

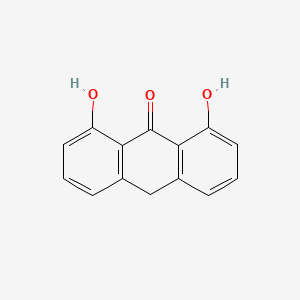

1. 1,8 Dihydroxy 9 Anthrone
2. 1,8,9-anthracenetriol
3. 1,8-dihydroxy-9(10h)-anthracenone
4. 1,8-dihydroxy-9-anthrone
5. Anthraforte
6. Anthranol
7. Cignolin
8. Cygnoline
9. Dihydroxyanthranol
10. Dithranol
11. Dithrocream
12. Ditranol Fna
13. Fna, Ditranol
14. Lasan
15. Micanol
16. Psoradrate
17. Psoricrme
1. Dithranol
2. 1143-38-0
3. 1,8-dihydroxyanthrone
4. Cignolin
5. 1,8-dihydroxy-9-anthrone
6. 1,8-dihydroxyanthracen-9(10h)-one
7. Chrysodermol
8. Cigthranol
9. 9(10h)-anthracenone, 1,8-dihydroxy-
10. Batridol
11. Psoriacid-stift
12. Lasan
13. Anthra-derm
14. 1,8-dihydroxy-10h-anthracen-9-one
15. Drithoscalp
16. Derobin
17. Drithocreme
18. Batidrol
19. Psodadrate
20. Psoriacide
21. Anthrone, 1,8-dihydroxy-
22. 1,8-dihydroxy-9(10h)-anthracenone
23. Nsc 43970
24. Anthraderm
25. Anthraline
26. Nsc 629313
27. Anthralin [usp]
28. Dithranol [inn]
29. Anthralin (dithranol)
30. Chebi:37510
31. Nsc-43970
32. U8cjk0jh5m
33. Nsc-629313
34. Chembl46469
35. Anthralin (usp)
36. Dithranol (inn)
37. Nsc629313
38. Ncgc00091330-01
39. Dsstox_cid_4538
40. 1,8-dihydroxy-9(10h)-anthracenone;anthralin
41. Dsstox_rid_77448
42. Dsstox_gsid_24538
43. Dithranolum
44. Dithranolum [inn-latin]
45. Zithranol-rr
46. Ccris 628
47. Cas-1143-38-0
48. Sr-05000002011
49. Einecs 214-538-0
50. Unii-u8cjk0jh5m
51. Mfcd00053409
52. Brn 2054360
53. Cignoline
54. Ccris 5592
55. Prestwick_528
56. Anthralin, Dithranol
57. Dithranol ,(s)
58. Nsc 403736
59. Brn 1976792
60. Anthrone,8-dihydroxy-
61. Spectrum_000056
62. Anthraderm (tn)
63. Anthralin [mi]
64. Dithranol [iarc]
65. Spectrum2_000111
66. Spectrum3_000304
67. Spectrum4_000151
68. Spectrum5_000820
69. Anthralin [vandf]
70. Dithranol [mart.]
71. Epitope Id:114081
72. 1,8-dihydroxy-9-anthrane
73. Anthralin [usp-rs]
74. Cid_2202
75. Dithranol [who-dd]
76. Dithranol [who-ip]
77. Schembl3197
78. Bspbio_001868
79. Kbiogr_000622
80. Kbioss_000436
81. 4-06-00-07602 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
82. Mls001332632
83. Mls002415712
84. 1,8,9-trihydroxyanthracene;
85. Divk1c_000021
86. Spectrum1500127
87. Spbio_000122
88. Zinc1322
89. Dithranol [ep Impurity]
90. Dithranol [ep Monograph]
91. Dithranol, >=90% (hplc)
92. Dtxsid7024538
93. Hms500b03
94. Kbio1_000021
95. Kbio2_000436
96. Kbio2_003004
97. Kbio2_005572
98. Kbio3_001368
99. Nuzwlkwwnnjhpt-uhfffaoysa-
100. Anthralin [usp Monograph]
101. Ninds_000021
102. Hms1920e07
103. Hms2091k07
104. Hms2271b09
105. Hms3715h19
106. Pharmakon1600-01500127
107. Hy-b0738
108. Nsc43970
109. 9(10h)-anthracenone,8-dihydroxy-
110. Tox21_111115
111. Tox21_201851
112. Tox21_300290
113. Bdbm50041802
114. Ccg-38920
115. Nsc755873
116. S4590
117. 1,8-dihydroxy-9-(10h)anthracenone
118. Akos015914122
119. Tox21_111115_1
120. Db11157
121. Ks-5183
122. Nsc-755873
123. Idi1_000021
124. 1,8-dihydroxy-9(10h)-anthracenone #
125. Ncgc00091330-02
126. Ncgc00091330-03
127. Ncgc00091330-04
128. Ncgc00091330-05
129. Ncgc00091330-07
130. Ncgc00253941-01
131. Ncgc00259400-01
132. Ac-14842
133. Nci60_004019
134. Sbi-0051286.p003
135. Db-060606
136. 1,8-dihydroxy-9,10-dihydroanthracen-9-one
137. Ft-0625372
138. C06831
139. D00233
140. D97650
141. Ab00051916_07
142. A803172
143. Q419397
144. Sr-05000002011-1
145. Sr-05000002011-2
146. W-108602
147. Dithranol, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
148. Anthralin, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
149. Anthralin (dithranol), Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
| Molecular Weight | 226.23 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C14H10O3 |
| XLogP3 | 3.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 226.062994177 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 226.062994177 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 57.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 287 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Stable plaque psoriasis of the skin and scalp. It is also used topically in the management of psoriasis, dermatoses, and alopecia areata. Anthralin is also used in biomedical research due to its effect on EGFR autophosphorylation.
Anthralin is a natural anthraquinone derivative, anti-psoriatic and anti-inflammatory agent. It controls skin growth by reducing the synthesis of DNA and the mitotic activity in the hyperplastic epidermis, normalizing the rate of cell proliferation and keratinization.
Dermatologic Agents
Drugs used to treat or prevent skin disorders or for the routine care of skin. (See all compounds classified as Dermatologic Agents.)
D - Dermatologicals
D05 - Antipsoriatics
D05A - Antipsoriatics for topical use
D05AC - Antracen derivatives
D05AC01 - Dithranol
Absorption
Anthralin penetrates damaged skin and psoriatic lesions faster and to a greater extent than normal skin, likely due to increased vascularity of psoriatic lesions.
Anthralin is administered topically. Although the extent of systemic absorption after topical application has not been determined, no traces of anthraquinone metabolites were detected in the urine of treated subjects in a limited clinical study of anthralin cream,. Anthralin does not inhibit hepatic microsomal enzyme activity.
Anthralin inhibits the proliferation of keratinocytes (epidermal skin cells), prevents the action of T-cells, and promotes cell differentiation, likely through mitochondrial dysfunction. In addition, the production of free radicals may contribute to its anti-psoriatic effect. In vitro studies demonstrate that anthralin prolongs the prophase component of mitosis for keratinocytes and leukocytes. Prophase is the first step of mitosis, the process separating the duplicated genetic material carried in the nucleus of a parent cell into two identical daughter cells. In vivo studies demonstrate that anthralin blocks DNA synthesis and can increase the release of reactive oxygen species. Anthralin is believed to normalize the rate of epidermal cell proliferation and keratinization by reducing the mitotic activity of the epidermal hyperplasia in psoriasis. Anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory effects of anthralin have been demonstrated on both psoriatic and healthy skin. The anti-proliferative effects of anthralin are thought to be due to a combination of inhibition of DNA synthesis and its strong reducing properties. The effectiveness of anthralin as an anti-psoriatic agent is partly owed to its ability to promote lipid peroxidation and reduce the concentration of endothelial adhesion molecules, which are found to be elevated in psoriatic patients,. Recent studies suggest that its ability to prevent T-lymphocyte activation and normalize keratinocyte differentiation may occur by a direct effect on mitochondria.

LOOKING FOR A SUPPLIER?