
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
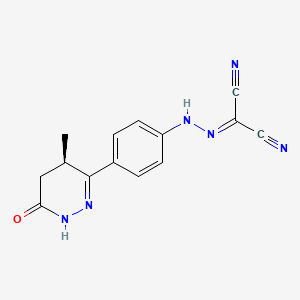

1. ((4-(1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-4-methyl-6-oxo-3-pyridazinyl)phenyl)hydrazono)propanedinitrile
2. Dextrosimendan
3. Or 1259
4. Or 1855
5. Or-1259
6. Or-1855
7. Simadax
8. Simendan
1. 141505-33-1
2. Simdax
3. (r)-simendan
4. (-)-or-1259
5. Or-1259
6. Simendan, (r)-
7. Chebi:50567
8. 2-[[4-[(4r)-4-methyl-6-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1h-pyridazin-3-yl]phenyl]hydrazinylidene]propanedinitrile
9. Nsc-759644
10. Levosimedan
11. C6t4514l4e
12. Or1259
13. (r)-((4-(1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-4-methyl-6-oxo-3-pyridazinyl)phenyl)hydrazono) Propanedintrile
14. (r)-n-(4-(4-methyl-6-oxo-1,4,5,6-tetrahydropyridazin-3-yl)phenyl)carbonohydrazonoyl Dicyanide
15. Levosimendan [inn]
16. Dsstox_cid_26445
17. Dsstox_rid_81620
18. Mesoxalonitrile (p-((r)-1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-4-methyl-6-oxo-pyridazinyl)phenyl)hydrazone
19. Dsstox_gsid_46445
20. Levosimendanum
21. Smr002529692
22. Simdax (tn)
23. Cas-141505-33-1
24. Levosimendan (usan/inn)
25. Levosimendan [usan:inn]
26. Or 1259
27. Unii-c6t4514l4e
28. ((4-(1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-4-methyl-6-oxo-3-pyridazinyl)phenyl)hydrazono)propanedinitrile
29. Levosimendan- Bio-x
30. Levosimendan [mi]
31. Levosimendan [usan]
32. Mesoxalonitrile (-)-(p((r)-1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-4-methyl-6-oxo-3-pyridazinyl)phenyl)hydrazone
33. Schembl83243
34. Levosimendan [mart.]
35. Mls003899227
36. Mls006010741
37. Levosimendan [who-dd]
38. Chembl2051955
39. Dtxsid9046445
40. Levosimendan, >=98% (hplc)
41. Hms3264g03
42. Hms3884n17
43. Kuc109648n
44. Pharmakon1600-01502356
45. Act02710
46. Bcp07048
47. Zinc3915645
48. Tox21_112191
49. Tox21_113768
50. Bdbm50469700
51. Mfcd00867135
52. Nsc759644
53. S2446
54. Akos015895214
55. Tox21_112191_1
56. Ac-1752
57. Am84381
58. Ccg-213048
59. Db00922
60. Ds-8918
61. Nsc 759644
62. ({4-[(4r)-4-methyl-6-oxo-1,4,5,6-tetrahydropyridazin-3-yl]phenyl}hydrazono)propanedintrile
63. 2-[[4-[(4r)-4-methyl-6-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1h-pyridazin-3-yl]phenyl]hydrazono]propanedinitrile
64. Ksc-210-010
65. Ncgc00253641-01
66. Ncgc00263564-01
67. Ncgc00263564-02
68. Bm164625
69. Hy-14286
70. L0320
71. Sw219172-1
72. A11874
73. D04720
74. N12889
75. Ab01562970_01
76. Ab01562970_02
77. 741l087
78. A807767
79. Q162541
80. Sr-01000931342
81. Sr-01000931342-2
82. 1-beta-d-ribofuranose-1h-1,2,4-triazole-3-methylcarbonate
83. (r)-(4-(4-methyl-6-oxo-1,4,5,6-tetrahydropyridazin-3-yl)phenyl)carbonohydrazonoyl Dicyanide
84. (r)-n-(4-(4-methyl-6-oxo-1,4,5,6-tetrahydropyridazin-3-yl)phenyl)carbonohydrazonoyldicyanide
85. 1-cyano-n-{4-[(4r)-4-methyl-6-oxo-1,4,5,6-tetrahydropyridazin-3-yl]phenyl}methanecarbohydrazonoyl Cyanide
86. 2-(2-(4-((4r)-1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-4-methyl-6-oxo-3-pyridazinyl)phenyl)hydrazinylidene)propanedinitrile
87. Mesoxalonitrile (-)-(p((r)-1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-4-methyl-6- Oxo-3-pyridazinyl)phenyl)hydrazone
88. Propanedinitrile, ((4-(1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-4-methyl-6-oxo-3-pyridazinyl)phenyl)hydrazono)-, (r)-
89. Propanedinitrile, 2-(2-(4-((4r)-1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-4-methyl-6-oxo-3-pyridazinyl)phenyl)hydrazinylidene)-
| Molecular Weight | 280.28 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H12N6O |
| XLogP3 | 2.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 280.10725903 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 280.10725903 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 113 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 549 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
For short term treatment of acutely decompensated severe chronic heart failure (CHF). Also being investigated for use/treatment in heart disease.
Levosimendan is a new Ca2+-sensitizing inotropic agent. Ca2+ sensitizers represent a new class of inotropic agents, which overcome the disadvantages associated with currently available inotropic agents in as they are not associated with an increased risk of arrhythmias, cell injury and death due to Ca2+ overload in myocardial cells; they do not increase the activation energy; and they have the potential to reverse contractile dysfunction under pathophysiologic conditions, such as acidosis or myocardial stunning. Levosimendan has not been approved for use in the U.S. or Canada.
Vasodilator Agents
Drugs used to cause dilation of the blood vessels. (See all compounds classified as Vasodilator Agents.)
Cardiotonic Agents
Agents that have a strengthening effect on the heart or that can increase cardiac output. They may be CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES; SYMPATHOMIMETICS; or other drugs. They are used after MYOCARDIAL INFARCT; CARDIAC SURGICAL PROCEDURES; in SHOCK; or in congestive heart failure (HEART FAILURE). (See all compounds classified as Cardiotonic Agents.)
Phosphodiesterase 3 Inhibitors
Compounds that specifically inhibit PHOSPHODIESTERASE 3. (See all compounds classified as Phosphodiesterase 3 Inhibitors.)
C - Cardiovascular system
C01 - Cardiac therapy
C01C - Cardiac stimulants excl. cardiac glycosides
C01CX - Other cardiac stimulants
C01CX08 - Levosimendan
Absorption
The bioavailability of oral levosimendan is 85 ± 6% in healthy volunteers and 84 ± 4% in patients.
Complete metabolism, with some active metabolites (OR-1855 and OR-1896) possibly extending the drug's haemodynamic effects.
Eliminination half-life is approximately 1 hour.
Levosimendan appears to increase myofilament calcium sensitivity by binding to cardiac troponin C in a calcium-dependent manner. This stabilizes the calcium-induced conformational change of troponin C, thereby (1) changing actin-myosin cross-bridge kinetics apparently without increasing the cycling rate of the cross-bridges or myocardial ATP consumption, (2) increasing the effects of calcium on cardiac myofilaments during systole and (3) improving contraction at low energy cost (inotropic effect). Calcium concentration and, therefore, sensitization decline during diastole, allowing normal or improved diastolic relaxation. Levosimendan also leads to vasodilation through the opening of ATP-sensitive potassium channels. By these inotropic and vasodilatory actions, levosimendan increases cardiac output without increasing myocardial oxygen demand. Levosimendan also has a selective phosphodiesterase (PDE)-III inhibitory action that may contribute to the inotropic effect of this compound under certain experimental conditions. It has been reported that levosimendan may act preferentially as a Ca2+ sensitizer at lower concentrations, whereas at higher concentrations its action as a PDE-III inhibitor becomes more prominent in experimental animals and humans.

API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Global Sales Information

Market Place

ABOUT THIS PAGE


LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?