxylated, the ester bond hydrolyzed, and the acid moiety is eliminated as the glucuronide and glycine conjugates.
Hartley, D. and H. Kidd (eds.). The Agrochemicals Handbook. 2nd ed. Lechworth, Herts, England: The Royal Society of Chemistry, 1987., p. A122/Aug 87
Intravenous disposition kinetics /in a female black Bengal goat/ using a dose of 0.2 mg/kg showed that the maximum blood concentration of deltamethrin was recorded at 0.5 min, followed by rapid decline, and a minimum concentration was detected at 6 min after administration. The following values were obtained: Vdarea 0.148 (+ or -0.02) L/kg; t1/2 (a) 0.22 (+ or -0.02) min; t1/2 (beta) 2.17 (+ or -0.37) min; Kel 1.05 (+ or -0.24) /min; AUC 4.30(+ or -0.45)ug min/mL; ClB 0.05 (+ or -0.006) L/kg/min; T~B 1.93 (+ or -0.58); fc 0.40(+ or -0.05). After 10 min, liver retained the maximum residue, and heart, adrenal gland, kidney, spleen, fat and brain also held the insecticide; liver, fat, heart and spleen retained residue after 30 min, and bone, liver and fat retained residue after 60 min of iv administration. Oral absorption of deltamethrin was poor and inconsistent, and approximately 65% of administered dose was recovered from feces and gastrointestinal contents. The excretion of deltamethrin through urine was meager, and only 0.01 and 0.013% of the administered dose was recovered after 3 and 5 days of oral administration respectively. All the tissues retained the residue after 3 days; while fat, rumen, reticulum, omasum, abomasum, large and small intestine and bone retained the residue after 5 days of oral administration; and the percentage recoveries were 1.73 and 0.027 respectively. ...
Juliet S et al; Environ Toxicol Chem 57 (3): 311-9 (2001)
Three young male human volunteers underwent a complete medical check-up one week prior to the morning of the study. Each of them received a single dose of 3 mg of (14)C deltamethrin mixed in 1 g glucose and diluted first in 10 mL polyethylene glycol300 and again in 150 mL water. Total radioactivity was 1.8 + or - 0.9 mBq. Samples of blood, urine, saliva, and feces were taken at intervals over 5 days. Clinical and biological examinations were performed every 12 hr during the trial and one week after its termination. Radioactivity in the biological samples was measured with a liquid scintillation spectrometer. The clinical and biological checks did not detect any abnormal findings. There were no signs of side effects ... either during or after the trial period. The maximum plasma radioactivity appeared between 1 and 2 hr after administration of the product, and remained over the detection limit (0.2 KBq/L) during the 48 hr. The apparent elimination half-life was between 10.0 and 11.5 hr. The radioactivity of blood cells, as well as the saliva, was extremely low. Urinary excretion was 51-50% of the initial radioactivity; 90% of this radioactivity was excreted during the 24 hr following absorption. The apparent half-life of urinary excretion was 10.0-13.5 hr, which is consistent with the plasma data. Fecal elimination at the end of the observation period represented 10-26% of the dose. The total fecal plus urine elimination was around 64-77% of the initial dose after 96 hr.
WHO; Environmental Health Criteria 97: Deltamethrin p.47 (1990)
In a feeding study, deltamethrin was administered twice daily to lactating dairy cows in portions of their daily feed at the rate of 2 or 10 mg/kg diet for 28 consecutive days. The level of 2 mg/kg diet was the residue level found in a recently treated pasture, whereas 10 mg/kg diet was five times this level. Deltamethrin residues in the milk were dose-dependent and appeared to reach a plateau between 7 and 9 days after the start of treatment. At the high deltamethrin intake of 10 mg/kg diet, the deltamethrin residue in milk was about 0.025 mg/L. Deltamethrin residues in tissues were measured 1, 4, and 9 days after the last dose. At the 10 mg/kg diet intake, very small amounts of deltamethrin residues were found in the liver (<0.005 mg/kg), kidney )<0.002 mg/kg), and muscle (0.002-0.014 mg/kg). Residues in fat were about 0.04 mg/kg and 0.2 mg/kg for the 2 and 10 mg/kg intake, respectively. Depletion of deltamethrin in milk was very rapid (estimated half-life was about 1 day); while in fat (renal and subcutaneous) the half-life was 7-9 days. Br2CA (3-(2,2-dibromovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopro-panecarboxylic acid) and PBacid (3-phenoxybenzoic acid) were the only metabolites detected in the milk and tissues of treated cows. In all cases, they were found at trace levels of < 0.0235 mg/L and < 0.034 mg/L, respectively. These two metabolites were also previously identified in rats and mice as the major degradation products of deltamethrin.
WHO; Environmental Health Criteria 97: Deltamethrin p.45 (1990)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for DELTAMETHRIN (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Deltamethrin (1 ug) was incubated at 37 C for 30 min with each of the following mouse microsome preparations; a) tetraethyl pyrophosphate (TEPP)-treated microsomes (no esterase and oxidase activity); b) normal microsomes (esterase acivity); c) TEPP-treated microsomes plus NADPH (oxidase activity); and d)normal microsomes plus NADPH (esterase plus oxidase activity). Deltamethrin was more rapidly metabolized under the oxidase system than under the esterase system. The major site of ring hydroxylation was 4'-position and the secondary site was the 5-position. The trans methyl group was an important site of hydroxylation of the esters and cis methyl oxidation was evident in the metabolites of the cleaved acid moiety. The preferred sites of hydroxylation were as follows; trans of dimethyl group, 4'-position in the phenol group, and cis of the dimethyl group was equal to the 5-position in the phenoxy group. Cleavage of deltamethrin to cyanohydrin may result from both esterase and oxidase enzyme activities, since larger amounts of the cleaved products were evident in the oxidase system. ... However, at a much higher (approximately 35-fold) concentration of deltamethrin than that in the above study, it was not detectably hydrolysed. ... Deltamethrin was hydrolysed by esterases in the blood, brain, kidney, and stomach of mice yielding PBald and PBacid.
WHO; Environmental Health Criteria 97: Deltamethrin p.46 (1990)
In a metabolic study, (14)C-deltamethrin was administered orally to lactating dairy cows at the rate of 10 mg/kg body weight per day for 3 consecutive days. It was poorly absorbed and mainly eliminated in the feces as unchanged deltamethrin. Only 4-6% of the administered (14)C was eliminated in the urine, and 0.42-1.62% was secreted in the milk. The radiocarbon contents of various tissues were generally very low with the exception of those of the liver, kidney, and fat, which were higher. Deltamethrin degradation occured by cleavage of the ester bond, as already reported in rats and mice. The enzymes responsible for the ester bond cleavage were located in cow liver homogenate, mainly in the microsomal fraction, as seen in an in vitro study. Metabolites resulting from ester bond cleavage further metabolized and/or conjugated, resulting in a large number of compounds excreted in the urine. In the milk, the major identifiable radiolabelled compound was deltamethrin.
WHO; Environmental Health Criteria 97: Deltamethrin p.45 (1990)
The major metabolic pathways of deltamethrin in mice were similar to those in rats, though there were some differences. These included the presence of more unchanged deltamethrin in mouse feces than in rat feces. In mouse feces, there were 4 monohydroxy ester metabolites (2'-OH-, 4'-OH-, 5-OH-, and trans-OH-deltamethrin and one dihydroxy metabolite (4'-OH-trans-OH- deltamethrin) that were not found in mouse urine. Major metabolites from the acid moiety in mice were Br2CA, trans-OH-Br2CA, and their glucuronide and sulfate conjugates. Among them, trans-OH-Br2CA-sulfate was detected only in mice, but not in rats. Compared with rats, much larger amounts of trans-OH-Br2CA and its conjugates were formed in mice. A major metabolite of the alcohol moiety in mice was the taurine conjugate of PBacid in the urine, which was not detected in rats. Generally, mice produced smaller amounts of phenolic compounds compared with rats. Also, 3-phenoxybenzaldehyde (PBald), 3-phenoxybenzyl alcohol (PBalc), and its glucuronide, and glucuronides of 3-(4-hydroxyphenoxy)benzyl alcohol (4'-OH-PBalc) and 5-hydroxy-3-penoxybenzoic acid (5-OH-PBacid) were found in mice, but not in rats. When mice were given an ip dose of (14) C-deltamethrin with or without piperonyl butoxide (PBO) and/or S,S,S-tributylphosphorotrithioate (DEF), the same metabolites were obtained as with oral administration. However, DEF decreased the hydrolytic products relative to the controls, while PBO decreased the oxidation products.
WHO; Environmental Health Criteria 97: Deltamethrin p.44 (1990)
Sulfate of 4'-OH-PBacid accounted for about 50% of the dose, together with small amounts of free (4%) and glucuronide forms (2%). The CN group was converted mainly to thiocyanate and, in small amounts, to ITCA. The trans-isomer of deltamethrin was also rapidly metabolized and yielded almost the same metabolties as deltamethrin, though 5-OH-derivative was found in the cis-isomer, but not in the trans-isomer.
WHO; Environmental Health Criteria 97: Deltamethrin p.43 (1990)
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for DELTAMETHRIN (19 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Deltamethrin has known human metabolites that include 4'-hydroxy-deltamethrin.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Following intravenous administration, the distribution and elimination half-times were ... 1.39 and 33.0 hours for deltamethrin.
U.S. Dept Health & Human Services/Agency for Toxic Substances & Disease Registry; Toxicological Profile for Pyrethrins and Pyrethroids p.102 (2003). Available from, as of January 4, 2011: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp155.pdf
In rats administered deltamethrin and its metabolite (4-OH-deltamethrin) intravenously, elimination half-times were 33 and 25 hours, respectively.
U.S. Dept Health & Human Services/Agency for Toxic Substances & Disease Registry; Toxicological Profile for Pyrethrins and Pyrethroids p.99 (2003). Available from, as of January 4, 2011: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp155.pdf
Deltamethrin has a half-life in rat brain of 1-2 days, but it is rather more persistent in body fat, with a half-life of 5 days.
Hayes, W.J., Jr., E.R. Laws, Jr., (eds.). Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. Volume 2. Classes of Pesticides. New York, NY: Academic Press, Inc., 1991., p. 595
Three young male human volunteers underwent a complete medical check-up one week prior to the morning of the study. Each of them received a single dose of 3 mg of (14)C deltamethrin mixed in 1 g glucose and diluted first in 10 mL polyethylene glycol300 and again in 150 mL water. Total radioactivity was 1.8 + or - 0.9 mBq. ... The apparent elimination half-life was between 10.0 and 11.5 hr. ... The apparent half-life of urinary excretion was 10.0-13.5 hr, which is consistent with the plasma data. ...
WHO; Environmental Health Criteria 97: Deltamethrin p.47 (1990)
The lowest concentration of deltamethrin to have an effect in crayfish stretch receptor neurons on sodium channels was 1X10-12 mol/L, but the response of the preparation to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) appeared to be unaffected by concentrations of deltamethrin up to 1X10-7 mol/L. Although 1X10-6 mol/l deltamethrin had a slight effect on the GABA response of the dactyl abductor muscle, it appears that the majority of the effects of cyano-pyrethroids in invertebrates could be accounted for solely by their action on sodium channels.
WHO; Environmental Health Criteria 97: Deltamethrin p.81 (1990)
The synthetic pyrethroids delay closure of the sodium channel, resulting in a sodium tail current that is characterized by a slow influx of sodium during the end of depolarization. Apparently the pyrethroid molecule holds the activation gate in the open position. Pyrethroids with an alpha-cyano group (e.g., fenvalerate) produce more prolonged sodium tail currents than do other pyrethroids (e.g., permethrin, bioresmethrin). The former group of pyrethroids causes more cutaneous sensations than the latter. /Pyrethroids/
Ellenhorn, M.J. and D.G. Barceloux. Medical Toxicology - Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. New York, NY: Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc. 1988., p. 1081
Interaction with sodium channels is not the only mechanism of action proposed for the pyrethroids. Their effects on the CNS have led various workers to suggest actions via antagonism of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-mediated inhibition, modulation of nicotinic cholinergic transmission, enhancement of noradrenaline release, or actions on calcium ions. Since neurotransmitter specific pharmacological agents offer only poor or partial protection against poisoning, it is unlikely that one of these effects represents the primary mechanism of action of the pyrethroids, & most neurotransmitter release is secondary to incr sodium entry. /Pyrethroids/
Hayes, W.J., Jr., E.R. Laws, Jr., (eds.). Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. Volume 2. Classes of Pesticides. New York, NY: Academic Press, Inc., 1991., p. 588
The interaction of a series of pyrethroid insecticides with the sodium channels in myelinated nerve fibers of the clawed frog, Xenopus laevis, was investigated using the voltage clamp technique. Of 11 pyrethroids, 9 insecticidally active cmpd induced a slowly decaying sodium tail current on termination of a step depolarization, whereas the sodium current during depolarization was hardly affected. /Pyrethroids/
PMID:6299340 Vijverberg HP M et al; Biochem Biophys Acta 728 (1): 73-82 (1983)
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for DELTAMETHRIN (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
ABOUT THIS PAGE
95
PharmaCompass offers a list of Deltamethrine API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Deltamethrine manufacturer or Deltamethrine supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Deltamethrine manufacturer or Deltamethrine supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Deltamethrine API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Deltamethrine API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Deltamethrine Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Deltamethrine Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Deltamethrine manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Deltamethrine, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Deltamethrine manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Deltamethrine API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Deltamethrine supplier is an individual or a company that provides Deltamethrine active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Deltamethrine finished formulations upon request. The Deltamethrine suppliers may include Deltamethrine API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
Deltamethrine Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Deltamethrine GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Deltamethrine GMP manufacturer or Deltamethrine GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Deltamethrine CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Deltamethrine's compliance with Deltamethrine specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Deltamethrine CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Deltamethrine CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Deltamethrine may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Deltamethrine EP), Deltamethrine JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Deltamethrine USP).
