
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
VMF
0
Australia

0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
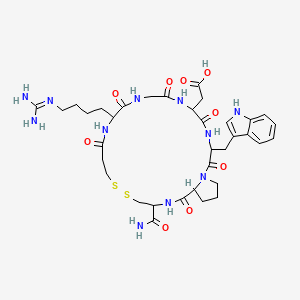

1. Eptifibatide Acetate
2. 148031-34-9
3. 188627-80-7
4. 2-[20-carbamoyl-12-[4-(diaminomethylideneamino)butyl]-3-(1h-indol-3-ylmethyl)-2,5,8,11,14,22-hexaoxo-17,18-dithia-1,4,7,10,13,21-hexazabicyclo[21.3.0]hexacosan-6-yl]acetic Acid
5. Eptifibatide (inn)
6. L-cysteinamide,n6-(aminoiminomethyl)-n2-(3-mercapto-1-oxopropyl)-l-lysylglycyl-l-a-aspartyl-l-tryptophyl-l-prolyl-, Cyclic (16)-disulfide
7. Eptifitide
8. Integrilin (tn)
9. Schembl1649793
10. Schembl8284422
11. Chembl4303580
12. Dtxsid60861477
13. Hms3743e11
14. Amy25372
15. Bcp02070
16. Db-044679
17. Ft-0602106
18. Ft-0652986
19. D06888
20. Sr-01000942234
21. Sr-01000942234-1
22. 148031-34-9;eptifibatide Acetate; Integrilin; Integrelin
23. {11-(4-carbamimidamidobutyl)-3-carbamoyl-20-[(1h-indol-3-yl)methyl]-1,9,12,15,18,21-hexaoxodocosahydro-7h-pyrrolo[2,1-g][1,2,5,8,11,14,17,20]dithiahexaazacyclotricosin-17-yl}acetic Acid
24. L-cysteinamide,n6-(aminoiminomethyl)-n2-(3-mercapto-1-oxopropyl)-l-lysylglycyl-l-a-aspartyl-l-tryptophyl-l-prolyl-, Cyclic (1?6)-disulfide
| Molecular Weight | 832.0 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C35H49N11O9S2 |
| XLogP3 | -2.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 10 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 12 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Exact Mass | 831.31561453 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 831.31561453 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 377 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 57 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 1520 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 5 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Integrilin |
| PubMed Health | Eptifibatide (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Platelet Aggregation Inhibitor |
| Drug Label | Eptifibatide is a cyclic heptapeptide containing 6 amino acids and 1 mercaptopropionyl (des-amino cysteinyl) residue. An interchain disulfide bridge is formed between the cysteine amide and the mercaptopropionyl moieties. Chemically it is N6-(aminoim... |
| Active Ingredient | Eptifibatide |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 2mg/ml; 75mg/100ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Schering |
| 2 of 2 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | Integrilin |
| PubMed Health | Eptifibatide (Injection) |
| Drug Classes | Platelet Aggregation Inhibitor |
| Drug Label | Eptifibatide is a cyclic heptapeptide containing 6 amino acids and 1 mercaptopropionyl (des-amino cysteinyl) residue. An interchain disulfide bridge is formed between the cysteine amide and the mercaptopropionyl moieties. Chemically it is N6-(aminoim... |
| Active Ingredient | Eptifibatide |
| Dosage Form | Injectable |
| Route | Injection |
| Strength | 2mg/ml; 75mg/100ml |
| Market Status | Prescription |
| Company | Schering |
Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings. Eptifibatide. Online file (MeSH, 2016). Available from, as of January 20, 2016: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/2016/mesh_browser/MBrowser.html
/CLINICAL TRIALS/ ClinicalTrials.gov is a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world. The Web site is maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Each ClinicalTrials.gov record presents summary information about a study protocol and includes the following: Disease or condition; Intervention (for example, the medical product, behavior, or procedure being studied); Title, description, and design of the study; Requirements for participation (eligibility criteria); Locations where the study is being conducted; Contact information for the study locations; and Links to relevant information on other health Web sites, such as NLM's MedlinePlus for patient health information and PubMed for citations and abstracts for scholarly articles in the field of medicine. Eptifibatide is included in the database.
NIH/NLM; ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available from, as of March 17, 2016: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=Eptifibatide&Search=Search
Integrilin is indicated to decrease the rate of a combined endpoint of death or new myocardial infarction (MI) in patients with ACS (unstable angina (UA)/non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI)), including patients who are to be managed medically and those undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Integrilin (Eptifibatide) Injection, Solution (Updated: January 2015). Available from, as of January 20, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=5423624f-a2d8-4273-8c62-51839fccfd7e
Integrilin is indicated to decrease the rate of a combined endpoint of death, new myocardial infarction (MI), or need for urgent intervention in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), including those undergoing intracoronary stenting. /Included in US product label/
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Integrilin (Eptifibatide) Injection, Solution (Updated: January 2015). Available from, as of January 20, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=5423624f-a2d8-4273-8c62-51839fccfd7e
Eptifibatide has been administered concomitantly with a thrombolytic agent (e.g., alteplase, tenecteplase) in a limited number of patients to prevent coronary artery reocclusion after an acute myocardial infarction. /NOT included in US product label/
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 1537
The most frequent and severe adverse effect of eptifibatide therapy is bleeding. Bleeding complications, which usually are minor and develop at vascular access (e.g., femoral puncture) sites (e.g., in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)), have been reported in 35-75% of patients receiving various dosages of eptifibatide in clinical studies. Bleeding is an extension of the pharmacologic action of eptifibatide and was classified in clinical trials principally according to criteria of the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) study groups. Minor bleeding generally was defined as spontaneous gross hematuria or spontaneous hematemesis; observed blood loss with a decrease in hemoglobin concentration of 3-5 g/dL or a reduction in hematocrit of at least 10%; or a decrease of 4-5 g/dL or 12-15% in hemoglobin or hematocrit, respectively, with no identifiable bleeding site. Major bleeding was defined as intracranial hemorrhage or overt bleeding associated with a hemoglobin or hematocrit decrease of at least 5 g/dL or at least 15%, respectively.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 1538
Because eptifibatide increases the risk of bleeding, the drug is contraindicated in patients with a history of bleeding diathesis or active abnormal bleeding (e.g., elevated hemostatic indices, recent noncompressible vascular punctures GI or genitourinary bleeding) within the previous 30 days. A low hematocrit value (less than 30%) at baseline could represent recent undetected bleeding, and patients with such values may not be able to tolerate additional bleeding episodes; eptifibatide should not be used in these patients. Eptifibatide also is contraindicated in patients with severe uncontrolled hypertension (systolic blood pressure exceeding 200 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure exceeding 110 mm Hg with antihypertensive therapy); recent (within 6 weeks) major surgery; history of stroke within 30 days or any history of hemorrhagic stroke; current or planned therapy with another GP IIb/IIIa-receptor inhibitor; and patients receiving renal dialysis. No data are available on the use of eptifibatide in patients with serum creatinine concentrations of 4 mg/dL or greater; the dosage should be reduced in patients with serum creatinine concentrations between 2-4 mg/dL.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 1539
FDA Pregnancy Risk Category: B /NO EVIDENCE OF RISK IN HUMANS. Adequate, well controlled studies in pregnant women have not shown increased risk of fetal abnormalities despite adverse findings in animals, or, in the absence of adequate human studies, animal studies show no fetal risk. The chance of fetal harm is remote but remains a possibility./
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Integrilin (Eptifibatide) Injection, Solution (Updated: January 2015). Available from, as of January 20, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=5423624f-a2d8-4273-8c62-51839fccfd7e
Safety and effectiveness of Integrilin in pediatric patients have not been studied.
NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Integrilin (Eptifibatide) Injection, Solution (Updated: January 2015). Available from, as of January 20, 2016: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=5423624f-a2d8-4273-8c62-51839fccfd7e
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Eptifibatide (15 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
/MILK/ It is not known whether eptifibatide is distributed into milk in humans.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 1541
Eptifibatide is approximately 25% bound to plasma proteins, principally (9-16%) to albumin.The volume of distribution of eptifibatide in patients with coronary artery disease is about 185-260 mL/kg and is somewhat higher (220-270 mL/kg) in healthy individuals.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 1541
Eptifibatide, a synthetic peptide inhibitor of the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor, has been studied as an antithrombotic agent in a variety of acute ischemic coronary syndromes. The purpose of the present study was to characterize the disposition of (14)C-eptifibatide in man after a single intravenous (i.v.) bolus dose. (14)C-Eptifibatide (approximately 50 uCi) was administered to eight healthy men as a single 135-ug/kg IV bolus. Blood, breath carbon dioxide, urine, and fecal samples were collected for up to 72 hours postdose and analyzed for radioactivity by liquid scintillation spectrometry. Plasma and urine samples were also assayed by liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry for eptifibatide and deamidated eptifibatide (DE). Mean (+/- SD) peak plasma eptifibatide concentrations of 879 +/- 251 ng/mL were achieved at the first sampling time (5 minutes), and concentrations then generally declined biexponentially, with a mean distribution half-life of 5 +/- 2.5 minutes and a mean terminal elimination half-life of 1.13 +/- 0.17 hours. Plasma eptifibatide concentrations and radioactivity declined in parallel, with most of the radioactivity (82.4%) attributed to eptifibatide. A total of approximately 73% of administered radioactivity was recovered in the 72-hour period following (14)C-eptifibatide dosing. The primary route of elimination was urinary (98% of the total recovered radioactivity), whereas fecal (1.5%) and breath (0.8%) excretion was small. Eptifibatide is cleared by both renal and nonrenal mechanisms, with renal clearance accounting for approximately 40% of total body clearance. Within the first 24 hours, the drug is primarily excreted in the urine as unmodified eptifibatide (34%), DE (19%), and more polar metabolites (13%).
PMID:9589822 Alton KB et al; Clin Ther 20 (2): 307-23 (1998)
Plasma clearance of eptifibatide is proportional to body weight and estimated creatinine clearance and inversely proportional to age. Following a single IV dose of (14)C-radiolabeled eptifibatide (135 ug/kg) in healthy men, renal clearance averaged approximately 40-50% of total body clearance. Clearance is reduced by 50% in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (estimated Clcr less than 50 mL/minute). Total body clearance in geriatric patients with coronary artery disease is lower than that in younger adults.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 1541
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Eptifibatide (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
(14)C-eptifibatide was extensively metabolized to deamidated eptifibatide and to several polar metabolites by both rats and monkeys. The drug-derived radioactivity excreted into the bile by rats, and identified as deamidated eptifibatide, was reabsorbed from the intestinal tract and further metabolized to more polar metabolites. The plasma and urine metabolite profiles in rats and monkeys indicate that the metabolic disposition of eptifibatide is similar for the two species.
Health Canada; Product Monograph for Integrilin (Eptifibatide Injection), Drug Identification Number (DIN): 02240351 p.25 (Date of Preparation: February 16, 2011).
Eptifibatide is metabolized principally through deamidation to a metabolite that has approximately 41% of the platelet-aggregation inhibitory activity of the parent compound, and through formation of other more polar metabolites. Approximately 27% of a dose of eptifibatide is broken down in plasma into naturally occurring amino acids; no major non-amino acid metabolites have been detected in plasma in humans.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 1541
In Cynomolgus monkeys, plasma concentrations of (14)C-eptifibatide-derived radioactivity declined with a half life of about 12 hours following a single 2 mg/kg IV dose of (14)C-eptifibatide. Unchanged eptifibatide, which accounted for approximately 93% of total plasma (14)C at 5 min post-dose, was eliminated rapidly with a half life of 17 min.
Health Canada; Product Monograph for Integrilin (Eptifibatide Injection), Drug Identification Number (DIN): 02240351 p.24 (Date of Preparation: February 16, 2011). Available from, as of March 8, 2016: https://webprod5.hc-sc.gc.ca/dpd-bdpp/start-debuter.do?lang=eng
In rats, plasma concentrations of (14)C-eptifibatide-derived radioactivity declined rapidly with a terminal phase half life of about 5 hours following a single 2 mg/kg IV dose of the radiolabeled drug. Unchanged eptifibatide declined with an apparent half life of about 8 min. Following single 2 and 20 mg/kg IV doses, the plasma concentrations of eptifibatide were dose-proportional and the half life (11 to 12 min) was dose-independent, indicating linear kinetics within the 2 to 20 mg/kg dose range.
Health Canada; Product Monograph for Integrilin (Eptifibatide Injection), Drug Identification Number (DIN): 02240351 p.24 (Date of Preparation: February 16, 2011). Available from, as of March 8, 2016: https://webprod5.hc-sc.gc.ca/dpd-bdpp/start-debuter.do?lang=eng
The half-life of eptifibatide in patients with coronary artery disease averages 2.5-2.8 hours. In healthy individuals, half-life of the drug reportedly averages 0.83-2.4 hours.
American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2015; Drug Information 2015. Bethesda, MD. 2015, p. 1541
... The purpose of the present study was to characterize the disposition of (14)C-eptifibatide in man after a single intravenous (IV) bolus dose. (14)C-Eptifibatide (approximately 50 uCi) was administered to eight healthy men as a single 135-ug/kg IV bolus. ... Mean (+/- SD) peak plasma eptifibatide concentrations of 879 +/- 251 ng/mL were achieved at the first sampling time (5 minutes), and concentrations then generally declined biexponentially, with a mean distribution half-life of 5 +/- 2.5 minutes and a mean terminal elimination half-life of 1.13 +/- 0.17 hours. ...
PMID:9589822 Alton KB et al; Clin Ther 20 (2): 307-23 (1998)
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS

Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
18
PharmaCompass offers a list of Eptifibatide API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Eptifibatide manufacturer or Eptifibatide supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Eptifibatide manufacturer or Eptifibatide supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Eptifibatide API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Eptifibatide API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Eptifibatide Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Eptifibatide Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Eptifibatide manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Eptifibatide, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Eptifibatide manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Eptifibatide API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Eptifibatide manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Eptifibatide supplier is an individual or a company that provides Eptifibatide active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Eptifibatide finished formulations upon request. The Eptifibatide suppliers may include Eptifibatide API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Eptifibatide suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Eptifibatide DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Eptifibatide active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Eptifibatide DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Eptifibatide USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Eptifibatide DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Eptifibatide USDMF includes data on Eptifibatide's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Eptifibatide USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Eptifibatide suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Eptifibatide as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Eptifibatide API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Eptifibatide as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Eptifibatide and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Eptifibatide NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Eptifibatide suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Eptifibatide Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Eptifibatide GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Eptifibatide GMP manufacturer or Eptifibatide GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Eptifibatide CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Eptifibatide's compliance with Eptifibatide specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Eptifibatide CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Eptifibatide CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Eptifibatide may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Eptifibatide EP), Eptifibatide JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Eptifibatide USP).
