Synopsis
Synopsis
0
API Suppliers
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book
0
Europe
0
Canada
0
Australia
0
South Africa
0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
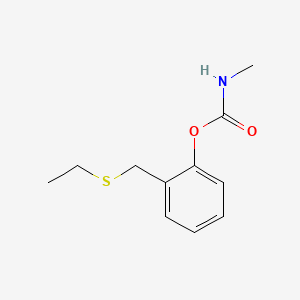

1. Croneton
2. Kroneton
1. 29973-13-5
2. Croneton
3. Arylmate
4. Kronetone
5. Croneton 500
6. Ethiophencarbe
7. 2-((ethylthio)methyl)phenyl Methylcarbamate
8. Ethiofencarb [bsi:iso]
9. Alpha-ethylthio-o-tolyl Methylcarbamate
10. 2-ethylthiomethylphenyl N-methylcarbamate
11. [2-(ethylsulfanylmethyl)phenyl] N-methylcarbamate
12. Hox 1901
13. 2-((ethylthio)methyl)phenol Methylcarbamate
14. Bay-hox-1901
15. Chox 1901
16. Alpha-(ethylthio)-o-tolyl Methylcarbamate
17. 2-[(ethylsulfanyl)methyl]phenyl Methylcarbamate
18. (2-ethylthiomethyl-phenyl)-n-methylcarbamate
19. 2-ethyl-mercaptomethyl-phenyl-n-methylcarbamate
20. Phenol, 2-((ethylthio)methyl)-, Methylcarbamate
21. Fy0yb813xv
22. Alpha-(ethylthio)-o-tolyl Methylcarbamate [iso:bsi]
23. Chembl493480
24. 2-[(ethylthio)methyl]phenyl N-methylcarbamate
25. Chebi:38483
26. Phenol, 2-[(ethylthio)methyl]-, Methylcarbamate
27. Carbamic Acid, Methyl-, 2-(ethylthiomethyl)phenyl Ester
28. Carbamic Acid, Methyl-, Alpha-(ethylthio)-o-tolyl Ester
29. Carbamic Acid, Methyl-, .alpha.-(ethylthio)-o-tolyl Ester
30. .alpha.-ethylthio-o-tolyl Methylcarbamate
31. 2-[(ethylsulfanyl)methyl]phenyl N-methylcarbamate
32. Caswell No. 263aa
33. Ethiophencarbe [iso-french]
34. Ethiofencarb [iso]
35. Hsdb 7140
36. Einecs 249-981-9
37. 2-((ethylthio)methyl)phenyl N-methylcarbamate
38. Unii-fy0yb813xv
39. Epa Pesticide Chemical Code 112101
40. Brn 2973224
41. Ai3-29007
42. Croneton-500
43. Ethiofencarb [hsdb]
44. Dsstox_cid_17545
45. Dsstox_rid_79333
46. Dsstox_gsid_37545
47. Schembl74938
48. Bay-hox 1901
49. Dtxsid3037545
50. Chox-1901
51. Heznviyqeuhlni-uhfffaoysa-
52. Hox-1901
53. Zinc2011298
54. Tox21_301356
55. Bdbm50253090
56. Mfcd00055463
57. Akos015888329
58. Alpha-ethylthio-o-tolylmethyl Carbamate
59. Ethiofencarb 100 Microg/ml In Methanol
60. 2-(ethylthiomethyl)phenyl Methylcarbamate
61. Ncgc00163882-01
62. Ncgc00255441-01
63. Ethiofencarb 100 Microg/ml In Cyclohexane
64. Cas-29973-13-5
65. Ethiofencarb 100 Microg/ml In Acetonitrile
66. 2-(ethylthiomethyl)phenyl Methylcarbamate, 9ci
67. C18649
68. N-methyl-o-(2-ethylthiomethyl) Phenylcarbamate
69. Ethiofencarb, Pestanal(r), Analytical Standard
70. .alpha.-(ethylthio)-o-tolyl Methylcarbamate
71. J-017713
72. Q3591963
73. Carbamic Acid, Methyl-,2-(ethylthiomethyl)phenyl Ester
74. O-cresol, .alpha.-(ethylthio)-, Methylcarbamate
75. Phenol, 2-((ethylthio)methyl)-, Methylcarbamate (9ci)
76. Phenol, 2-((ethylthio)methyl)-, 1-(n-methylcarbamate
77. Pesticide2_ethiofencarb_c11h15no2s_phenol, 2-[(ethylthio)methyl]-, Methylcarbamate
| Molecular Weight | 225.31 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C11H15NO2S |
| XLogP3 | 1.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 225.08234989 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 225.08234989 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 63.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 15 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 199 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
In animals, 14C-ethiofencarb is rapidly excreted.
Tomlin CDS, ed. ethiofencarb (29973-13-5). In: The e-Pesticide Manual, Version 2.2 (2002). Surrey UK, British Crop Protection Council.
When administered as a single oral dose to rats, 41% of the carbonyl-labelled compound was eliminated in the urine and 7% in the feces (within 72 hr), while 47% was eliminated as 14CO2. When similarly administered but in ring-labelled form, 96% was eliminated in the urine and 2% in the feces within 72 hr. The compound, therefore, undergoes hydrolysis, producing a phenol and a carbamic acid derivative which breaks down further to CO2.
International Programme on Chemical Safety's Joint Meeting on Pesticide Residues (JMPR). Ethiofencarb (Pesticide residues in food: 1977 evaluations). Available from, as of July 18, 2003: https://www.inchem.org/documents/jmpr/jmpmono/v077pr26.htm
Maintenance of rats on a diet containing 6.6 ppm of ethiofencarb gave ...total excretion (urine plus feces) decreasing to 1% of one day's intake by the third day after return of the animals to the normal diet. The major metabolites identified were the sulfoxide and sulfone of ethiofencarb and the sulfoxide and sulfone of the phenol; the latter two compounds were excreted mainly as conjugates, and the parent compound was detected in the urine only in trace amounts. Tissue residues detected after either a single oral dose of 0.5 mg/kg bw or administration of 6.6 ppm in the diet for one week were below 1 mg/kg, and these declined more rapidly after administration of the ring-labelled than the carbonyl-labelled compound. This suggests that the carbonyl-labelled residues were incorporated into normal tissues components, as would be expected.
International Programme on Chemical Safety's Joint Meeting on Pesticide Residues (JMPR). Ethiofencarb (Pesticide residues in food: 1977 evaluations). Available from, as of July 18, 2003: https://www.inchem.org/documents/jmpr/jmpmono/v077pr26.htm
Bile-duct-cannulated rats were orally administered 14C-ethiofencarb. Biliary radioactive carbon measurements made two days after administration revealed the following percentage of the dose 20.2%. /Most/ of the dose was eliminated in the urine, while the feces did not exceed an elimination rate of 3%. Enterohepatic circulation of metabolites is suggested by these findings.
Marshall T et al; Pestic. Biochem. Physiol 11(1-3): 56-63 (1979)
A lactating Holstein cow and a male Yorkshire pig treated with a single oral dose (0.5 mg/kg) of ring (14C) croneton excreted 97.8% and 90.0% of the dose, respectively, in the urine after 24 hr. None of the swine tissues examined 24 hr after treatment contained detectable residues, and of the bovine tissues, only the kidney, liver, and skin contained detectable activity (0.016, 0.017, and 0.05 ppm 14C-croneton equivalents, respectively). Milk collected from the cow 6 hr after treatment contained 128 ppb 14C residues; 60% of this was as the free carbamate metabolites, croneton sulfoxide and sulfone. White Leghorn hens given ring 14C-croneton as a single oral dose (0.5 mg/kg) or in twice-daily doses (0.5 mg/kg) over 7 consecutive days showed patterns of metabolism and excretion similar to those observed in the pig and cow. Birds sacrificed 4 hr after the last dose contained from 0.019 ppm 14C-croneton equivalents in the fat to 0.324 ppm in the kidney. By 24 hr, only the liver and kidney (0.044 and 0.022 ppm, respectively) contained residues in excess of 0.01 ppm, and within 4 days the residues in these organs were 0.01 ppm or less. Residues in eggs laid by these hens were 0.03 to 0.04 ppm 14C-croneton equivalents 2 days after treatment; egg residues reached a maximum of 0.06 to 0.07 ppm 7 days after treatment and declined rapidly following the termination of treatment. About 75% of the radiocarbon in the eggs occurred as free phenol sulfoxide and sulfone, 10% occurred as free croneton sulfoxide and croneton sulfone, 5% occurred as water-soluble metabolites, and 5% occurred as unextracted residues. The remaining 5% was accounted for by unknown metabolites in the organo-extractable fraction.
Ivie, G, Dorough, H, eds; Fate of Pesticides in Large Animals p. 233-251 (1977)
The main metabolites are ethiofencarb sulfoxide and sulfone, ethiofencarb phenol and the corresponding sulfoxide and sulfone.
Tomlin CDS, ed. ethiofencarb (29973-13-5). In: The e-Pesticide Manual, Version 2.2 (2002). Surrey UK, British Crop Protection Council.
The first step in the metabolism of carbamates is hydrolysis to carbamic acid, which decomposes to carbon dioxide (CO2) and the corresponding amine. The mechanism of hydrolysis is different for N -methyl and N -dimethyl derivatives. The N -methyl carbamates pass through an isocyanate intermediate, whereas in the hydrolysis of N - dimethylcarbamates, an addition product with a hydroxyl ion is formed yielding the alcohol and N -dimethyl substituted acid. The rate of hydrolysis by esterases is faster in mammals than in plants and insects. Apart from hydrolysis, oxidation also takes place including: hydroxylation of the aromatic ring, O -dealkylation, N -methyl hydroxylation, N -dealkylation, oxidation of aliphatic side chains, and sulfoxidation to the corresponding sulfone. Oxidation is associated with the mixed-function oxidase (MFO) enzymes. Conjugation leads to the formation of O - and N -glucuronides, sulfates, and mercapturic acid derivatives in mammals. Glycosides and phosphates are conjugation products more common in plants. /Carbamate Pesticides/
WHO; Environ Health Criteria 64: Carbamate pesticides (1986). Available from, as of July 3,2003: https://www.inchem.org/pages/ehc.html
The fate of Croneton, 2-ethylthiomethylphenyl N-methylcarbamate, was determined in rats following single oral or dietary exposure to the 14C-carbonyl- and 14C-ring-labeled insecticide. Greater than 95% of the (14C)Croneton equivalents was excreted in the urine or as a combination of 14CO2 (47%) and urinary products (41%) 72 hr after a single oral dose. The feces contained 27% of the dose. A similar excretion pattern was observed during a 7-day feeding period. The principal urinary metabolites were Croneton sulfoxide (23-28% of the dose), phenol sulfoxide (20-23%), phenol sulfone (9-25%), and Croneton sulfone (3-11%) after a single oral dose and similar in the long term study. The carbamates were excreted primarily as free metabolites while the phenolic constituents were eliminated as acid labile conjugates.
PMID:1254817 Nye D et al; J. Agric. Food Chem. 24(2): 371-377 (1976)
The comparative ester hydrolysis and selective toxicity of carbamate insecticides were studied in 4 mammalian species. Hydrolysis rates of carbaryl and ethiofencarb (Croneton) were examined in the rat, mouse, guinea pig and gerbil. Respiratory 14CO2 resulting from the hydrolysis of orally administered (carbonyl-14C)carbamates (0.2 mg/kg) was taken as measure of in vivo hydrolytic capabilities. Ester hydrolysis was greater for ethiofencarb in all species tested, although the relative order of hydrolysis among species was the same with both compounds. After 24 hr, gerbils had hydrolyzed 91% of the ethiofencarb an 65% of the carbaryl. Guinea pigs hydrolyzed somewhat less of the compounds, 65 and 85%, but more than rats and mice, 40 and 25%.
Benson W et al; Pestic Biochem Physiol 21 (2):199-206 (1984)
About 75% of the radiocarbon in the eggs /from White Leghorn hens given one to 14 oral doses of croneton/ occurred as free phenol sulfoxide and sulfone, 10% occurred as free croneton sulfoxide and croneton sulfone, 5% occurred as water-soluble metabolites, and 5% occurred as unextracted residues. The remaining 5% was accounted for by unknown metabolites in the organo-extractable fraction.
Ivie, G, Dorough, H, eds; Fate of Pesticides in Large Animals p. 233-251 (1977)
Carbamates are effective insecticides by virtue of their ability to inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in the nervous system. They also inhibit other esterases. The carbamylation of the enzyme is unstable, and the regeneration of AChE is relatively rapid compared with that from a phosphorylated enzyme. Thus, carbamate pesticides are less dangerous with regard to human exposure than organophosphorus pesticides. The ratio between the dose required to produce death and the dose required to produce minimum symptoms of poisoning is substantially larger for carbamate compounds than for organophosphorus compounds. /Carbamate Pesticides/
WHO; Environ Health Criteria 64: Carbamate pesticides (1986). Available from, as of July 3,2003: https://www.inchem.org/pages/ehc.html
ABOUT THIS PAGE
58
PharmaCompass offers a list of Ethiofencarb API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Ethiofencarb manufacturer or Ethiofencarb supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Ethiofencarb manufacturer or Ethiofencarb supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Ethiofencarb API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Ethiofencarb API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Ethiofencarb Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Ethiofencarb Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Ethiofencarb manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Ethiofencarb, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Ethiofencarb manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Ethiofencarb API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Ethiofencarb supplier is an individual or a company that provides Ethiofencarb active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Ethiofencarb finished formulations upon request. The Ethiofencarb suppliers may include Ethiofencarb API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
Ethiofencarb Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Ethiofencarb GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Ethiofencarb GMP manufacturer or Ethiofencarb GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Ethiofencarb CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Ethiofencarb's compliance with Ethiofencarb specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Ethiofencarb CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Ethiofencarb CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Ethiofencarb may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Ethiofencarb EP), Ethiofencarb JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Ethiofencarb USP).

