
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
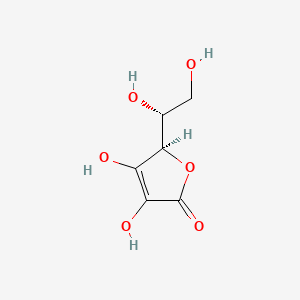

1. D-araboascorbic Acid
2. Erythroascorbic Acid
3. Isoascorbic Acid
4. Isoascorbic Acid, Disodium Salt
5. Isoascorbic Acid, Monosodium Salt
6. Isoascorbic Acid, Sodium Salt
7. Sodium Erythorbate
1. Isoascorbic Acid
2. D-isoascorbic Acid
3. 89-65-6
4. D-araboascorbic Acid
5. Araboascorbic Acid
6. D-erythorbic Acid
7. Isovitamin C
8. D-(-)-isoascorbic Acid
9. Saccharosonic Acid
10. Glucosaccharonic Acid
11. 2,3-didehydro-d-erythro-hexono-1,4-lactone
12. Fema No. 2410
13. Erycorbin
14. Neo-cebicure
15. D-erythro-hex-2-enonic Acid, .gamma.-lactone
16. (5r)-5-[(1r)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-3,4-dihydroxyfuran-2(5h)-one
17. (r)-5-((r)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl)-3,4-dihydroxyfuran-2(5h)-one
18. D-erythro-hex-2-enonic Acid Gamma-lactone
19. Chebi:51438
20. (2r)-2-[(1r)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-3,4-dihydroxy-2h-furan-5-one
21. D-ascorbic Acid, Iso
22. D-erythro-hex-2-enono-1,4-lactone
23. 311332oii1
24. D(-)-isoascorbic Acid (erythorbic Acid)
25. Mercate 5
26. Erythroascorbic Acid, D-
27. Mfcd00005378
28. Fema Number: 2410
29. Ccris 6568
30. Hsdb 584
31. Erythorbic Acid [nf]
32. Nsc 8117
33. D-erythro-3-oxohexonic Acid Lactone
34. Einecs 201-928-0
35. D-erythro-3-ketohexonic Acid Lactone
36. 3-oxohexonic Acid Lactone, D-erythro-
37. Brn 0084271
38. Nsc-8117
39. 3-keto-d-erythro-hexonic Acid Gamma-lactone
40. Hex-2-enonic Acid Gamma-lactone, D-erythro-
41. (5r)-5-((1r)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl)-3,4-dihydroxyfuran-2(5h)-one
42. Unii-311332oii1
43. D-iso-ascorbic Acid
44. Erythorbate
45. Isoascorbic-acid
46. 1f9g
47. E315
48. D-erythro-hex-2-enonic Acid, Gamma-lactone,
49. Dsstox_cid_6537
50. Ec 201-928-0
51. Dsstox_rid_78143
52. Dsstox_gsid_26537
53. Schembl18678
54. Erythorbic Acid [ii]
55. 5-18-05-00026 (beilstein Handbook Reference)
56. Erythorbic Acid [fcc]
57. Isoascorbic Acid [mi]
58. Erythorbic Acid [fhfi]
59. Erythorbic Acid [hsdb]
60. Erythorbic Acid [inci]
61. Chembl486293
62. Ins No.315
63. Schembl3700961
64. Dtxsid6026537
65. Erythorbic Acid [mart.]
66. Erythorbic Acid [usp-rs]
67. Ins-315
68. D-(-)-isoascorbic Acid, 98%
69. Hy-n7079
70. Tox21_201111
71. Ac8021
72. Akos015856346
73. D-erythro-hex-2-enoic Acid ?-lactone
74. Zinc100006772
75. Zinc100057602
76. Cas-89-65-6
77. D-erythro-hex-2-enonic Acid, G-lactone
78. Ncgc00258663-01
79. D-erythro-hex-2-enoic Acid Gamma-lactone
80. D-isoascorbic Acid, >=99%, Fcc, Fg
81. A0520
82. Cs-0014152
83. E-315
84. C20364
85. A843272
86. Q424531
87. D-isoascorbic Acid 1000 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
88. J-506944
89. 7179c406-7ccf-4c07-9125-aa71e28fb983
90. Erythorbic Acid, United States Pharmacopeia (usp) Reference Standard
91. (5r)-5-[(1r)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-3,4-dihydroxyfuran-2(5h)-one (d-isoascorbic Acid)
92. (5r)-5-[(1r)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-3,4-dihydroxyfuran-2(5h)-one (non-preferred Name)
| Molecular Weight | 176.12 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C6H8O6 |
| XLogP3 | -1.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Exact Mass | 176.03208797 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 176.03208797 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 107 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 12 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 232 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Erythorbic acid is a stereoisomer of l-ascorbic acid, and is used as an antioxidant in foods and oral pharmaceutical formulations. It has approximately 5% of the vitamin C activity of l-ascorbic acid.
Rowe, R.C., Sheskey, P.J., Quinn, M.E.; (Eds.), Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients 6th edition Pharmaceutical Press, London, England 2009, p. 250
Antioxidants
Naturally occurring or synthetic substances that inhibit or retard oxidation reactions. They counteract the damaging effects of oxidation in animal tissues. (See all compounds classified as Antioxidants.)
Erythorbic acid is readily absorbed and metabolized. Following an oral dose of 500 mg of erythorbic acid to human subjects the blood level curves for ascorbic acid and erythorbic acid showed a similar rise. In five human subjects, an oral dose of 300 mg was shown to have no effect on urinary excretion of ascorbic acid.
WHO; Food Additives Series 28 (1991). Available from, as of August 6, 2010: https://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/v28je03.htm
In hamster, rat and rabbit, for which ascorbate is not an essential vitamin, intestinal absorption of L-ascorbic acid is low and takes place by passive diffusion; conversely, in guinea pig and human, ascorbate absorption is mediated by a saturable, sodium- dependent, active transport mechanism. It follows that the former species are not suitable models for human absorption. Since the active transport system is saturable but since passive diffusion might also be significant at high dose levels, the absorption of ascorbic acid is dose dependent. Erythorbic acid appears to be another but much poorer substrate for the same transport system and may thus act as a weak competitive inhibitor of L-ascorbate uptake. In studies using isolated brush border vesicles from guinea pig ileum, the K1 has variously been estimated at about 11 mM and around 20 mM; this compares with an apparent Km for ascorbate uptake of about 0.3 mM in the same system.
WHO; Food Additives Series 28 (1991). Available from, as of August 6, 2010: https://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/v28je03.htm
The reason for lack of a stronger antiscorbutic action of erythorbic acid is probably the incapacity of the tissues to retain it in the quantities that ascorbic acid is stored.
Gilman, A. G., L. S. Goodman, and A. Gilman. (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 6th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc. 1980., p. 1577
The absorption of erythorbic acid through the human buccal mucosa was studied in healthy adult subjects. Absorption of a solution of 10 mM erythorbic acid, buffered to pH 6, was 13.0 +/- 0.74 umol/5 minutes. No statistical difference was found between the absorptions of Erythorbic Acid and L-ascorbic acid.
Cosmetic Ingredient Expert Review Panel; Final Report on the Safety Assessment of Ascorbyl Palmitate, Ascorbyl Dipalmitate, Ascorbyl Stearate, Erythorbic Acid, and Sodium Erythorbate; International Journal of Toxicology 18 ( Suppl 3): 1-26 (1999).
For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Erythorbic acid (13 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
In dogs, this resulted in a half-life of approximately 30 minutes for erythorbic acid in the plasma.
Cosmetic Ingredient Expert Review Panel; Final Report on the Safety Assessment of Ascorbyl Palmitate, Ascorbyl Dipalmitate, Ascorbyl Stearate, Erythorbic Acid, and Sodium Erythorbate; International Journal of Toxicology 18 ( Suppl 3): 1-26 (1999).
Market Place

REF. STANDARDS & IMPURITIES

ABOUT THIS PAGE
65
PharmaCompass offers a list of Erythorbic Acid API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Erythorbic Acid manufacturer or Erythorbic Acid supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Erythorbic Acid manufacturer or Erythorbic Acid supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Erythorbic Acid API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Erythorbic Acid API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Erythorbic Acid Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Erythorbic Acid Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Erythorbic Acid manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Erythorbic Acid, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Erythorbic Acid manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Erythorbic Acid API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Erythorbic Acid supplier is an individual or a company that provides Erythorbic Acid active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Erythorbic Acid finished formulations upon request. The Erythorbic Acid suppliers may include Erythorbic Acid API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
Erythorbic Acid Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Erythorbic Acid GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Erythorbic Acid GMP manufacturer or Erythorbic Acid GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Erythorbic Acid CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Erythorbic Acid's compliance with Erythorbic Acid specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Erythorbic Acid CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Erythorbic Acid CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Erythorbic Acid may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Erythorbic Acid EP), Erythorbic Acid JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Erythorbic Acid USP).
