
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
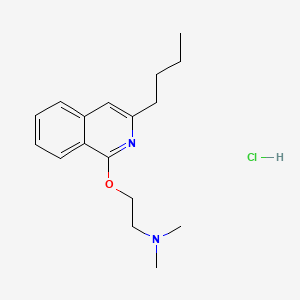

1. 3-butyl-1-(2-dimethylaminoethoxy)isoquinoline
2. Dimethisoquin
3. Dimethisoquin Monohydrochloride, Monohydrate
4. Isochinol
5. Quinisocaine
6. Quotane
1. 2773-92-4
2. Quinisocaine Hydrochloride
3. Dimethisoquin Hcl
4. Quinisocaine Hcl
5. Quotane
6. Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride (2 G)
7. Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride [usan]
8. Dsstox_cid_25373
9. Dsstox_rid_80835
10. Dsstox_gsid_45373
11. Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride (usan)
12. 2-(3-butylisoquinolin-1-yl)oxy-n,n-dimethylethanamine;hydrochloride
13. 3-butyl-1-(2-(dimethylamino)ethoxy)isoquinoline Monohydrochloride
14. Smp2689462
15. Ethanamine, 2-((3-butyl-1-isoquinolinyl)oxy)-n,n-dimethyl-, Monohydrochloride
16. Ncgc00016618-01
17. Cas-2773-92-4
18. N-{2-[(3-butyl-1-isoquinolinyl)oxy]ethyl}-n,n-dimethylamine
19. Mls002153920
20. Schembl467135
21. Chembl1533364
22. Dtxsid6045373
23. Hms1569n22
24. Tox21_110528
25. Dimethisoquinhydrochloride(2g)
26. Akos024326188
27. Tox21_110528_1
28. Ccg-220630
29. Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride [mi]
30. Ncgc00016618-04
31. Quinisocaine Hydrochloride [mart.]
32. Smr000769826
33. Quinisocaine Hydrochloride [who-dd]
34. D06661
35. Sr-01000854196
36. Sr-01000854196-2
37. Q27289288
38. 2-(3-butylisoquinolin-1-yl)oxy-n,n-dimethylethanamine,hydrochloride
39. 2-[(3-butyl-1-isoquinolinyl)oxy]-n,n-dimethylethanamine Hydrochloride
40. (2-(3-butyl-isoquinolin-1-yloxy)-ethyl)-dimethyl-amine, Hydrochloride
| Molecular Weight | 308.8 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H25ClN2O |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Exact Mass | 308.1655411 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 308.1655411 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 25.4 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 270 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
Anesthetics, Local
Drugs that block nerve conduction when applied locally to nerve tissue in appropriate concentrations. They act on any part of the nervous system and on every type of nerve fiber. In contact with a nerve trunk, these anesthetics can cause both sensory and motor paralysis in the innervated area. Their action is completely reversible. (From Gilman AG, et. al., Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 8th ed) Nearly all local anesthetics act by reducing the tendency of voltage-dependent sodium channels to activate. (See all compounds classified as Anesthetics, Local.)
Market Place

ABOUT THIS PAGE
22
PharmaCompass offers a list of Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride manufacturer or Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride manufacturer or Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride supplier is an individual or a company that provides Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride finished formulations upon request. The Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride suppliers may include Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride GMP manufacturer or Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride's compliance with Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride EP), Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Dimethisoquin Hydrochloride USP).
