
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
VMF
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
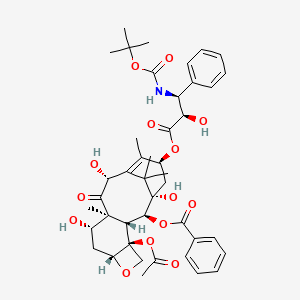

1. Docetaxel Anhydrous
2. Docetaxel Hydrate
3. Docetaxel Trihydrate
4. Docetaxol
5. N Debenzoyl N Tert Butoxycarbonyl 10 Deacetyltaxol
6. N-debenzoyl-n-tert-butoxycarbonyl-10-deacetyltaxol
7. Nsc 628503
8. Rp 56976
9. Rp-56976
10. Rp56976
11. Taxoltere Metro
12. Taxotere
1. 114977-28-5
2. Taxotere
3. Docetaxel Anhydrous
4. Docetaxol
5. Rp-56976
6. Docetaxel Winthrop
7. Docetaxel [inn]
8. Emdoc
9. Docefrez
10. Nsc 628503
11. N-debenzoyl-n-tert-butoxycarbonyl-10-deacetyltaxol
12. Rp 56976
13. Txl
14. Taxotere (tn)
15. Nsc-628503
16. N-debenzoyl-n-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-10-deacetyltaxol
17. Chebi:4672
18. 699121phca
19. Nsc628503
20. N-debenzoyl-n-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-10-deacetylpaclitaxel
21. Dsstox_cid_20464
22. Dsstox_rid_79497
23. Dsstox_gsid_40464
24. (2alpha,5beta,7beta,10beta,13alpha)-4-(acetyloxy)-13-({(2r,3s)-3-[(tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino]-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl}oxy)-1,7,10-trihydroxy-9-oxo-5,20-epoxytax-11-en-2-yl Benzoate
25. [(1s,2s,3r,4s,7r,9s,10s,12r,15s)-4-acetyloxy-1,9,12-trihydroxy-15-[(2r,3s)-2-hydroxy-3-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxycarbonylamino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]oxy-10,14,17,17-tetramethyl-11-oxo-6-oxatetracyclo[11.3.1.03,10.04,7]heptadec-13-en-2-yl] Benzoate
26. Docetaxel, Trihydrate
27. Taxotel
28. Docetaxolum
29. Taxoel
30. Docetaxel Kabi
31. Docetaxel Intermediate
32. Bind 014
33. Taxotere(r)
34. Ckd-810
35. (1s,2s,3r,4s,7r,9s,10s,12r,15s)-4-(acetyloxy)-15-{[(2r,3s)-3-{[(tert-butoxy)carbonyl]amino}-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl]oxy}-1,9,12-trihydroxy-10,14,17,17-tetramethyl-11-oxo-6-oxatetracyclo[11.3.1.0^{3,10}.0^{4,7}]heptadec-13-en-2-yl Benzoate
36. (2ar,4s,4as,6r,9s,11s,12s,12ar,12bs)-12b-acetoxy-9-(((2r,3s)-3-((tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino)-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl)oxy)-4,6,11-trihydroxy-4a,8,13,13-tetramethyl-5-oxo-2a,3,4,4a,5,6,9,10,11,12,12a,12b-dodecahydro-1h-7,11-methanocyclodeca[3,4]benzo[1,2-b]oxet-12-yl Benzoate
37. Cas-114977-28-5
38. Docetaxolum [inn-latin]
39. Docecad
40. Unii-699121phca
41. Docetaxel Teva
42. Docetaxel Accord
43. Mfcd00871399
44. Docetaxel 114977-28-5
45. Dtxsid0040464
46. Hsdb 6965
47. Xrp-6976l
48. Anx-514
49. Sdp-014
50. Sid 530
51. Docetaxel (tn)
52. Docetaxel- Bio-x
53. Ncgc00181306-01
54. Ncgc00181306-02
55. 5?,20-epoxy-1,7?,10?-trihydroxy-9-oxotax-11-ene-2?,4,13?-triyl 4-acetate 2-benzoate 13-[(2r,3s)-3-[[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]amino]-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoate]
56. Taxotere (aventis)
57. Docetaxel, Anhydrous
58. Cid148124
59. N-debenzoyl-n-boc-10-deacetyl Taxol
60. Docetaxel - Taxotere
61. Docetaxel Mylan
62. Rp56976
63. Bind-014
64. Docetaxel (jan/inn)
65. Docetaxel [jan]
66. Docetaxel [mi]
67. Chembl92
68. Docetaxel [hsdb]
69. Schembl4419
70. Docetaxel Teva Pharma
71. Gtpl6809
72. Bind 014 [who-dd]
73. Bdbm36351
74. Syp-0704a
75. Zdzotljhxycwba-vcvyqwhssa-
76. Amy4356
77. 114977-28-5, Docetaxel
78. Hms2089k08
79. Ex-a1206
80. Hy-b0011
81. Tox21_112781
82. Tox21_113088
83. Ac-383
84. Docetaxel Anhydrous [who-dd]
85. Zinc85537053
86. Akos015960718
87. Akos024457953
88. Tox21_112781_1
89. Cs-1144
90. Db01248
91. Ks-1452
92. Isocyanatoethylmethacrylatepolymer
93. Docetaxel, Purum, >=97.0% (hplc)
94. Ncgc00181306-04
95. Ncgc00242509-01
96. 4-(acetyloxy)-13alpha-({(2r,3s)-3-[(tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino]-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl}oxy)-1,7beta,10beta-trihydroxy-9-oxo-5beta,20-epoxytax-11-en-2alpha-yl Benzoate
97. Bd164373
98. Benzenepropanoic Acid, Beta-(((1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl)amino)-alpha-hydroxy-, 12b-(acetyloxy)-12-(benzoyloxy)-2a,3,4,4a,5,6,9,10,11,12,12a,12b-dodecahydro-4,6,11-trihydroxy-4a,8,13,13-tetramethyl-5-oxo-7,11-methano-1h-cyclodeca(3,4)benz(1,2-b)oxet-9-yl Ester
99. Cabazitaxel Metabolite (rp56976)
100. D4102
101. D07866
102. Ab01273941-01
103. Ab01273941-02
104. Q420436
105. Sr-01000003023
106. W-60384
107. Q-100074
108. Sr-01000003023-5
109. Brd-k30577245-001-04-3
110. Brd-k30577245-341-01-9
111. Z1551429742
112. Anhydrous Docetaxel, European Pharmacopoeia (ep) Reference Standard
113. (2ar,4s,4as,6r,9s,11s,12s,12ar,12bs)-12b-(acetyloxy)-12-(benzoyloxy)-2a,3,4,4a,5,6,9,10,11,12,12a,12b-dodecahydro-4,6,11-trihydroxy-4a,8,13,13-tetramethyl-5-oxo-7,11-methano-1h-cyclodeca[3,4]benz[1,2-b]oxet-9-yl (ar,bs)-b-[[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]amino]-a-hydroxybenzenepropanoate
114. (2beta,5beta,7alpha,8alpha,10alpha,13alpha)-4-(acetyloxy)-13-({(2r,3s)-3-[(tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino]-2-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl}oxy)-1,7,10-trihydroxy-9-oxo-5,20-epoxytax-11-en-2-yl Benzoate
115. (2r,3s)-n-carboxy-3-phenylisoserine, N-tert-butyl Ester, 13-ester With 5.beta.,20-epoxy-1,2.alpha.,4,7.beta.,10.beta.,13.alpha.-hexahydroxytax-11-en-9-one 4-acetate 2-benzoate
116. [2ar-[2a?,4?,4a?,6?,9?(?r*,?s*),11?,12?,12a?,12b?]]-?-[[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]amino]-?-hydroxy-12b-(acetyloxy)-12-(benzoyloxy)-2a,3,4,4a,5,6,9,10,11,12,12a,12b-dodecahydro-4,6,11-trihydroxy-4a,8,13,13-tetramethyl-5-oxo-7,11-methano-1h-cyclodeca[3,4]benz[1,2-b]oxet-9-yl Ester Benzenepropanoic Acid
117. [acetoxy-[(2r,3s)-3-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)-2-hydroxy-3-phenyl-propanoyl]oxy-trihydroxy-tetramethyl-oxo-[?]yl] Benzoate
118. 114915-20-7
119. Benzenepropanoic Acid, Beta-(((1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl)amino)-alpha-hydroxy-, (2ar,4s,4as,6r,9s,11s,12s,12ar,12bs)-12b-(acetyloxy)-12-(benzoyloxy)-2a,3,4,4a,5,6,9,10,11,12,12a,12b-dodecahydro-4,6,11-trihydroxy-4a,8,13,13-tetramethyl-5-oxo-7,11-methano-1h-cyclodeca(3,4)benz(1,2-b)oxet-9-yl Ester, (alphar,betas)-
120. Benzenepropanoic Acid,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]amino]-.alpha.-hydroxy-, (2ar,4s,4as,6r,9s,11s,12s,12ar,12bs)-12b-(acetyloxy)-12-(benzyloxy)-2a,3,4,4a,5,6,9,10,11,12,12a,12b-dodecahydro-4,6,11-trihydroxy-4a,8,13,13-tetramethyl-5-oxo-7,11-methano-1h-cyclodeca[3,4]benz[1,2-b]oxet-9-yl Ester, (.alpha.r,.beta.s)
| Molecular Weight | 807.9 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C43H53NO14 |
| XLogP3 | 1.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 14 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 13 |
| Exact Mass | 807.34660536 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 807.34660536 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 224 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 58 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1660 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 11 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Docefrez |
| PubMed Health | Docetaxel (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Active Ingredient | Docetaxel |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 80mg/vial; 20mg/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sun Pharma Global |
| 2 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Docetaxel |
| Drug Label | Docetaxel is an antineoplastic agent belonging to the taxoid family. It is prepared by semisynthesis beginning with a precursor extracted from the renewable needle biomass of yew plants. The chemical name for docetaxel is (2R,3S)-N-carboxy-3-phenylis... |
| Active Ingredient | Docetaxel |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 160mg/16ml (10mg/ml); 130mg/13ml (10mg/ml); 80mg/4ml (20mg/ml); 200mg/20ml (10mg/ml); 80mg/8ml (10mg/ml); 20mg/2ml (10mg/ml); 80mg/2ml (40mg/ml); 160mg/8ml (20mg/ml); 20mg/ml (20mg/ml); 140mg/7ml (20mg/ml); 20mg/0.5ml (40mg/ml) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira; Accord Hlthcare; Pfizer Labs; Sandoz; Actavis |
| 3 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Taxotere |
| PubMed Health | Docetaxel (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | Docetaxel is an antineoplastic agent belonging to the taxoid family. It is prepared by semisynthesis beginning with a precursor extracted from the renewable needle biomass of yew plants. The chemical name for docetaxel is (2R,3S)-N-carboxy-3-phenylis... |
| Active Ingredient | Docetaxel |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 160mg/8ml (20mg/ml); 80mg/4ml (20mg/ml); 20mg/ml (20mg/ml) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sanofi Aventis Us |
| 4 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Docefrez |
| PubMed Health | Docetaxel (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Active Ingredient | Docetaxel |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 80mg/vial; 20mg/vial |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sun Pharma Global |
| 5 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Docetaxel |
| Drug Label | Docetaxel is an antineoplastic agent belonging to the taxoid family. It is prepared by semisynthesis beginning with a precursor extracted from the renewable needle biomass of yew plants. The chemical name for docetaxel is (2R,3S)-N-carboxy-3-phenylis... |
| Active Ingredient | Docetaxel |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 160mg/16ml (10mg/ml); 130mg/13ml (10mg/ml); 80mg/4ml (20mg/ml); 200mg/20ml (10mg/ml); 80mg/8ml (10mg/ml); 20mg/2ml (10mg/ml); 80mg/2ml (40mg/ml); 160mg/8ml (20mg/ml); 20mg/ml (20mg/ml); 140mg/7ml (20mg/ml); 20mg/0.5ml (40mg/ml) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Hospira; Accord Hlthcare; Pfizer Labs; Sandoz; Actavis |
| 6 of 6 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Taxotere |
| PubMed Health | Docetaxel (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Antineoplastic Agent |
| Drug Label | Docetaxel is an antineoplastic agent belonging to the taxoid family. It is prepared by semisynthesis beginning with a precursor extracted from the renewable needle biomass of yew plants. The chemical name for docetaxel is (2R,3S)-N-carboxy-3-phenylis... |
| Active Ingredient | Docetaxel |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 160mg/8ml (20mg/ml); 80mg/4ml (20mg/ml); 20mg/ml (20mg/ml) |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Sanofi Aventis Us |
Antineoplastic Agents; Tubulin Modulators
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Docetaxel. Online file (MeSH, 2014). Available from, as of December 18, 2014: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2014/mesh_browser/MBrowser.html
Taxotere is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer after failure of prior chemotherapy. Taxotere in combination with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide is indicated for the adjuvant treatment of patients with operable node-positive breast cancer. /Included in US product labeling/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Taxotere (Docetaxel) Injection, Solution, Concentrate (Updated: November 2014). Available from, as of March 25, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=45e6dce4-92e2-4ad1-bf11-bbcefb753636
Taxotere as a single agent is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer after failure of prior platinum-based chemotherapy. Taxotere in combination with cisplatin is indicated for the treatment of patients with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer who have not previously received chemotherapy for this condition. /Included in US product labeling/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Taxotere (Docetaxel) Injection, Solution, Concentrate (Updated: November 2014). Available from, as of March 25, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=45e6dce4-92e2-4ad1-bf11-bbcefb753636
Taxotere in combination with prednisone is indicated for the treatment of patients with androgen independent (hormone refractory) metastatic prostate cancer. /Included in US product labeling/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Taxotere (Docetaxel) Injection, Solution, Concentrate (Updated: November 2014). Available from, as of March 25, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=45e6dce4-92e2-4ad1-bf11-bbcefb753636
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for DOCETAXEL (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: TOXIC DEATHS. The incidence of treatment-related mortality associated with Taxotere therapy is increased in patients with abnormal liver function, in patients receiving higher doses, and in patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma and a history of prior treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy who receive Taxotere as a single agent at a dose of 100 mg/sq m.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Taxotere (Docetaxel) Injection, Solution, Concentrate (Updated: November 2014). Available from, as of March 25, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=45e6dce4-92e2-4ad1-bf11-bbcefb753636
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: HEPATOTOXICITY. Taxotere should not be given to patients with bilirubin > upper limit of normal (ULN), or to patients with AST and/or ALT >1.5 x ULN concomitant with alkaline phosphatase >2.5 x ULN. Patients with elevations of bilirubin or abnormalities of transaminase concurrent with alkaline phosphatase are at increased risk for the development of grade 4 neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, infections, severe thrombocytopenia, severe stomatitis, severe skin toxicity, and toxic death. Patients with isolated elevations of transaminase >1.5 x ULN also had a higher rate of febrile neutropenia grade 4 but did not have an increased incidence of toxic death. Bilirubin, AST or ALT, and alkaline phosphatase values should be obtained prior to each cycle of Taxotere therapy
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Taxotere (Docetaxel) Injection, Solution, Concentrate (Updated: November 2014). Available from, as of March 25, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=45e6dce4-92e2-4ad1-bf11-bbcefb753636
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: NEUTROPENIA. Taxotere therapy should not be given to patients with neutrophil counts of <1500 cells/cu mm. In order to monitor the occurrence of neutropenia, which may be severe and result in infection, frequent blood cell counts should be performed on all patients receiving Taxotere.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Taxotere (Docetaxel) Injection, Solution, Concentrate (Updated: November 2014). Available from, as of March 25, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=45e6dce4-92e2-4ad1-bf11-bbcefb753636
/BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS. Severe hypersensitivity reactions characterized by generalized rash/erythema, hypotension and/or bronchospasm, or very rarely fatal anaphylaxis, have been reported in patients who received a 3-day dexamethasone premedication. Hypersensitivity reactions require immediate discontinuation of the Taxotere infusion and administration of appropriate therapy Taxotere must not be given to patients who have a history of severe hypersensitivity reactions to Taxotere or to other drugs formulated with polysorbate 80.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Taxotere (Docetaxel) Injection, Solution, Concentrate (Updated: November 2014). Available from, as of March 25, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=45e6dce4-92e2-4ad1-bf11-bbcefb753636
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for DOCETAXEL (45 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
For the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer after failure of prior chemotherapy. Also used as a single agent in the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer after failure of prior platinum-based chemotherapy. It is also used in combination with prednisone, in the treatment of patients with androgen independent (hormone refractory) metastatic prostate cancer. Furthermore, docetaxel has uses in the treatment of gastric adenocarinoma and head and neck cancer.
FDA Label
* Breast cancer :
Docetaxel Accord in combination with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide is indicated for the adjuvant treatment of patients with:
- operable node-positive breast cancer ;
- operable node-negative breast cancer .
For patients with operable node-negative breast cancer , adjuvant treatment should be restricted to patients eligible to receive chemotherapy according to internationally established criteria for primary therapy of early breast cancer .
Docetaxel Accord in combination with doxorubicin is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer who have not previously received cytotoxic therapy for this condition.
Docetaxel Accord monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer after failure of cytotoxic therapy. Previous chemotherapy should have included an anthracycline or an alkylating agent.
Docetaxel Accord in combination with trastuzumab is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer whose tumours overexpress HER2 and who previously have not received chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
Docetaxel Accord in combination with capecitabine is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer after failure of cytotoxic chemotherapy. Previous therapy should have included an anthracycline.
* Non-small-cell lung cancer :
Docetaxel Accord is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of prior chemotherapy.
Docetaxel Accord in combination with cisplatin is indicated for the treatment of patients with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer , in patients who have not previously received chemotherapy for this condition.
* Prostate cancer :
Docetaxel Accord in combination with prednisone or prednisolone is indicated for the treatment of patients with hormone refractory metastatic prostate cancer .
* Gastric adenocarcinoma:
Docetaxel Accord in combination with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic gastric adenocarcinoma, including adenocarcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction, who have not received prior chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
* Head and neck cancer :
Docetaxel Accord in combination with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil is indicated for the induction treatment of patients with locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
* Breast cancer :
Taxotere in combination with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide is indicated for the adjuvant treatment of patients with:
- operable node-positive breast cancer ;
- operable node-negative breast cancer .
For patients with operable node-negative breast cancer , adjuvant treatment should be restricted to patients eligible to receive chemotherapy according to internationally established criteria for primary therapy of early breast cancer .
Taxotere in combination with doxorubicin is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer who have not previously received cytotoxic therapy for this condition.
Taxotere monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced ormetastatic breast cancer after failure of cytotoxic therapy. Previous chemotherapy should have included an anthracycline or an alkylating agent.
Taxotere in combination with trastuzumab is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer whose tumours overexpress HER2 and who previously have not received chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
Taxotere in combination with capecitabine is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer after failure of cytotoxic chemotherapy. Previous therapy should have included an anthracycline.
* Non-small-cell lung cancer :
Taxotere is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of prior chemotherapy.
Taxotere in combination with cisplatin is indicated for the treatment of patients with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer , in patients who have not previously received chemotherapy for this condition.
* Prostate cancer :
Taxotere in combination with prednisone or prednisolone is indicated for the treatment of patients with hormone refractory metastatic prostate cancer .
* Gastric adenocarcinoma:
Taxotere in combination with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic gastric adenocarcinoma, including adenocarcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction, who have not received prior chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
* Head and neck cancer :
Taxotere in combination with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil is indicated for the induction treatment of patients with locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
* Breast cancer :
Docetaxel Winthrop in combination with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide is indicated for the adjuvant treatment of patients with:
- operable node-positive breast cancer ;
- operable node-negative breast cancer .
For patients with operable node-negative breast cancer , adjuvant treatment should be restricted to patients eligible to receive chemotherapy according to internationally established criteria for primary therapy of early breast cancer .
Docetaxel Winthrop in combination with doxorubicin is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer who have not previously received cytotoxic therapy for this condition.
Docetaxel Winthrop monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer after failure of cytotoxic therapy. Previous chemotherapy should have included an anthracycline or an alkylating agent.
Docetaxel Winthrop in combination with trastuzumab is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer whose tumours overexpress HER2 and who previously have not received chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
Docetaxel Winthrop in combination with capecitabine is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer after failure of cytotoxic chemotherapy. Previous therapy should have included an anthracycline.
* Non-small-cell lung cancer :
Docetaxel Winthrop is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of prior chemotherapy.
Docetaxel Winthrop in combination with cisplatin is indicated for the treatment of patients with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer , in patients who have not previously received chemotherapy for this condition.
* Prostate cancer :
Docetaxel Winthrop in combination with prednisone or prednisolone is indicated for the treatment of patients with hormone-refractory metastatic prostate cancer .
* Gastric adenocarcinoma:
Docetaxel Winthrop in combination with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic gastric adenocarcinoma, including adenocarcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction, who have not received prior chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
* Head and neck cancer :
Docetaxel Winthrop in combination with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil is indicated for the induction treatment of patients with locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
* Breast cancer :
Taxespira in combination with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide is indicated for the adjuvant treatment of patients with:
- operable node-positive breast cancer ;
- operable node-negative breast cancer .
For patients with operable node-negative breast cancer , adjuvant treatment should be restricted to patients eligible to receive chemotherapy according to internationally established criteria for primary therapy of early breast cancer .
Taxespira in combination with doxorubicin is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer who have not previously received cytotoxic therapy for this condition.
Taxespira monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer after failure of cytotoxic therapy. Previous chemotherapy should have included an anthracycline or an alkylating agent.
Taxespira combination with trastuzumab is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer whose tumours over express HER2 and who previously have not received chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
Taxespira in combination with capecitabine is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer after failure of cytotoxic chemotherapy. Previous therapy should have included an anthracycline.
* Non-small cell lung cancer :
Taxespira indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer after failure of prior chemotherapy.
Taxespira in combination with cisplatin is indicated for the treatment of patients with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer , in patients who have not previously received chemotherapy for this condition.
* Prostate cancer :
Taxespira in combination with prednisone or prednisolone is indicated for the treatment of patients with hormone refractory metastatic prostate cancer .
* Gastric adenocarcinoma:
Taxespira in combination with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic gastric adenocarcinoma, including adenocarcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction, who have not received prior chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
* Head and neck cancer :
Taxespira in combination with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil is indicated for the induction treatment of patients with locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
* Breast cancer :
Docetaxel Teva in combination with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide is indicated for the adjuvant treatment of patients with:
- operable node-positive breast cancer ;
- operable node-negative breast cancer .
For patients with operable node-negative breast cancer , adjuvant treatment should be restricted to patients eligible to receive chemotherapy according to internationally established criteria for primary therapy of early breast cancer .
Docetaxel Teva in combination with doxorubicin is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer who have not previously received cytotoxic therapy for this condition.
Docetaxel Teva monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer after failure of cytotoxic therapy.
Previous chemotherapy should have included an anthracycline or an alkylating agent.
Docetaxel Teva in combination with trastuzumab is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer whose tumours overexpress HER2 and who previously have not received chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
Docetaxel Teva in combination with capecitabine is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer after failure of cytotoxic chemotherapy. Previous therapy should have included an anthracycline.
* Non-small-cell lung cancer :
Docetaxel Teva is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of prior chemotherapy.
Docetaxel Teva in combination with cisplatin is indicated for the treatment of patients with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer , in patients who have not previously received chemotherapy for this condition.
* Prostate cancer :
Docetaxel Teva in combination with prednisone or prednisolone is indicated for the treatment of patients with hormone refractory metastatic prostate cancer .
* Gastric adenocarcinoma:
Docetaxel Teva in combination with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic gastric adenocarcinoma, including adenocarcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction, who have not received prior chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
* Head and neck cancer :
Docetaxel Teva in combination with cisplatin and 5 fluorouracil is indicated for the induction treatment of patients with locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
* Breast cancer :
Docetaxel Kabi in combination with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide is indicated for the adjuvant treatment of patients with:
- operable node-positive breast cancer ;
- operable node-negative breast cancer .
For patients with operable node-negative breast cancer , adjuvant treatment should be restricted to patients eligible to receive chemotherapy according to internationally established criteria for primary therapy of early breast cancer .
Docetaxel Kabi in combination with doxorubicin is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer who have not previously received cytotoxic therapy for this condition.
Docetaxel Kabi monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer after failure of cytotoxic therapy. Previous chemotherapy should have included an anthracycline or an alkylating agent.
Docetaxel Kabi in combination with trastuzumab is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer whose tumours overexpress HER2 and who previously have not received chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
Docetaxel Kabi in combination with capecitabine is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer after failure of cytotoxic chemotherapy. Previous therapy should have included an anthracycline.
* Non-small-cell lung cancer :
Docetaxel Kabi is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of prior chemotherapy.
Docetaxel Kabi in combination with cisplatin is indicated for the treatment of patients with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer , in patients who have not previously received chemotherapy for this condition.
* Prostate cancer :
Docetaxel Kabi in combination with prednisone or prednisolone is indicated for the treatment of patients with castration-resistant metastatic prostate cancer .
Docetaxel Kabi in combination with androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT), with or without prednisone or prednisolone, is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer .
* Gastric adenocarcinoma:
Docetaxel Kabi in combination with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic gastric adenocarcinoma, including adenocarcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction, who have not received prior chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
* Head and neck cancer :
Docetaxel Kabi in combination with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil is indicated for the induction treatment of patients with locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
Treatment of breast cancer , special forms of lung cancer (non-small-cell lung cancer ), prostate cancer , gastric cancer , or head and neck cancer .
* Breast cancer :
Docetaxel Teva Pharma monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer after failure of cytotoxic therapy. Previous chemotherapy should have included an anthracycline or an alkylating agent.
* Non-small-cell lung cancer :
Docetaxel Teva Pharma is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of prior chemotherapy.
Docetaxel Teva Pharma in combination with cisplatin is indicated for the treatment of patients with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer , in patients who have not previously received chemotherapy for this condition.
* Prostate cancer :
Docetaxel Teva Pharma in combination with prednisone or prednisolone is indicated for the treatment of patients with hormone refractory metastatic prostate cancer .
Breast cancer
Docetaxel in combination with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide is indicated for the adjuvant treatment of patients with operable node-positive breast cancer .
Docetaxel in combination with doxorubicin is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer who have not previously received cytotoxic therapy for this condition.
Docetaxel monotherapy is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer after failure of cytotoxic therapy. Previous chemotherapy should have included an anthracycline or an alkylating agent.
Docetaxel in combination with trastuzumab is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer whose tumours over express HER2 and who previously have not received chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
Docetaxel in combination with capecitabine is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer after failure of cytotoxic chemotherapy. Previous therapy should have included an anthracycline.
Non-small cell lung cancer
Docetaxel is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer after failure of prior chemotherapy.
Docetaxel in combination with cisplatin is indicated for the treatment of patients with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer , in patients who have not previously received chemotherapy for this condition.
Prostate cancer
Docetaxel in combination with prednisone or prednisolone is indicated for the treatment of patients with hormone refractory metastatic prostate cancer .
Gastric adenocarcinoma
Docetaxel in combination with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic gastric adenocarcinoma, including adenocarcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction, who have not received prior chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
Head and neck cancer
Docetaxel in combination with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil is indicated for the induction treatment of patients with locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Docetaxel is a taxoid antineoplastic agent. It promotes the assembly of microtubules from tubulin dimers and stabilizes microtubules by preventing depolymerization. This stability results in the inhibition of the normal dynamic reorganization of the microtubule network that is essential for vital interphase and mitotic cellular functions. In addition, docetaxel induces abnormal arrays or "bundles" of microtubules throughout the cell cycle and multiple asters of microtubules during mitosis.
Tubulin Modulators
Agents that interact with TUBULIN to inhibit or promote polymerization of MICROTUBULES. (See all compounds classified as Tubulin Modulators.)
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
L01CD02
L01CD02
L01CD02
L01CD02
L01CD02
L01CD02
L01CD02
L01CD02
L01CD02
L01CD02
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01C - Plant alkaloids and other natural products
L01CD - Taxanes
L01CD02 - Docetaxel
Absorption
The pharmacokinetic profile is consistent with a three-compartment model. The area under the curve (AUC) was dose proportional following doses of 70 mg/m2 to 115 mg/m2 with infusion times of 1 to 2 hours.
Route of Elimination
Docetaxel was eliminated in both the urine and feces following oxidative metabolism of the tert-butyl ester group, but fecal excretion was the main elimination route. Within 7 days, urinary and fecal excretion accounted for approximately 6% and 75% of the administered radioactivity, respectively.
Volume of Distribution
The initial rapid decline represents distribution to the peripheral compartments and the late (terminal) phase is due, in part, to a relatively slow efflux of docetaxel from the peripheral compartment.
113 L
Clearance
21 L/h/m2 [Total body clearance, cancer patients after IV administration of 20115 mg/m2]
The initial rapid decline represents distribution to the peripheral compartments and the late (terminal) phase is due, in part, to a relatively slow efflux of docetaxel from the peripheral compartment. Mean steady state volume of distribution was 113 L. In vitro studies showed that docetaxel is about 94% protein bound, mainly to alpha1-acid glycoprotein, albumin, and lipoproteins. In three cancer patients, the in vitro binding to plasma proteins was found to be approximately 97%. Dexamethasone does not affect the protein binding of docetaxel.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Taxotere (Docetaxel) Injection, Solution, Concentrate (Updated: November 2014). Available from, as of March 25, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=45e6dce4-92e2-4ad1-bf11-bbcefb753636
A study of (14)C-docetaxel was conducted in three cancer patients. Docetaxel was eliminated in both the urine and feces following oxidative metabolism of the tert-butyl ester group, but fecal excretion was the main elimination route. Within 7 days, urinary and fecal excretion accounted for approximately 6% and 75% of the administered radioactivity, respectively. About 80% of the radioactivity recovered in feces is excreted during the first 48 hours as 1 major and 3 minor metabolites with very small amounts (less than 8%) of unchanged drug.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Taxotere (Docetaxel) Injection, Solution, Concentrate (Updated: November 2014). Available from, as of March 25, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=45e6dce4-92e2-4ad1-bf11-bbcefb753636
The pharmacokinetics of docetaxel have been evaluated in cancer patients after administration of 20 mg/m2 to 115 mg/sq m in phase 1 studies. The area under the curve (AUC) was dose proportional following doses of 70 mg/sq m to 115 mg/sq m with infusion times of 1 to 2 hours. Docetaxel's pharmacokinetic profile is consistent with a three-compartment pharmacokinetic model, with half-lives for the alpha, beta, and gamma phases of 4 min, 36 min, and 11.1 hr, respectively. Mean total body clearance was 21 L/hr/sq m.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Taxotere (Docetaxel) Injection, Solution, Concentrate (Updated: November 2014). Available from, as of March 25, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=45e6dce4-92e2-4ad1-bf11-bbcefb753636
It is not known whether docetaxel is excreted in human milk.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Taxotere (Docetaxel) Injection, Solution, Concentrate (Updated: November 2014). Available from, as of March 25, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=45e6dce4-92e2-4ad1-bf11-bbcefb753636
Hepatic. In vitro drug interaction studies revealed that docetaxel is metabolized by the CYP3A4 isoenzyme (1 major, 3 minor metabolites).
Docetaxel, a potent antimicrotubule agent widely used in the treatment of ovarian, breast and lung cancer, is extensively metabolized in various animal species, including humans. The metabolism of docetaxel to its primary metabolite, hydroxydocetaxel, is mediated by cytochrome P450 isozymes CYP3A2 and CYP3A4 in rats and humans, respectively....
PMID:11561777 Nallani SC et al; Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 48 (2): 115-22 (2001)
In vitro drug interaction studies revealed that docetaxel is metabolized by the CYP3A4 isoenzyme, and its metabolism may be modified by the concomitant administration of compounds that induce, inhibit, or are metabolized by cytochrome P450 3A4.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Taxotere (Docetaxel) Injection, Solution, Concentrate (Updated: November 2014). Available from, as of March 25, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=45e6dce4-92e2-4ad1-bf11-bbcefb753636
Docetaxel has known human metabolites that include Hydroxy-Docetaxel.
S73 | METXBIODB | Metabolite Reaction Database from BioTransformer | DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4056560
Dose-dependent. Doses of 70 mg per square meter of body surface area (mg/m 2 ) or higher produce a triphasic elimination profile. With lower doses, assay limitations precluded detection of the terminal elimination phase. The half-life of the alpha, beta, and gamma phase are 4 minutes, 36 minutes, and 11.1 hours, respectively.
Docetaxel interferes with the normal function of microtubule growth. Whereas drugs like colchicine cause the depolymerization of microtubules in vivo, docetaxel arrests their function by having the opposite effect; it hyper-stabilizes their structure. This destroys the cell's ability to use its cytoskeleton in a flexible manner. Specifically, docetaxel binds to the β-subunit of tubulin. Tubulin is the "building block" of microtubules, and the binding of docetaxel locks these building blocks in place. The resulting microtubule/docetaxel complex does not have the ability to disassemble. This adversely affects cell function because the shortening and lengthening of microtubules (termed dynamic instability) is necessary for their function as a transportation highway for the cell. Chromosomes, for example, rely upon this property of microtubules during mitosis. Further research has indicated that docetaxel induces programmed cell death (apoptosis) in cancer cells by binding to an apoptosis stopping protein called Bcl-2 (B-cell leukemia 2) and thus arresting its function.
Docetaxel is an antineoplastic agent that acts by disrupting the microtubular network in cells that is essential for mitotic and interphase cellular functions. Docetaxel binds to free tubulin and promotes the assembly of tubulin into stable microtubules while simultaneously inhibiting their disassembly. This leads to the production of microtubule bundles without normal function and to the stabilization of microtubules, which results in the inhibition of mitosis in cells. Docetaxel's binding to microtubules does not alter the number of protofilaments in the bound microtubules, a feature which differs from most spindle poisons currently in clinical use.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Taxotere (Docetaxel) Injection, Solution, Concentrate (Updated: November 2014). Available from, as of March 25, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=45e6dce4-92e2-4ad1-bf11-bbcefb753636
Docetaxel, a semisynthetic taxane, has exhibited significant single-agent activity against prostatic tumors. In phase I/II studies, single-agent docetaxel and the combination of docetaxel plus estramustine were effective in inducing prostate-specific antigen reductions of > or = 50% in men with androgen-independent prostate cancer (AIPC). The underlying reason for docetaxel's clinical activity against prostate cancer has been a focus of ongoing research. Docetaxel is believed to have a twofold mechanism of antineoplastic activity: (1) inhibition of microtubular depolymerization, and (2) attenuation of the effects of bcl-2 and bcl-xL gene expression. Taxane-induced microtubule stabilization arrests cells in the G(2)M phase of the cell cycle and induces bcl-2 phosphorylation, thereby promoting a cascade of events that ultimately leads to apoptotic cell death. In preclinical studies, docetaxel had a higher affinity for tubulin and was shown to be a more potent inducer of bcl-2 phosphorylation than paclitaxel. Laboratory evidence also supports the clinical evaluation of docetaxel-based combinations that include agents such as trastuzumab and/or estramustine. The pathways for docetaxel-induced apoptosis appear to differ in androgen-dependent and androgen-independent prostate cancer cells. Further elucidation of these differences will be instrumental in designing targeted regimens for the treatment of localized and advanced prostate cancer.
Pienta KJ; Semin Oncol 28 (4 Suppl 15): 3-7 (2001)

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS

Related Excipient Companies

Excipients by Applications
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
37
PharmaCompass offers a list of Docetaxel API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Docetaxel manufacturer or Docetaxel supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Docetaxel manufacturer or Docetaxel supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Docetaxel API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Docetaxel API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Docetaxel Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Docetaxel Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Docetaxel manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Docetaxel, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Docetaxel manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Docetaxel API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Docetaxel manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Docetaxel supplier is an individual or a company that provides Docetaxel active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Docetaxel finished formulations upon request. The Docetaxel suppliers may include Docetaxel API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Docetaxel suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Docetaxel DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Docetaxel active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Docetaxel DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Docetaxel USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Docetaxel DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Docetaxel USDMF includes data on Docetaxel's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Docetaxel USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Docetaxel suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Docetaxel Drug Master File in Japan (Docetaxel JDMF) empowers Docetaxel API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Docetaxel JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Docetaxel JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Docetaxel suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Docetaxel Drug Master File in Korea (Docetaxel KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Docetaxel. The MFDS reviews the Docetaxel KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Docetaxel KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Docetaxel KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Docetaxel API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Docetaxel suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
A Docetaxel CEP of the European Pharmacopoeia monograph is often referred to as a Docetaxel Certificate of Suitability (COS). The purpose of a Docetaxel CEP is to show that the European Pharmacopoeia monograph adequately controls the purity of Docetaxel EP produced by a given manufacturer. Suppliers of raw materials can prove the suitability of Docetaxel to their clients by showing that a Docetaxel CEP has been issued for it. The manufacturer submits a Docetaxel CEP (COS) as part of the market authorization procedure, and it takes on the role of a Docetaxel CEP holder for the record. Additionally, the data presented in the Docetaxel CEP (COS) is managed confidentially and offers a centralized system acknowledged by numerous nations, exactly like the Docetaxel DMF.
A Docetaxel CEP (COS) is recognised by all 36 nations that make up the European Pharmacopoeia Convention. Docetaxel CEPs may be accepted in nations that are not members of the Ph. Eur. at the discretion of the authorities there.
click here to find a list of Docetaxel suppliers with CEP (COS) on PharmaCompass.
A Docetaxel written confirmation (Docetaxel WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Docetaxel manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Docetaxel active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Docetaxel APIs or Docetaxel finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Docetaxel WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Docetaxel suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Docetaxel as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Docetaxel API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Docetaxel as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Docetaxel and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Docetaxel NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Docetaxel suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Docetaxel Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Docetaxel GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Docetaxel GMP manufacturer or Docetaxel GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Docetaxel CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Docetaxel's compliance with Docetaxel specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Docetaxel CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Docetaxel CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Docetaxel may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Docetaxel EP), Docetaxel JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Docetaxel USP).
