
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
EU WC
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
South Africa
0
Listed Dossiers
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
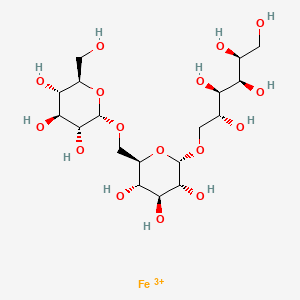

1. 1345510-43-1
2. Iron(3+);(2s,3r,4r,5r)-6-[(2s,3r,4s,5s,6r)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-[[(2s,3r,4s,5s,6r)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]oxan-2-yl]oxyhexane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol
3. Db15617
| Molecular Weight | 562.3 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C18H34FeO16+3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 12 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 16 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Exact Mass | 562.119621 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 562.119621 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 280 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 35 |
| Formal Charge | 3 |
| Complexity | 598 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 14 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 2 |
This drug is indicated for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in adult patients who have experienced intolerance to oral iron preparations or insufficient clinical response to orally administered iron. Ferric derisomaltase is also indicated for patients with non-hemodialysis dependent chronic kidney disease. In Australia and United Kingdom, ferric derisomaltase is indicated for cases in which rapid delivery of iron is required.
FDA Label
Ferric derisomaltase increases the reticulocyte count and ultimately increases hemoglobin, treating iron deficiency anemia and its various symptoms. Parenteral iron, such as ferric derisomaltose, may cause false elevations in serum bilirubin levels and falsely reduced serum calcium.
Absorption
After a single 1000 mg dose, the Cmax and AUC of serum iron were 408 g/mL and 17730 g.h /mL, respectively. Serum ferritin concentrations reach their peak about 7 days after a single dose of intravenous ferric derisomaltose. A note on concomitant oral iron The absorption of oral iron is decreased when administered with intravenous iron. The administration of oral iron should be delayed until at least 5 days after the last ferric derisomaltose injection.
Route of Elimination
Renal elimination was not a significant route of elimination in single-dose pharmacokinetic studies. Iron can often accumulate in the body leading to iron overload followed by toxic effects. Small amounts of ferric derisomaltose are excreted in the urine and feces.
Volume of Distribution
Ferric derisomaltose or released iron that was released is found in cells of the reticuloendothelial system (RES). It is found to be highly concentrated in the liver and spleen. The volume of distribution of other forms of intravenous iron is 3L, on average, in a 70 kg adult. Though the specific volume of distribution of ferric derisomaltose is not readily available in the literature, it is likely similar to other intravenous forms of iron.
Clearance
Intravenous iron is cleared from the plasma. Ferric derisomaltose is not eliminated via the kidneys, as the size of the complex is large and cannot be excreted via the nephron.
Iron in the circulation is taken up by the plasma by cells of the RES. This binds proteins that form hemosiderin or ferritin, as well transferrin. Following this step, the bound iron replenishes low hemoglobin (Hb) and iron.
The plasma-half live of intravenous iron is about 1-4 days.
This drug is a complex made of iron (III) hydroxide and derisomaltose, which is an iron carbohydrate oligosaccharide that works to releases iron. The released iron then binds to the transport protein, transferrin, and is taken to erythroid precursor cells for incorporation into the hemoglobin molecule.
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
ABOUT THIS PAGE
28
PharmaCompass offers a list of Ferric Derisomaltose API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Ferric Derisomaltose manufacturer or Ferric Derisomaltose supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Ferric Derisomaltose manufacturer or Ferric Derisomaltose supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Ferric Derisomaltose API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Ferric Derisomaltose API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Ferric Derisomaltose Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Ferric Derisomaltose Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Ferric Derisomaltose manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Ferric Derisomaltose, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Ferric Derisomaltose manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Ferric Derisomaltose API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Ferric Derisomaltose manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Ferric Derisomaltose supplier is an individual or a company that provides Ferric Derisomaltose active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Ferric Derisomaltose finished formulations upon request. The Ferric Derisomaltose suppliers may include Ferric Derisomaltose API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Ferric Derisomaltose suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) established the Japan Drug Master File (JDMF), also known as the Master File (MF), to permit Japanese and foreign manufacturers of drug substances, intermediates, excipients, raw materials, and packaging materials (‘Products’) to voluntarily register confidential information about the production and management of their products in Japan.
The Ferric Derisomaltose Drug Master File in Japan (Ferric Derisomaltose JDMF) empowers Ferric Derisomaltose API manufacturers to present comprehensive information (e.g., production methods, data, etc.) to the review authority, i.e., PMDA (Pharmaceuticals & Medical Devices Agency).
PMDA reviews the Ferric Derisomaltose JDMF during the approval evaluation for pharmaceutical products. At the time of Ferric Derisomaltose JDMF registration, PMDA checks if the format is accurate, if the necessary items have been included (application), and if data has been attached.
click here to find a list of Ferric Derisomaltose suppliers with JDMF on PharmaCompass.
Ferric Derisomaltose Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Ferric Derisomaltose GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Ferric Derisomaltose GMP manufacturer or Ferric Derisomaltose GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Ferric Derisomaltose CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Ferric Derisomaltose's compliance with Ferric Derisomaltose specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Ferric Derisomaltose CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Ferric Derisomaltose CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Ferric Derisomaltose may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Ferric Derisomaltose EP), Ferric Derisomaltose JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Ferric Derisomaltose USP).

