
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
USDMF
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
KDMF
0
NDC API
0
VMF
0
Listed Suppliers
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
FDF Dossiers
0
FDA Orange Book

0
Europe

0
Canada

0
Australia

0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
US Patents
0
US Exclusivities
0
Health Canada Patents
US Medicaid
NA
Annual Reports
NA
Regulatory FDF Prices
NA
0
API
0
FDF
0
Data Compilation #PharmaFlow
0
Stock Recap #PipelineProspector
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers
0
News #PharmaBuzz
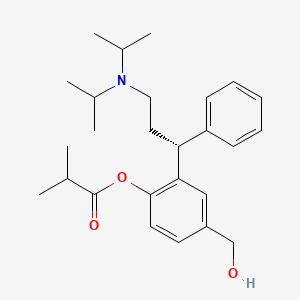

1. Fesoterodine Fumarate
2. Toviaz
1. 286930-02-7
2. (r) Fesoterodine
3. Fesoterodine (inn)
4. [2-[(1r)-3-[di(propan-2-yl)amino]-1-phenylpropyl]-4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl] 2-methylpropanoate
5. Fesoterodine [inn]
6. (r)-2-(3-(diisopropylamino)-1-phenylpropyl)-4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl Isobutyrate
7. 621g617227
8. Propanoic Acid, 2-methyl-, 2-((1r)-3-(bis(1-methylethyl)amino)-1-phenylpropyl)-4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl Ester
9. Fesoterodine [inn:ban]
10. [2-[(1r)-3-(di(propan-2-yl)amino)-1-phenylpropyl]-4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl] 2-methylpropanoate
11. Unii-621g617227
12. Feso
13. Starbld0000599
14. Fesoterodine [mi]
15. Fesoterodine [vandf]
16. Fesoterodine [mart.]
17. Fesoterodine [who-dd]
18. Schembl121127
19. Gtpl7473
20. Chembl1201764
21. Dtxsid80182853
22. Chebi:135920
23. Cs-m2392
24. Zinc1552908
25. Akos015841710
26. Db06702
27. Ncgc00346540-01
28. Ncgc00346540-02
29. Ncgc00346540-03
30. Ac-32493
31. Hy-70053
32. D07226
33. Ab01274866-01
34. Ab01274866_02
35. 930f027
36. Q4482372
37. 2-[(1r)-3-[bis(propan-2-yl)amino]-1-phenylpropyl]-4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl 2-methylpropanoate
| Molecular Weight | 411.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C26H37NO3 |
| XLogP3 | 5.5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Exact Mass | 411.27734404 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 411.27734404 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 49.8 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 491 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| 1 of 1 | |
|---|---|
| Drug Name | TOVIAZ |
| Active Ingredient | FESOTERODINE FUMARATE |
| Company | PFIZER (Application Number: N022030. Patents: 6858650, 7384980, 7807715, 7855230, 7985772, 8088398, 8338478, 8501723) |
For the treatment of overactive bladder (with symptoms of urinary frequency, urgency, or urge incontinence).
FDA Label
Treatment of the symptoms (increased urinary frequency and / or urgency and / or urgency incontinence) that may occur in patients with overactive-bladder syndrome.
In-vivo the fesoteridine prodrug is broken down into its active metabolite, 5-hydroxymethyl tolterodine (5-HMT), by plasma esterases. The 5-hydroxymethyl metabolite, which exhibits an antimuscarinic activity. Both urinary bladder contraction and salivation are mediated via cholinergic muscarinic receptors. Therefore, acting as a competitive muscarinic receptor antagonist, fesoterodine ultimately acts to decrease the detrusor pressure by its muscarinic antagonism, thereby decreasing bladder contraction and consequently, the urge to urinate.
Muscarinic Antagonists
Drugs that bind to but do not activate MUSCARINIC RECEPTORS, thereby blocking the actions of endogenous ACETYLCHOLINE or exogenous agonists. Muscarinic antagonists have widespread effects including actions on the iris and ciliary muscle of the eye, the heart and blood vessels, secretions of the respiratory tract, GI system, and salivary glands, GI motility, urinary bladder tone, and the central nervous system. (See all compounds classified as Muscarinic Antagonists.)
Urological Agents
Drugs used in the treatment of urological conditions and diseases such as URINARY INCONTINENCE and URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS. (See all compounds classified as Urological Agents.)
G04BD11
G04BD11
S76 | LUXPHARMA | Pharmaceuticals Marketed in Luxembourg | Pharmaceuticals marketed in Luxembourg, as published by d'Gesondheetskeess (CNS, la caisse nationale de sante, www.cns.lu), mapped by name to structures using CompTox by R. Singh et al. (in prep.). List downloaded from https://cns.public.lu/en/legislations/textes-coordonnes/liste-med-comm.html. Dataset DOI:10.5281/zenodo.4587355
G - Genito urinary system and sex hormones
G04 - Urologicals
G04B - Urologicals
G04BD - Drugs for urinary frequency and incontinence
G04BD11 - Fesoterodine
Absorption
Tmax (5-HMT): 5 hours post-adminitration of fesoterodine. AUC (0,)= 49.5 ngh/ ml Bioavailability, 5-HMT = 52%
Route of Elimination
Renal: 70% of fesoterodine was recovered in urine as 5-HMT; 35% carboxy metabolite; 18% carboxy-N-desisopropylmetabolite, and 1% N-desisopropyl metabolite Fecal: 7% Hepatic: fesoterodine elimination via CYP2D6 and CYP3A4
Volume of Distribution
IV, 5-HMT: 169 L
Clearance
5-HMT, healthy subjects: 14.4 L/h 5-HMT is also secreted into the nephron.
Metabolized by ubiquitous, nonspecific esterases to transform fesoterodine into 5-HMT Extensive metabolism via CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 into inactive metabolites
7-8 hours for the active metabolite 5-hydroxymethyl tolterodine
Fesoterodine, once converted to its active metabolite, 5-hydroxymethyltolterodine, acts as a competitive antagonists at muscarinic receptors. This results in the inhibition of bladder contraction, decrease in detrusor pressure, and an incomplete emptying of the bladder.
ABOUT THIS PAGE
15
PharmaCompass offers a list of Fesoterodine Maleate API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Fesoterodine Maleate manufacturer or Fesoterodine Maleate supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Fesoterodine Maleate manufacturer or Fesoterodine Maleate supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Fesoterodine Maleate API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Fesoterodine Maleate API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Fesoterodine Maleate Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Fesoterodine Maleate Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Fesoterodine Maleate manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Fesoterodine Maleate, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Fesoterodine Maleate manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Fesoterodine Maleate API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
A Fesoterodine Maleate supplier is an individual or a company that provides Fesoterodine Maleate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Fesoterodine Maleate finished formulations upon request. The Fesoterodine Maleate suppliers may include Fesoterodine Maleate API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Fesoterodine Maleate suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Fesoterodine Maleate written confirmation (Fesoterodine Maleate WC) is an official document issued by a regulatory agency to a Fesoterodine Maleate manufacturer, verifying that the manufacturing facility of a Fesoterodine Maleate active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) adheres to the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) regulations of the importing country. When exporting Fesoterodine Maleate APIs or Fesoterodine Maleate finished pharmaceutical products to another nation, regulatory agencies frequently require a Fesoterodine Maleate WC (written confirmation) as part of the regulatory process.
click here to find a list of Fesoterodine Maleate suppliers with Written Confirmation (WC) on PharmaCompass.
Fesoterodine Maleate Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Fesoterodine Maleate GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Fesoterodine Maleate GMP manufacturer or Fesoterodine Maleate GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Fesoterodine Maleate CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Fesoterodine Maleate's compliance with Fesoterodine Maleate specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Fesoterodine Maleate CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Fesoterodine Maleate CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Fesoterodine Maleate may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Fesoterodine Maleate EP), Fesoterodine Maleate JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Fesoterodine Maleate USP).
