
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
Australia

DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
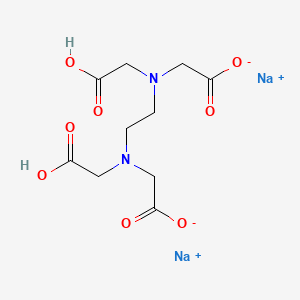

1. Acid, Edetic
2. Acid, Ethylenediaminetetraacetic
3. Acid, Ethylenedinitrilotetraacetic
4. Calcitetracemate, Disodium
5. Calcium Disodium Edetate
6. Calcium Disodium Versenate
7. Calcium Tetacine
8. Chelaton 3
9. Chromium Edta
10. Copper Edta
11. Coprin
12. Dicobalt Edta
13. Dinitrilotetraacetate, Disodium Ethylene
14. Dinitrilotetraacetate, Ethylene
15. Disodium Calcitetracemate
16. Disodium Edta
17. Disodium Ethylene Dinitrilotetraacetate
18. Disodium Versenate, Calcium
19. Distannous Edta
20. Edathamil
21. Edetate Disodium Calcium
22. Edetate, Calcium Disodium
23. Edetates
24. Edetic Acid
25. Edetic Acid, Calcium Salt
26. Edetic Acid, Calcium, Sodium Salt
27. Edetic Acid, Chromium Salt
28. Edetic Acid, Dipotassium Salt
29. Edetic Acid, Disodium Salt
30. Edetic Acid, Disodium Salt, Dihydrate
31. Edetic Acid, Disodium, Magnesium Salt
32. Edetic Acid, Disodium, Monopotassium Salt
33. Edetic Acid, Magnesium Salt
34. Edetic Acid, Monopotassium Salt
35. Edetic Acid, Monosodium Salt
36. Edetic Acid, Potassium Salt
37. Edetic Acid, Sodium Salt
38. Edta
39. Edta, Chromium
40. Edta, Copper
41. Edta, Dicobalt
42. Edta, Disodium
43. Edta, Distannous
44. Edta, Gallium
45. Edta, Magnesium Disodium
46. Edta, Potassium
47. Edta, Stannous
48. Ethylene Dinitrilotetraacetate
49. Ethylene Dinitrilotetraacetate, Disodium
50. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid
51. Ethylenedinitrilotetraacetic Acid
52. Gallium Edta
53. Magnesium Disodium Edta
54. N,n'-1,2-ethanediylbis(n-(carboxymethyl)glycine)
55. Potassium Edta
56. Stannous Edta
57. Tetacine, Calcium
58. Tetracemate
59. Versenate
60. Versenate, Calcium Disodium
61. Versene
1. 139-33-3
2. Edta Disodium Salt
3. Disodium Edetate
4. Edta Disodium
5. Titriplex Iii
6. Disodium Edta
7. Disodium Edta, Anhydrous
8. Cheladrate
9. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Disodium Salt
10. Disodium Versene
11. Endrate Disodium
12. Sodium Versenate
13. Disodium Salt Of Edta
14. Metaquest B
15. Kiresuto B
16. Chelaplex Iii
17. Complexon Iii
18. Diso-tate
19. Chelaton Iii
20. Versene Na
21. Triplex Iii
22. Chelaton 3
23. Disodium Versenate
24. Edathamil Disodium
25. Trilon Bd
26. Versene Na2
27. Disodium Sequestrene
28. Disodium Tetracemate
29. F 1 (complexon)
30. Disodium Ethylenediaminetetraacetate
31. Sequestrene Sodium 2
32. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid, Disodium Salt
33. Disodium Edta Dihydrate
34. Perma Kleer Di Crystals
35. Edetic Acid Disodium Salt
36. Disodium Edetate Dihydrate
37. Disodium Dihydrogen Ethylenediaminetetraacetate
38. Disodium Ethylenediamine-n,n,n',n'-tetraacetate
39. Glycine, N,n'-1,2-ethanediylbis[n-(carboxymethyl)-, Disodium Salt
40. Edta-na2
41. Edta Disodium Salt (anhydrous)
42. Edetate Disodium Anhydrous
43. Perma Kleer 50 Crystals Disodium Salt
44. Disodium Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid
45. Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid, Disodium Salt
46. Disodium (ethylenedinitrilo)tetraacetate
47. Sodium Ethylenediaminetetraacetate
48. Cbc 50152966
49. Dr-16133
50. Ethylenediaminetetraacetate, Disodium Salt
51. Disodium Diacid Ethylenediaminetetraacetate
52. Mfcd00070672
53. Disodium (ethylenedinitrilo)tetraacetic Acid
54. Trilon B
55. Disodium Dihydrogen(ethylenedinitrilo)tetraacetate
56. Glycine, N,n'-1,2-ethanediylbis(n-(carboxymethyl)-, Disodium Salt
57. Endrate (tn)
58. Chelest B
59. Komplexon Iii
60. Clewat N
61. Disodium Edathamil
62. Zonon D
63. Dotite 2na
64. Selekton B 2
65. Tetracemate Disodium
66. Mavacid Ed 4
67. Na2-edta
68. Disodium Edetate Hydrate
69. Versonol 120
70. Chelest 200
71. Anhydrous Disodium Edetate
72. Veresene Disodium Salt
73. Edetate Disodium, Anhydrous
74. 8nlq36f6mm
75. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Disodium Salt Solution
76. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Disodium Salt, 0.050m Standardized Solution
77. Disodium 2-({2-[(carboxylatomethyl)(carboxymethyl)amino]ethyl}(carboxymethyl)amino)acetate
78. Chebi:64734
79. Acetic Acid, (ethylenedinitrilo)tetra-, Disodium Salt
80. Nsc-2760
81. Ccris 3658
82. E.d.t.a. Disodique [french]
83. F 1 (van)
84. E.d.t.a. Disodique
85. Nsc-759604
86. Nsc 2760
87. Einecs 205-358-3
88. Unii-8nlq36f6mm
89. Ethylenediamine Tetraacetic Acid Disodium Salt
90. Dinatrium Ethylendiamintetraacetat [czech]
91. Ai3-18049
92. Ethylenebis(iminodiacetic Acid) Disodium Salt
93. Dinatrium Ethylendiamintetraacetat
94. Hsdb 8013
95. Disodium 2-((2-((carboxylatomethyl)(carboxymethyl)amino)ethyl)(carboxymethyl)amino)acetate
96. (ethylenedinitrilo)-tetraacetic Acid Disodium Salt
97. Na2edta
98. 0.5m Sodium Edta
99. Disodium Edetate (tn)
100. Na2.edta
101. N,n'-1,2-ethanediylbis(n-(carboxymethyl)glycine) Disodium Salt
102. Ec 205-358-3
103. Edta Disodium Salt Anhydrous
104. Chembl1749
105. Dtxsid9027073
106. Disodium N,n'-1,2-ethanediylbis(n-(carboxymethyl)glycine)
107. Disodium Ethylenediamine-tetraacetate
108. Db14600
109. Sb40706
110. E386
111. Ethylenediaminetetracetic Acid Disodium Salt
112. Db-042467
113. Ethylenediaminetetra-acetic Acid Disodium Salt
114. D03945
115. P17519
116. J-007267
117. J-521348
118. Q4532977
119. Glycine, N,n'-1,2-ethanediylbis(n-(carboxymethyl)-, Sodium Salt (1:2)
120. (ethylenedinitrilo)tetraacetic Acid Disodium Salt, Edta Disodium Salt, Edta-na2
121. Disodium;2-[2-[carboxylatomethyl(carboxymethyl)amino]ethyl-(carboxymethyl)amino]acetate
122. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Disodium Salt, 0.100n (0.050m) Standardized Solution
123. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Disodium Salt, 0.115n (0.0575m) Standardized Solution
124. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Disodium Salt, 0.200n (0.1m) Standardized Solution
125. Disodium 2-({2-[(carboxylatomethyl)(carboxymethyl)amino]ethyl(carboxymethyl)amino)acetate
| Molecular Weight | 336.21 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H14N2Na2O8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Exact Mass | 336.05455397 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 336.05455397 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 161 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 336 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 3 |
Anticoagulants; Chelating Agents; Food Additives
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 2009)
Endrate (Edetate Disodium Injection, USP) is indicated in selected patients for the emergency treatment of hypercalcemia and for the control of ventricular arrhythmias associated with digitalis toxicity. /Included in US product label/
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Endrate (edetate disodium, anhydrous) injection, solution (May 2006). Available from, as of February 16, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=290c3e9c-c0c6-440a-1a9c-46e3e2b07a77
Disodium edentate is also used therapeutically as an anticoagulant as it will chelate calcium and prevent the coagulation of blood in vitro. Concentrations of 0.1% w/v are used in small volumes for hematological testing and 0.3% w/v in transfusions.
Rowe, R.C., Sheskey, P.J., Quinn, M.E.; (Eds.), Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients 6th edition Pharmaceutical Press, London, England 2009, p. 243
Disodium EDTA is used occasionally to terminate the effects of injected calcium, to antagonize digitalis toxicity, or to suppress tachyarrhythmias. /Former/
Cosmetic Ingredient Expert Review Panel; Final Final Report on the Safety Assessment of EDTA, Calcium, Disodium EDTA, Diammonium EDTA, Dipotassium EDTA, Disodium EDTA, TEA-EDTA, Tetrasodium EDTA, Tripotassium EDTA, Trisodium EDTA, HEDTA, and Trisodium HEDTA. International Journal of Toxicology 21 (S2): 95-142 (2002)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Disodium EDTA (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
/BOXED WARNING/ The use of this drug in any particular patient is recommended only when the severity of the clinical condition justifies the aggressive measures associated with this type of therapy.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Endrate (edetate disodium, anhydrous) injection, solution (May 2006). Available from, as of February 16, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=290c3e9c-c0c6-440a-1a9c-46e3e2b07a77
Clinical studies of edetate disodium did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Endrate (edetate disodium, anhydrous) injection, solution (May 2006). Available from, as of February 16, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=290c3e9c-c0c6-440a-1a9c-46e3e2b07a77
Fatal medication errors have occurred that involve confusion between edetate calcium disodium (calcium EDTA) and edetate disodium (no longer commercially available in the US). Children and adults have mistakenly received edetate disodium instead of edetate calcium disodium; at least 5 deaths have occurred as a result of inadvertent administration of edetate disodium. Although both edetate calcium disodium and edetate disodium are heavy metal antagonists, the 2 drugs were originally approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for different uses and have different effects; edetate disodium was formerly FDA approved for use in selected patients for the emergency treatment of hypercalcemia or for the control of ventricular arrhythmias associated with cardiac glycoside toxicity. Use of edetate disodium may result in a substantial, and sometimes fatal, decrease in serum calcium concentrations. In June 2008, FDA withdrew its prior approval for edetate disodium because of safety concerns following a review of the risk-benefit profile of the drug. FDA stated that it was not considering additional action regarding edetate calcium disodium at that time; most of the fatalities following administration of an EDTA drug have involved medication errors in which edetate disodium was administered instead of edetate calcium disodium. FDA has not received reports of any fatalities resulting from the administration of edetate calcium disodium that involve a medication error.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2011; Drug Information 2011. Bethesda, MD. 2011
Edetate Disodium Injection is contraindicated in anuric patients. It is not indicated for the treatment of generalized arteriosclerosis associated with advancing age.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Endrate (edetate disodium, anhydrous) injection, solution (May 2006). Available from, as of February 16, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=290c3e9c-c0c6-440a-1a9c-46e3e2b07a77
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Disodium EDTA (22 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Edetate disodium is indicated for emergency treatment of hypercalcemia and digitalis toxicity associated ventricular arrhythmias.
Edetate disodium anhydrous is a polyvalent ion chelator that reduces blood concentrations of calcium or digitalis. It has a long duration of action as patients are generally given 1 daily dose. The therapeutic index is wide, as high doses are generally well tolerated. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of postural hypotension, effects of myocardial contractility, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, and hypoglycemia.
Anticoagulants
Agents that prevent BLOOD CLOTTING. (See all compounds classified as Anticoagulants.)
Calcium Chelating Agents
Substances that bind to and sequester CALCIUM ions. (See all compounds classified as Calcium Chelating Agents.)
Food Additives
Substances used in the processing or storage of foods or animal feed including ANTIOXIDANTS; FOOD PRESERVATIVES; FOOD COLORING AGENTS; FLAVORING AGENTS; ANTI-INFECTIVE AGENTS; EXCIPIENTS and other similarly used substances. Many of the same substances are used as PHARMACEUTIC AIDS. (See all compounds classified as Food Additives.)
Route of Elimination
After intravenous administration, 95% of the dose is recovered in the urine after 24 hours. Oral administration in rats leads to 5.3% recovery in urine and 88.5% recovery in feces.
Volume of Distribution
Data regarding the volume of distribution of edetate disodium anhydrous is not readily available.
Clearance
The mean clearance of edetate in 1 month olds is 54.6mL/min/1.73m2. 2-17 year olds have a mean clearance of 113.9 24.4 mL/min/1.73m2.
After intravenous administration, the chelate formed is excreted in the urine with 50% appearing in 1 hour and over 95% in 24 hours.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Endrate (edetate disodium, anhydrous) injection, solution (May 2006). Available from, as of February 16, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=290c3e9c-c0c6-440a-1a9c-46e3e2b07a77
Disodium edentate ... /is/ poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and /is/ associated with few adverse effects when used as an excipient in pharmaceutical preparations.
Rowe, R.C., Sheskey, P.J., Quinn, M.E.; (Eds.), Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients 6th edition Pharmaceutical Press, London, England 2009, p. 243
Twenty male Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into four groups of five animals each. Rats in group 1 received ip injections of (14)C Disodium EDTA, group 2 received this compound on depilated skin, rats in group 3 received this compound on depilated and abraded skin (abraded every 2 or 3 cm over treated area), and group 4 was the control group. The specific activity of the (14)C Disodium EDTA was 21.6 mCi/mM and it was dissolved in saline to yield a final solution of 50 pCi/mL. Animals that received ip injections got 0.5 mL of this solution, or 25 pCi of (14)C Disodium EDTA. Animals that had the compound applied to the skin received 25 pCi of (14)C Disodium EDTA in the form of an ointment (modulan, mineral oil, petrolatum, cetyl alcohol 35:21 :25:12) spread over an area of 50 sq cm spread over a sheet of thin polyethylene. This sheet was taped to the trunk of each animal. A collar was fixed around the neck of the rats. All animals were decapitated 24 hours after treatment. The tissue distribution (per 100 mg wet organ weight) of (14)C Disodium EDTA 24 hours after ip administration was as follows: liver 577+/- 13, small intestine 631 +/- 25, large intestine 696 +/- 19, and kidney 1964 +/- 220. Twenty-four hours after application on normal skin the tissue distribution was as follows: liver 6 +/- 4, small intestine 99 +/- 22, large intestine 107 +/- 24, and kidneys 29 +/- 12. Twenty-four hours after application on abraded skin the tissue distribution was as follows: liver 139 +/- 34, small intestine 214 +/- 76, large intestine 309 +/- 115, and kidneys 222 +/- 30.
Cosmetic Ingredient Expert Review Panel; Final Final Report on the Safety Assessment of EDTA, Calcium, Disodium EDTA, Diammonium EDTA, Dipotassium EDTA, Disodium EDTA, TEA-EDTA, Tetrasodium EDTA, Tripotassium EDTA, Trisodium EDTA, HEDTA, and Trisodium HEDTA. International Journal of Toxicology 21 (S2): 95-142 (2002)
/Investigators/ reported that rats fed 0.5%, 1.0%, and 5.0% Disodium EDTA for 12 weeks excreted 82.2%, 44.5%, and 45.4%, respectively, of the ingested dose in the urine and feces. The feces contained 99.4%, 98.2%, and 97.5% of the excreted material and the urine contained 0.6%, 1.8%, and 2.5% of the material for the respective doses.
Cosmetic Ingredient Expert Review Panel; Final Final Report on the Safety Assessment of EDTA, Calcium, Disodium EDTA, Diammonium EDTA, Dipotassium EDTA, Disodium EDTA, TEA-EDTA, Tetrasodium EDTA, Tripotassium EDTA, Trisodium EDTA, HEDTA, and Trisodium HEDTA. International Journal of Toxicology 21 (S2): 95-142 (2002)
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Disodium EDTA (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Edetate is almost completely unmetabolized _in vivo_.
After intravenous administration, the chelate formed is excreted in the urine with 50% appearing in 1 hour and over 95% in 24 hours.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Endrate (edetate disodium, anhydrous) injection, solution (May 2006). Available from, as of February 16, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=290c3e9c-c0c6-440a-1a9c-46e3e2b07a77
Edetate disodium anhydrous chelates divalent and trivalent ions such as magnesium, zinc, and calcium. The chelate is excreted in the urine, reducing concentrations of these ions in the blood.
Edetate disodium injection forms chelates with the cations of calcium and many divalent and trivalent metals. Because of its affinity for calcium, edetate disodium will produce a lowering of the serum calcium level during intravenous infusion. Slow infusion over a protracted period may cause mobilization of extracirculatory calcium stores. Edetate disodium exerts a negative inotropic effect upon the heart.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Endrate (edetate disodium, anhydrous) injection, solution (May 2006).
Edetate disodium likewise forms chelates with other polyvalent metals and produces increases in urinary excretion of magnesium, zinc and other trace elements. It does not form a chelate with potassium but may reduce the serum level and increase urinary loss of potassium.
US Natl Inst Health; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Endrate (edetate disodium, anhydrous) injection, solution (May 2006). Available from, as of February 16, 2012: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/lookup.cfm?setid=290c3e9c-c0c6-440a-1a9c-46e3e2b07a77
 Laboratorium Ofichem, offering a flexible, high-tech environment to produce broad range of APIs for Human & Vet pharmaceutical markets.
Laboratorium Ofichem, offering a flexible, high-tech environment to produce broad range of APIs for Human & Vet pharmaceutical markets.
 Click Us!
Click Us! 
GDUFA
DMF Review : Reviewed
Rev. Date : 2022-08-30
Pay. Date : 2022-08-03
DMF Number : 36993
Submission : 2022-07-13
Status : Active
Type : II

NDC Package Code : 62675-2751
Start Marketing Date : 2023-04-24
End Marketing Date : 2026-12-31
Dosage Form (Strength) : POWDER (1kg/kg)
Marketing Category : BULK INGREDIENT
 Laboratorium Ofichem, offering a flexible, high-tech environment to produce broad range of APIs for Human & Vet pharmaceutical markets.
Laboratorium Ofichem, offering a flexible, high-tech environment to produce broad range of APIs for Human & Vet pharmaceutical markets.

NDC Package Code : 62675-2350
Start Marketing Date : 2021-10-11
End Marketing Date : 2026-12-31
Dosage Form (Strength) : POWDER (1kg/kg)
Marketing Category : BULK INGREDIENT

GDUFA
DMF Review : Reviewed
Rev. Date : 2020-11-24
Pay. Date : 2020-10-22
DMF Number : 35275
Submission : 2020-10-01
Status : Active
Type : II

NDC Package Code : 68022-7059
Start Marketing Date : 2018-12-26
End Marketing Date : 2025-12-31
Dosage Form (Strength) : POWDER (1kg/kg)
Marketing Category : BULK INGREDIENT FOR HUMAN PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING

GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 10759
Submission : 1994-03-03
Status : Inactive
Type : II

GDUFA
DMF Review : N/A
Rev. Date :
Pay. Date :
DMF Number : 10760
Submission : 1994-03-03
Status : Inactive
Type : II






 FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Global Sales Information

Dosage Form :
Dosage Strength : 5 Vials 0.5 G 5 Ml
Price Per Pack (Euro) : 11.65
Published in :
Country : Italy
RX/OTC/DISCN : Class C

Dosage Form :
Dosage Strength : 5 Ampoules 2 G 10 Ml
Price Per Pack (Euro) : 13.9
Published in :
Country : Italy
RX/OTC/DISCN : Class C

MONICO SpA
Dosage Form :
Dosage Strength : 5 Ampoules 1 G 10 Ml
Price Per Pack (Euro) : 8.67
Published in :
Country : Italy
RX/OTC/DISCN : Class C

Portfolio PDF
Product Web Link
Virtual Booth
Digital Content
Website
Corporate PDF
MONICO SpA
Dosage Form :
Dosage Strength : 5 Vials 0.5 G 5 Ml
Price Per Pack (Euro) : 10.05
Published in :
Country : Italy
RX/OTC/DISCN : Class C

Portfolio PDF
Product Web Link
Virtual Booth
Digital Content
Website
Corporate PDF
MONICO SpA
Dosage Form :
Dosage Strength : 5 Ampoules 2 G 10 Ml
Price Per Pack (Euro) : 11.73
Published in :
Country : Italy
RX/OTC/DISCN : Class C

Portfolio PDF
Product Web Link
Virtual Booth
Digital Content
Website
Corporate PDF
SALF SpA
Dosage Form :
Dosage Strength : 5 Ampoules 1 G 10 Ml
Price Per Pack (Euro) : 8.67
Published in :
Country : Italy
RX/OTC/DISCN : Class C

Portfolio PDF
Product Web Link
Virtual Booth
Digital Content
Website
Corporate PDF
SALF SpA
Dosage Form :
Dosage Strength : 5 Vials 0.5 G 5 Ml
Price Per Pack (Euro) : 10.05
Published in :
Country : Italy
RX/OTC/DISCN : Class C

Portfolio PDF
Product Web Link
Virtual Booth
Digital Content
Website
Corporate PDF
SALF SpA
Dosage Form :
Dosage Strength : 5 Ampoules 2 G 10 Ml
Price Per Pack (Euro) : 11.73
Published in :
Country : Italy
RX/OTC/DISCN : Class C

Portfolio PDF
Product Web Link
Virtual Booth
Digital Content
Website
Corporate PDF
 FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]
FULL SCREEN VIEW Click here to open all results in a new tab [this preview display 10 results]Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ANALYTICAL

ABOUT THIS PAGE
18
PharmaCompass offers a list of Edetate Calcium Disodium API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Edetate Calcium Disodium manufacturer or Edetate Calcium Disodium supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Edetate Calcium Disodium manufacturer or Edetate Calcium Disodium supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Edetate Calcium Disodium API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Edetate Calcium Disodium API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Edetate Calcium Disodium Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Edetate Calcium Disodium Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Edetate, Calcium Disodium manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Edetate, Calcium Disodium, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Edetate, Calcium Disodium manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Edetate, Calcium Disodium API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Edetate, Calcium Disodium manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Edetate, Calcium Disodium supplier is an individual or a company that provides Edetate, Calcium Disodium active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Edetate, Calcium Disodium finished formulations upon request. The Edetate, Calcium Disodium suppliers may include Edetate, Calcium Disodium API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Edetate, Calcium Disodium suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Edetate, Calcium Disodium DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Edetate, Calcium Disodium active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Edetate, Calcium Disodium DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Edetate, Calcium Disodium USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Edetate, Calcium Disodium DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Edetate, Calcium Disodium USDMF includes data on Edetate, Calcium Disodium's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Edetate, Calcium Disodium USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Edetate, Calcium Disodium suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Edetate, Calcium Disodium as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Edetate, Calcium Disodium API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Edetate, Calcium Disodium as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Edetate, Calcium Disodium and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Edetate, Calcium Disodium NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Edetate, Calcium Disodium suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Edetate, Calcium Disodium Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Edetate, Calcium Disodium GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Edetate, Calcium Disodium GMP manufacturer or Edetate, Calcium Disodium GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Edetate, Calcium Disodium CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Edetate, Calcium Disodium's compliance with Edetate, Calcium Disodium specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Edetate, Calcium Disodium CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Edetate, Calcium Disodium CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Edetate, Calcium Disodium may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Edetate, Calcium Disodium EP), Edetate, Calcium Disodium JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Edetate, Calcium Disodium USP).
