
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
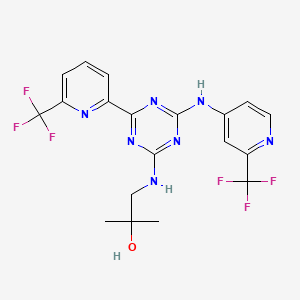

1. Ag-221
2. Idhifa
1. 1446502-11-9
2. Ag-221
3. Ag-221 (enasidenib)
4. Enasidenib [inn]
5. Cc-90007 Free Base
6. Idhifa
7. Ag 221
8. 2-methyl-1-(4-(6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl)-6-(2-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-4-ylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-ylamino)propan-2-ol
9. 3t1ss4e7ag
10. 2-methyl-1-((4-(6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl)-6-((2-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-4-yl)amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)amino)propan-2-ol
11. 2-methyl-1-[(4-[6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl]-6-{[2-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-4-yl]amino}-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)amino]propan-2-ol
12. 2-methyl-1-[[4-[6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl]-6-[[2-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-4-yl]amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl]amino]propan-2-ol
13. 2-propanol, 2-methyl-1-((4-(6-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinyl)-6-((2-(trifluoromethyl)-4-pyridinyl)amino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)amino)-
14. 2-propanol, 2-methyl-1-[[4-[6-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinyl]-6-[[2-(trifluoromethyl)-4-pyridinyl]amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl]amino]-
15. Unii-3t1ss4e7ag
16. Enasidenibum
17. Ag221
18. 2-methyl-1-({4-[6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl]-6-{[2-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-4-yl]amino}-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl}amino)propan-2-ol
19. Ag-221(enasidenib)
20. Ag-221; Enasidenib
21. Enasidenib; Ag-221
22. Enasidenib [mi]
23. Enasidenib (usan/inn)
24. Enasidenib [usan:inn]
25. Enasidenib [usan]
26. Enasidenib [who-dd]
27. Gtpl8960
28. Ag 221 [who-dd]
29. Chembl3989908
30. Schembl15102202
31. Ex-a654
32. Chebi:145374
33. Dtxsid801027942
34. Hms3873d03
35. Amy38698
36. Bcp16041
37. Bdbm50503251
38. Mfcd29472245
39. Nsc788120
40. S8205
41. Akos026750439
42. Zinc222731806
43. Ccg-269476
44. Cs-5017
45. Db13874
46. Nsc-788120
47. Sb19193
48. Ncgc00479249-03
49. Ncgc00479249-05
50. Ac-31318
51. As-75164
52. Hy-18690
53. Ft-0700204
54. D10901
55. A857662
56. J-690181
57. Q27077182
58. B0084-470859
59. Ag-221; Ag 221; Ag221; Cc-90007; Cc 90007; Cc90007
60. 1802003-09-3
61. 69q
| Molecular Weight | 473.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H17F6N7O |
| XLogP3 | 3.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 14 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 473.13987716 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 473.13987716 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 109 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 33 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 635 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 1 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | IDHIFA |
| Active Ingredient | ENASIDENIB MESYLATE |
| Company | CELGENE CORP (Application Number: N209606. Patents: 9512107, 9732062, 9738625) |
Indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with an isocitrate dehydrogenase-2 (IDH2) mutation.
FDA Label
Treatment of acute myeloid leukaemia
In a study involving adult patients with relapsed or refractory AML, overall response rate of 40.3% was achieved in enasidenib therapy which was associated with cellular differentiation and maturation, typically without evidence of aplasia. Enasidenib is not shown to cause QTc prolongation.
L - Antineoplastic and immunomodulating agents
L01 - Antineoplastic agents
L01X - Other antineoplastic agents
L01XX - Other antineoplastic agents
L01XX59 - Enasidenib
Absorption
Following a single oral dose of 100mg enasidenib, the peak plasma concentration of 1.3 mcg/mL is reached at 4 hours after ingestion. The absolute bioavailability is aproximately 57% and the steady-state plasma levels are reached within 29 days of once-daily dosing.
Route of Elimination
Elimination of enasidenib involves 89% of fecal excretion and 11% of renal excretion. Unchanged drug accounts for 34% and 0.4% of the total drug detected in the feces and urine, respectively.
Volume of Distribution
The mean volume of distribution is 55.8L.
Clearance
Enasidenib displays a mean total body clearance (CL/F) of 0.74 L/hour.
Enasidenib undergoes N-dealkylation mediated by multiple CYP (CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4) and UGT (UGT1A1, UGT1A3, UGT1A4, UGT1A9, UGT2B7, and UGT2B15) enzymes to form AGI-16903, as suggested by in vitro studies. AGI-16903 can be further metabolized by CYP1A2, CYP2C19, CYP3A4, UGT1A1, UGT1A3, and UGT1A9. The parent drug accounts for 89% of total detectable drug in the circulation, while AGI-16903 represents 10% of circulating total drug.
Enasidenib has a terminal half-life of 137 hours.
Enasidenib is a selective inhibitor of IDH2, a mitochondria-localized enzyme involved in diverse cellular processes, including adaptation to hypoxia, histone demethylation and DNA modification. Wild-type IDH proteins play a cruicial role in the Krebs/citric acid cycle where it catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to -ketoglutarate. In comparison, mutant forms of IDH2 enzyme mediates a neomorphic activity and catalyze reduction of -KG to the (R) enantiomer of 2-hydroxyglutarate, which is associated with DNA and histone hypermethylation, altered gene expression and blocked cellular differentiation of hematopoietic progenitor cells. Enasidenib primarily targets the mutant IDH2 variants R140Q, R172S, and R172K with higher potency than the wild type enzyme form. Inhibition of the enzyme leads to decreased levels of 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG) and promotion of proper differentiation and clonal proliferation of cells of the myeloid lineage.
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
ABOUT THIS PAGE
59
PharmaCompass offers a list of Enasidenib API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Enasidenib manufacturer or Enasidenib supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Enasidenib manufacturer or Enasidenib supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Enasidenib API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Enasidenib API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Enasidenib Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Enasidenib Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Enasidenib mesylate manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Enasidenib mesylate, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Enasidenib mesylate manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Enasidenib mesylate API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Enasidenib mesylate manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Enasidenib mesylate supplier is an individual or a company that provides Enasidenib mesylate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Enasidenib mesylate finished formulations upon request. The Enasidenib mesylate suppliers may include Enasidenib mesylate API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Enasidenib mesylate suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
Enasidenib mesylate Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Enasidenib mesylate GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Enasidenib mesylate GMP manufacturer or Enasidenib mesylate GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Enasidenib mesylate CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Enasidenib mesylate's compliance with Enasidenib mesylate specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Enasidenib mesylate CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Enasidenib mesylate CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Enasidenib mesylate may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Enasidenib mesylate EP), Enasidenib mesylate JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Enasidenib mesylate USP).
