
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
FDF
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Finished Drug Prices
NA
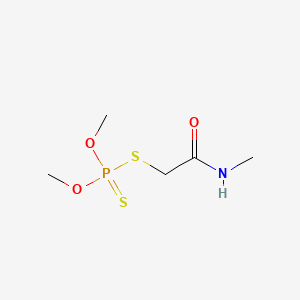

1. Bi 58
2. Bi-58
3. Bi58
4. Phosphamide
5. Rogor
1. 60-51-5
2. Phosphamide
3. Rogor
4. Phosphamid
5. Lurgo
6. Aadimethoal
7. Fosfamid
8. Fosfotox
9. Perfecthion
10. Perfekthion
11. Rebelate
12. Sinoratox
13. Sistemin
14. Systoate
15. Daphene
16. Dimeton
17. Dimevur
18. Racusan
19. Roxion
20. Cygon
21. Tara
22. Fosfatox R
23. Fosfotox R
24. Cygon Insecticide
25. De-fend
26. Fostion Mm
27. Rogor L
28. Rogor P
29. Cygon 4e
30. Fosfotox R 35
31. Cygon 2-e
32. Rogor 40
33. Cygon 400
34. Tara 909
35. American Cyanamid 12880
36. 8014 Bis Hc
37. Pei 75
38. 2-dimethoxyphosphinothioylthio-n-methylacetamide
39. Bi 58
40. 2-dimethoxyphosphinothioylsulfanyl-n-methylacetamide
41. Cl 12880
42. O,o-dimethyl S-(2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl) Phosphorodithioate
43. O,o-dimethyl S-methylcarbamoylmethyl Phosphorodithioate
44. L-395
45. O,o-dimethyl S-[2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl] Dithiophosphate
46. Phosphorodithioic Acid, O,o-dimethyl S-(2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl) Ester
47. S-methylcarbamoylmethyl O,o-dimethyl Phosphorodithioate
48. O,o-dimethyl S-(n-methylcarbamoylmethyl) Dithiophosphate
49. Phosphorodithioic Acid, O,o-dimethyl Ester, S-ester With 2-mercapto-n-methylacetamide
50. O,o-dimethyl S-(n-methylcarbamoylmethyl) Phosphorodithioate
51. Chebi:34714
52. W6u08b045o
53. Fip
54. Cekuthoate
55. Devigon
56. Dimetate
57. Dimethogen
58. Ferkethion
59. Rogodan
60. Sevigor
61. Trimetion
62. O,o-dimethyl S-[2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl] Phosphorodithioate
63. Salut
64. Solut
65. Dsstox_cid_479
66. Fortion Nm
67. Phosphorodithioic Acid, O,o-dimethyl S-[2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl] Ester
68. Phosphorodithioic Acid, O,o-dimethyl S-[2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl]ester
69. Roxion Ua
70. Dsstox_rid_75615
71. Dsstox_gsid_20479
72. Fosfamid (ussr)
73. Dimethoaat [dutch]
74. Dimethoat [german]
75. Dimethoate 30 Ec
76. Demos-l40
77. Rogor 20l
78. Dimate 267
79. Dimethoat Tech 95%
80. Caswell No. 358
81. Dimethoaat
82. Dimethoat
83. Bi-58
84. Rcra Waste Number P044
85. Cas-60-51-5
86. Ditimur 40; Ent 24650; Experimental Insecticide 12880; Fip; Fosfatox R; Fosfotox
87. Ccris 245
88. Dimethoate [ansi:bsi:iso]
89. Bi 58 Ec
90. Oms 94
91. Hsdb 1586
92. Experimental Insecticide 12,880
93. Nci-c00135
94. Einecs 200-480-3
95. Rcra Waste No. P044
96. Ent 24,650
97. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 035001
98. Brn 1785339
99. Ac-12880
100. Ac-18682
101. Ei-12880
102. Turbair
103. Unii-w6u08b045o
104. Ai3-24650
105. O,o-dimethyl Methylcarbamoylmethyl Phosphorodithioate
106. O,o-dimethyl S-((methylcarbamoyl)methyl)phosphorodithioate
107. Rogor 20 L
108. Spectrum_001793
109. N-monomethylamide Of O,o-dimethyldithiophosphorylacetic Acid
110. O,o-dimethyl S-(n-methylcarbamylmethyl) Thiothionophosphate
111. O,o-dimethyl-s-(2-oxo-3-aza-butyl)-dithiophosphat [german]
112. Dimethoate [mi]
113. Specplus_000384
114. O,o-dimethyl-dithiophosphorylessigsaeure Monomethylamid [german]
115. O,o-dimethyl-s-(n-monomethyl)-carbamyl Methyl Dithiophosphate
116. O,o-dimethyldithiophosphorylacetic Acid, N-monomethylamide Salt
117. O,o-dimetil-s-(n-metil-carbamoil-metil)-ditiofosfato [italian]
118. Dimethoate [iso]
119. Acetic Acid, O,o-dimethyldithiophosphoryl-, N-monomethylamide Salt
120. O,o-dimethyl-s-(n-methyl-carbamoyl)-methyl-dithiofosfaat [dutch]
121. Spectrum2_001861
122. Spectrum3_000812
123. Spectrum4_000652
124. Spectrum5_001934
125. Dimethoate [hsdb]
126. Dithiophosphate De O,o-dimethyle Et De S(-n-methylcarbamoyl-methyle) [french]
127. Dimethoate [mart.]
128. Phosphorodithioic Acid O,o-dimethyl Ester, Ester With 2-mercapto-n-methylacetamide
129. Schembl18159
130. Bspbio_002303
131. Kbiogr_001023
132. Kbioss_002286
133. Spectrum330020
134. Mls002207196
135. Bidd:er0567
136. Dimercaptan Triethylene Glycol
137. Divk1c_006480
138. O,o-dimethyl-s-(2-oxo-3-aza-butyl)-dithiophosphat
139. Spbio_001702
140. Dimethoate, Analytical Standard
141. O,o-dimethyl-dithiophosphorylessigsaeure Monomethylamid
142. O,o-dimetil-s-(n-metil-carbamoil-metil)-ditiofosfato
143. Chembl1569524
144. Dtxsid7020479
145. Schembl20525536
146. Experimental Insecticide 12880
147. Kbio1_001424
148. Kbio2_002284
149. Kbio2_004852
150. Kbio2_007420
151. Kbio3_001803
152. Mcwxgjitazmzev-uhfffaoysa-
153. Dimethoate-d6(o,o-dimethyl-d6)
154. O,o-dimethyl-s-(n-methyl-carbamoyl)-methyl-dithiofosfaat
155. O,o-dimethyl-s-(n-methyl-carbamoyl-methyl)-dithiophosphat
156. Hy-b1946
157. Tox21_202246
158. Tox21_301161
159. Ccg-39399
160. Dimethoate 100 Microg/ml In Hexane
161. Dithiophosphate De O,o-dimethyle Et De S(-n-methylcarbamoyl-methyle)
162. Ent-24650
163. Mfcd00053676
164. O,o-dimethyl-s-(n-methyl-carbamoyl-methyl)-dithiophosphat [german]
165. Dimethoate 100 Microg/ml In Acetone
166. Akos015960721
167. Dimethoate 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
168. O,o-dimethyl Phosphorodithioate S-ester With 2-mercapto-n-methylacetamide
169. Dimethoate 1000 Microg/ml In Acetone
170. Dimethoate 10 Microg/ml In Cyclohexane
171. Dimethoate 1000 Microg/ml In Methanol
172. Ncgc00094518-01
173. Ncgc00094518-02
174. Ncgc00094518-03
175. Ncgc00094518-04
176. Ncgc00094518-05
177. Ncgc00094518-06
178. Ncgc00094518-07
179. Ncgc00094518-08
180. Ncgc00255059-01
181. Ncgc00259795-01
182. As-16078
183. Dimethoate 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
184. L395
185. Smr000777935
186. Db-053635
187. Cs-0014051
188. Ft-0603252
189. Ft-0667209
190. L 395
191. Dimethoate, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
192. 053d676
193. Q421371
194. Brd-k94763113-001-02-5
195. O,o-dimethyl S-[2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl] Dithiophosphate #
196. O,o-dimethyl S-[2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl]phosphorodithioate
197. O,o-dimethyl S-2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl Phosphorodithioate
198. (z)-2-{[dimethoxy(sulfanylidene)-
199. E?-phosphanyl]sulfanyl}-n-methylethanimidic Acid
| Molecular Weight | 229.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C5H12NO3PS2 |
| XLogP3 | 0.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 228.99962259 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 228.99962259 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 105 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 12 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 191 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Medication (Vet): Also used experimentally in many species by many routes (spray, oral, sc, im, pour on, etc), and has shown particular effectiveness against grubs in cattle and reindeer (10 and 30 mg/kg upper safe limits, respectively) and oestrus ovis in sheep (25 mg/kg sc- avoid use in hot or tired animals). Older materials may be more toxic to animals.
Rossoff, I.S. Handbook of Veterinary Drugs. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 1974., p. 179
Cholinesterase Inhibitors
Drugs that inhibit cholinesterases. The neurotransmitter ACETYLCHOLINE is rapidly hydrolyzed, and thereby inactivated, by cholinesterases. When cholinesterases are inhibited, the action of endogenously released acetylcholine at cholinergic synapses is potentiated. Cholinesterase inhibitors are widely used clinically for their potentiation of cholinergic inputs to the gastrointestinal tract and urinary bladder, the eye, and skeletal muscles; they are also used for their effects on the heart and the central nervous system. (See all compounds classified as Cholinesterase Inhibitors.)
Insecticides
Pesticides designed to control insects that are harmful to man. The insects may be directly harmful, as those acting as disease vectors, or indirectly harmful, as destroyers of crops, food products, or textile fabrics. (See all compounds classified as Insecticides.)
Qualitatively, metabolism of dimethoate in mammals is essentially identical to that occurring in insects. There are... quantitative differences. In general, dimethoate, is much more rapidly degraded in mammals and eliminated via urine. For example, 87-90% of oral dose given cattle was found in urine after 24 hr, mainly as hydrolysis products.
White-Stevens, R. (ed.). Pesticides in the Environment: Volume 1, Part 1, Part 2. New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc., 1971., p. 168
...After ingestion of dimethoate, rats eliminate 60% of dose in 24 hr in urine and expired air.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 1: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1960 and 1969. London: The Chemical Society, 1970., p. 282
... Dimethoate rapidly penetrated isolated sections of /mouse/ small intestine, colon, and rectum, with the highest rates of penetration occurring in the colon and rectum. The age of the mice had no significant effects on the extent of penetration. /Initial dose not specified/
Shah PV, Guthrie FE; Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 25: 621-4 (1973) as cited in USEPA/ECAO; Health and Environmental Effects Profile for Dimethoate (Final Draft) p.9 (1984) ECAO-CIN-PO81
... Following aerial spraying with 38% dimethoate animal tissues contained higher concentrations of dimethoate than did soil, water or plants. ... The tissue containing the highest concentrations were brain and intially, lung. ...
Fedrorenko AP et al; Vestn Zool 4: 89-92 (1981) as cited in USEPA/ECAO; Health Effects Profile for Dimethoate (Final Draft) p.9-10 (1984) ECAO-CIN-PO81
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for DIMETHOATE (23 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
... Detoxification pathway ... involves the hydrolysis of carboxyester or carboxyamide linkages in some insecticides by tissue or plasma carboxylesterases (sometimes called aliesterase). Malathion and dimethoate are examples.
Doull, J., C.D.Klassen, and M.D. Amdur (eds.). Casarett and Doull's Toxicology. 3rd ed., New York: Macmillan Co., Inc., 1986., p. 534
Rabbit and rat liver microsomes converted dimethoate to oxygen analog and des-N-methyl derivatives.
Menzie, C. M. Metabolism of Pesticides, An Update. U.S. Department of the Interior, Fish, Wild-life Service, Special Scientific Report - Wildlife No. 184, Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, l974., p. 166
After dimethoate was administered to rats, the following compounds were found in urine: 1. dimethoate, 2. dimethoxon, 3. dimethoate carboxylic acid, 4. dimethylphosphorodithioate, 5. dimethyl phosphorothioate, 6. dimethylphosphate, 7. monomethylphosphate, 8. phosphorothioate, 9. formate, and 10. N-methyl 2-glucuronate acetamide.
Menzie, C. M. Metabolism of Pesticides, An Update. U.S. Department of the Interior, Fish, Wild-life Service, Special Scientific Report - Wildlife No. 184, Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, l974., p. 166
Oxidative desulfuration of dimethoate to give O-analog took place rapidly in rabbits and rats. Both dimethoate and O-analog underwent subsequent oxidative N-dealkylation coupled with formation of N-hydroxymethyl intermediates.
The Chemical Society. Foreign Compound Metabolism in Mammals. Volume 2: A Review of the Literature Published Between 1970 and 1971. London: The Chemical Society, 1972., p. 287
For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for DIMETHOATE (28 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Dimethoate has known human metabolites that include Omethoate.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Organophosphorus derivatives act by combining with and inactivating the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE). ... The inactivation of cholinesterase by cholinesterase inhibitor pesticides allows the accumulation of large amounts of acetylcholine, with resultant widespread effects that may be ... separated into 4 categories: (1) Potentiation of postganglionic parasympathetic activity. ... (2) Persistent depolarization of skeletal muscle ... (3) Initial stimulation following depression of cells of central nervous system ... (4) Variable ganglionic stimulation or blockade ... /Cholinesterase inhibitor pesticides/
Dreisbach, R.H. Handbook of Poisoning. 12th ed. Norwalk, CT: Appleton and Lange, 1987., p. 113
They act principally by inhibition of acetyl cholinesterase (AChE) at the cholinergic synapses. /organophosphorus insecticides/
WHO; Environ Health Criteria Number 90: Dimethoate p.50 (1989)
The signs of poisoning due to organophosphorus cmpd are those due to accumulation of acetylcholine & hence overstimulation of parasympathetic nervous system. It is usual to divide them under 3 headings: muscarinic, nicotinic & central. Muscarinic signs ... consist of hypersalivation, lacrimation, sweating & nasal discharge. Miosis, dyspnea, vomiting, diarrhea & frequency of urination ... Nicotinic effects consist of fasciculation of muscles, weakness & paralysis. Central nervous system effects include nervousness, apprehension, ataxia, convulsions & coma. Death is due to resp failure, or sometimes cardiac arrest. There is little difference between signs produced by different organophosphorus compounds, but route of absorption may influence one system more than another. /Organophosphorus cmpd/
Clarke, M. L., D. G. Harvey and D. J. Humphreys. Veterinary Toxicology. 2nd ed. London: Bailliere Tindall, 1981., p. 153
Toxicants of this class phosphorylate almost irreversibly varying amt of acetylcholinesterase enzyme of tissues, allowing accum of acetylcholine at cholinergic neuro-effector junctions (muscarinic effects), & at skeletal muscle myoneural junctions & in autonomic ganglia (nicotinic effects). /Organophosphate pesticides/
Morgan, D. P. Recognition and Management of Pesticide Poisonings. 2nd ed. EPA 540/9-76-011, Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, Aug. 1976., p. 4
For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for DIMETHOATE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Market Place

ABOUT THIS PAGE


LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?