
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
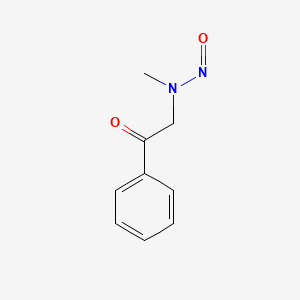

1. Endostatins
1. N-methyl-n-phenacylnitrous Amide
2. 55984-52-6
3. 187888-07-9
4. Ethanone, 2-(methylnitrosoamino)-1-phenyl-
5. 2-oxo-2-phenylethylmethylnitrosamine
6. Dtxsid10204557
7. Zinc5965474
| Molecular Weight | 178.19 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H10N2O2 |
| XLogP3 | 1.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 178.074227566 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 178.074227566 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 49.7 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 13 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 188 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Investigated for use/treatment in cancer/tumors (unspecified), macular degeneration, and diabetic retinopathy.
Angiogenesis Inhibitors
Agents and endogenous substances that antagonize or inhibit the development of new blood vessels. (See all compounds classified as Angiogenesis Inhibitors.)
Antineoplastic Agents
Substances that inhibit or prevent the proliferation of NEOPLASMS. (See all compounds classified as Antineoplastic Agents.)
Endostatin is an endogenous antitumor protein. Endostatin is a 20-kDa C-terminal fragment derived from type XVIII collagen which inhibits cell proliferation and migration, and induces endothelial cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. It is proposed that endostatin's effects are due to inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) tyrosine phosphorylation of KDR/F1k-1 (VEGF receptor 2), the cell surface receptor for VEGF. VEGF is an important mediator of angiogensis. Endostatin additionally blocks activation of extracellular signal related kinases, or ERK, protein 38 mitogen activated protein kinase, or p38 MAPK (signal transduction pathways involving kinases that couple growth factors to cell surface receptors), as well as focal adhesion kinase (p125FAK). Studies are being done to determine if endostatin has possible impact on other pathways, and may also target E-selectin and block activity of metalloproteinases 2, 9 and 13. There is further research into a possible mechanistic link involving endostatin's angiogenic and zinc binding ability.
ABOUT THIS PAGE
90
PharmaCompass offers a list of Endostatin API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Endostatin manufacturer or Endostatin supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Endostatin manufacturer or Endostatin supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Endostatin API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Endostatin API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Endostatin Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Endostatin Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Endostatin manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Endostatin, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Endostatin manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Endostatin API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Endostatin supplier is an individual or a company that provides Endostatin active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Endostatin finished formulations upon request. The Endostatin suppliers may include Endostatin API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
Endostatin Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Endostatin GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Endostatin GMP manufacturer or Endostatin GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Endostatin CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Endostatin's compliance with Endostatin specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Endostatin CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Endostatin CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Endostatin may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Endostatin EP), Endostatin JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Endostatin USP).
