
Synopsis
Synopsis
0
CEP/COS
0
JDMF
0
EU WC
0
VMF
0
EDQM
0
USP
0
JP
0
Others
0
South Africa

0
Listed Dossiers
DRUG PRODUCT COMPOSITIONS
0
FDF
0
Weekly News Recap #Phispers

1. Bay 94-8862
2. Kerendia
1. 1050477-31-0
2. Kerendia
3. Bay 94-8862
4. Bay94-8862
5. Finerenone (bay 94-8862)
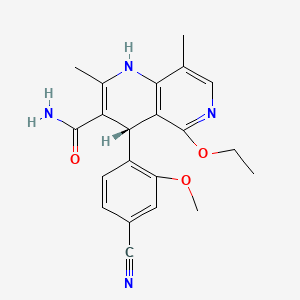
6. (4s)-4-(4-cyano-2-methoxyphenyl)-5-ethoxy-2,8-dimethyl-1,4-dihydro-1,6-naphthyridine-3-carboxamide
7. Bay-94-8862
8. De2o63yv8r
9. 1,6-naphthyridine-3-carboxamide, 4-(4-cyano-2-methoxyphenyl)-5-ethoxy-1,4-dihydro-2,8-dimethyl-, (4s)-
10. Finerenone [usan:inn]
11. Unii-de2o63yv8r
12. Finerenone [inn]
13. Finerenone [jan]
14. Finerenone [usan]
15. Finerenone [who-dd]
16. Finerenone (jan/usan/inn)
17. Gtpl8678
18. Schembl8157011
19. Finerenone [orange Book]
20. Amy9115
21. Dtxsid10146928
22. Bcp24177
23. Ex-a2845
24. Bay948862
25. Bay 948862
26. Bay-948862
27. Ac-30916
28. Hy-111372
29. Cs-0040097
30. J3.584.878i
31. D10633
32. F53302
33. Q21099046
34. Bay94-8862; Bay 94-8862; Bay-94-8862; Bay948862; Bay 948862; Bay-948862
| Molecular Weight | 378.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C21H22N4O3 |
| XLogP3 | 2.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 378.16919058 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 378.16919058 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 110 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 670 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
Finerenone is indicated to reduce the risk of sustained decline in glomerular filtration rate, end stage kidney disease, cardiovascular death, heart attacks, and hospitalization due to heart failure in adults with chronic kidney disease associated with type II diabetes mellitus.
Kerendia is indicated for the treatment of chronic kidney disease (stage 3 and 4 with albuminuria) associated with type 2 diabetes in adults.
Treatment of chronic kidney disease
Treatment of heart failure
Finerenone is a non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist indicated to reduce the risk of sustained decline in glomerular filtration rate, end stage kidney disease, cardiovascular death, heart attacks, and hospitalization due to heart failure in adults with chronic kidney disease associated with type II diabetes mellitus. It has a moderate duration of action as it is taken once daily, and a wide therapeutic window as patients were given doses from 1.25 mg to 80 mg in clinical trials. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of hyperkalemia.
C09
C - Cardiovascular system
C03 - Diuretics
C03D - Aldosterone antagonists and other potassium-sparing agents
C03DA - Aldosterone antagonists
C03DA05 - Finerenone
Absorption
A 10 mg oral dose of finerenone reaches a Cmax of 351 g/L, with a Tmax of 1.5 hours, and an AUC of 2820 g\*h/L in plasma. The same dose of finerenone reaches a Cmax of 226 g/L, with a Tmax of 1.5 hours, and an AUC of 1840 g\*h/L in whole blood. Regular doses of 20 mg of finerenone reach a geometric mean steady state Cmax of 160 g/L with an AUC of 686 g\*h/L.
Route of Elimination
The majority of the dose recovered in urine was in the form of the M2, M3 (47.8%), and M4 metabolites; <1.3% of the dose recovered in the urine was as the unchanged parent compound. The majority of the dose recovered in the feces was as the M5 metabolite, with only 0.2% eliminated as the unchanged parent compound. The M1 metabolite made up <1.5% of the recovered dose in urine and feces. Finerenone is not expected to be metabolized by the intestinal microflora.
Volume of Distribution
The volume of distribution of finerenone as steady state is 52.6L.
Clearance
The systemic clearance of finerenone is approximately 25 L/h.
Finerenone is approximately 90% metabolized by CYP3A4, and 10% metabolized by CYP2C8. There is a minor contribution to metabolism by CYP1A1. Finerenone has no active metabolites. Finerenone is aromatized to the M1 metabolite by CYP3A4 and CYP2C8, which is further hydroxylated by CYP3A4 to the M2 metabolite, and finally oxidized bye CYP3A4 to the M3 metabolite. Alternatively, finerenone can undergo epoxidation and possibly hydrolysis by CYP3A4 and CYP2C8 to form the M4 metabolite, which is hydroxylated again by CYP3A4 to the M5 metabolite, and oxidized to the M8 metabolite. Finerenone can also be hydroxylated by CYP2C8 to the M7 metabolite, and further oxidized to the M9 metabolite. The M10 metabolite is formed by the demethylation, oxidation, and ring opening of finerenone. The M13 metabolite is formed through de-ethylation of finerenone by CYP1A1, and the M14 metabolite is formed through an undefined multi-step process involving CYP2C8 and CYP3A4.
The half life of a 10 mg dose of finerenone in 4 healthy men was 17.4 hours in plasma and 12.3 hours in whole blood. The terminal half life of finerenone is approximately 2-3 hours.
Finerenone is a non-steroidal selective mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) antagonist with no significant affinity or activity at androgen, progesterone, estrogen, and glucocorticoid receptors. Animal studies have shown that finerenone binding to the MR reduces inflammation and fibrosis, and phase 2 clinical trials showed a reduction in albuminuria. Aldosterone is a mineralocorticoid hormone involved in the regulation of blood pressure, sodium reabsorption, and potassium excretion. In 1943, agonism of the MR along with increased salt was shown to be associated with malignant hypertension, which could progress to inflammation and fibrosis of organs. Binding of aldosterone, an MR agonist, to the MR causes a conformational change, which dissociates the receptor from inactivating chaperone proteins. The active MR translocates to the nucleus along with a complex of other coactivators to induce transcription of a number of genes. Finerenone's binding to the MR prevents binding of MR coactivators, which in turn prevents pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic gene transcription. Clinical trial data shows that blocking the mineralocorticoid receptor reduces mortality and morbidity in patients with chronic severe congestive heart failure with an ejection fraction 35%. Patients taking finerenone developed new onset atrial fibrillation or flutter (AFF) with a hazard ratio of 0.71. Finerenone lowered the risk of first onset of kidney failure, a sustained eGFR decrease of 40%, or death from a renal cause to a hazard ratio of 0.82. Cardiovascular outcomes including cardiovascular death, nonfatal heart attacks, nonfatal strokes, and hospitalization for heart failure in patients taking finerenone had a hazard ratio of 0.86 in patients with a history of AFF and 0.85 in patients without a history of AFF.

API/FDF Prices: Book a Demo to explore the features and consider upgrading later
API Imports and Exports
| Importing Country | Total Quantity (KGS) |
Average Price (USD/KGS) |
Number of Transactions |
|---|
Upgrade, download data, analyse, strategize, subscribe with us
Global Sales Information

Market Place

Patents & EXCLUSIVITIES
ABOUT THIS PAGE
23
PharmaCompass offers a list of Finerenone API manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by GMP, USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, Price,and more, enabling you to easily find the right Finerenone manufacturer or Finerenone supplier for your needs.
Send us enquiries for free, and we will assist you in establishing a direct connection with your preferred Finerenone manufacturer or Finerenone supplier.
PharmaCompass also assists you with knowing the Finerenone API Price utilized in the formulation of products. Finerenone API Price is not always fixed or binding as the Finerenone Price is obtained through a variety of data sources. The Finerenone Price can also vary due to multiple factors, including market conditions, regulatory modifications, or negotiated pricing deals.
A Finerenone manufacturer is defined as any person or entity involved in the manufacture, preparation, processing, compounding or propagation of Finerenone, including repackagers and relabelers. The FDA regulates Finerenone manufacturers to ensure that their products comply with relevant laws and regulations and are safe and effective to use. Finerenone API Manufacturers are required to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure that their products are consistently manufactured to meet established quality criteria.
click here to find a list of Finerenone manufacturers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PhamaCompass.
A Finerenone supplier is an individual or a company that provides Finerenone active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or Finerenone finished formulations upon request. The Finerenone suppliers may include Finerenone API manufacturers, exporters, distributors and traders.
click here to find a list of Finerenone suppliers with USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP, GMP, COA and API Price related information on PharmaCompass.
A Finerenone DMF (Drug Master File) is a document detailing the whole manufacturing process of Finerenone active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in detail. Different forms of Finerenone DMFs exist exist since differing nations have different regulations, such as Finerenone USDMF, ASMF (EDMF), JDMF, CDMF, etc.
A Finerenone DMF submitted to regulatory agencies in the US is known as a USDMF. Finerenone USDMF includes data on Finerenone's chemical properties, information on the facilities and procedures used, and details about packaging and storage. The Finerenone USDMF is kept confidential to protect the manufacturer’s intellectual property.
click here to find a list of Finerenone suppliers with USDMF on PharmaCompass.
In Korea, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is in charge of regulating pharmaceutical products and services.
Pharmaceutical companies submit a Finerenone Drug Master File in Korea (Finerenone KDMF) to the MFDS, which includes comprehensive information about the production, processing, facilities, materials, packaging, and testing of Finerenone. The MFDS reviews the Finerenone KDMF as part of the drug registration process and uses the information provided in the Finerenone KDMF to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the drug.
After submitting a Finerenone KDMF to the MFDS, the registered manufacturer can provide importers or distributors with the registration number without revealing confidential information to Korean business partners. Applicants seeking to register their Finerenone API can apply through the Korea Drug Master File (KDMF).
click here to find a list of Finerenone suppliers with KDMF on PharmaCompass.
National Drug Code is a comprehensive database maintained by the FDA that contains information on all drugs marketed in the US. This directory includes information about finished drug products, unfinished drug products, and compounded drug products, including those containing Finerenone as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
The FDA updates the NDC directory daily. The NDC numbers for Finerenone API and other APIs are published in this directory by the FDA.
The NDC unfinished drugs database includes product listing information submitted for all unfinished drugs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), drugs intended for further processing and bulk drug substances for compounding.
Pharmaceutical companies that manufacture Finerenone as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) must furnish the FDA with an updated record of all drugs that they produce, prepare, propagate, compound, or process for commercial distribution in the US at their facilities.
The NDC directory also contains data on finished compounded human drug products that contain Finerenone and are produced by outsourcing facilities. While these outsourcing facilities are not mandated to assign a Finerenone NDC to their finished compounded human drug products, they may choose to do so.
click here to find a list of Finerenone suppliers with NDC on PharmaCompass.
Finerenone Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is produced in GMP-certified manufacturing facility.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices, which is a system used in the pharmaceutical industry to make sure that goods are regularly produced and monitored in accordance with quality standards. The FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices requirements are referred to as cGMP or current GMP which indicates that the company follows the most recent GMP specifications. The World Health Organization (WHO) has its own set of GMP guidelines, called the WHO GMP. Different countries can also set their own guidelines for GMP like China (Chinese GMP) or the EU (EU GMP).
PharmaCompass offers a list of Finerenone GMP manufacturers, exporters & distributors, which can be sorted by USDMF, JDMF, KDMF, CEP (COS), WC, API price, and more, enabling you to easily find the right Finerenone GMP manufacturer or Finerenone GMP API supplier for your needs.
A Finerenone CoA (Certificate of Analysis) is a formal document that attests to Finerenone's compliance with Finerenone specifications and serves as a tool for batch-level quality control.
Finerenone CoA mostly includes findings from lab analyses of a specific batch. For each Finerenone CoA document that a company creates, the USFDA specifies specific requirements, such as supplier information, material identification, transportation data, evidence of conformity and signature data.
Finerenone may be tested according to a variety of international standards, such as European Pharmacopoeia (Finerenone EP), Finerenone JP (Japanese Pharmacopeia) and the US Pharmacopoeia (Finerenone USP).
