
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
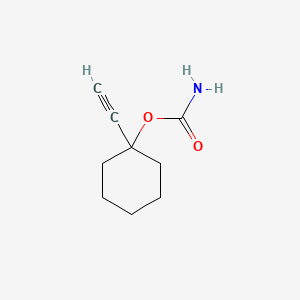

1. 1-ethynylcyclohexylcarbamate
2. Ethinamat
3. Valamid
4. Valamin
5. Valmidate
1. Valmid
2. Ethinamat
3. Etinamate
4. Valmidate
5. Valamin
6. Volamin
7. 1-ethynylcyclohexyl Carbamate
8. Valaminettae
9. Valaminetten
10. 1-ethynylcyclohexanol Carbamate
11. Usaf El-42
12. 126-52-3
13. 1-ethinylcyclohexyl Carbamate
14. Ethinamatum
15. Ethinimate
16. Etinamato
17. Cyclohexanol, 1-ethynyl-, Carbamate
18. Aethinyl-cyclohexyl-carbamat
19. Carbamic Acid, 1-ethynylcyclohexyl Ester
20. (1-ethynylcyclohexyl) Carbamate
21. Carbamate De L'ethinylcyclohexanol
22. Nsc 11538
23. Nsc-11538
24. Cyclohexanol, 1-ethynyl-, 1-carbamate
25. Chebi:4884
26. Ian371pp48
27. Valaminetta
28. Cyclohexanol, Carbamate
29. Ethinamatum [inn-latin]
30. Ethynylcyclohexyl Carbamate
31. Etinamato [inn-spanish]
32. 1-ethinylcyclohexyl Carbonate
33. Wln: L6tj Aovz A1uu1
34. Aethinyl-cyclohexyl-carbamat [german]
35. Valmid (tn)
36. Hsdb 3325
37. Carbamate De L'ethinylcyclohexanol [french]
38. Ethinamate (jan/inn)
39. Einecs 204-789-4
40. Brn 1946056
41. Unii-ian371pp48
42. Dea No. 2545
43. Ethinamate [usp:inn:ban:jan]
44. Ethinamate [mi]
45. Ethinamate [inn]
46. Ethinamate [jan]
47. Ethinamate [hsdb]
48. Ethinamate [vandf]
49. Ethinamate [mart.]
50. Chembl1576
51. Ethinamate [who-dd]
52. Schembl44635
53. Ethinamate, Analytical Standard
54. Gtpl7325
55. Zinc1385
56. Dtxsid7023013
57. Ethinamate [orange Book]
58. Nsc11538
59. Nsc30282
60. Nsc31618
61. Nsc-30282
62. Nsc-31618
63. Nsc524623
64. Cs-6642
65. Db01031
66. Nsc-524623
67. [(1-ethynylcyclohexyl)oxy]methanimidic Acid
68. Hy-101584
69. Ethynamate Ethynylcyclohexyl Carbamate
70. C07832
71. D00703
72. Q410225
| Molecular Weight | 167.20 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C9H13NO2 |
| XLogP3 | 1.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Exact Mass | 167.094628657 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 167.094628657 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 52.3 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 12 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 220 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Sedatives, Nonbarbiturate
National Library of Medicine's Medical Subject Headings online file (MeSH, 1999)
SHORT-ACTING MILD HYPNOTIC USEFUL FOR INDUCTION OF SLEEP IN SIMPLE INSOMNIA.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1005
CONSEQUENTLY, IT MAY BE USEFUL TO INSOMNIAC WHO HAS DIFFICULTY FALLING ASLEEP BUT NOT TO ONE WHO HAS LONG PERIODS OF WAKEFULNESS DURING NIGHT. ITS EFFECT ON REM SLEEP IS UNKNOWN.
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 126
The primary Medication Classification of the US Veterans Administration is CN309: Sedatives/Hypnotics, Other
United States Pharmacopeial Convention; USP Dispensing Information 12th ed Vol IA p.1362 (1992)
For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for ETHINAMATE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
LONG-TERM USE OF LARGER THAN RECOMMENDED DOSES MAY LEAD TO PSYCHIC & PHYSICAL DEPENDENCE. ABSTINENCE SYNDROME IS SIMILAR TO THAT FOR BARBITURATES ...
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 368
WITHDRAWAL SYMPTOMS, INCL CONVULSIONS, MAY OCCUR WHEN ETHINAMATE IS DISCONTINUED ABRUPTLY.
American Medical Association. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1991. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1991., p. 227
ETHINAMATE SHOULD NOT BE TAKEN CONCURRENTLY WITH ALC OR OTHER CNS DEPRESSANTS & PATIENT ON THIS DRUG SHOULD BE WARNED AGAINST OPERATING MOTOR VEHICLE OR OPERATING HAZARDOUS MACHINERY FOR @ LEAST 4 OR 5 HR AFTER TAKING DRUG.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1005
ALTHOUGH NO MATERNAL OR FETAL ADVERSE EFFECTS HAVE BEEN REPORTED, SUFFICIENT LAB WORK HAS NOT BEEN DONE IN THIS AREA TO WARRANT ITS USE IN PREGNANT & LACTATING WOMEN. ... ETHINAMATE HAS NOT BEEN STUDIED IN CHILDREN; HENCE, IT IS NOT RECOMMENDED FOR PEDIATRIC USE. ... USED WITH CAUTION IN PATIENTS WITH HISTORY OF DRUG ABUSE.
Osol, A. and J.E. Hoover, et al. (eds.). Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences. 15th ed. Easton, Pennsylvania: Mack Publishing Co., 1975., p. 1005
For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for ETHINAMATE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page.
Used for the short-term treatment of insomnia, however, it generally has been replaced by other sedative-hypnotic agents.
Ethinamate is used to treat insomnia (trouble in sleeping). However, it has generally been replaced by other medicines for the treatment of insomnia. If ethinamate is used regularly (for example, every day) to help produce sleep, it is usually not effective for more than 7 days. Structurally, it does not resemble the barbiturates, but it shares many effects with this class of drugs; the depressant effects of ethinamate are, however, generally milder than those of most barbiturates. Continued and inappropriate use of ethinamate can lead to tolerance and physical dependence, with withdrawal symptoms very similar to those of the barbiturates.
Absorption
Rapidly absorbed following oral administration.
ETHINAMATE IS INACTIVATED @ LEAST PARTLY BY LIVER, BY HYDROXYLATION OF CYCLOHEXYL RING; PRODUCT IS CONJUGATED & EXCRETED AS GLUCURONIDE.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 368
IT IS EXTENSIVELY METABOLIZED, BUT PRELIMINARY EXPERIENCE INDICATES APPRECIABLE QUANTITIES CAN BE REMOVED BY EXTRACORPOREAL HEMODIALYSIS. ... HIGH LIPID SOLUBILITY ... .
Gosselin, R.E., H.C. Hodge, R.P. Smith, and M.N. Gleason. Clinical Toxicology of Commercial Products. 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, 1976., p. II-224
ABSORPTION & CLEARANCE OF ETHINAMATE WAS STUDIED AFTER SINGLE ORAL DOSAGES IN THERAPEUTIC RANGE TO NONFASTING SUBJECTS. MEAN MAX PLASMA LEVEL WAS OBSERVED AFTER 1 HR (T/2 IN BLOOD 2.3 HR).
PMID:4604053 CLIFFORD JM ET AL; CLIN PHARMACOL THER 16 (2): 376 (1974)
Rapidly absorbed. ... Renal elimination. Approximately 36% of administered dose appears in urine within 24 hours.
United States Pharmacopeial Convention; USP Dispensing Information 12th ed Vol IA p.1362 (1992)
Ethinamate is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is in part metabolized by the liver. The major of three metabolites is hydroxyethinamate (yielded by hydroxylation of the cyclohexyl ring), and it is yet unclear whether this metabolite has any pharmacologic effect. Hydroxyethinamate is combined with glucuronide to form approximately equal quantities with free hydroxyethinamate. Maximum blood concentrations are reached within 60 minutes after ingestion. From the absorbed ethinamate, 10 per cent is metabolized to CO2 while the rest is excreted by the kidney, mainly as hydroxyethinamate glucuronides (89 per cent), and metabolites (9%); only 2% of free ethinamate is excreted in the urine.
Haddad, L.M., Clinical Management of Poisoning and Drug Overdose. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders Co., 1990., p. 850
Hepatic.
ETHINAMATE IS INACTIVATED @ LEAST PARTLY BY LIVER, BY HYDROXYLATION OF CYCLOHEXYL RING; PRODUCT IS CONJUGATED & EXCRETED AS GLUCURONIDE.
Gilman, A.G., T.W. Rall, A.S. Nies and P. Taylor (eds.). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th ed. New York, NY. Pergamon Press, 1990., p. 368
Ethinamate is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is in part metabolized by the liver. The major of three metabolites is hydroxyethinamate (yielded by hydroxylation of the cyclohexyl ring), and it is yet unclear whether this metabolite has any pharmacologic effect. Hydroxyethinamate is combined with glucuronide to form approximately equal quantities with free hydroxyethinamate.
Haddad, L.M., Clinical Management of Poisoning and Drug Overdose. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders Co., 1990., p. 850
2.5 hours
Half-life 2.5 hours. Duration of action about 3 to 5 hours.
United States Pharmacopeial Convention; USP Dispensing Information 12th ed Vol IA p.1362 91992)
135 MINUTES
Haddad, L.M., Clinical Management of Poisoning and Drug Overdose. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders Co., 1990., p. 850
The mechanism of action is not known. However, studies have shown that ethinamate inhibits carbonic anhydrases I and II (J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25044-50). This inhibition by ethinamate is not sufficiently strong, however, to implicate carbonic anhydrases I and II in the mechanism of action.
... ETHINAMATE ... /IS/ NON-SELECTIVE CNS /DEPRESSANT/ ... .
Goodman, L.S., and A. Gilman. (eds.) The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 5th ed. New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1975., p. 126
ABOUT THIS PAGE
73
PharmaCompass offers a list of Ethinamate API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Ethinamate manufacturer or Ethinamate supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Ethinamate manufacturer or Ethinamate supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Ethinamate API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Ethinamate API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Ethinamate Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Ethinamate Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Ethinamate manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Ethinamate, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Ethinamate manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Ethinamate API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Ethinamate supplier is an individual or a company that provides Ethinamate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Ethinamate finished formulations upon request. The Ethinamate suppliers may include Ethinamate API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Ethinamate suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Ethinamate DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Ethinamate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Ethinamate DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Ethinamate USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Ethinamate DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Ethinamate USDMF includes data on Ethinamate's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Ethinamate USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Ethinamate suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
Ethinamate Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Ethinamate GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Ethinamate GMP manufacturer or Ethinamate GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Ethinamate CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Ethinamate's compliance with Ethinamate specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Ethinamate CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Ethinamate CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Ethinamate may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Ethinamate EP), Ethinamate JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Ethinamate USP).
